3. SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT PROCESS MODELS
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
180 Terms
What are the three key elements essential for creating a successful software product?
People, projects, and processes.
What role do processes play in software development?
They guide project tasks and ensure the quality of the final product.
Why is choosing the right process model critical in software development?
A poor selection can negatively impact project quality.
What can software development models be tailored to fit?
The specific needs of an organization based on its size, maturity, and the complexity of the software being developed.
What are the three generic stages of the software development process?
Definition, Implementation, and Maintenance.
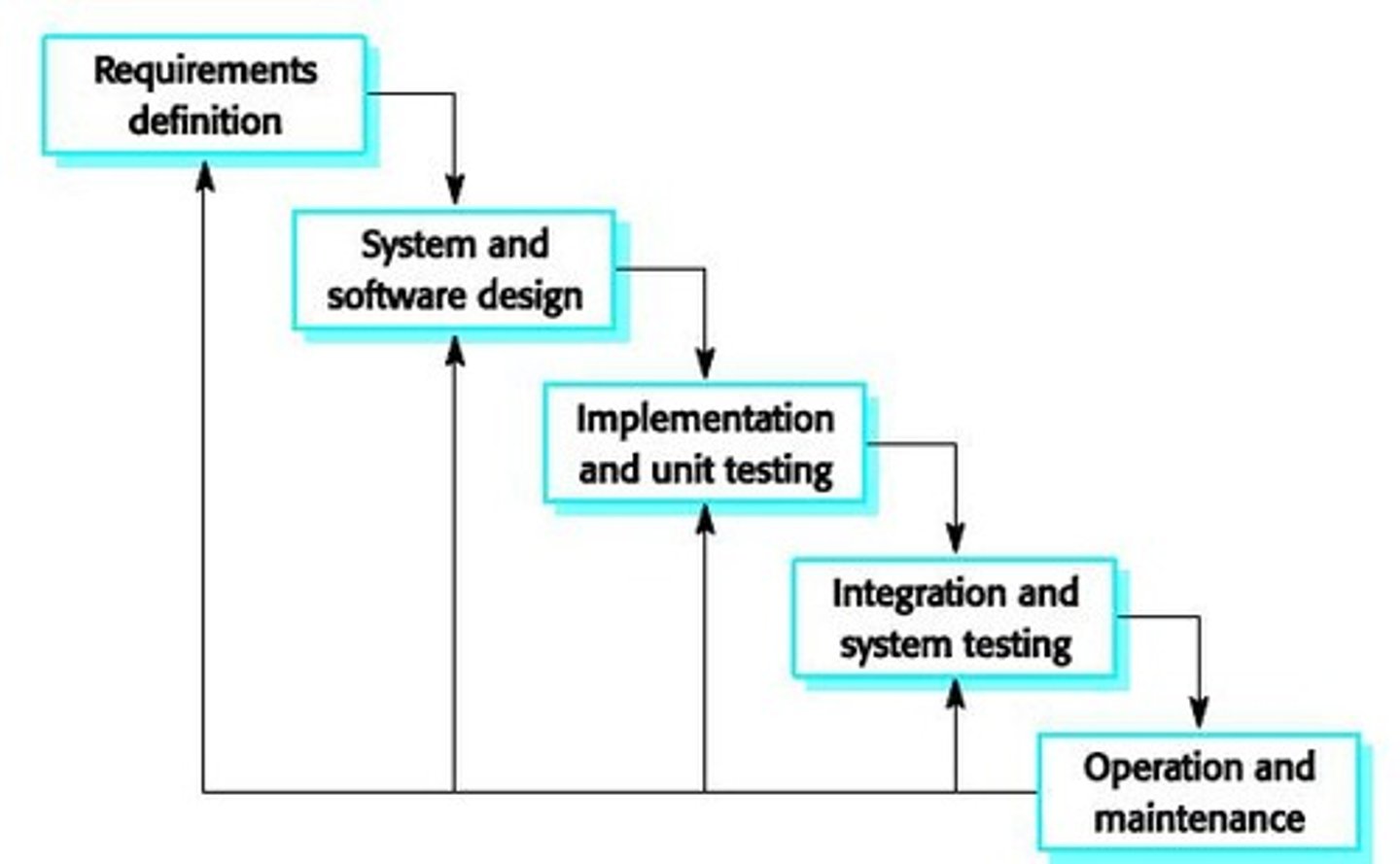
What is the Classic System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) also known as?
