9th grade Biology EOC
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
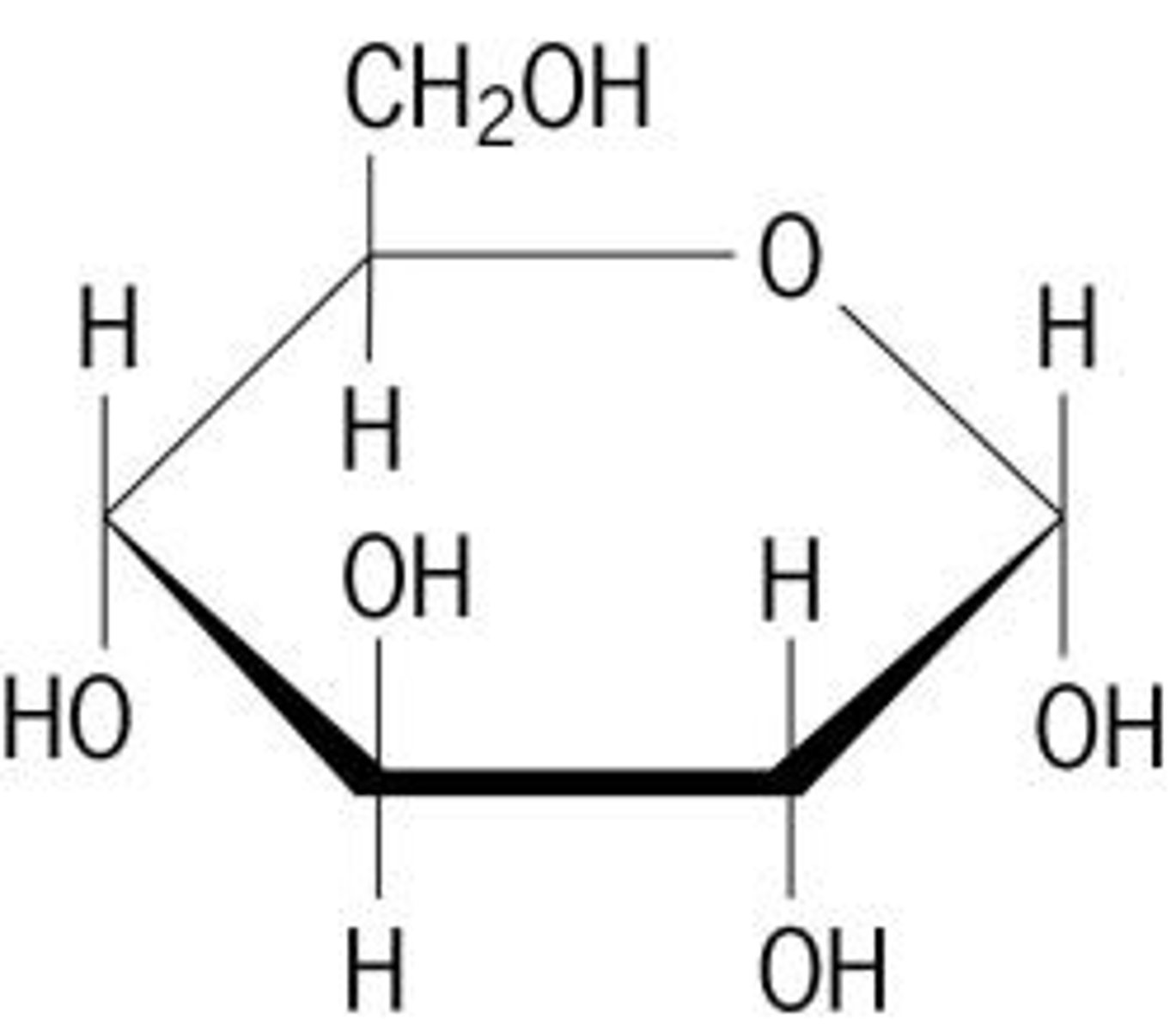
Carbohydrate
Contains: C,H,O
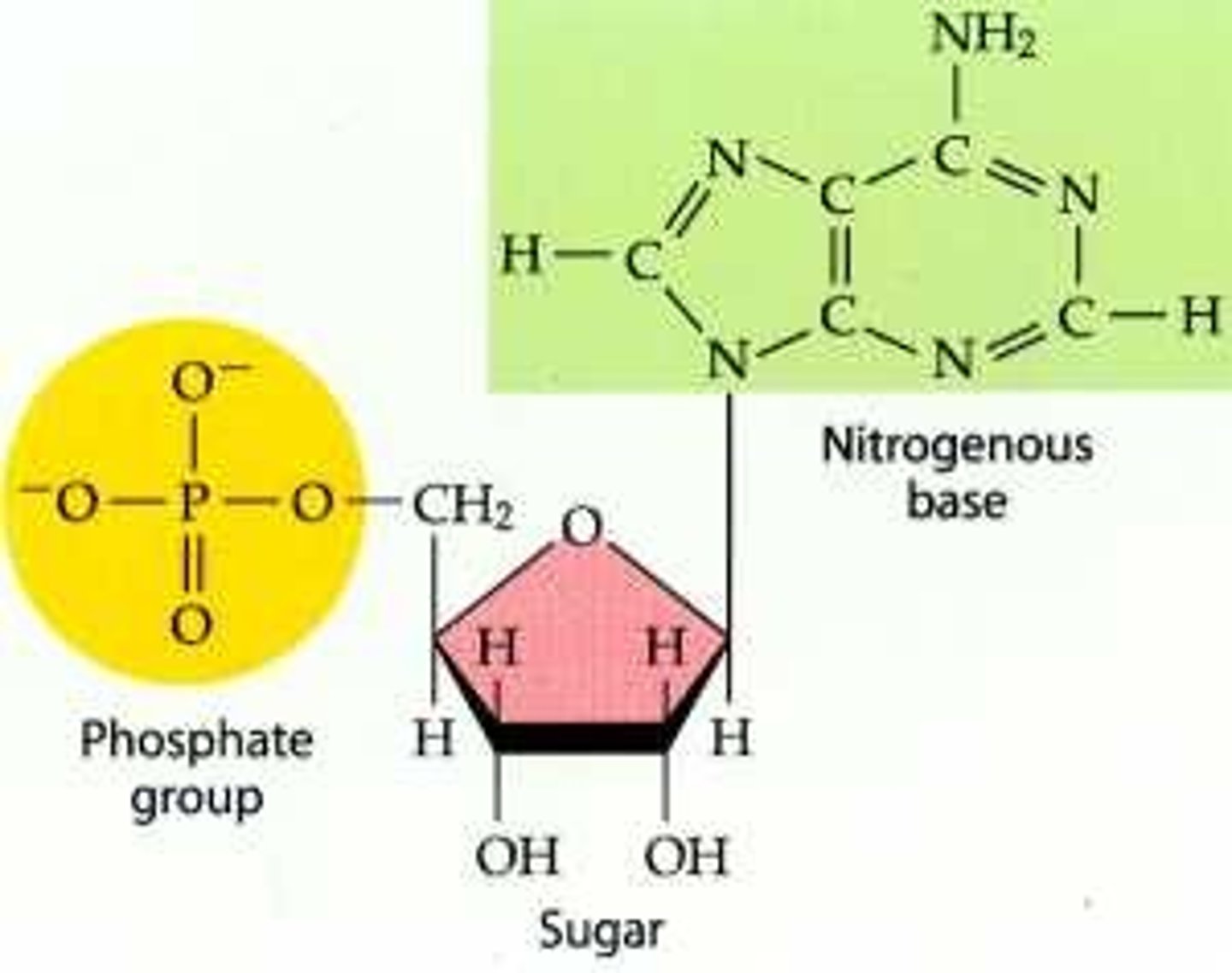
Nucleic Acid
Contains: C,H,O,N,P
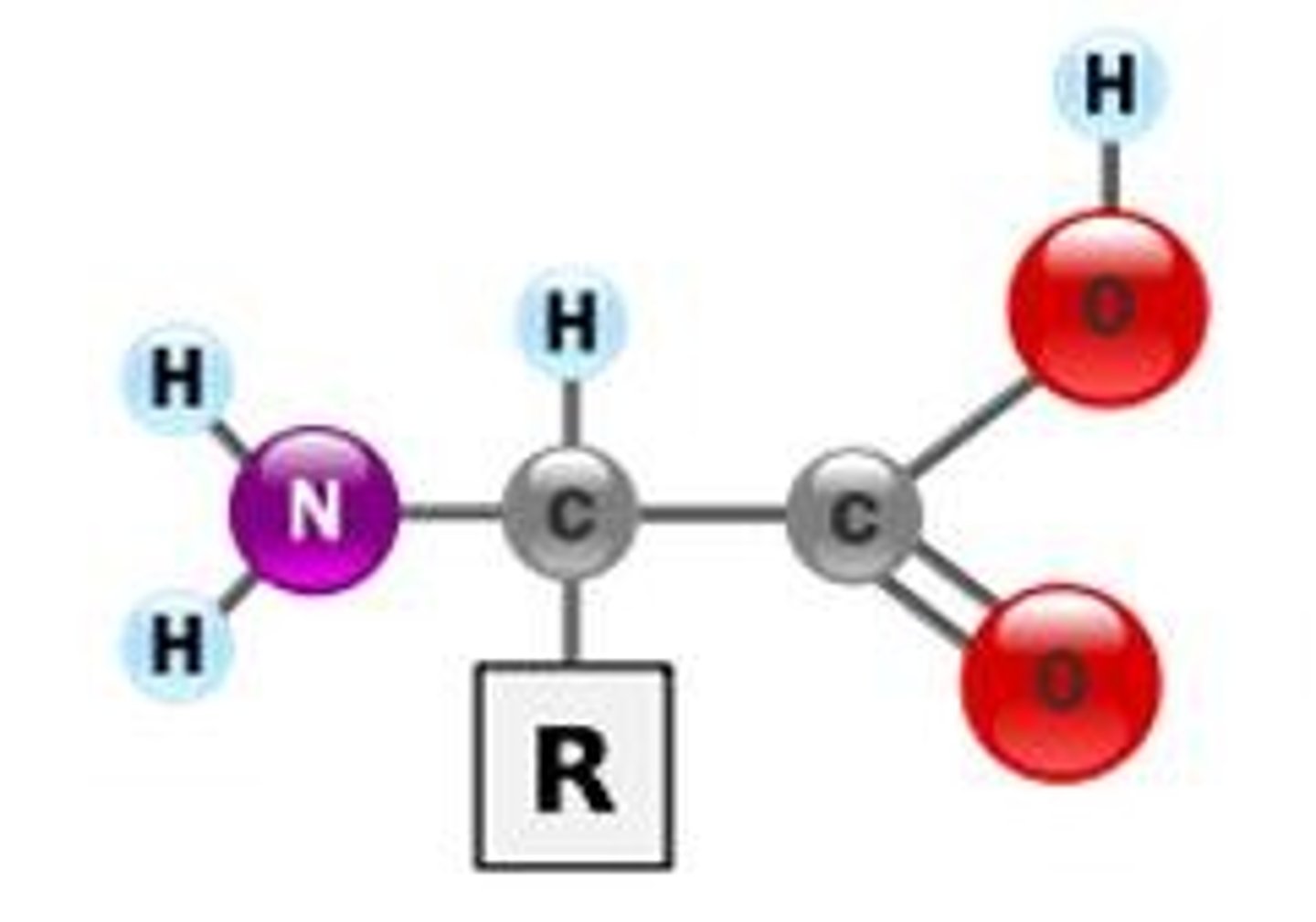
Proteins
Contains: C,H,O,N
Nucleotide
Function: store information (DNA & RNA)
Interphase
