Dysrhythmias, MCSD (mechanical circulatory support devices) ch. 38 & 39
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Short or long-term MCS device:
Intraaortic balloon pumps (IABP)
Short
Short or long-term MCS device:
LVAD, BiVAD, PVAD
Long
Short or long-term MCS device:
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO)
Short
Short or long-term MCS device:
Continual flow pumps
Short
Provides temporary circulatory support by reducing afterload, increasing aortic diastolic pressure, & increasing coronary blood flow
IABP
__________ Contraindications:
irreversible brain damage
Mod. to Severe aortic insufficiency
Abdominal aortic and thoracic aneurysms
Terminal or untreated diseases of any major organ system
Generalized peripheral vascular disease (e.g, aortoiliac disease)
Major coagulopathy (e.g, disseminated intravascular coagulation [DIC])
IABP
IABP contraindication:
Generalized peripheral vascular disease (e.g, aortoiliac disease) may inhibit balloon placement & a relative contra.; ____________ insertion may be used
Sheathless
IABP placement:
Inserted percutaneously or surgically into the ______________ artery
Balloon is moved toward the heart & placed in the descending thoracic aorta, just below the ______________ artery
Placement is confirmed by an _________
Femoral, L. Subclavian, X-ray
Arterial trauma caused by insertion or displacement of balloon:
Assess & mark ____________ before inserting balloon to use as a baseline after insertion
Peripheral pulses
Arterial trauma caused by insertion or displacement of balloon
Assess perfusion to both upper & lower extremities at least every ________
Hour
Arterial trauma caused by insertion or displacement of balloon
Measure urine output at least every __________ (occlusion of renal arteries causes severe decrease in urine output)
Hour
Arterial trauma caused by insertion or displacement of balloon
Observe ____________ waveforms for sudden changes
Arterial
Arterial trauma caused by insertion or displacement of balloon
keep HOB no higher than _______ degrees
DO NOT _____________ at the hip
45, flex cannulated leg
Arterial trauma caused by insertion or displacement of balloon
Immobilize cannulated leg to prevent ______ using a draw sheet tucked under the mattress, soft ankle restraint, or knee immobilizer
