PD II Head
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
What is a burr hole?
small holes to cranium to relieve intracranial pressure
Describe dandruff
loose white flakes
Describe lice infestation
tiny white ovoid nits
How do you differentiate between dandruff and a nit?
dandruff is easily moveable, nits are more attached and harder to remove
Describe seborrheic dermatitis or psoriasis
redness and scaling
PWS
port wine stain; nevus flammeus
Sturge-weber syndrome
overabundance of capillaries around the trigeminal nerve that leads to port-wines stain on the scalp, upper eyelid and one side of the face and seizures and cerebellar classifications
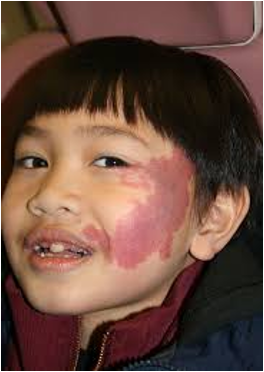
In sturge weber syndrome, what occurs on the same side of the birthmark?
abnormal blood vessels on the brain surface, loss of nerve cells and calcification of underlying tissue in the cerebral cortex
Ramsey hunt syndrome clinical presentation
facial paresis, hyperacusia, unilateral loss of taste, reduced tear formation, reduced salivation, pain in ear and vesicles in the ear canal and ear drum

What is the cause of Ramsey Hunt Syndrome?
involvement of geniculate ganglion by herpes zoster; occurs when a shingles outbreak affects the facial nerve near one of your ears
What is hyperacusis?
increased sensitivity to sound and a low tolerance for environmental noise
What are some causes for otalgia?
otitis externa, otitis media, or referred from head or neck: TMJ, Teeth, C2, C3, CN V, VII, IX, X
What are causes for bloody otorrhea?
carcinoma, trauma- perforation, barotrauma
What are causes for clear otorrhea?
CSF leak secondary to trauma (halo test)
What are causes for purulent otorrhea?
otitis externa, otitis media with the rupture of TM
What is Vertigo?
hallucination of movement provoked by rapid change of position of the head
What is benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV)?
extra ocular eye movement provokes vertigo
How do you diagnose vertigo?
Dix Hallpike maneuver
How do you treat vertigo?
Epley Maneuver
What are causes for sensorineural hearing loss?
rubella during pregnancy (congenital), medications such as tobramycin, gentamicin, ASA (acquired), systemic disease, viral infection, neoplasm, (delayed onset)
What are causes for conductive hearing loss?
cerumen impaction, Eustachian tube dysfunction, foreign body
What are history questions you would ask for the ear?
How is your hearing? Have you had any trouble with your ears- one or both? When did it start and has it gotten worse or better? Do you feel dizzy / nauseated / vomit? Do you feel lightheaded or like you are going to pass out? Do you have ringing in your ears? Do you have any pain in your ears?
What other organ abnormalities can ear malformations be associated with? Why?
kidney abnormalities bc the ears and kidneys develop at the same time during fetal development
How is the external ear cartilage normally?
firm in texture and moveable
What may pain with movement of the tragus indicate?
otitis externa
What may a swollen, tender, and red cartilage indicate?
polychondritis
What is ochronosis? What may cause this?
blue discoloration of tissues such as ear cartilage; homogentisic acid accumulation in the cartilage (autosomal recessive metabolic disorder)
What are two causes for a lifting of the ear lobes?
enlarged parotid glands, mastoiditis
If you notice a small external ear, what should you check for?
congenital abnormalities of the kidney
What cancers may be found on the external ear?
squamous cell, basal cell, melanoma
Describe how the auditory canal should normally appear during an otoscope examination.
yellow to brown cerumen with some hair
Describe how the tympanic membrane should normally appear during otoscope examination.
pinkish gray, translucent, in neutral position, mobile with air inflation
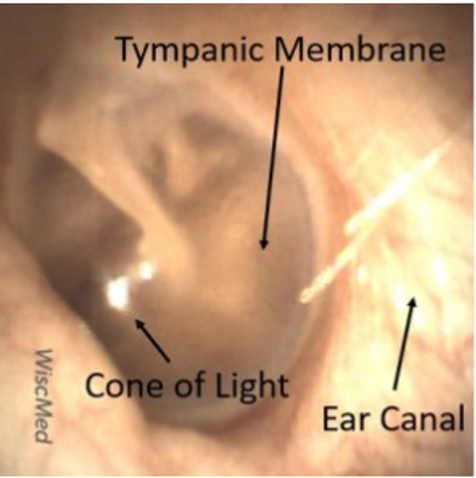
What speculum should you use for otoscopic exam of the ear?
