Leaves
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Leaves
constitutes the shoot of the plant body
principal function is to act as the main site of photosynthesis in a plant
epidermis
outermost layer of cells
Epidermal Cells
secrete a waxy substance that forms a covering over the outer dermal cells rendering these cells impermeable to water
Cuticle
waxy covering in a leaf
dorsiventral
There is an upper epidermis and a lower epidermis in a leaf with ________ orientation.
Stomates
openings in the epidermis
guard cells
The stomates are formed in between specialized epidermal cells called
trichomes (hairs)
found on the undersurface of the leaves and herbaceous stems
help reduce the evaporation of water from plants or protect young shoots from herbivores
Function of trichomes (hairs) in leaves
mesophyll tissue
comprises all of the cells between the upper and lower epidermis and is usually divided into two parts
vascular bundles
The mesophyll tissue comprises all of the cells between the upper and lower epidermis except…
palisade layer
cells toward the upper epidermis, which are elongated, make up the
spongy layer
zone below the palisade layer, composed of irregularly shaped cells
Inter-cellular air spaces
What is found between mesophyll cells?
isobilateral
In some monocots, there are no distinct palisade and spongy layers because the leaves are _______
True
True or False
All the parenchyma cells with chloroplast between the upper and lower epidermis comprise the mesophyll layer.
supporting and conducting tissue
Function of vascular bundles
xylem and phloem
What is the vascular bundle composed of?
Vein
collective name for the conducting tissues that are surrounded by vascular bundle sheath cells
shoot apical meristem
Where is the leaf derived from?
Blade
The leaf consists of a flattened laminar portion called
Petiole
stalk of the leaf that is attached to the blade of the stem
sessile
If the blade is attached directly to the stem, the leaf is described as what?
Apical or lateral bud
Where do leaves arise from in dicots?
bud scales
In dicots, leaves arise from an apical or lateral bud that is often protected by _______
Stipules
small leaf-like structures that develop in pairs on each side of the leaf during the growing season.
Twigs
What can some plants have that is similar to stipules?
Narrow
What is the usual shape of the blade in monocots?
Sheath
What is the base of a monocot leaf that wholly or partly encloses the stem
auricles and ligules
appendages between the blade and sheath of monocots
True
True or False
There is usually a persistent meristem at the base of the leaf that allows it to grow indefinitely.
Veins
The blade and lamina of a leaf is line with what?
midrib
middle portion of the blade usually has a prominent central vein
netted
venation of dicots
parallel
venation of monocots
margin
edge of a blade
apex
leaf tip
leaf base
part near the petiole
simple and compound
types of leaves
simple leaf
has a single blade or lamina, opposite arrangement, petiole or leaf stalk, axillary buds or growth node, and pulvirus or swelling
compound leaf
composed of two or more separate leaflets.
pinnately compound and palmately compound
subtypes of compound leaf
pinnately compound leaf,
leaflets occur in a linear sequence lined up along both sides of a central axis
rachis
sides of a central axis in leaves
palmately compound leaf
one in which three, five, seven or more leaflets are all attached at one point near the tip of the petiole and they radiate out from this ti
False
True or False
The branch will have a terminal bud and a compound leaf will also have a terminal branch.
Phyllotaxy
Leaf arrangement
alternate or spiral arrangement
one leaf occurs at each node
distichous
A variation of alternate is _______ in which the leaves occur only on two rows.
opposite arrangement
two leaves at a node facing each other.
decussate
A variation of opposite is _______ in which two opposite leaves are perpendicular to the two opposite leaves below or above them.
whorled arrangement
has three or more leaves at one node.
Leaf Attachment
how a leaf connects to the stem of a plant
Reproductive
Modified leaves where plantlets are produced along the margins of its leaves.
New plants fall off and become separate from the main plant
Asexual reproduction
Is this asexual or sexual reproduction
Modified leaves where plantlets are produced along the margins of its leaves.