G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase
sugars
Function: Quick energy
Mitosis
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telephase
Fatty acid
Function: makes enzymes that speed up reactions
G1 phase
The cell is growing
S phase
The cell replicates it's DNA
G2 phase
The cell is growing and starts preparing for mitosis
Prophase
Metaphase
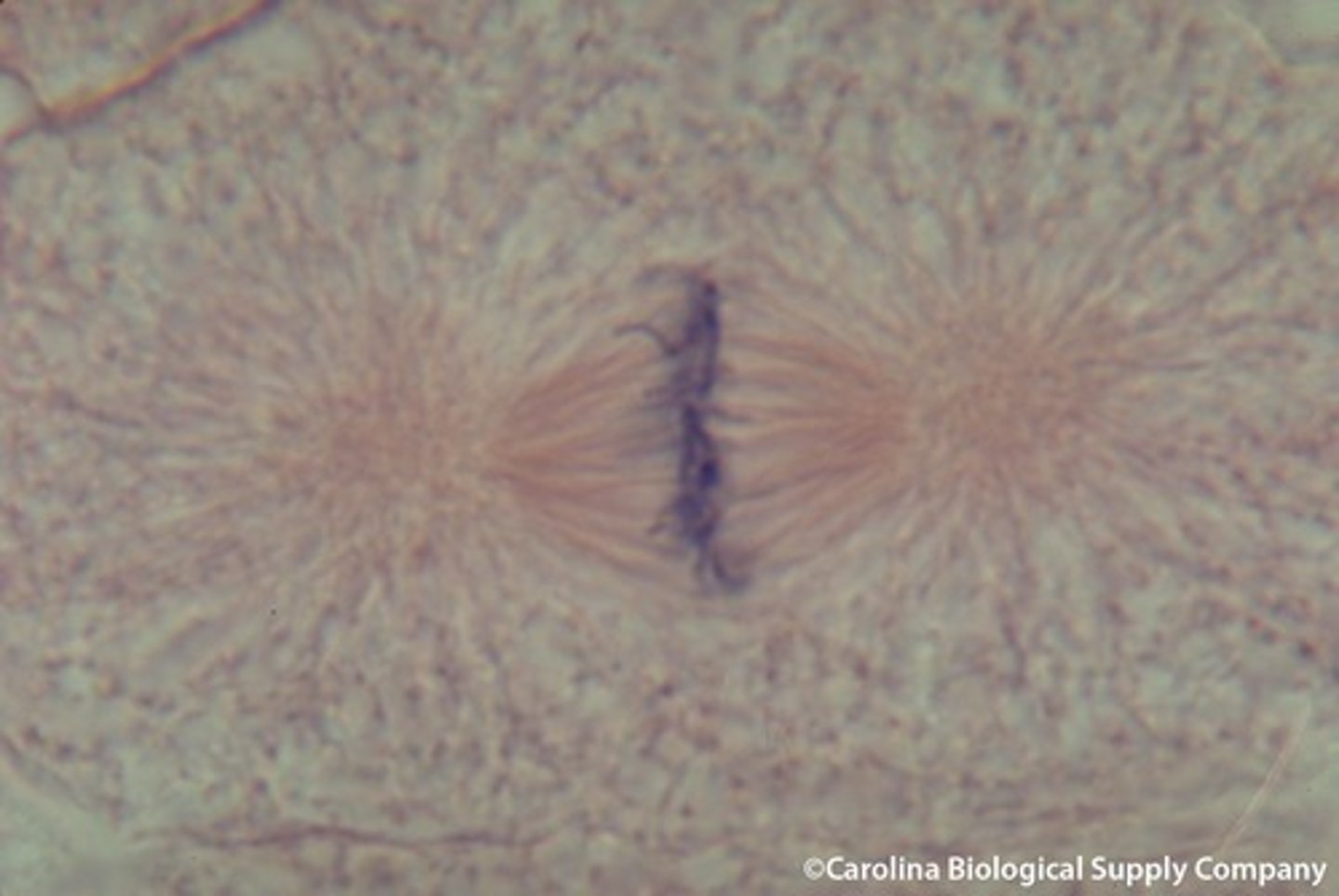
Anaphase
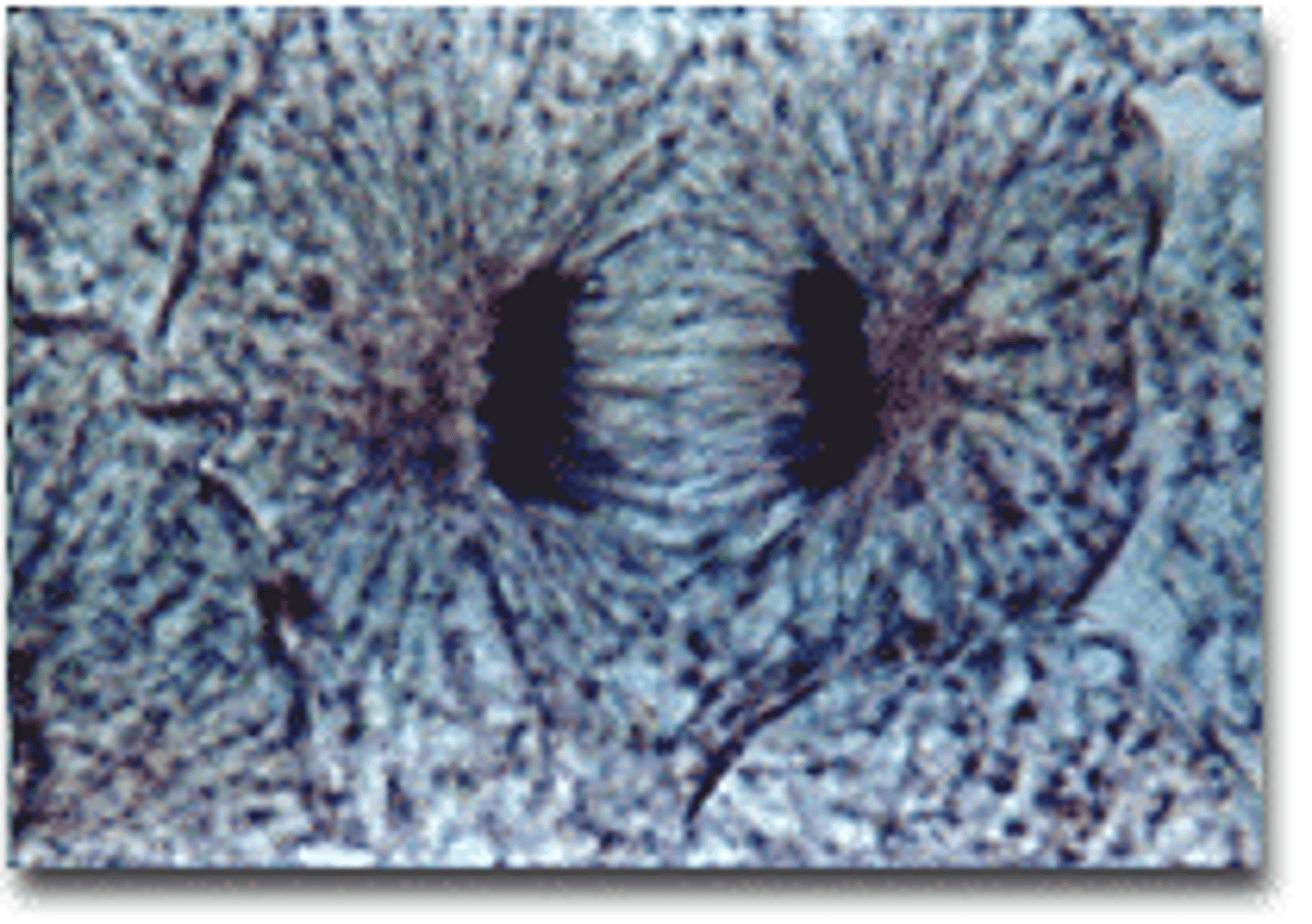
Telaphase
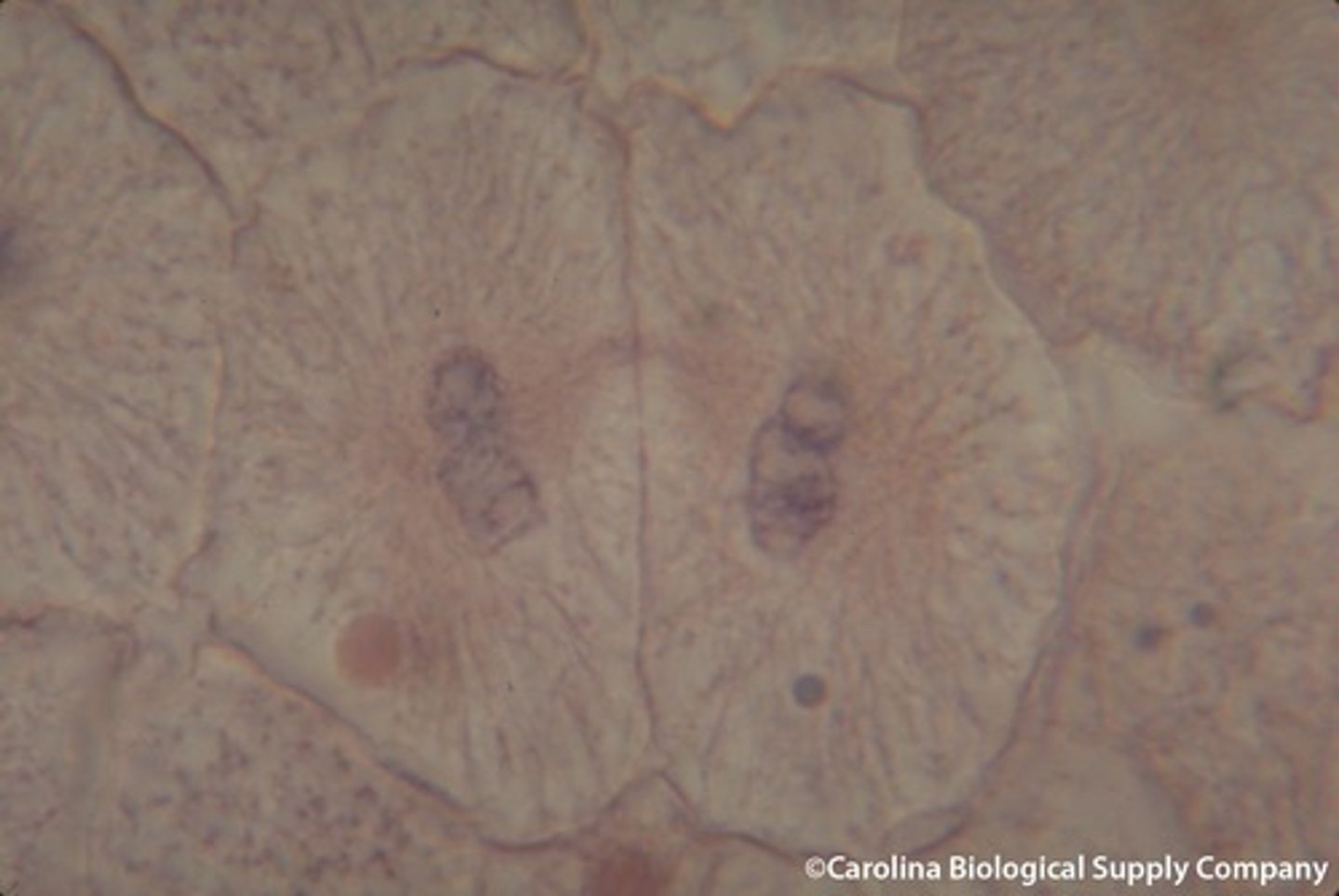
Cytokinesis
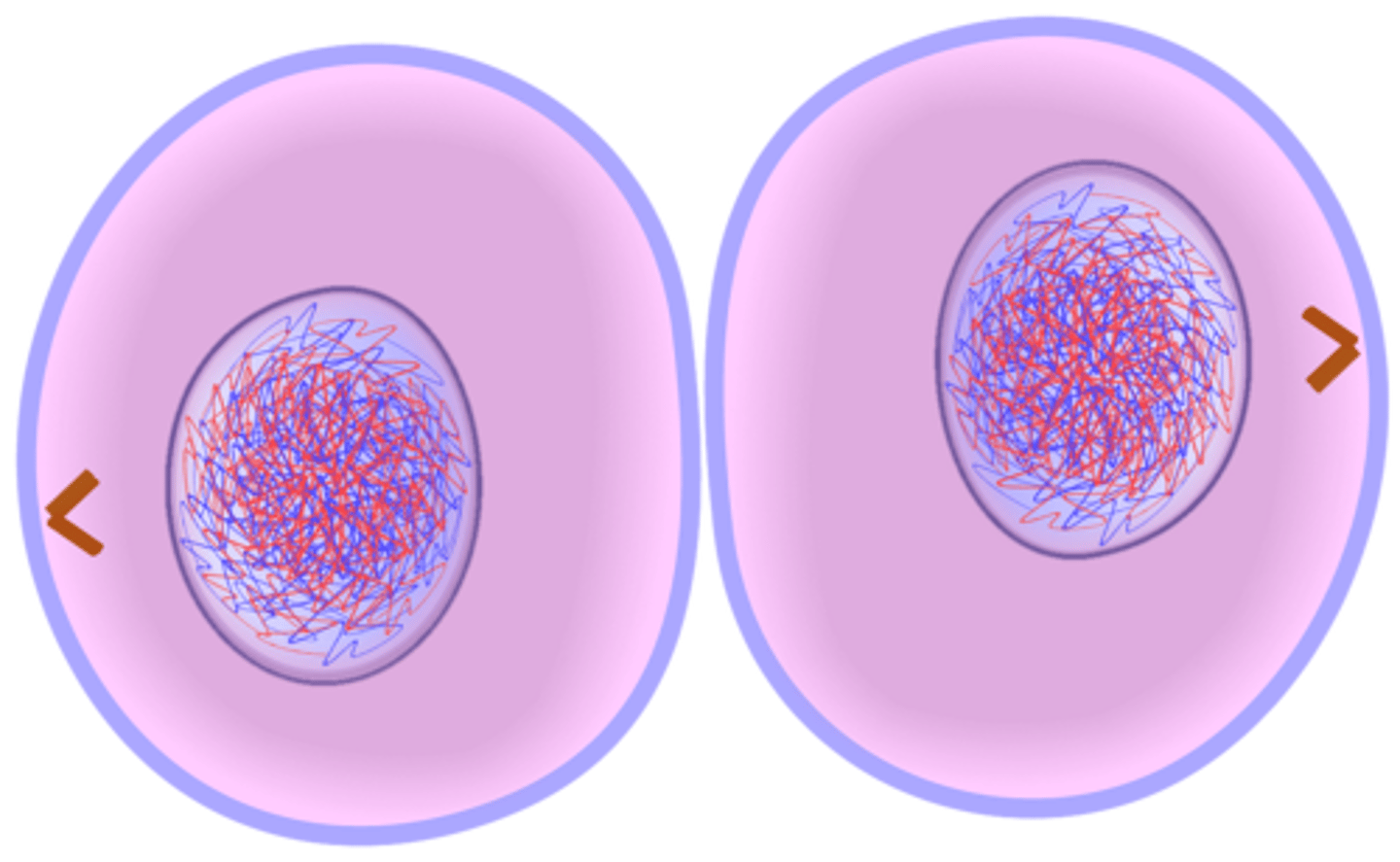
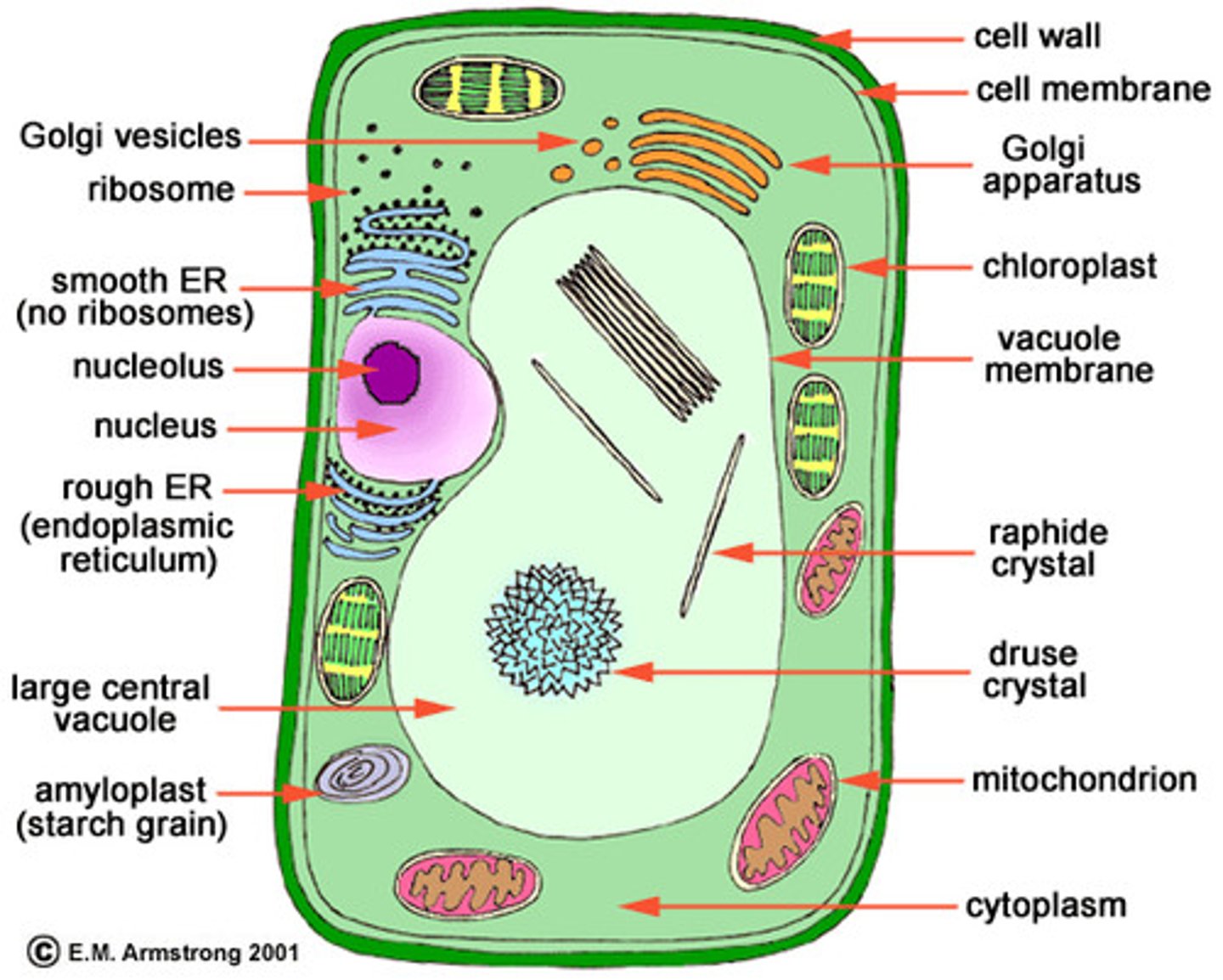
Plant Cell
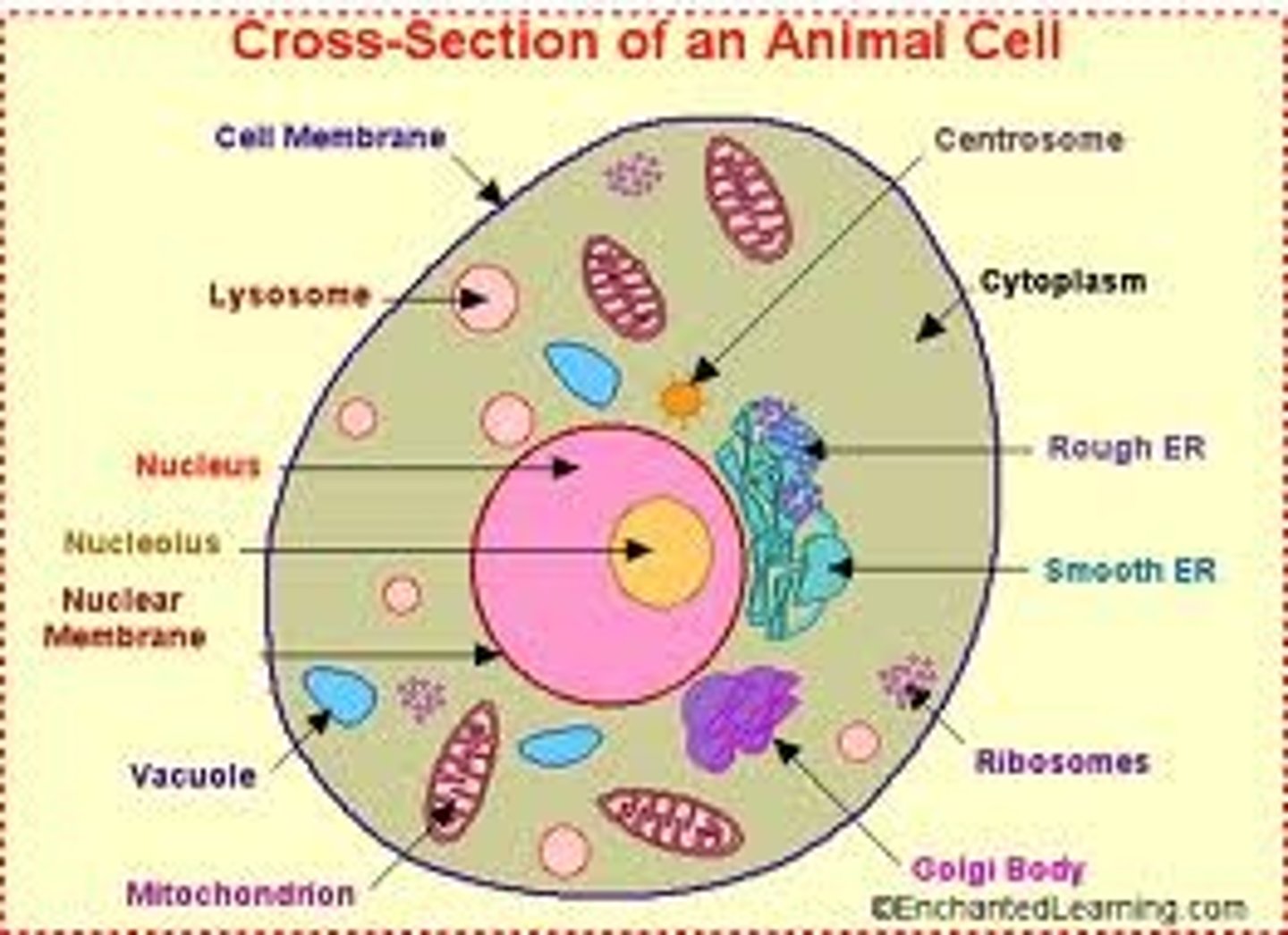
Animal cell
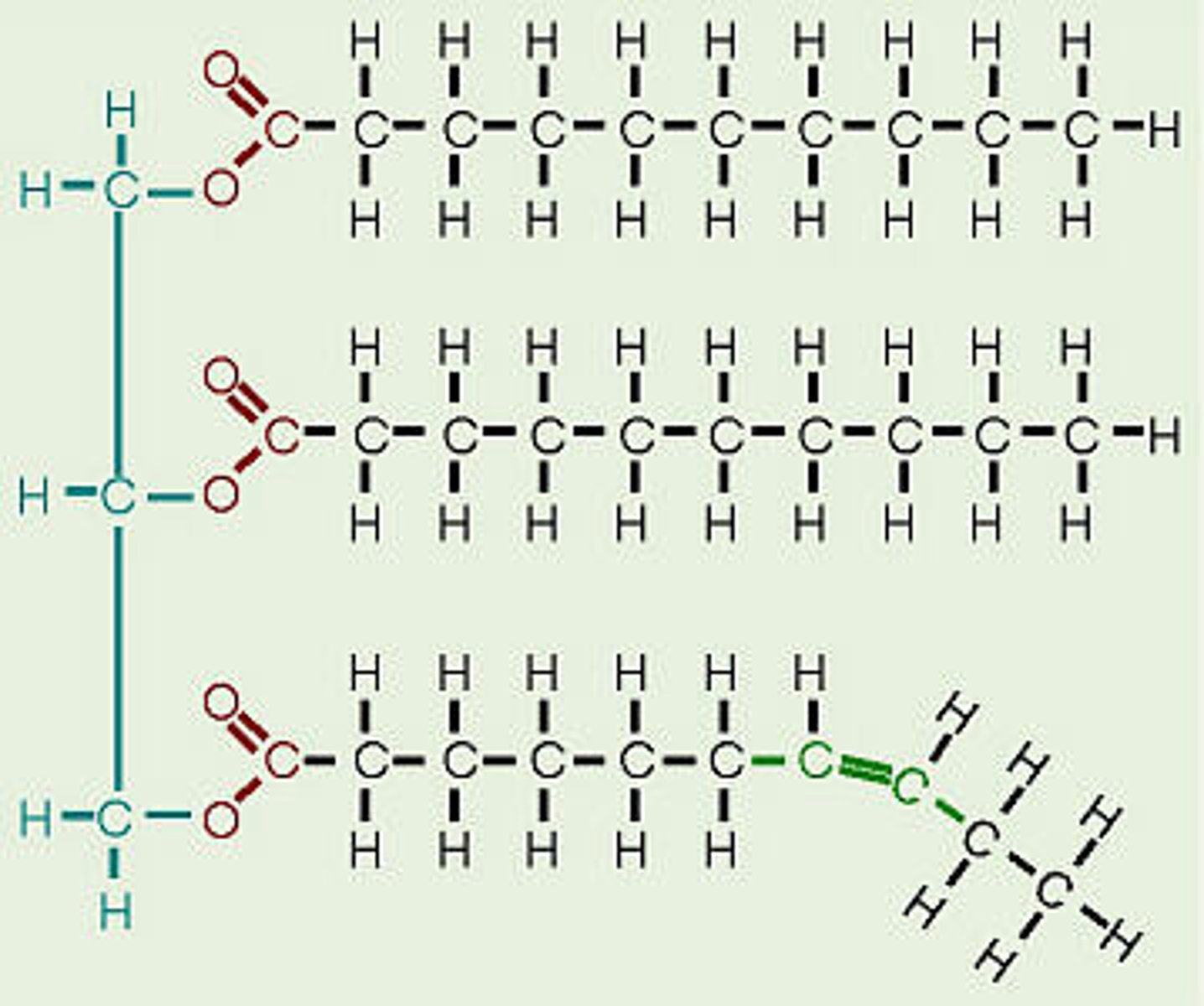