The Waterfall Approach or Linear Sequential Model.
What is the first phase of the Classic SDLC?
Analysis, which establishes system requirements through user consultations.
What is produced during the Analysis phase of the Classic SDLC?
The Requirements Specification Document and other deliverables like the acceptance test plan and project plan.
What is the focus of the System/Software Design phase in the Classic SDLC?
Developing the overall architecture, including high-level and detailed designs, database schema, and interfaces.
What key outputs are produced during the System/Software Design phase?
Design Specifications Documents detailing the system's components and interactions.
What occurs during the Implementation phase of the Classic SDLC?
Translating design into executable code using a programming language and integrating the database.
What is the purpose of the Testing and Integration phase in the Classic SDLC?
To execute test plans to verify that the software meets requirements and specifications.
What happens during the Operation and Maintenance phase of the Classic SDLC?
The system is installed for practical use, usability is tested, and client acceptance is obtained.
What deliverables are included in the Operation and Maintenance phase?
An acceptance document and the operational software system.
What are the three major categories of software engineering process models?
Linear Models and Variants, Iterative Models, and Agile Models.
What is the significance of proven software development and maintenance models?
They offer structured approaches often supported by useful tools.
How can software development models impact project outcomes?
By providing a framework that can enhance the quality and efficiency of the software development process.
What is a potential consequence of not following a structured software development model?
Increased risk of project failure and lower quality of the final product.
What is the relationship between software engineering models and project controls?
The choice of model influences the methods, tools, controls, and deliverables required for the project.
Why is user consultation important in the Analysis phase?
It helps establish accurate system requirements.
What is the end goal of the Testing and Integration phase?
To ensure the final integrated software meets all specified requirements.
What does the term 'deliverables' refer to in the context of software development?
The tangible outputs produced at various stages of the development process, such as documents and software.
What are the characteristics of project development phases in the Waterfall Model?
They are sequential, generally one-way, with deadlines determined early, unambiguous required results, and milestone documents that signal the start of subsequent phases.
What is a key advantage of the Waterfall Model in project management?
It divides large and complex tasks into smaller, manageable tasks, allowing for careful planning and clear delineation of authorities and responsibilities.
What is a significant disadvantage of the Waterfall Model?
Real projects rarely follow the sequential flow, making it difficult to accommodate changes once the process is underway.
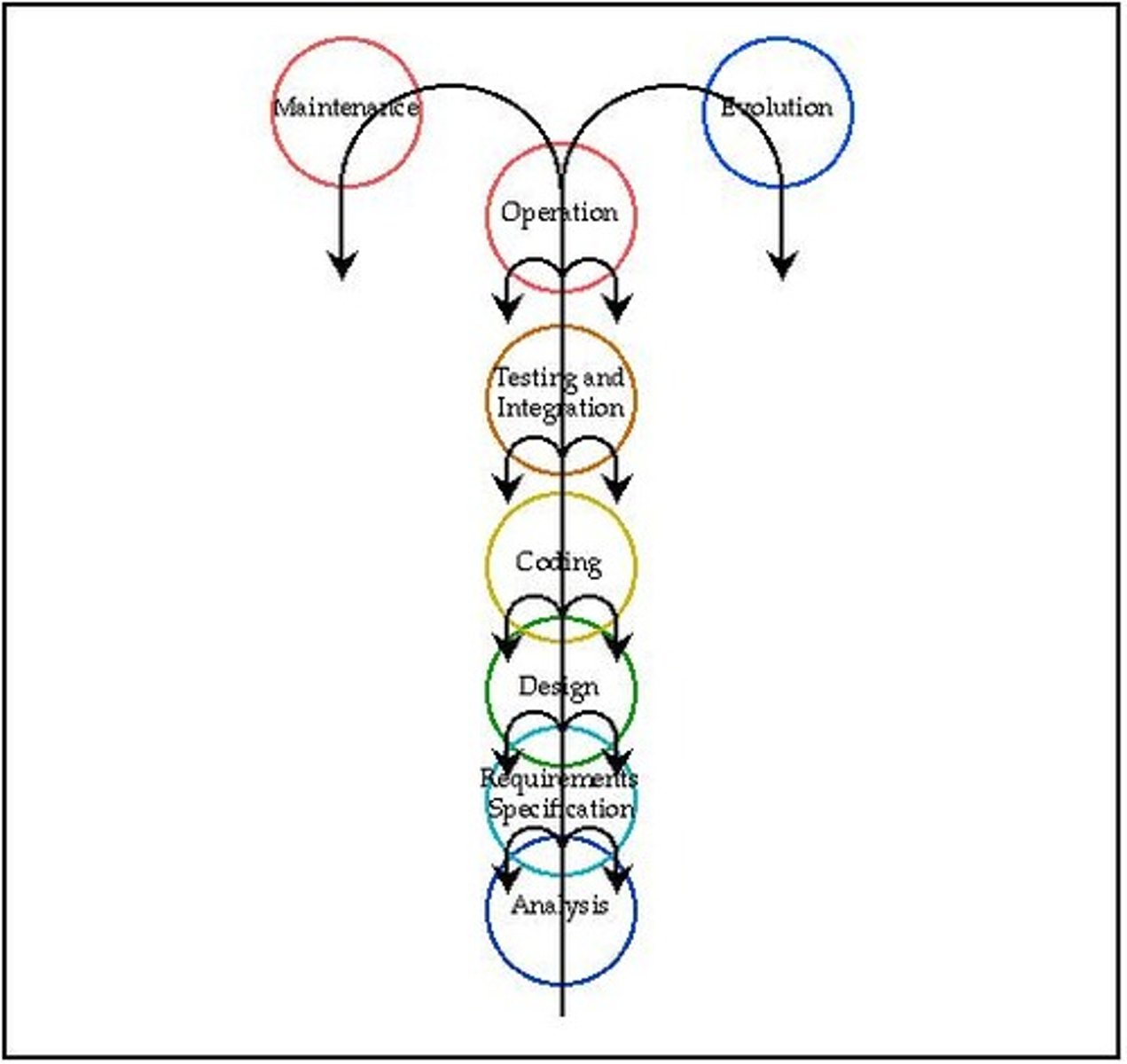