Flexion
IABP: balloon leak or rupture
Priority action: ______________
prepare for emergent removal & possible reinsertion
Call HCP
IABP: hematologic problems d/t platelet aggregation along the balloon (e.g., thrombocytopenia)
monitor _________ profiles, _____, & ____________
Coagulation, hct, platelet count
IABP: hemorrhage from insertion site
Check site for bleeding at least every _______
Monitor VS for s/sx of ___________ with each check
Hour, hypovolemia
IABP: infection at site
Use ___________ technique for insertion and dressing changes for all lines
Cover all insertion sites with occlusive dressings
Give prescribed _____________ for entire course of therapy
Strict aseptic, prophylactic antibiotic
IABP: issues r/t immobilization (e.g., pressure injuries)
Reposition the pt at least every _________, maintaining proper positioning
Use appropriate pressure-relieving devices
2 hrs
IABP: VTE caused by trauma, balloon obstruction of blood flow distal to catheter
give prophylactic _______ therapy (if ordered)
Assess pulses, urine output, & level of consciousness at least every __________
Check circulation, sensation, & movement in both legs at least every _________
Heparin, hour, hour
Most important MSC device complications
Cardiac tamponade, dysrhythmias
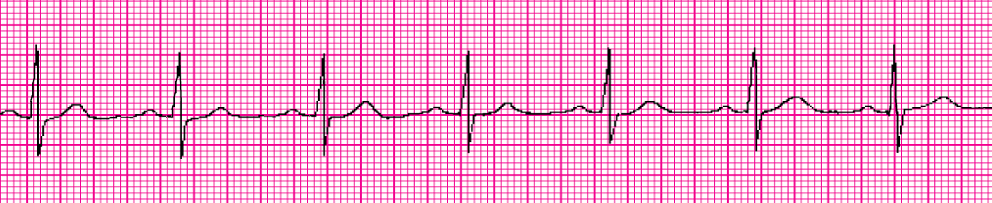
Sinus rhythm
Bradycardia treatment (symptomatic):
Address the cause
IV __________
Transcutaneous ________
IV _________ or ____________ infusion
Atropine, pacemaker, dopamine, epinephrine
Sinus tachycardia: treatment
Address the cause
___________
IV _________ or ____________
Vagal maneuvers, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers
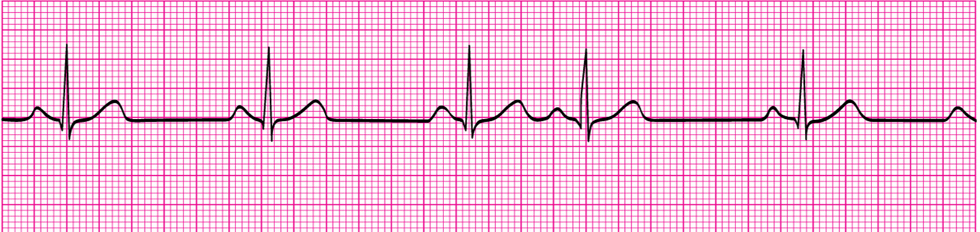
Premature atrial contractions
Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
True of false?
In healthy hearts, not a problem
T
Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs): treatment
Address the cause
____________
Beta blockers
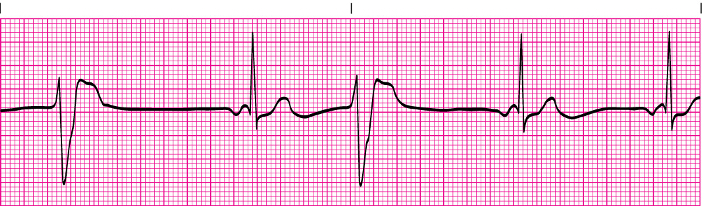
Premature ventricular contractions
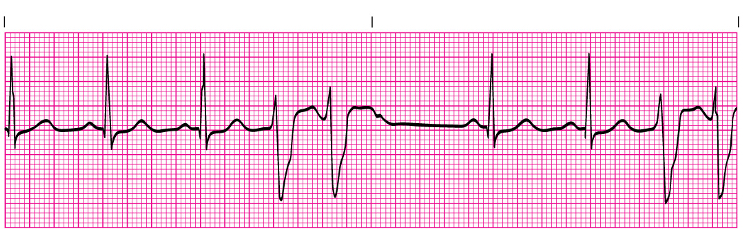
Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs)- treatment
Address the cause
If symptomatic: ____________, ___________, or ____________
Beta blockers, lidocaine, amiodarone
T or F?
Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs): Usually not harmful in healthy hearts
T
PVCs: may decrease CO in patients with
Heart disease
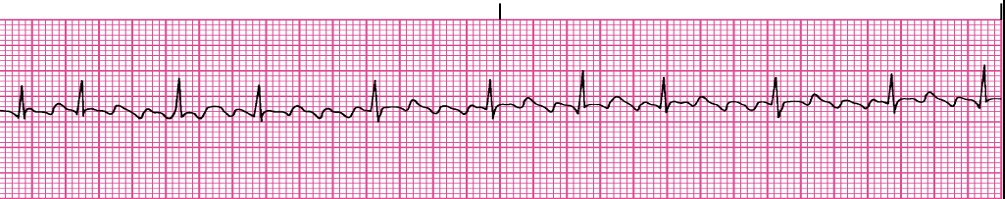
AF
loss of atrial kick & high ventricular rate = decreased CO
Atrial flutter, a fib
Biggest Atrial Flutter risk
stroke risk
Atrial Flutter- treatment
Beta blockers or CCB
___________
_______________
____________
Amiodarone, catheter ablation, anticoagulants
If AFlutter unstable:
Synchronized cardioversion
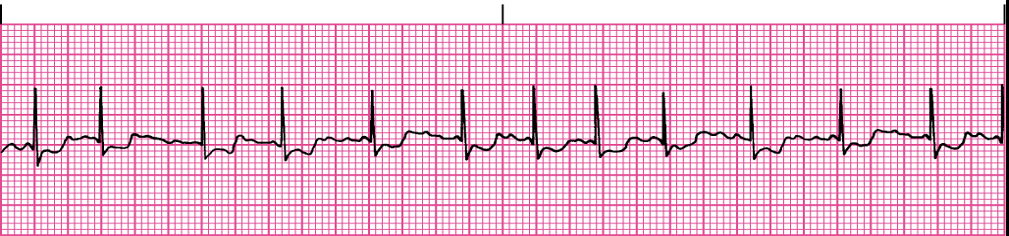
A. fib
Atrial Fibrillation: treatment
Same as a. flutter
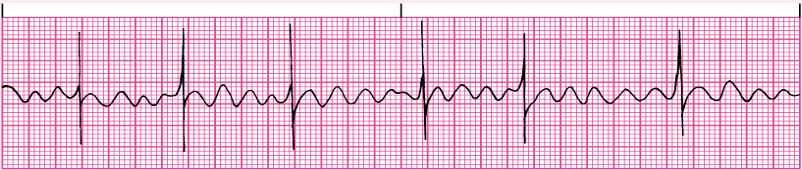
Atrial flutter
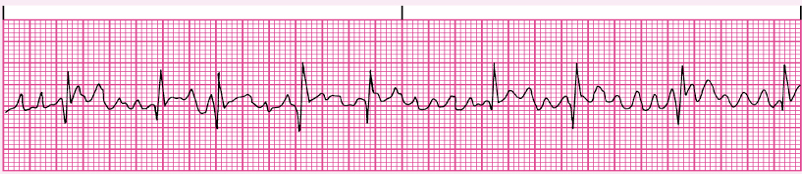
A fib
Supraventricular tachycardia- hr
150-220
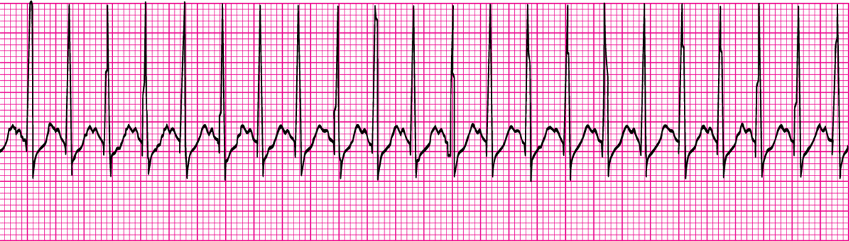
PSVT
Supraventricular Tachycardia (aka PSVT, atrial tachycardia)
If prolonged, will cause decreased CO d/t decreased ____
SV
Supraventricular Tachycardia (aka PSVT, atrial tachycardia) : treatment
______________
Drug of choice; _____________
___________ or _____________
Vagal maneuvers, adenosine, IV beta blockers or ccb
Supraventricular Tachycardia (aka PSVT, atrial tachycardia)
