Fossil fuels on the carbon cycle
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is the carbon cycle
the natural process by which carbon moves between the atmosphere, oceans, land, and living organisms, involving processes like photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and combustion
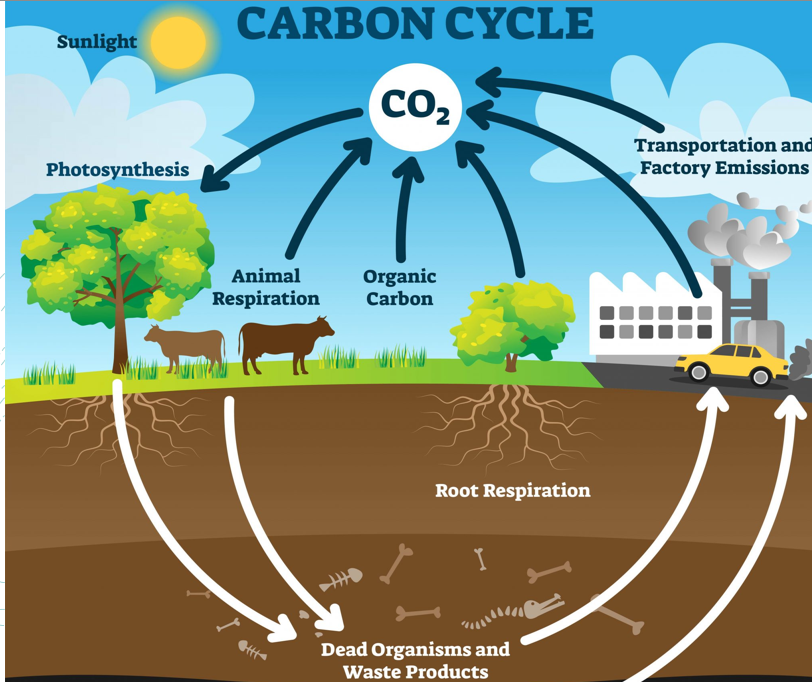
How much of the extra carbon from human activities is absorbed by land plants and oceans
About 55% is absorbed; the remaining 45% stays in the atmosphere
How long may some of the extra atmospheric CO₂ remain in the atmosphere
Up to many thousands of years, with around 20% potentially remaining long-term
How does excess carbon in the atmosphere affect the planet
It warms the planet and can enhance plant growth on land
How does excess carbon in the ocean affect marine life
It makes the water more acidic, putting marine life in danger
Why is the persistence of CO₂ in the atmosphere significant
CO₂ is the most important gas for controlling Earth’s temperature
What percentage of Earth’s greenhouse effect is caused by CO₂, water vapor, and clouds
CO₂: ~20%, water vapor: ~50%, clouds: ~25%
What contributes to the remaining portion of the greenhouse effect
Small particles (aerosols) and minor greenhouse gases like methane
How do water vapor concentrations in the air depend on temperature
Warmer temperatures increase evaporation and humidity; cooler temperatures cause condensation and precipitation
How does rising CO₂ affect water vapor in the atmosphere
Higher CO₂ raises air temperatures, which increases evaporation, adding more water vapor and amplifying the greenhouse effect
Why is CO₂ considered the “gas that sets the temperature”
Because it controls the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere, determining the size of the greenhouse effect
How much anthropogenic CO₂ is absorbed by ocean surfaces
Approximately 30%
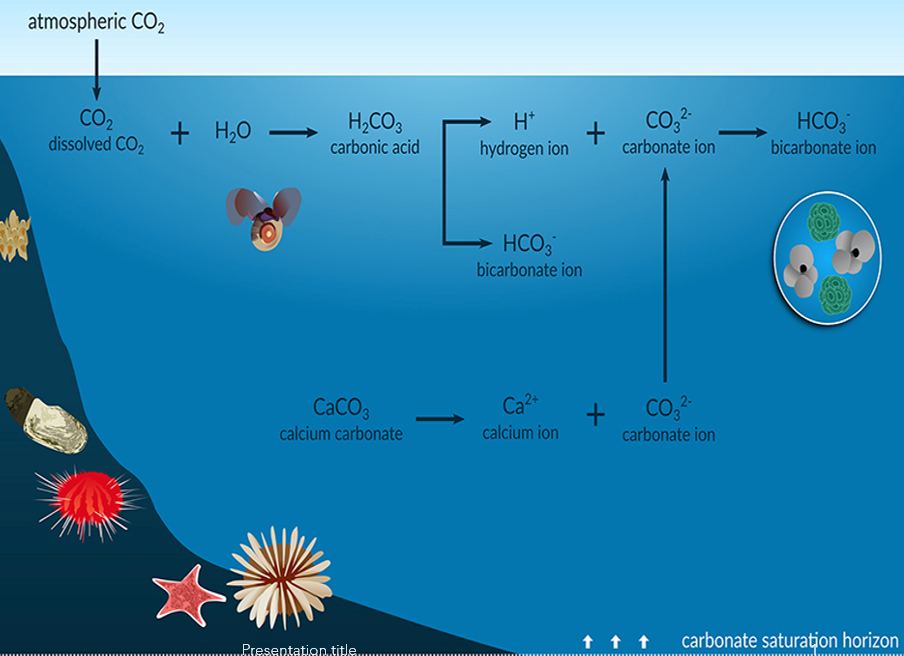
What happens to CO₂ when it dissolves in seawater
It forms carbonic acid, causing ocean acidification and impacting aquatic ecosystems
How does ocean acidification affect marine life
Corals, mussels, and some plankton have deformed or eaten-away shells, disrupting the food chain
How is the ocean’s ability to absorb CO₂ changing
Warm waters are less effective than cool waters, slowing carbon uptake and leaving more CO₂ in the atmosphere
What is the atmospheric lifetime of CO₂
Approximately 300–1,000 years