How does the Fountain Model differ from the traditional Waterfall Model?
The Fountain Model allows for upward flow and supports iterations back to previous phases, acknowledging the need to revisit earlier stages.
What is the purpose of the Business Modeling phase in the Rapid Application Development (RAD) Model?
To analyze information flow among business functions to determine what information drives processes, who generates it, and where it goes.
What does the Data Modeling phase in the RAD Model focus on?
It refines the information flow into data objects needed for the business, identifying each object's attributes and relationships.
What is the goal of the Process Modeling phase in the RAD Model?
To transform data objects to create the necessary information flow for implementing business functions, detailing processes for managing data.
What does the Application Generation phase in the RAD Model utilize?
It utilizes fourth-generation techniques, focusing on reusing existing program components and automated tools for software construction.
What is a major drawback of the Waterfall Model regarding customer requirements?
It is often difficult for the customer to state all requirements explicitly, which can lead to issues later in the project.
What happens if an ambiguity in software requirements is discovered during the design phase of the Waterfall Model?
The designer must report the error to the manager, and the analysis team must address the ambiguity, which can lead to higher repair costs if ignored.
What is a common issue with the documentation in the Waterfall Model?
The amount of documentation can be excessive, potentially leading to increased maintenance costs.
What does the linear sequential nature of the Waterfall Model discourage?
It discourages late changes, as one phase must be completed before moving on to the next.
What is the ideal scenario for applying the Waterfall Model?
It is ideal when resources are available and standard procedures are fully documented.
What is the significance of milestone documents in the Waterfall Model?
Milestone documents conclude each project phase and, when approved, signal the start of the subsequent phase.
What is a potential consequence of the linear sequential nature of the Waterfall Model?
It may lead to a 'blocking state' where progress is halted due to unresolved issues in earlier phases.
How does the Fountain Model improve upon the Waterfall Model?
It allows for revisiting earlier stages, making it more adaptable to changes and issues identified during development.
What is the focus of the Application Generation phase in the RAD Model?
It emphasizes reusing existing program components and using automated tools to expedite software construction.
What is a notable feature of the RAD Model compared to the Waterfall Model?
RAD is designed for short development cycles through component-based construction.
What is one of the main challenges of managing the Fountain Model?
It necessitates effective change control procedures due to its iterative nature.
What is a key benefit of having clearly specified inputs, deliverables, and milestones in project phases?
It allows management to assess project progress and take corrective action if necessary.