largest speculum for that patient
How do you straighten the ear canal when looking in adults?
up and back
How do you straighten the ear canal when looking in children?
down and back
Describe air insufflation otoscopy (pneumatic-otoscope)
apply positive and negative pressures to the TM with a rubber squeeze bulb to assess the mobility; useful to evaluate middle ear diseases
Describe a cerumen impaction
yellow to brown sticky hard cerumen obscuring the drum
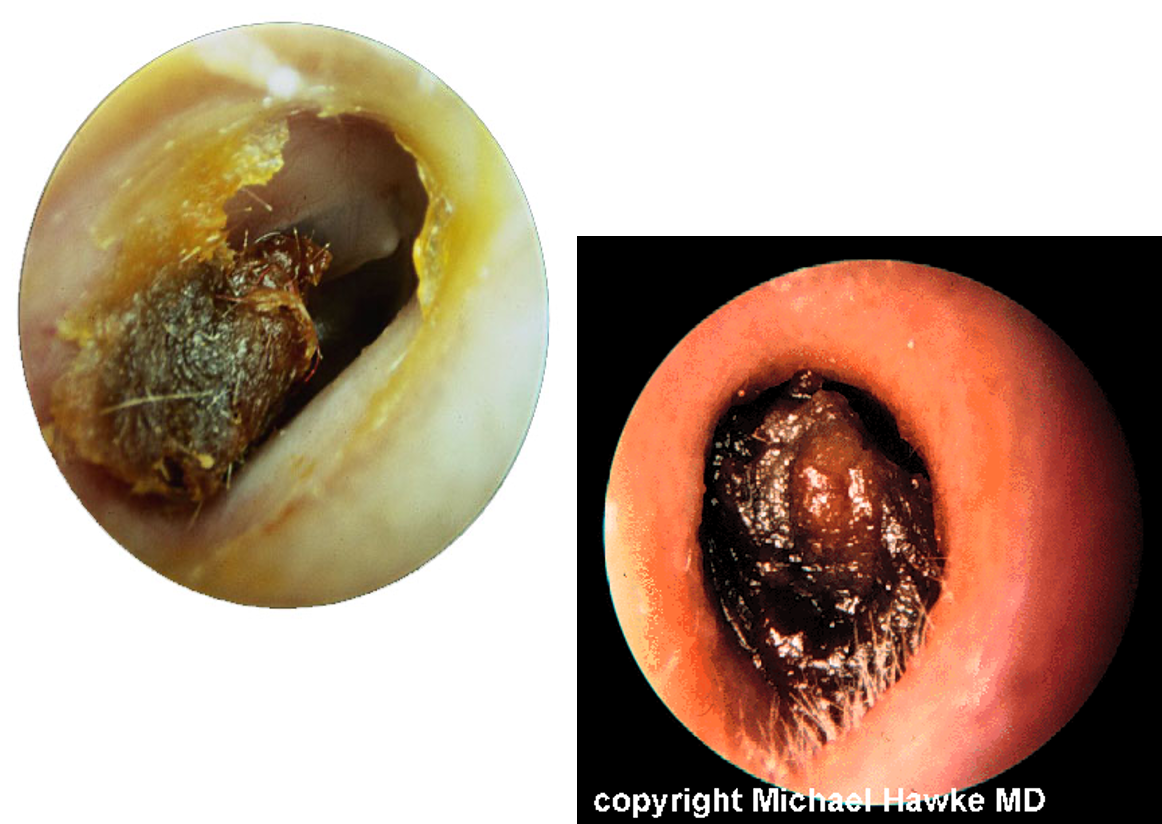
What would the following be signs of: tenderness on pulling auricle and canal is swollen, narrowed, and purulent
otitis externa
What would retraction of TM or white plaques be due to?
tympanosclerosis
What would a red TM and loss of landmarks suggest?
Acute otitis media (AOM)
What would an amber TM suggest?
serous effusion (barotrauma) or AOM
What would a bulging of the TM with erythema suggest?
