Dental Terminology Ch. 13
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Endodontics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Endodontia
The branch of dentistry concerned with the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases of the dental pulp and its surrounding periradicular (around root) tissues
Diagnostic Conditions of Pulpitis
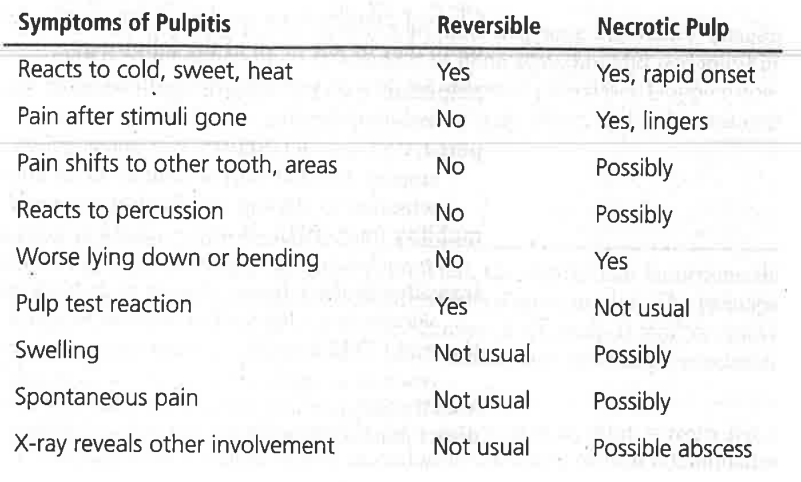
Pulpitis
Inflamed pulpal condition
Necrotic
Pertaining to dead or nonvital, it’s irreversible
Subjective sumptoms
Conditions as described by the patient
Objective signs
Conditions observed by someone other than the patient
Palpation
Application of finger pressure to body tissues, including gingiva
Percussion
(tapping of body tissue, tooth) Usually done by tapping a dental mirror handle on an affected tooth and comparing the sensation to tapping on a healthy or control tooth
Mobility
(capable of movement) Movement of a tooth in its socket during outside force or pressure application
Transillumination
(Passage of light through object/tissue) a light refraction test to reveal fractured tooth tissue
Thermal
(Pertaining to temperature) Pulp sensitivity test with reaction to applications of heat and/or cold to tooth surface
Anesthesia
Numbing the questionable root or nerve ending to dissipate pain
Direct dentin stimulation
Scratching the exposed dentin with an explorer; the presence of pain indicates inflamed or irritated pulp tissue
Electric pulp testing
Applying an electrical current on the enamel surface of the tooth to register the tooth’s pulpal sensitivity and presence of irritability
Radiograph
X-ray examination with digital zoom and color contrasting ability permits a deeper insight to the pulp canal
Miscellaneous tests
Radiovisionography and magnetic resonance imaging to demonstrate early changes of bone structure and periapical involvement of suspected tooth with an inflamed pulp; laser Doppler flowmetry to determine blood flow of pulp tissue, and pulse oximetry to assess pulp vitality
Periodontitis
In acute apical periodontitis, a sharp, painful inflammation of tissues occurs around an affected tooth, pain is lessened or eliminated by removal of the inflamed or necrotic pulp, a chronic apical periodontitis requires management similar to the acute symptoms
Abscess
(local pus infection) an infection that may be an acute or chronic apical abscess; aka suppurative (producing or generating pus)
Pericementitis
Inflammation and necrosis of the alveoli of the tooth
Cyst
Abnormal, closely walled fluid or exudates-filled sac in or around periapical tissues
Cellulitis
Inflammation of cellular or connective tissue
Osteomylitis
An inflammation of the bone and bone marrow, usually caused by bacterial infection
Pulpotomy
Partial excision of the dental pulp, usually reserved for children’s teeth
Pulpectomy
Surgical removal of pulp from the tooth, aka root canal treatment
Apicoectomy
Surgical amputation of a root apex
Retreat
Endodontic retreatment of failed pulpal canal and core treatment with removal of existing filling material and re-obturation of the tooth
anesthesia
Local injection to relieve pain occurring during the procedure
Isolation of the operative area
Accomplished to provide safety and to assure an aseptic (without disease) site
Extirpation
(to root out) removing the pulpal tissue after the pulpal opening
Debridement
(removal of foreign or decayed matter) removing necrotic pulpal tissue and cleaning out the area
Irrigation and cleansing
Using chemicals and instruments to remove tissue dust and material matter from the pulp and pulp canals
Obturation
(to close or stop up) filling and closing the canal area, this may consist of filling from the pulp to the apex or may be completed in a retrograde (backward step) process of filling the canal beginning from the apex of the tooth to the pulp chamber, aka a retrofill endodontic restoration
Restoration
Returning the tooth to normal function and purpose, either permanent or temporary, so that the patient may return to their personal referring dentist for the final step
Dental dam material
Thin layer of latex or nonlatex sheeting that varies in thickness, color, and size
Dental dam frame
device used to hold material in place; may be metal or plastic, rigid or adjustable
Dental dam punch
Device used to place selected holes in the dam material for isolation of a tooth or teeth
Dental dam forceps
Hand device used to transport and place clamps or trainers around the selected tooth
Rubber dam stamp and pad
Marking stamper and pad devices used to indicate alignment spots for puncturing the material with the punch
Dental dam clamp
Retaining device used to hold the material around the tooth; may be metal or resin and vary in size, shape, and style
Dental dam ligature
Material used to hold and secure the dam material in the mouth; can be dental floss, latex stabilizing cord, or a small piece of dental dam material
Broach
A thin, barbed, wired instrument inserted into the root canal to ensnare and remove the pulp tissue and nay natural or placed matter, such as paper points or cotton pellets
Reamer
A thin, twisted, sharp-edged instrument inserted into the canal and rotated clockwise to enlarge and taper the root canal
File
A thin, rough-edged instrument used to plane and smooth pulpal walls, there are K-files, Hedstrom files, and flex files
K-file
Has twisted edges and is used to enlarge as well as to smooth walls; color-coded to denote size
Hedstrom file
