Chapter 4 Study Guide Questions
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What are the two groups of living gnathostome fishes?
-Condrichthyes (sharks, Rays, Skates, Chimaeras)
-Osteichthyes (bony fishes).
What were the two major developments in vertebrate evolution that took place in ancient fish?
-Jaws
-Paired Fins
What did the evolution of the jaw allow vertebrates to do?
-Allowed vertebrates eat a larger variety of food
What are the four stages proposed by Mallet for vertebrate evolution?
-Ancestral Vertebrates (unjointed branchial arches)
-Early Preganthostomes (Jointed internal arches)
-Late Pregnathostomes (With mouth closing)
-Early Gnathostomes (Feeding jaw)
What are the three theories for the origin of paired fins?
-Gill Arch Theory
-Fin Fold Theory
-Fin Spine Theory
Explain the “Gill Arch Theory”
-Posterior gill arches because Girdles for both pectoral and pelvic fins
-Skeleton of fins formed from modified gill rays
-Paired fins come from evolved gill arches
Explain “Fin Fold Theory”
-Suggests that paired fins come from folds in the body wall
-Continuous folds in the body wall somehow became a series of paired appendages
Explain “Fin Spine Theory”
-Pelvic and Pectoral fins originated from a series of sharp spines (served as stabilizers)
-Called Fin Spines
-Relatively new theory
Who were the acanthodians and placoderms, and what are their characteristics?
-Acanthodians: -Spiny Sharks that have a bony internal skeleton, Ganiod scales, and operculum (Only in Bony fish)
-Placoderms: -Armored fish (covered in bony plates) with jaws. Has internal skeleton of cartilage and bone
What vertebrates comprise the class Chondrichthyes?
-Sharks
-rays
-Chimaeras
-Skates
What characteristics distinguish the class Chondrichthyes?
-Cartilaginous skeleton
-Placoid Scales (Looks like spines)
-Cartilaginous fish!!!
What are the two subclasses of Chondrichthyes?
-Elasmobranchi: -sharks, rays, skates
-Holocephali: -chimeras or ratfish
What vertebrates comprise the class Osteichthyes?
-97% of all known fish
-Lungfish
-Ray Finned Fish
-Salmon
What are the two major groups of Osteichthyes?
-Ray-finned fishes (Actinopterygii) (ak·tee·now·teh·ruh·jee)
-Lobe-finned fishes (Sarcopterygii) (sar-cope-teh-g-re-i)
What are the different types of scales in fish?
-Placoid scales (Cartilaginous Fish)
-Cycloid and Ctenoid scales (Bony ray finned fish)
-Cosmoid Scales (lobe fin fish)
-Ganoid Scales (Gars)
Explain Placoid scales and the characteristics
-Spines projecting through the epidermis
-Characteristic of Chondrichthyes
-Shark teeth, barbs, spines
Explain Cosmoid Scales and its characteristic
-Small thick scales with cosmine overlaid by thin layers of enamel
-Characteristic of lobe-finned fish
Explain Ganoid scales and its characteristics
-Rhomosidal in shape
-Composed of bone and ganoin
-Characteristic of paddlfish, gars, sturgeons
Explain Cycloid and Ctenoid Scales
-Overlap-like shingles
-Allows for flexibility
-Characteristic of Bony Ray Finned Fish and Telecast
What are chromatophores?
-Pigment containing cells in fish that provide color
What are most common in Chromatophores?
-Melanins (Black, Grey, Brown)
-Carotenoids (Orange, Yellow, Red)
-Purines (Iridescent colors)
What does the skeletal system provide for fish?
-Protection and foundation for brain, spinal cord, and organs
What are the axial and appendicular skeleton?
-Axial skeleton: -Skull, vertebrae collar
-Appendicular skeleton: -Fins and limbs
What are the different fins of a fish?
-Dorsal Fin
-Pectoral Fin
-Pelvic Fin
-Anal Fin
-Caudal Fin
-Adipose Fin
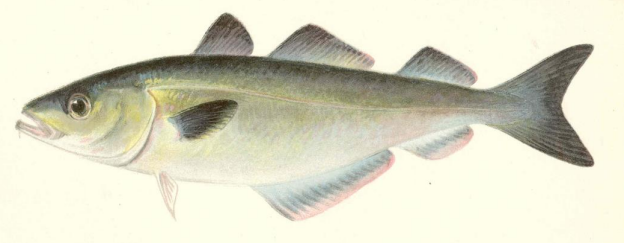
What are the different positions of the pelvic fin?
-Thoracic Position (Directly below Pectoral Fin, under chest)
-Abdominal Position (toward the fish rear end)
-Jugular Position (Pelvic Fin comes before Pectoral Fin, under the head)
-Sub Abdominal Position (Pelvic fin is slight behind Pectoral fin)
What is this position of the pelvic fin called
Jugular Position