Nucleotide acid
Function: long-term energy and makes up the cell membrane
Lipids
Contains: C,H,O
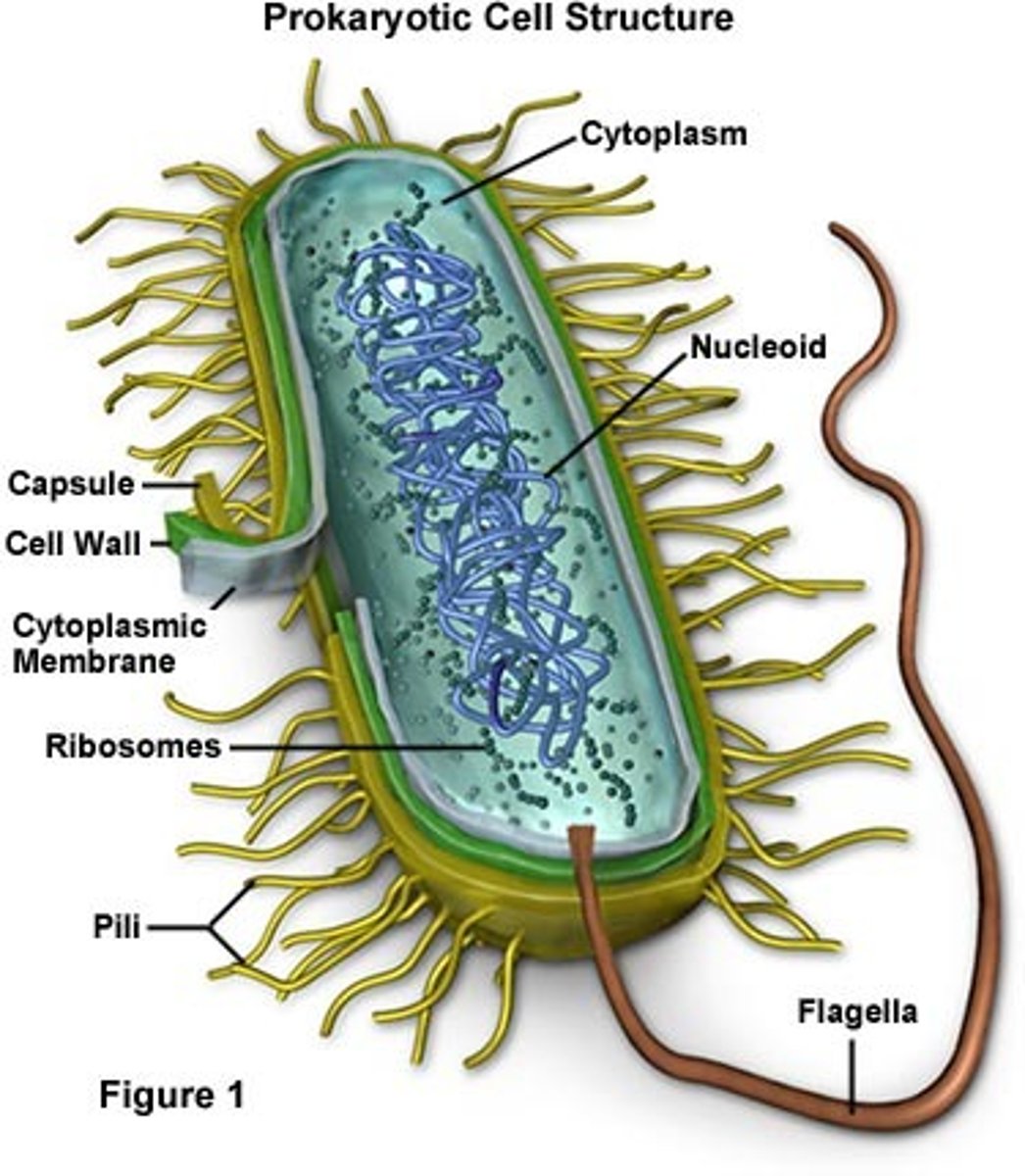
Bacteria Cell
Eukaryotic
a cell that contains a nucleus (and membrane bound organelles)
Prokaryotic
a cell that doesn't contain a nucleus (no membrane bound organelles)
photosynthesis equation
6CO2+6H2O+energy=C6H12O6+6O2