AOM
What would hemorrhagic vesicles of the TM suggest?
bullous myringitis
When would you refer to ENT for a perforated TM?
when its on the edge (central is fine)
What should you do to an insect before removing it from an ear?
kill it
How do you kill an insect in an ear canal?
lidocaine 2% or mineral oral
What instruments would you use to remove a foreign body from an ear canal?
otoscope with operative head, micro alligator forceps, cerumen curettes, suction catheter, ear irrigation (do not use if button battery)
How would you remove styrofoam or super glue from the ear?
acetone
What shape in the TM?
concave
What does the TM separate?
external and middle ear
How many layers makes up the TM?
3
Which is the superior aspect- pars flaccid or pars tensa?
pars flaccida
Which is the inferior aspect- pars flaccida or pars tensa?
pars tensa
What would cause sluggish movement of the TM?
obstructed eustachian tube
What would absence of movement in the TM indicate?
fluid in the middle ear and increase suspicion of infection
What does serous otitis media / otitis media with effusion look like?
multiple air bubbles
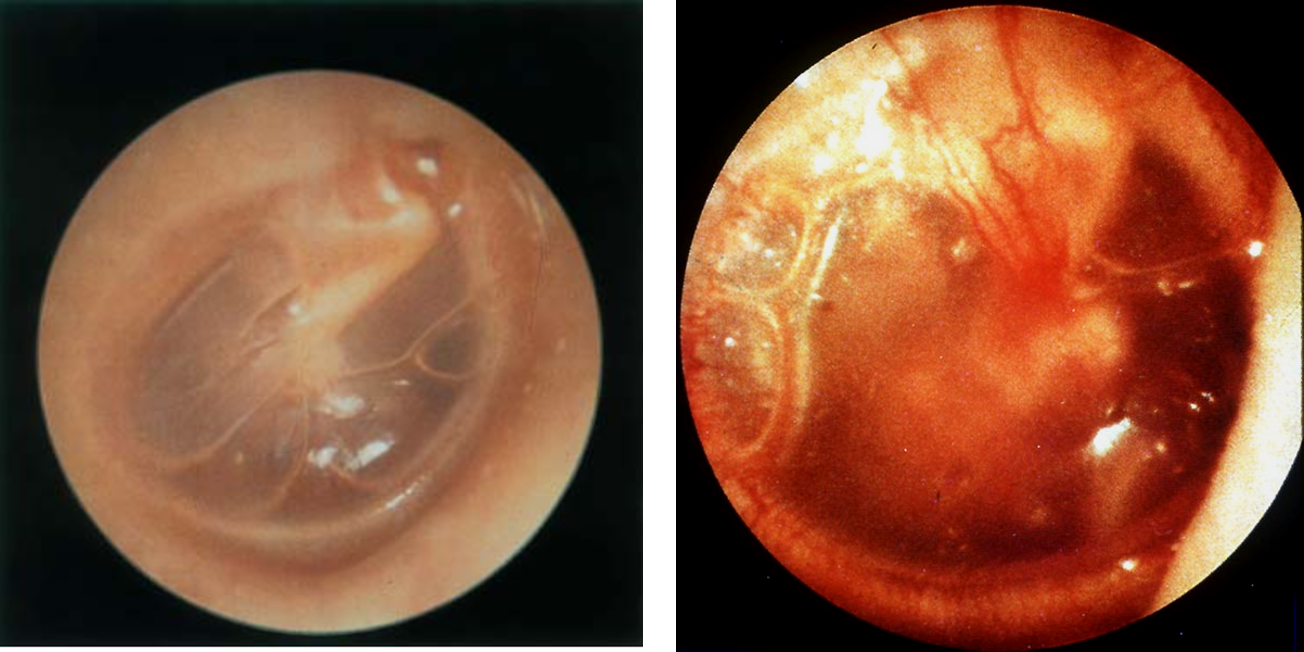
What is a cholesteatoma?
abnormal collection of skin cells deep inside the ear; rare
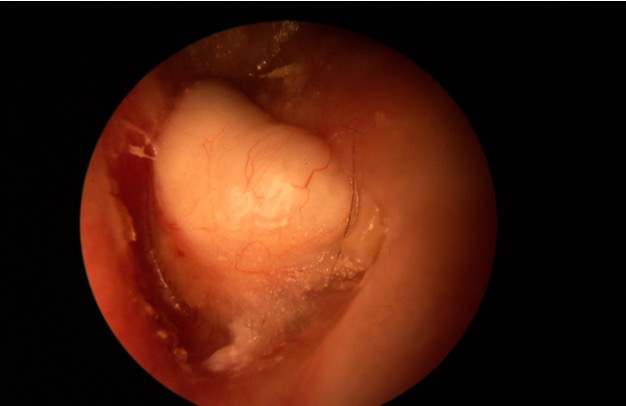
What happens to cholesteatoma if left untreated?