How has ocean pH changed since pre-industrial times
Pre-industrial pH was 8.2; in 2022 it is 8.1—a 30% increase in acidity
How do warmer oceans affect phytoplankton abundance
Warmer oceans reduce phytoplankton abundance because they grow better in cool, nutrient-rich waters
How could reduced phytoplankton affect the carbon cycle
It limits the ocean’s ability to take carbon from the atmosphere through the fast carbon cycle
Can increased CO₂ fertilize phytoplankton and ocean plants
Some species that directly take up CO₂, like certain phytoplankton and sea grasses, may grow more
Does increased CO₂ benefit all ocean plant and phytoplankton species
No, most species are not helped by higher CO₂ levels
How much of human-emitted CO₂ has been absorbed by land plants
Approximately 25%
How has plant carbon uptake changed since 1960
Plants have generally absorbed more CO₂, though only some of this increase is directly due to fossil fuel emissions
What is carbon fertilization
Increased plant growth due to higher levels of CO₂ available for photosynthesis
How much might plant growth increase if atmospheric CO₂ doubled
Models predict a 12–76% increase, assuming no other limiting factors like water shortages
What factors besides CO₂ are essential for plant growth
Water, sunlight, and nutrients (especially nitrogen)
Is there a limit to how much CO₂ plants can absorb
Yes, the limit varies by region and depends on availability of water, nutrients, and other growth factors
How do higher CO₂ and temperatures affect plants
They can extend the growing season and increase growth, but warmer temperatures can also stress plants
How does a longer, warmer growing season affect plants
Plants need more water; water shortages can slow growth, especially in summer in the Northern Hemisphere
Why are dry, water-stressed plants more vulnerable
They are more susceptible to fires, which release carbon from plants and soil into the atmosphere
How does warming affect tropical forests
Reduced water slows tree growth, lowers carbon uptake, or causes trees to die and release stored carbon
What happens when soil warms, particularly permafrost
Organic matter decays faster, releasing carbon as methane and CO₂ into the atmosphere
How much carbon is stored in Northern Hemisphere permafrost
Approximately 1,672 billion tons (Petagrams) of organic carbon
What could happen if 10% of permafrost thaws
It could release enough carbon to raise global temperatures by ~0.7°C (1.3°F) by 2100