(carbon dioxide+water+sunlight=glucose+oxygen)
Cellular Respiration equation
6O2+C6H12O6=6CO2+6H2O+energy
(oxygen+glucose=carbon dioxide+water+ATP)
diploid
a full set of chromosomes (46)
haploid
1/2 the amount of chromosomes (23)
mitosis
produces 2 genetically identical diploid body cells
meiosis
produces 4 genetically different haploid sex cells
cancer
uncontrolled growth of cells causes tumors or masses of tissue that block normal function of organs
nucleotide
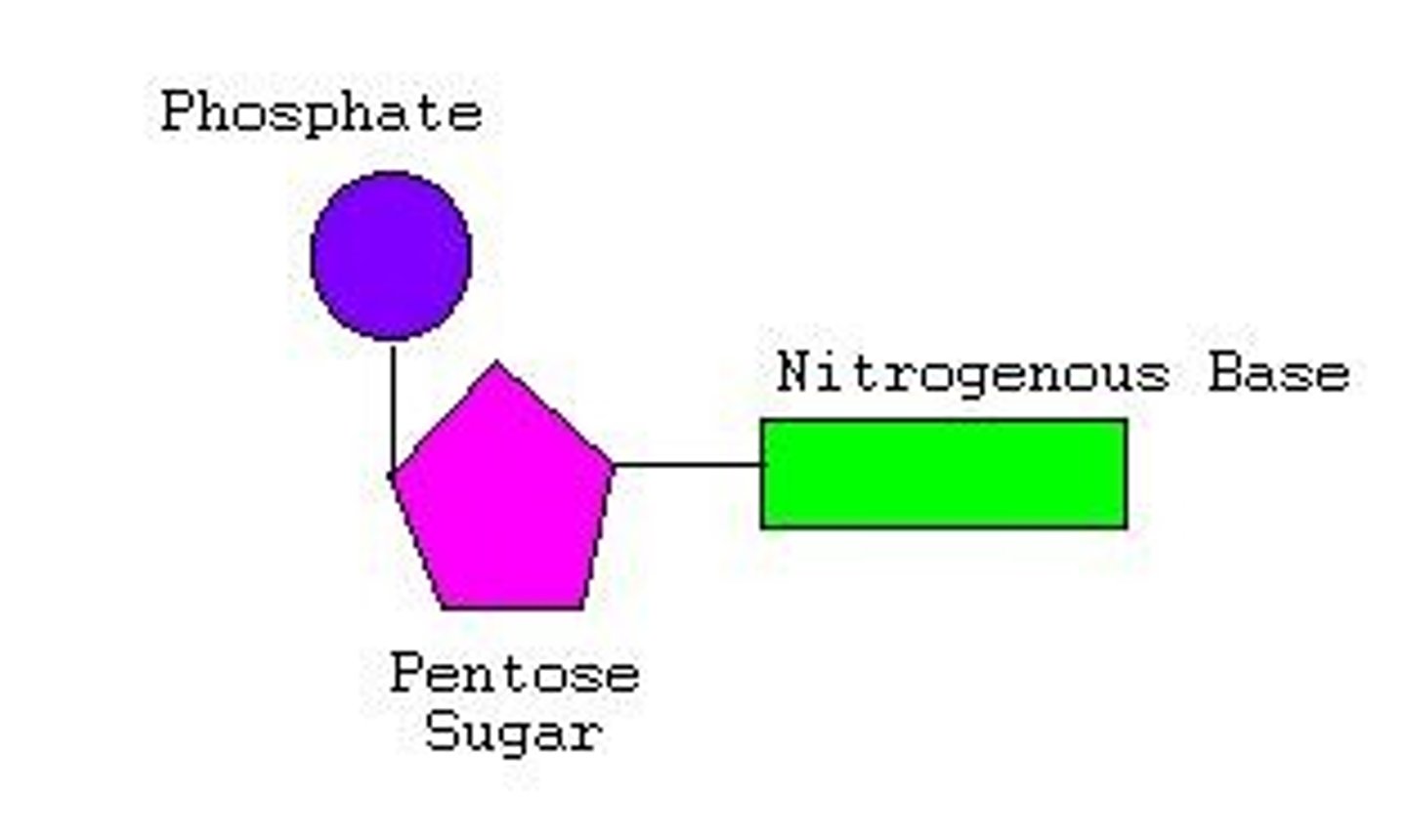
(DNA) C
G
(DNA) A
T
genetic code
the sequence of nitrogen bases (the steps on the ladder)
DNA Replication product
2 identical DNA strands
1st step of DNA replication
The 2 original DNA strands are "unzipped" down the hydrogen bond by and enzyme.
2nd step of DNA replication
complimentary DNA nucleotides are added to the split strands
3rd step of DNA replication
2 identical DNA models are left over
incomplete dominance
when one allele is NOT dominant over the other (example: a cross between a red flower and a white flower will result in a pink flower.)