damage delicate structures inside ear that are essential for hearing and balance
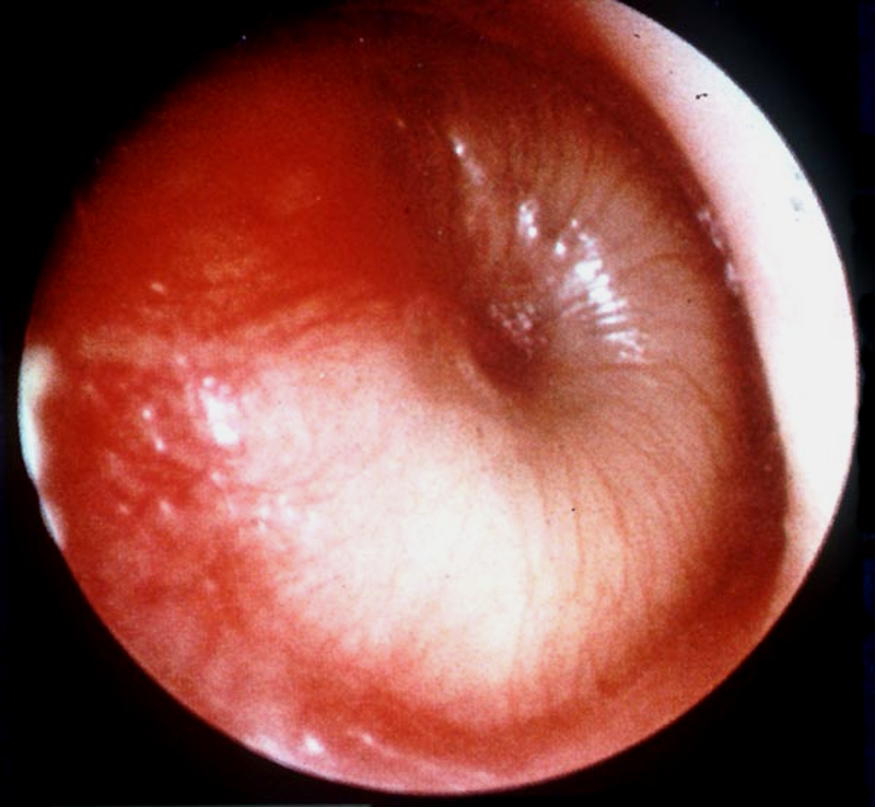
What does acute otitis media look like?
bulging, erythema, pus
At what distance should a patient be able to hear the physicians fingers rubbing together during a hearing test?
3-4 inches
What is presbycusis?
bilateral age related hearing loss; sensorineural loss
What results would you expect from a weber test to indicate sensorineural hearing loss?
sound lateralized to unaffected ear
What results would you expect from a rinne test to indicate sensorineural hearing loss?
AC greater than BC (2:1)
What is sensorineural hearing loss?
inner ear/cochlear nerve less able to transmit impulses regardless of how vibrations reach cochlea
What results would you expect from a weber test to indicate conductive hearing loss?
sound lateralized to impaired ear
What results would you expect from a rinne test to indicate conductive hearing loss?
BC greater than or equal to AC
What is conductive hearing loss?
conduction through EAC impaired, vibration through bone bypass problem to reach cochlea
What is kiesselbach’s plexus?
vascular supply of nose
Which turbinate is the largest and most visible lateral structure on the internal surface of the nare?
inferior turbinate
What is a nare?
orifice into the nose
What is philtrum?
area between nose and upper lip
What is the bridge of the nose?
bone that is the major support of nose
What would recurrent nasal/sinus symptoms indicate?
allergies
What would recurrent epistaxis suggest?
systemic problems,- thrombocytopenia, coagulopathy, medication
What might be causes of a unilateral occlusion?
foreign body, tumor, deviated septum
What are possible causes for epistaxis?
self inflicted, dryness in winter, trauma, systemic problem
What might thick and purulent discharge from the nose indicate?
bacterial infection
What might thin and watery discharge from the nose indicate?
viral infection
What might bloody discharge from the nose indicate?
chronic sinusitis, malignancy, trauma
What can you use to inspect the nasal passages?