If unstable: ___________
Synchronized cardioversion
Adenosine:
Explain that the pt may feel ________ after receiving
Injection site should be as close to the heart as possible
Give IV dose ______ & follow with a rapid __________. Use a ________ setup to make sure adenosine gets to the heart quickly
Chest pressure, rapidly, 20ml NS flush, stopcock
Adenosine:
Monitor ECG continuously, brief period of ________ is common
Assess pt for flushing, dizziness, chest pain, or palpitations
Asystole
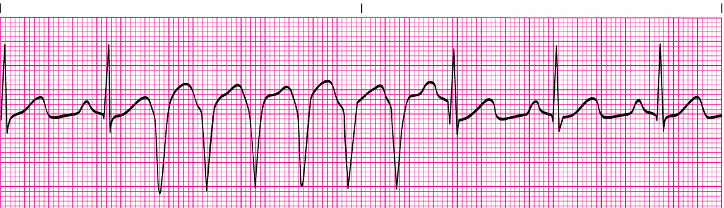
VT
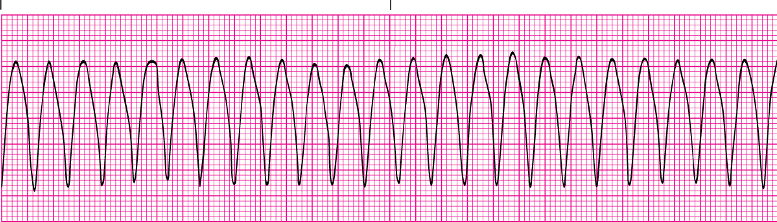
VT
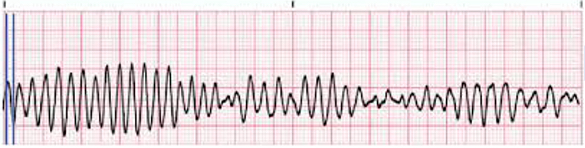
VT torsade de pointes
VT, unstable means pt
Pulseless
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT): medications
__________, _________, or ___________
Lidocaine, amiodarone, procainamide
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT): Device
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD)
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT): Stable action
Cardioversion
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT): Unstable action (no pulse)
Defibrillation, CPR, epinephrine