Codominance
when BOTH alleles contribute to one's physical features. (Example: a black and white cow when both alleles are expressed)
Dominant
the form of the allele that shows up over the other (Example: Dark brown hair (D) is dominant over blonde hair (b)).
Recessive
the form of one allele that is masked by another (Example: Dark brown hair (D) is dominant over blonde hair (b)).
Allele
Different forms of a gene (Example: BB,Bb,bb)
Genotype
the alleles for the gene (Example: BB,Bb,bb)
Phenotype
the physical expression of the gene (Example: Blonde hair, Brown hair, Red hair, etc.)
(RNA) G
C
(RNA) A
U
transcription
in the nucleus, mRNA makes a copy of the DNA templet.
translation
in the cytoplasm, tRNA brings the amino acids and puts them in order along the mRNA molecule. after linking in a chain they eventually form a protein.
____ Nitrogen bases = 1 codon
3 (Example: AGT)
____ codons = 1 amino acid
1 (Example: AGT)
mutation
A change in the DNA
Silent Mutation
When the Amino Acid sequence stays the same after the mutation
Missense mutation
If it changes 1 Amino Acid
Nonsense mutation
If it causes a STOP codon the protein is nonfunctional, this is the worst kind.
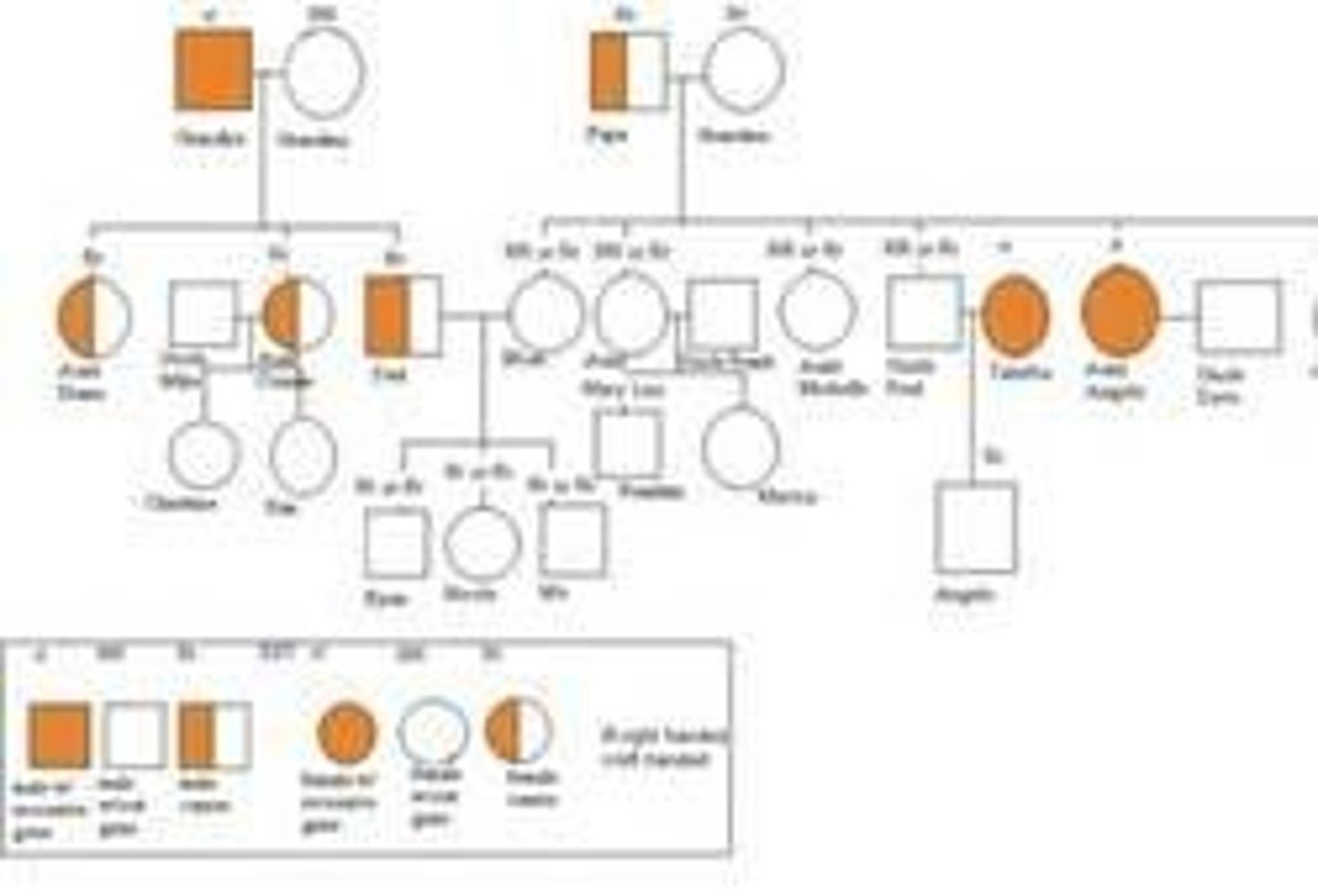
Pedigree chart
a "family tree" of inheritable disorders within a family.
Binomial Nomenclature
Scientist around the world invented this latin 2 word naming system for all species. The first name is always the 'Genus' and is always capitalized. The second name is always the 'species' and is always lowercased.
Taxonomy divisions
Kingdom-Phylum-Class-Order-Family-Genus-Species
Largest taxonomy division
Kingdom
The 6 kingdoms
Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia
"Hi, I am eukaryotic and I am mostly unicellular but part of me is colonial, I am both autotrophic and heterotrophic, Who am I"?
Protista (Examples:seaweeds)
"Hi, I am eukaryotic and I am multicellular, heterotrophic, and I have no chloroplast, Who am I"?
Animalia (Example: Gorilla)
"Hi, I am prokaryotic, unicellular person who can live in extreme environments, but I don't have peptidoglycan (PTG), Who am I"?
Archaebacteria (Example:Thermophiles)
Autotrophic
When an organism can make it's own food.
"Hi, I am eukaryotic and I am mostly multicellular, heterotrophic, and I have cell walls made of chitin, Who am I"?
Fungi (Example: mushrooms)
"Hi, I am eukaryotic and I am multicellular, autotrophic, and I have cell walls made of cellulose, Who am I"?
Plantae (Example: plant)
"Hi, I am prokaryotic, I cause bacteria, I am unicellular, autotrophic or heterotrophic, and I have cell walls made of peptidoglycan (PTG), Who am I"?
Eubacteria (Example: Strep Throat)
Heterotroph
An organism that must find and kill their food
The name for and extra copy of chromosome 13
Trisomy
1st name in binomial nomenclature
Genus (uppercase)
2nd name in binomial nomenclature
Species (lowercase)
Evolution
The change in a population over time
Theory
Twelve supported testable explanation
Darwin's theory of evolution
Adaption that causes an organism to be more suited for its environment