large otoscope or speculum
Describe how the nasal cavity normally appears
septum in the middle and turbinates project into nasal passages; sufficient room for nasal passages; mucous membrane is red and compact over turbinates; small amount of thin secretion
What would edematous and erythematous mucous membrane of nose suggest?
acute rhinitis
What would swollen, pale, boggy, gray mucous membrane of the nose suggest?
allergic rhinitis
How does a nasal polyps present?
mobile, soft, pale gray semi translucent mass in nasal passage
What are findings of sinus disease?
colored nasal discharge, cough, sneezing, maxillary toothache, poor response to nasal decongestants, abnormal transillumination, tenderness to palpation or percussion
What does granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) affect?
ears, nose, throat, lungs, kidneys; may slow blood flow to organs and tissues causing damage; sx include sinus pain, cough, fever, joint aches, blood in urine, and hearing loss
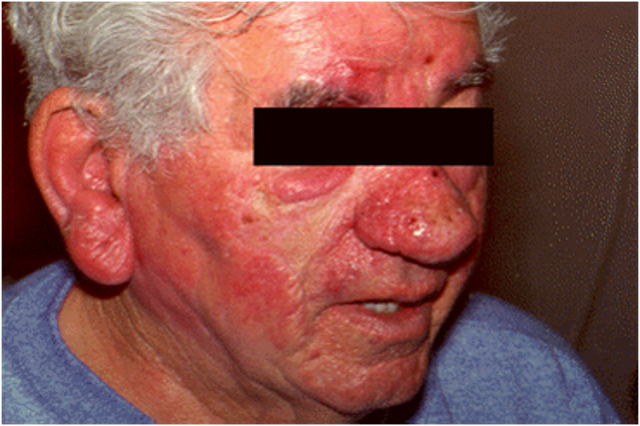
What is rhinophyma?
condition causing development of large, bulbous nose associated with granulomatous infiltration, commonly due to untreated rosacea
What are the stensens ducts and where are they located?
parotid ducts that open onto buccal mucosa near upper second molar
What are the Wharton’s ducts and where are they located?
submandibular gland ducts located under the tongue and pass forward and medially
What is angular cheilitis?
fissuring angles of the mouth; caused by yeast or B2 (riboflavin) and B12 deficiency
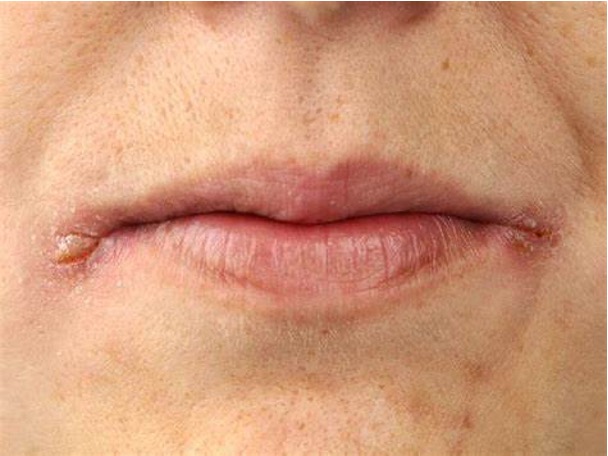
What is Peutz-Jeghers syndrome?
autosomal dominant genetic disorder characterized by the development benign hamartomatous polyps in the GI tract and hyperpigmented macule on the lips and oral mucosa
What is Behcet disease?
auto-inflammatory systemic vasculitis of unknown etiology characterized by mucocutaneous manifestations likeW recurrent oral and genital ulcerations, ocular manifestations, especially chronic relapsing uveitis, and systemic vasculitis involving arteries and veins of all sizes
What is actinic cheilitis?
precancerous condition that can create rough, scaly, discolored patches on lips, usually the lower, caused by prolonged sun exposure
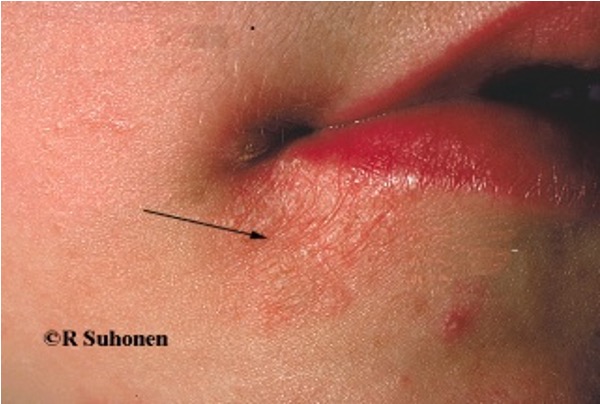
How does Sjorgrens syndrome present in the mucous membrane?