New plants fall off and become separate from the main plant
False
True or False
New plants of modified leaves under reproduction are different from the mother plant
Storage
Modified leaves that function to store water and/or nutrients for the plant
Tendrils
modified leaves used for climbing or support.
Carnivorous
These type of leaves have evolved due to low nutrient availability in the soil where it grows, so plants with these leaves are able to gather nitrogen and other nutrients from the bodies of the insects they trap
Sundrews (Drosera sp.)
Example of a carnivorous modified leaf where its glands secrete mucilage used for trapping insects
Spines
A sharp-pointed , hardened structure derived from leaf or stipule
used for protection against herbivores.
They have also evolved as a water-saving strategy in some plants.
Axillary buds
develop at the axils of leaves
bring forth more leaves and branches (vegetative shoots) as well as flowers (reproductive shoots).
Lower part of the plant since new leaves grow upwards
Where would you find older leaves on a stem, near the tip or near the lower part?
orderly
Is the formation of leaf primordia and stem tissues orderly or random?
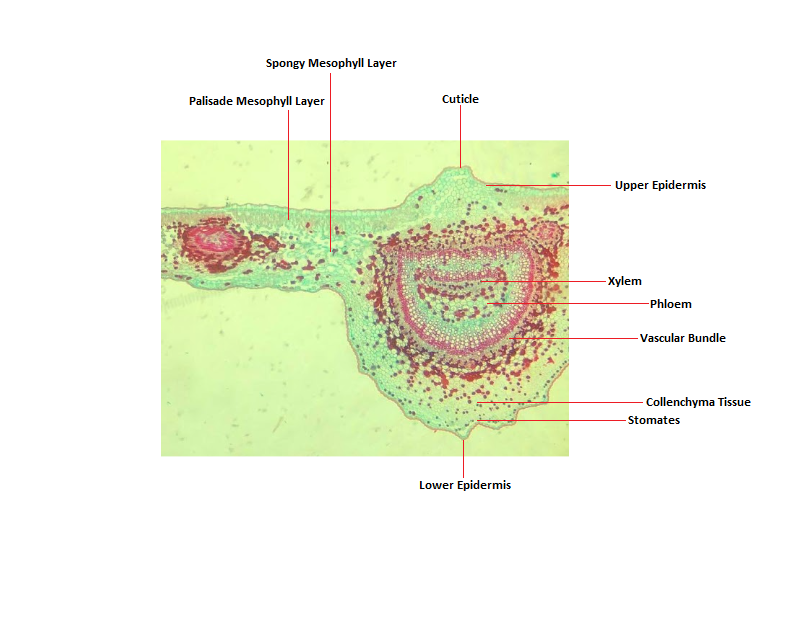
Monocot leaf
What kind of leaf is this?