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT): Medication for Torsades de pointes: __________
IV magnesium
If VT untreated can lead to
VF
Cardioversion:
Synch: _____
client awake and sedated
LOWER JOULES THAN DFIB
Consent form, EKG monitor
On
V. Fib/ V. Tach without pulse:
EMEGENCY → ________
Defibrillation
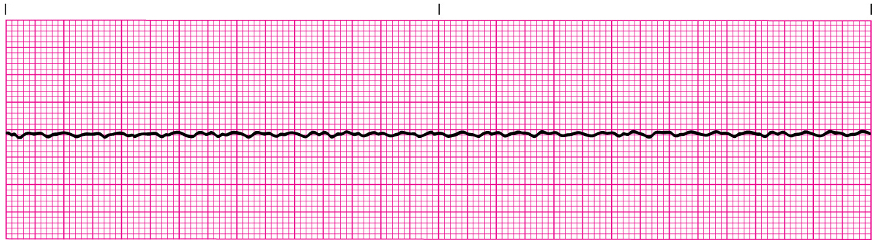
VF
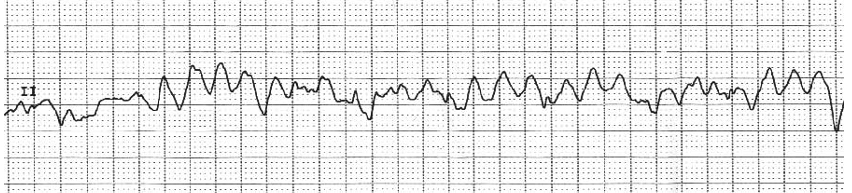
VF
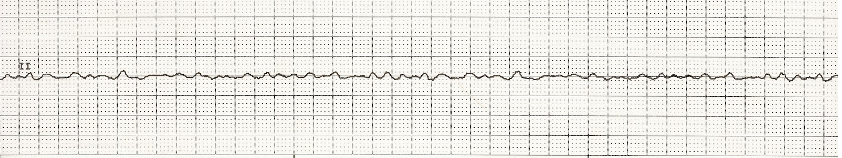
VF
Ventricular Fibrillation (VF): treatment
_________ (ASAP** stop compressions/breaths) & CPR
_________
__________ or ___________
Defibrillation, epinephrine, amiodarone, lidocaine
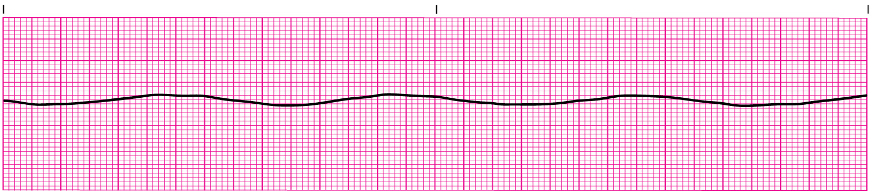
Asystole
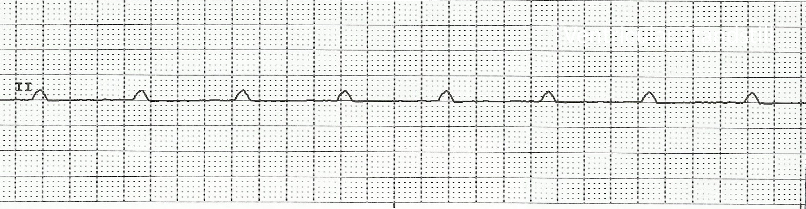
Asystole
Asystole: unresponsive, pulseless, & apneic
Treatment:
________ & _____________
NO DEFIBRILLATION (NO SHOCKS - flat line, no activity to fix)
CPR, epinephrine
Pulseless Electrical activity (PEA):
Organized electrical activity WITHOUT a pulse
Always check pt first, not monitor
Treatment: _____ & ______
CPR, epinephrine
R far from P
First degree
Longer, longer, longer, drop
Wenkebach
If some Ps don’t get through, then u have