What is this position of the pelvic fin called
Abdominal Position

What is this position of the pelvic fin called
Thoracic Position
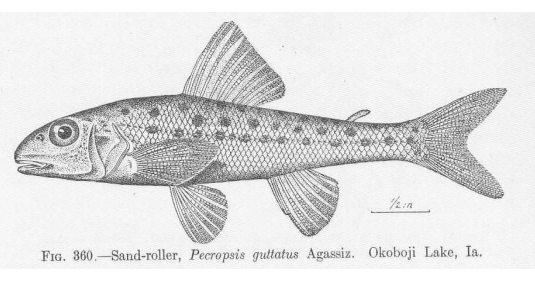
What is this position of the pelvic fin called
Sub Abdominal Position (Sand Rollers)
What are the four ways caudal fins are modified?
-Protocercal
-Diphycercal
-Heterocercal (Epicercal and Hypocercal)
-Homocercal
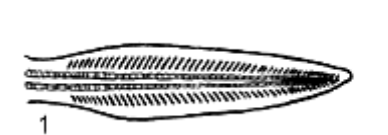
What Caudal fin is this
Protocercal

What Caudal fin is this
Heterocercal
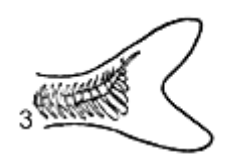
What Caudal fin is this
Homocercal
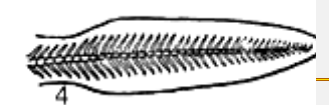
What Caudal fin is this
Diphycercal
What is the difference between white muscles and red muscles in fish?
White: -Thick Fibers
-Anaerobic Metabolism
-No Fat or Myoglobin
-Most Fish and can be up to 90% of body
-Flounder and Salmon
Red: -Thin Diameter Fibers
-Aerobic respiration
-Fat and Myoglobin
-Tuna and marlin
What path does blood take in the cardiovascular system of fish?
-Heart to the gills for oxygenation (aeration), then to the rest of the body
-Blood only passes through a singular circuit (heart once)
What do the terms acrodont, thecodont, and polyphyodont dentition mean?
-Acrodont Dentition: -Teeth attached to outer surface of jaw bones
-Thecodont Dentition: -Teeth rooted in individual bony sockets
-Polyphyodont Dentition: -Teeth that are continually replaced (injured or injured teeth) (Sharks)
What are the different mouth positions of fish?
-Terminal (Perch)
-Ventral and Back From Tip (Dogfish)
-Projecting Lower Jaw
-Elongated Upper Jaw (Marlin and Swordfish)

What mouth position is this?
Terminal
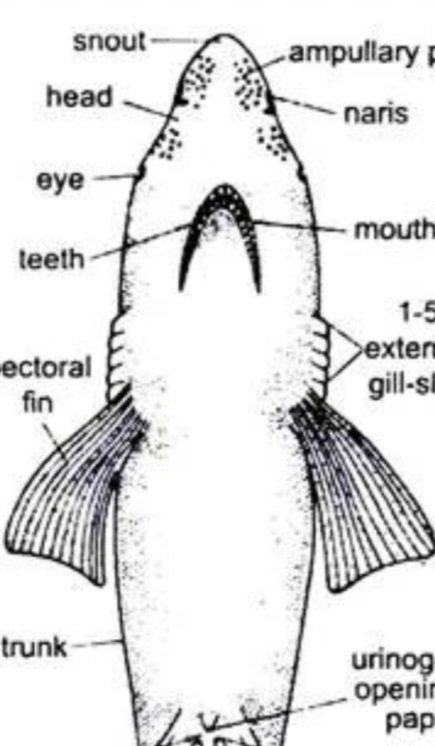
What mouth position is this?
Ventral and Back From Tip
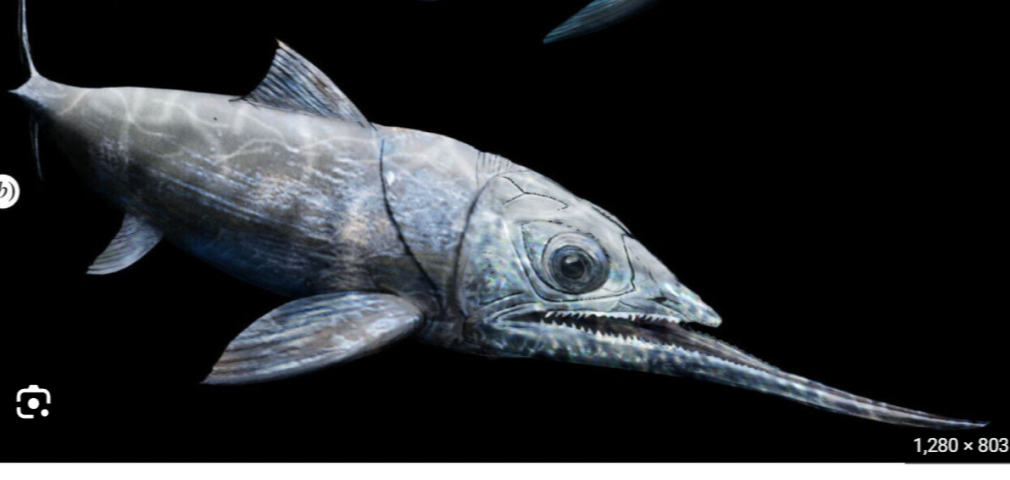