(U-shape and S-shaped) Cone-shaped, twisted edged instrument used for enlargement and smoothing; nickel titanium alloy files provide more flexibility
Flex file
Stainless steel or nickel titanium alloy file that is stronger and provides more flexibility; used in narrow, curved canals
Pesso reamers
Thicker, engine-driven reamer with larger and longer parallel cutting edges for use in canal openings
Gates-Glidden drills
Engine-driven, latch-type burs with flame-shaped tip; used to provide an opening and access
Paper points
Small, narrow, absorbent, paper tips that may be inserted into the prepared canal; used to dry the prep site or to carry medication to the area; are available in various gauges and millimeter-marked lengths or may have tips cut off the accommodate size
Stopper
A small piece of elastic band or commercial plug that is moved up or down the shaft of the endo instrumnet; used to mark and indicate the length of penetration; also used to measure insertion length with X-ray view
Rotary burs and stones
Friction grip burs with diamond or carbide tips used to gain access through restorations and crowns
Microsurgery Curettes
Used to incise and elevate periodontal tissue and fibers permitting easier and faster healing time
Root canal spreader
Longer shank with pointed nib; used to carry and insert cement or filling material
Root canal condenser
Handled, long-tip instrument that may be heated and used to condense gutta-percha to the canal walls
Lentulo spiral drill
Thin, twisted-wire, latch-type rotary instrument used to spread calcium hydroxide or cement into the canal, materials may also be spread by small inserts from ultrasonic machines
Ultrasonic and sonic instruments
Vibration energy waves for debridement, irrigating canals, and spreading medicaments or cement; used in conjunction with hand instrumentation
Apex locator machines
Determine the proximity of the test file to the root apex and relate the information to a PC board screen during preparation of the canal
Electric endodontic handpieces
Permits use of instruments at slow speeds for finger instrumentation
Heat carrier machines
Provide adjustable heat to soften, deliver, and condense gutta-percha to the canal
Laser Doppler flowmetry and pulse oximetry
Devices used to test blood circulation and vitality of the pulp in question
Magnifying loupe eyeware
Enlarge vision in working area
SOM
(surgical operation microscope) worn as headgear, similar to loupes, but with intense magnification possibilities and improved halogen lighting
Assorted instruments
Include explorer, spoon excavator, and paddle-ended blades, have increased nib, blade, or neck-length to accommodate extra depth to the working surfaces
Luer-loc syringe
A barrel-type syringe with a piston force plunger, used to inject fluids into the cavity
Gutta-percha points
Tapered points made of a thermoplastic compound; similar in size to silver points or endodontic instruments, and used to fill the root canal; may be millimeter marked along length to help determine penetration insert length
Silver points
Tapered silver points comparable in size to files and reamers; used to fil canals
Cement pastes and fillers
Zinc oxide and eugenol mixes and commercial materials; used to cement points in canal
Chemicals
Chemical action used in conjunction with operator treatment produce a result termed biomechanical action
Chelators
Chemical ion softener
Disccant
(dry up, remove) methanol or ethanol alcohol used to dry the area or clear away other chemical traces
Medicament
(medicine or remedy) used for antimicrobial action, to prevent pain, and to neutralize the pulpal area
Curettage
(scraping of a cavity) scraping of the apical area; may be necessary to remove necrotic tissue
Apicoectomy
A procedure that may be necessary to remove the root apex, particularly where there is a radicular cyst involvement of the affected tooth, aka root end resection
Root amputation
Separating and removing molar roots of affected tooth at the junction to the crown
Root hemisection
Cutting tissue of organ in half, surgical division of multi-rooted teeth that may be performed in a lengthwise manner
Bicuspidization
Surgical division of a tooth retaining booth sides
Traumatized
Wounded
Luxation
Dislocation, tooth movement that may be classified in concussion, subluxation, lateral luxation or extruded
Concussion
Shaken violently, tooth loosened as a result of a blow; usually recovers with minimal attention
Subluxation
Tooth partially dislocated; evidence of bleeding but requires only minor attention
Lateral luxation
Tooth may be partially displaced with the root apex tilted forward
Extruded luxation
Tooth may be forced partially out of its socket
Fracture
breakage; may be a broken cusp, broken crown, broken root, of a spit tooth
Avulsion replantation
Replacing teeth that have been accidentally lost; may undergo RCT at this time or at a future appointment
Care of an avulsed tooth involves
Do not touch tooth root
Rinse with tepid water
Reinsert into tooth socket, hold in place with finger; if unable, tuck under lip, or keep moist in milk or lightly salted water
Seek immediate treatment-fast-because time is important
Replantation
Replacing an avulsed tooth in its tooth socket
Transplantation
Transfer of a tooth from one alveolar socket to another; may be completed through autogenous, homogenous, or heterogenous manners
Autogenous
Moving a tooth from 1 position in the oral cavity to another area in the same cavity
Homogenous
Transferring and inserting a tooth from one patient to another
Heterogenous
Transfer from one species to another; not yet a feasible practice