Mobitz II
Ps and Qs don’t agree, you have
Third degree
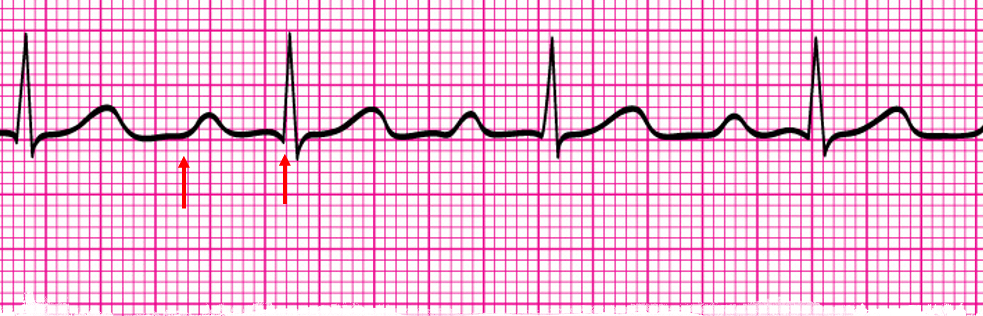
NSR w/ 1st degree AV block
The only difference between NSR and NSR w/ a First Degree AV Block is a lengthened PR interval (greater than __ small squares or 1 big box)
5
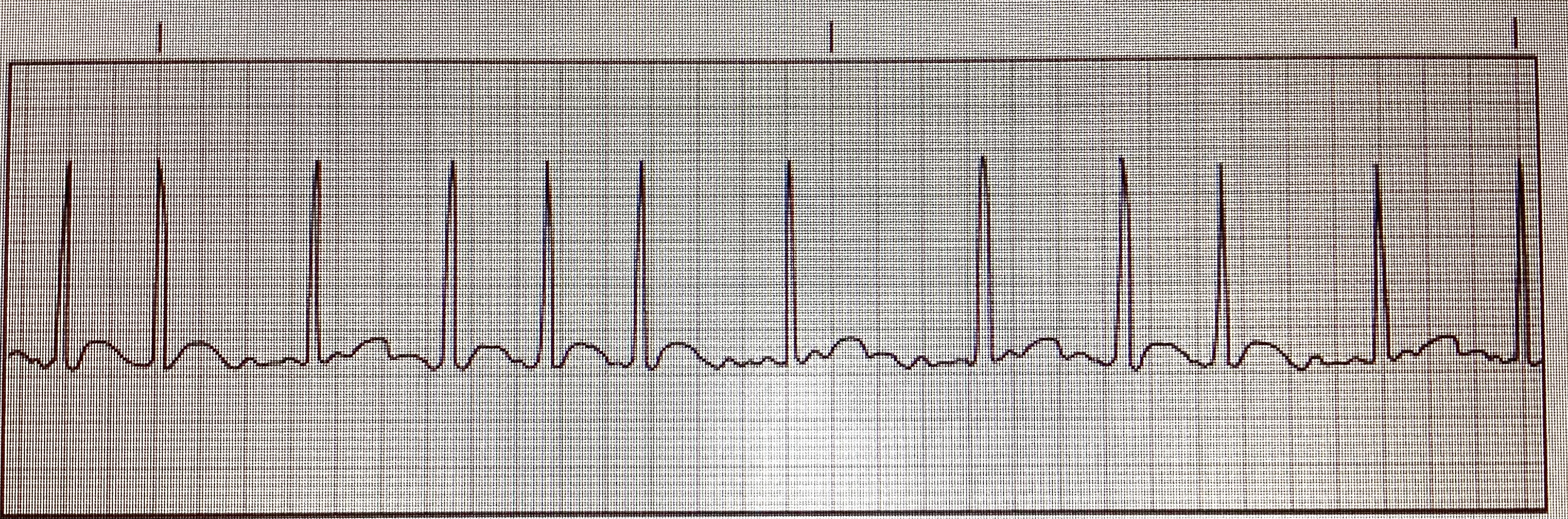
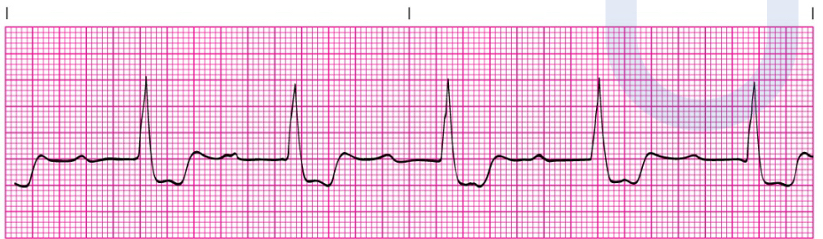
1st degree AV block
First degree AV Block:
Usually not ________
asymptomatic
Serious
First-degree AV Block: treatment
Monitor ecg changes
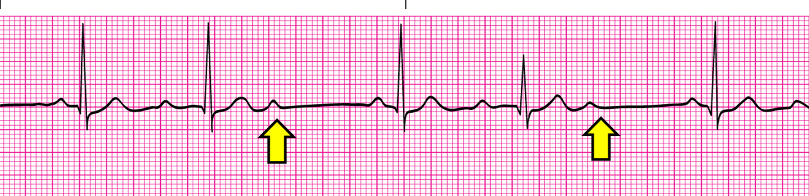
Wenckebach
2nd degree AV Block Type I (Wenkeback):
Usually transient & well-tolerated
May be a warning sign of a more serious _________
dsyrhythmia
2nd degree AV Block Type I (Wenkebach):
If symptomatic- __________, ______________
Atropine, pacemaker
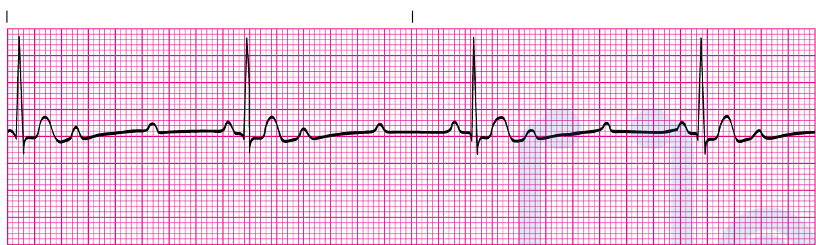
Mobitz II
2nd degree AV Block Type II (Mobitz II)
Often progresses to 3rd degree AV block
Treatment: ________________
Symptomatic treatment: ________________
Permanent pacemaker, temporary transcutaneous pacemaker
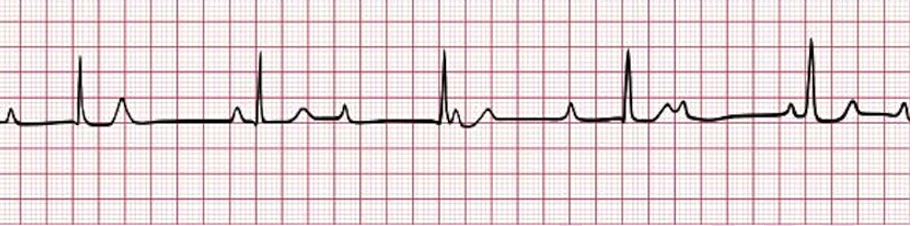
3rd degree AV Block
3rd Degree AV Block (complete heart block)