What mouth position is this?
Projecting Lower Jaw
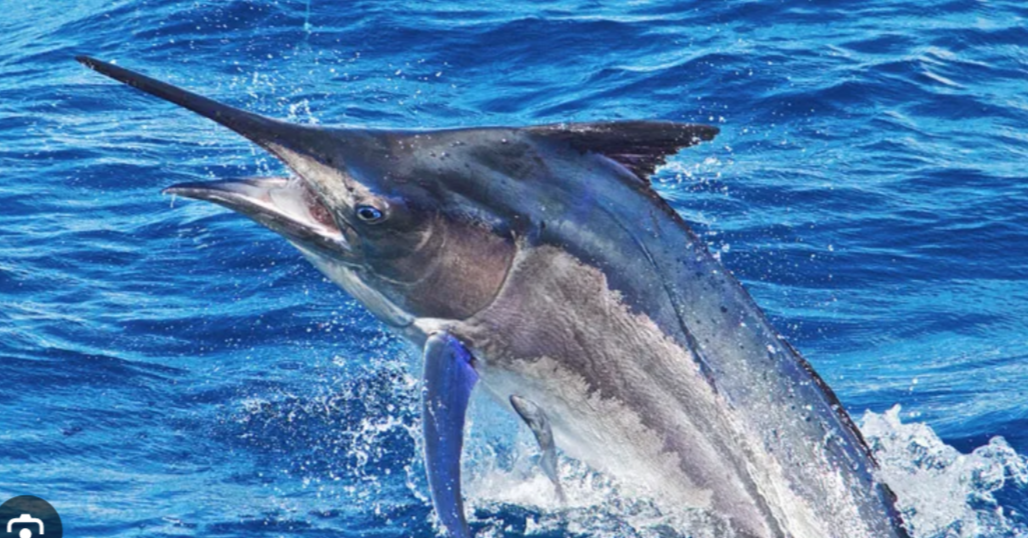

What mouth position is this?
-Elongated Upper Jaw
What does the swim bladder do?
-Maintain buoyancy and stability
Are swim bladders present in Cartilaginous Fish or Bony Fish?
-Bony Fish
How do cartilaginous fish adapt without a swim bladder?
-Oil-filled livers assists in buoyancy
What do physostomes and physoclists mean in reference to swim bladders?
-Physostomes: -Swim bladder conncets to digestive tract (Salmon and Catfish)
-Physoclists: -Closed off swim bladder (Perch)
What is the neuromast system in fish?
-Consists of sensory structures (Fluid filled pits and canals)
-Can be on surface of skin or beneath skin
-Helps sense shape, size, and movements of soundings
What do the terms hypotonic and hypertonic mean?
-Hypotonic: -Lower salt concentration in their body compared to the water they live
-Hypertonic: -Higher salt concentration to the water they live
What do the terms anadromous, catadromous, and diadromous mean?
-Anadromous: -Migrate to Freshwater from Marine to Breed (Most life span in ocean) (Chinook Salmon)
-Catadromous: -Migrate to Marine from Freshwater to spawn (American Eel)
-Diadromous: -Migrate to Marine from Freshwater (Not For Breeding) (Bull Shark)
What are synchronous and sequential hermaphrodites?
-Synchronous hermaphrodites: -Both male and female sex organs at the same time
-Sequential hermaphrodites: -Change sex as they grown
What are the two forms of Sequential hermaphroditism and which is more common?
-Protogyny: -Female first then male (Blue headed wrasse)
-More common
-Protandry: -Male first then female (Moray eels and damselfishes)
What examples of fish exhibit viviparity and oviparity?
-Viviparous: -Includes some sharks and rays
-Oviparous: -Include salmon and most egg-laying species
What are different methods of egg deposition in fishes?
-Laying eggs on substrates (gravel or rocks)
-Laying eggs in nests
-Laying eggs externally in water
-Holding eggs in mouth
What are examples of ways fish exhibit parental care?
-Guarding eggs/young from others
-Holding eggs/offspring in mouth
-Carrying eggs until they hatch
-Prepare nests
-Oxygenate eggs
What are the four life stages of fish?
-Embryo: -Past in egg, nutrient from yolk sac
-Larva: -Begins when they are able to catch own food
-Juvenile: -Rapid growth
-Adult: -Mature gonads and able to spawn