What does the term 'blocking state' refer to in the context of the Waterfall Model?
It refers to a situation where progress is halted due to unresolved issues from earlier phases.
What is the role of authorities and responsibilities in the Waterfall Model?
They can be clearly delineated, which aids in project management and accountability.
What does RAD emphasize in testing and turnover?
The reuse of tested components, reducing overall testing time while ensuring new components and interfaces are thoroughly tested.
What are the requirements for successful RAD implementation?
Sufficient human resources to create RAD teams, and commitment from customers and developers to rapid-fire activities.
In what situations is RAD not appropriate?
1) When the system cannot be properly modularized, 2) When high performance is needed, 3) When technical risks are high due to interoperability issues.
What are some linear life-cycle strategies customized for specific organizations?
1) Model Systems Ltd used by NCC-UK, 2) Foundation used by Andersen Consulting, 3) Structured Project Life-cycle used by Yourdon group.
What is the purpose of creating a software prototype in the iterative or prototyping process?
To better understand customer requirements before delivering the final system.
What is a key characteristic of the iterative or prototyping approach?
Development starts with incomplete requirements and full requirements are derived from user interaction on a prototype.
What are the three types of prototyping based on the amount of code retained in the final system?
1) Prototyping with disposable system, 2) Prototyping with working system, 3) Evolutionary prototyping.
What is the goal of prototyping with a disposable system?
To test proposed solutions, formalize requirements based on feedback, and discard the prototype before following a linear sequential model.
What does prototyping with a working system involve?
Building a prototype of critical functions that is expanded into a fully functional system upon acceptance.
What is the focus of evolutionary prototyping?
Adapting to changing requirements, with subsequent prototypes evolving into the operational system for deployment.
When is the iterative or prototyping approach ideal?
For systems where requirements may be defined but human-computer interface suitability is not yet known.
What are some advantages of the iterative or prototyping approach?
1) System requirements can change during the project, 2) Delivers clear system definitions, 3) Enhances communication and user involvement.
What is a disadvantage of the iterative or prototyping approach?
Rising expectations of the end user, who may see a working version of the software without understanding the quality and maintainability issues.
How does the iterative approach enhance communication?
It increases end user involvement and satisfaction regarding the suitability of human-computer interfaces.
What can the iterative approach quickly test?
The development environment.
What can the iterative approach be used to demonstrate?
Technical, economic, and political feasibility.
What is a potential issue with user expectations in iterative development?
Users may demand fixes for the product thinking it is a complete working system, unaware of overall software quality concerns.
What is the main focus of the APC-model in prototyping?
It depicts human-machine interactions and focuses on the functional aspects related to the graphical user interface.
What does the iterative process continue until?
The customer is satisfied with the developed model.
What is the role of customer feedback in the prototyping process?
It is gathered to implement functions required of the system in subsequent prototypes.
What is a key benefit of developing a prototype before the final system?
It allows for better understanding and refinement of customer requirements.
What is the significance of user interaction in the prototyping process?
It helps derive full requirements from initial incomplete requirements.
What is the outcome of the iterative approach in terms of system delivery?
A system that evolves through iterations based on user feedback and changing requirements.
What is a danger of never-ending development in software projects?
It arises from user-developer interactions during development.
What planning aspects can be neglected in software development?
Planning, verification, validation, backup procedures, and documentation.
What is a risk of modeling before analyzing current and desired results?
It can lead to inadequate understanding and poor design outcomes.
What compromises might be made to quickly get a prototype working?
Design and implementation compromises.
Why should building on top of a prototype be avoided?
It often leads to software project failure unless the prototype accurately reflects customer desires.
What is the purpose of prototyping in software development?
To clarify requirements and explore design alternatives, addressing weaknesses in the Waterfall Model.
How does prototyping help in the software development process?
It facilitates requirement review and approval, reducing the risk of changes and minimizing revisions.
What is the starting point of the evolutionary software process model?
The problem domain that needs to be solved by means of a software system.
What are the steps in the evolutionary software process model?
1. Define functional boundaries of the desired system; 2. Split the system into microsystems; 3. Develop and put the microsystem into production; 4. Reassess long-term goals and adjust subsequent microsystems.
What characterizes the evolutionary model in software development?
It is product-oriented, iterative, and involves continuous testing and re-planning.
What are some advantages of the evolutionary model?
Faster results for developers, quick responses for end users and management, fast reactions to changing goals, and better manageability.