Treatment:
Requires permanent pacemaker
If symptomatic: _______________
Drugs: ________, ____________
Temporary transcutaneous pacemaker, dopamine, epinephrine
Not effective against third degree AV block
Atropine
Pacemakers: _______ device inhibits the pacemaker when the HR is adequate
Sensing
Pacemakers: ______ device triggers the pacemaker when noQRS complexes occur within a preset time
Pacing
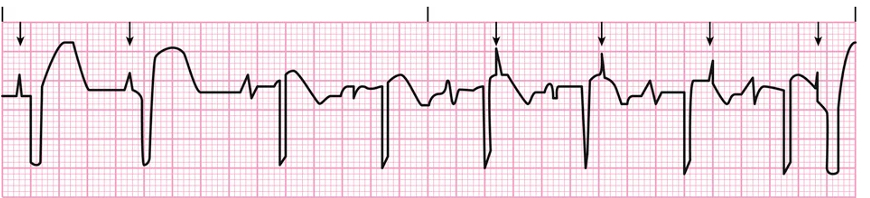
Failure to sense
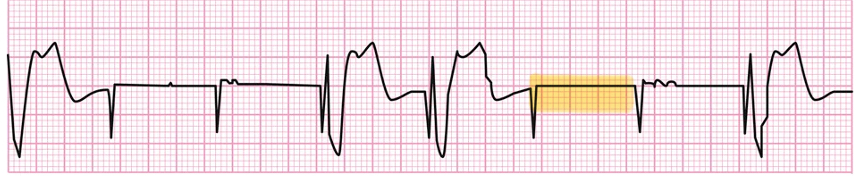
Failure to Capture
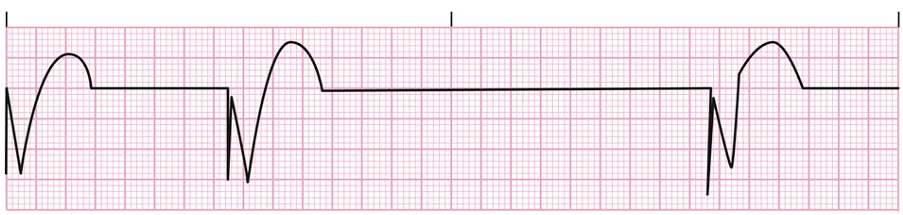
Pacemaker
Failure to Pace
Pacemaker Troubleshooting:
Monitor continuous ECG & pt.s vital signs while troubleshooting problems
Make sure all connections are hooked up correctly & tight
Check that generator has power (plug in the equipment or use a new battery each time)
Place the patient on _________ to promote contact of the trans venous pacing wire with the epicardium
Adjust settings (sensitivity, electrical charge) as indicated
___________ immediately if basic troubleshooting does not work, as pt could have a lead wire displaced or a defective lead wire
Left side, contact HCP