dry mouth
What is ranula?
fluid collection or cyst under the tongue
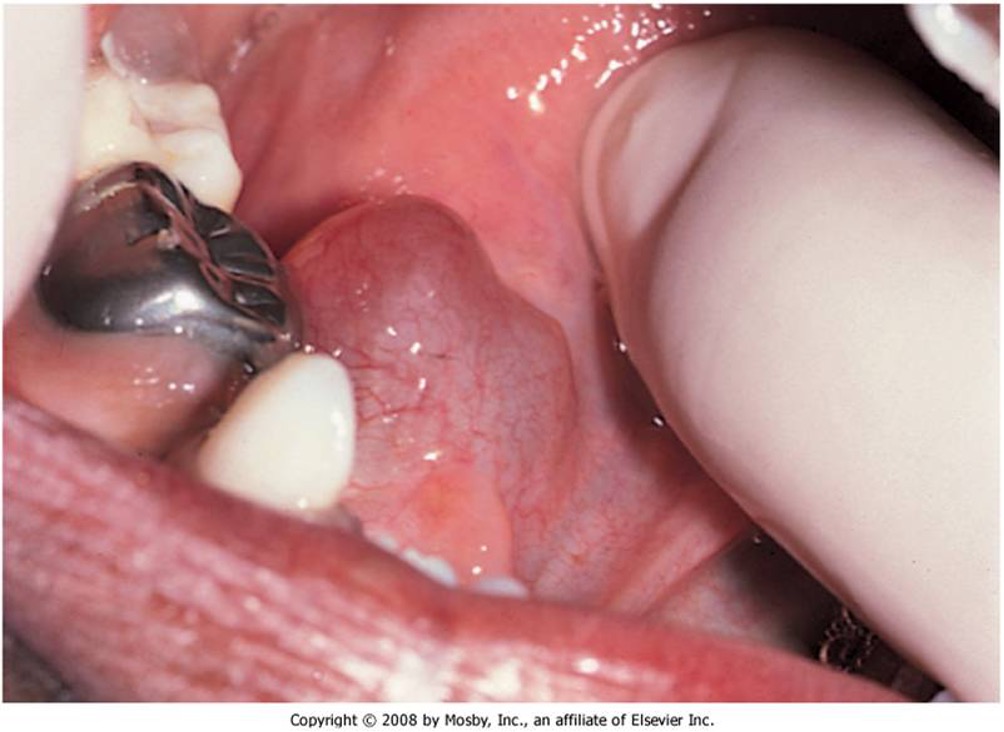
What is an amalgam tattoo?
benign, painless, common discoloration in th mouth that occurs when amalgam (dental filling material) is embedded into oral tissues during dental procedures
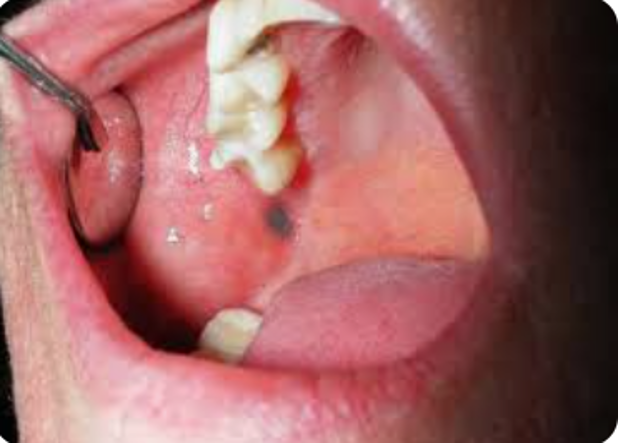
What is sialolithiasis? Where do they most commonly happen?
condition where a calcified mass forms within a salivary gland; wharton’s duct
What is the clinical presentation of sialolithiasis?
sudden enlargement and pain of gland (sialadenitis); symptoms worse with eating or anticipation of eating
Sialolithiasis management / treatment
remove stone by massage or milking gland- ENT referral if stone doesn’t pass in 5-7 days;
oral antibiotics- augmentin, cefzil, ceftin;
sialogogues- lemon drops induce salivation to help clear stone;
maintain hydration w/ 64oz of water and avoid diuretics (caffeine or alcohol)
Where are 85% of lingual cancers found?
on the lateral margins of the tongue