What are some disadvantages of the evolutionary model?
No recursion to previous microsystems is scheduled, changing environments might obliterate long-term goals, and it could be costly.
What is the Incremental Model in software development?
It combines elements of the linear sequential model with the iterative philosophy of prototyping, producing deliverable increments of software.
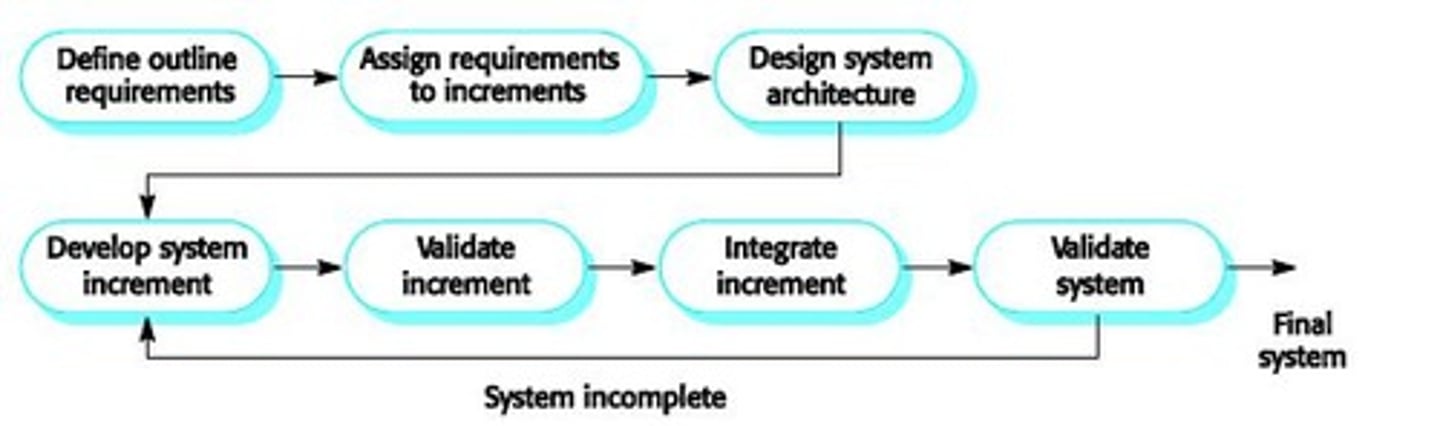
What happens after the core product is evaluated in the Incremental Model?
A plan is developed for the next increment or release, addressing medium priority requirements and additional features.
What is an advantage of the Incremental Model?
An operational product is produced with each intermediate progress/version.
How does the Incremental Model reduce risk?
It reduces the risk of failure and changing requirements.
What is a disadvantage of the Incremental Model regarding process visibility?
It lacks visibility; it is difficult to determine how far the product is from the final version.
What is a common issue with systems developed using the Incremental Model?
They are often poorly structured.
What can users do with the Incremental Model?
Users can adjust to new technology in incremental steps.
What is the main purpose of the Incremental Model in software development?
It is useful when technical requirements or staffing are unavailable for complete implementation by the business deadline.
What are the key requirements for using the Incremental Model?
Requirements should be clearly defined, releases should be carefully scheduled, and a specifications document should be produced before coding.
What is a significant advantage of the Spiral Model?
It combines the iterative nature of prototyping with the systematic approach of the linear sequential model, allowing for incremental releases.