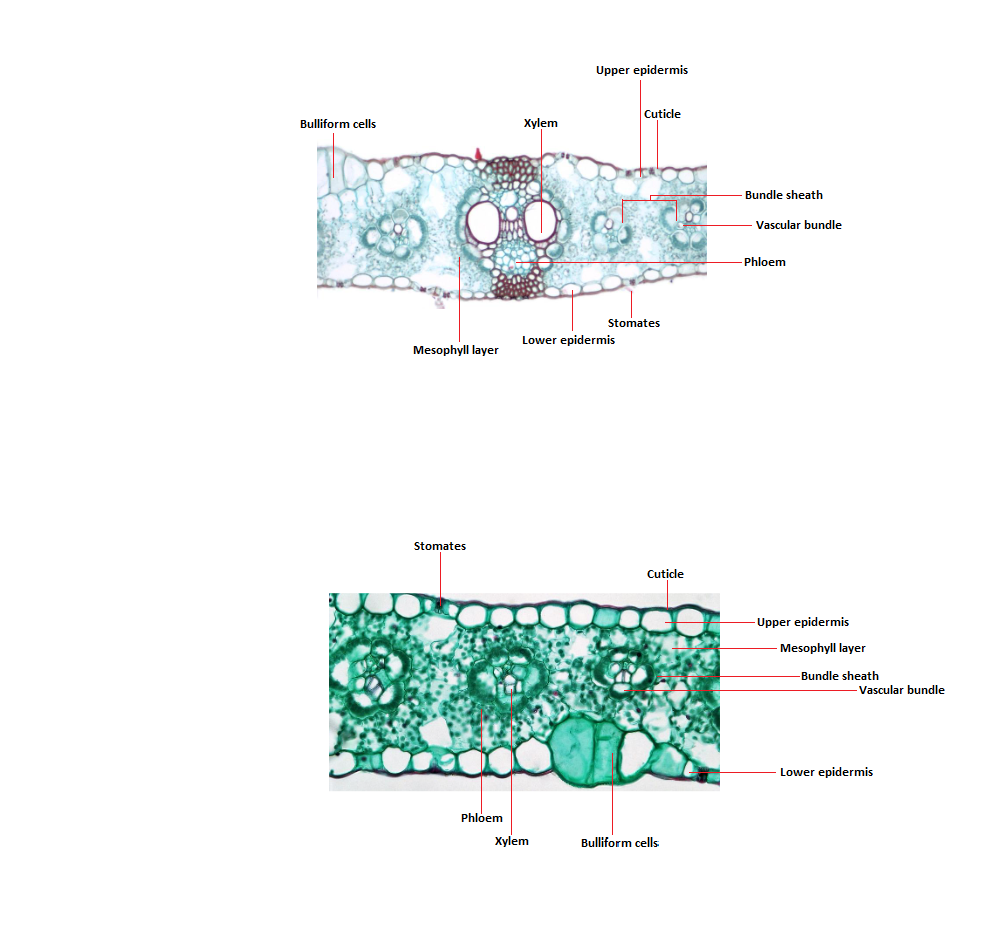
Dicot leaf
What kind of leaf is this?
scaly leaves
what is the modified leaf of onions and garlic?
colored bracts
what is the modified leaf of poinsettia?
carnivorous
what is the modified leaf of the pitcher plant?
reproductive
what is the modified leaf of kalanchoe?
phylloclade
what is the modified leaf of cacti?
cotyledon
what is the modified leaf of bean seeds?
aquatic
what is the modified leaf of Hydrilla?
epiphyte
what is the modified leaves of ficus/balete?
thorns
what is the modified leaves of roses?
tendrils
what is the modified leaves in squash?
for light absorption in photosynthesis
Why are the blades of most leaves flat?
they are attached directly to the stem without a petiole
What is the counterpart of the petiole of the dicot leaf in monocots?
allows the upper epidermis to properly face the sun
How does the petiole aid in the photosynthetic function of the leaves?
big or broad-leaved species
Which leaf shape predominates in rainy regions?
smaller leaf shapes
Which leaf shape predominates in dry regions? Why?
Bulliform cells
facilitate the curling of the leaf to reduce evaporation process and avoid excessive water loss, especially in extremely high temperatures
Adaxial portion
Where can you find bulliform cells?
Chlorenchyma
What is the type of parenchyma cells for the palisade layer?
aerenchyma
What is the type of parenchyma cells for the spongy layer?
Humid conditions because there is more water for the plants to utilize in photosynthesis
which has higher stomata? dry or humid conditions?
Present on the lowerside only of the leaf, away from direct sunlight
what is the position of the stomata during dry conditions?
Present on both lowerside and upperside of the leaf
what is the position of the stomata during humid conditions?
Smaller and almost closed to conserve water
what is the size of the stomata during dry conditions?
Larger and open since there is less risk of water loss
what is the size of the stomata during humid conditions?
amphistomatic
what do you call leaves with equal amounts of stomata on the upper and lower side of the leaf
Bulliform cells
What is present in monocots that cannot be seen in dicots?