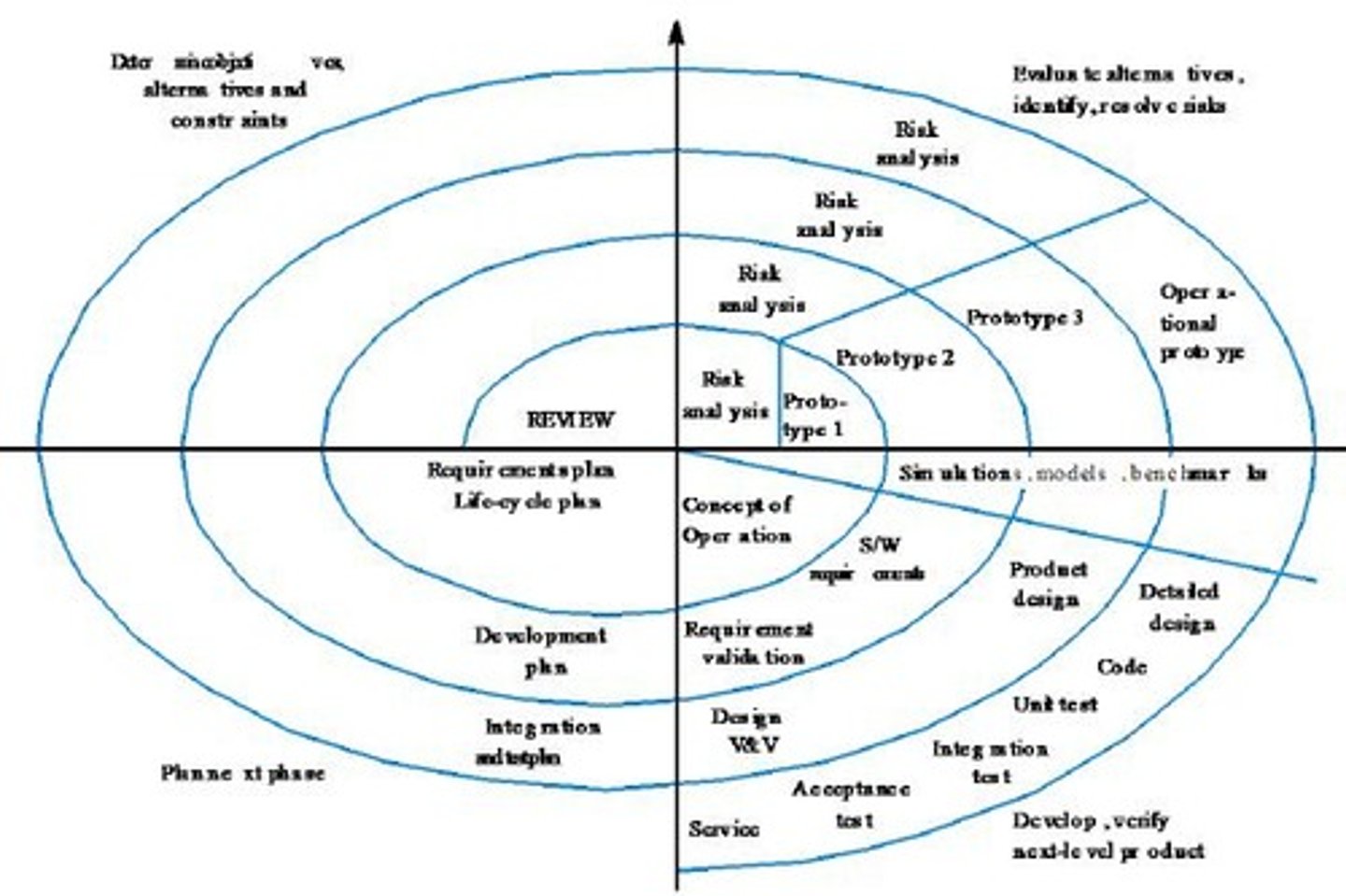
List the framework activities involved in the Spiral Model.
1. Customer Communication 2. Planning 3. Risk Analysis 4. Engineering 5. Construction and Release 6. Customer Evaluation.
How does the Spiral Model address risks in software development?
It emphasizes risk assessment and may include throwaway prototypes to reduce risks.
What are some advantages of the Spiral Model?
It splits large development efforts into small chunks, allows for incremental release, and enables cumulative cost assessment.
What are the disadvantages of the Spiral Model?
The model is complex, may be too costly, lacks clear distinct phases, and requires additional documentation for intermediate stages.
In what situations is the Spiral Model ideally applicable?
It is ideal for large-scale systems, when there are too many risks involved, when procedures and technology are dynamic, and when there is a lack of expertise.
How does the Spiral Model improve upon the Waterfall Model?
It incorporates formal and continuous risk management throughout the software development process.
What is the Concurrent Development Model also known as?
Concurrent Engineering.
What is the main function of the Concurrent Development Model?
It allows tracking of the status of complex sets of activities that occur simultaneously during any one phase.
What does the Concurrent Development Model define regarding software engineering activities?
It defines a network of activities that exist simultaneously rather than confining them to a sequence of events.
What is a key recommendation for using the Incremental Model?
It is applicable for small companies in a growing stage, especially when the budget is limited.
What should be done before coding in the Incremental Model?
A specifications document should be produced.