HN220 Midterm 1
1/358
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
359 Terms
What are the levels of organization of the body?
1) cells
2) tissues
3) organ
4) organ system
What is a cell?
Basic unit of life
What is tissue made of?
Group of cells
What is an organ made of?
A group of tissues that work together
What is an organ system made of?
multiple organs working together
What is an organism made of?
multiple organ systems
What four groups can cells be classified into?
1) Neurons
2) Muscle cells
3) Epithelial cells
4) Connective tissue cells
What are neurons?
nerve cells
- excitable cells that transmit electrical signals
What are muscle cells?
Specialised cells that can contract and relax
What are the three types of muscle cells?
1) Skeletal
2) Cardiomyocytes
3) Smooth muscle
What are cardiomyocytes?
heart muscle cells
What are epithelial cells?
Cells that line organs and tubes
What are connective tissue cells?
Cells that make up any structure whos primary function is to provide physical support for other structures, anchor them, or link them together
- e.g. blood cells, skin cells, bone cells
What is the most diverse type of cell?
connective tissue cells
What are the four major types of tissue?
1) nerve tissue
2) muscle tissue
3) epithelium (epithelial tissue)
4) connective tissue
What is homeostasis?
The body's ability to maintain a constant internal environment
what are the components of the internal environment that are regulated?
1) temperature
2) volume
3) composition
What are afferent signals
signals arriving to the brain
- travel from receptors to the control center in the brain
- sensory signals
what are efferent signals
signals travelling from the brain
- travel from control center to effectors
- motor signals
What is generated when skeletal muscle contracts?
heat
What are some examples of receptors?
1) thermoreceptors
2) chemoreceptors
3) baroreceptors
What are thermoreceptors?
detect changes in temperature
What are chemoreceptors?
Chemically sensitive cells
- serve as sensory receptors
What are baroreceptors?
pressure and stretch receptors
What is a common example of where baroreceptors are found?
Your heart and blood vessels
- helps with blood pressure
What do integrating centers do?
orchestrates an appropriate response
- many integrating centers are found in the brain
- can be the cell itself
Where are effectors?
muscles and glands
- respond to nerve impulses
What are signals?
allow components to communicate
- neurotransmitters and hormones
Explain the pathway of achieving homeostasis
- receptor send an input signal to an integrating center (afferent)
- integrating center sends an output signal to an effector (efferent)
How many cells are in the human body
75 trillion
What are the 2 basic types of ways cells communicate with each other
- Electrical signals
Involves changes in membrane potential
- Chemical signals
What is the most common way cells communicate with each other
-Most common way cells communicate with each other in the human body is using chemical signals
Describe chemical signaling in terms of communication between cells in the body
-Secretion of a chemical
-Chemical messengers in the form of cytokines, hormones, amino acids, neurotransmitters, etc circulate with the body locally and allow them to communicate near adjacent and distant cells
-Secreted into the Extracellular fluid
Fill in the blank:
Cells responding in cell to cell communication are called ________ __________
Target cells
What are the fundamental stages to signal transduction?
1. Reception
2. Transduction
3. Response
Describe Reception in Signal Transduction
Signal molecule has an affinity to bind to a protein
Key and Lock model
Describe Transduction in Signal Transduction
Cell won't understand what the chemical signal is after Reception stage
It converts/transduces it into a message that causes a response within a cell
Ex. Kinases can phosphorylate proteins within the cell which triggers a response in the cell
How do Cells communicate locally?
Using special junctions
WHat are the types of special junctions
Tight Junctions
Desmosomes
Gap junctions
How do cells communicate long distance?
-Combination of electricala nd chemical signals
Electrical via nerve cells
Chemical via blood (hormones)
Where are tight junctions found
Found in epithelium
Fill in the blank:
The binding in tight junctions between adjacent cells are formed by proteins called ________
Occludins
What are occludins
-Integral proteins that fuse adjacent cells in TIGHT JUNCTIONS
-Form a nearly impermeable barrier
-Forces a molecule to cross the epithelial cell layer
Describe the steps communication occurs in tight junctions
Lumen (apical membrane) --> Epithelial cell cytosol --> Basolateral membrane (ECF)
Describe Desmosomes
-Provide adherence between adjacent cells
- Filamentous junction between cells
-Bind cells together for strength
-Found in tissue subject to mechanical stress
Ex. Smooth muscle cells and cardiac muscle cells
Describe Gap Junctions
- Link the cytosol of 2 adjacent cells
-Ions and molecules moving between cells acts as a signal
-Direct communication between cells
-Composed of membrane proteins
What proteins are associated with gap junctions?
Connexins
What are Connexins
-Gap junction protein
-Spans membrane creating a channel
-When channel is open, cells act as 1
-20 diff types of connexins
Intercellular communication coordinates cell activity for _______
Homeostasis
How is direct intercellular communication achieved?
-Gap junctions
Ex. cAMP, Ca2+
How is indirect intercellular communication achieved
- Chemical messengers in the form of neurotransmitters impart their effect on end target cells
True or False:
Indirect intercellular communication via neurotransmitters always impart their effect on other neurons
False
Can go to another neuron but it can also be other cells such as a skeletal muscle cell
What are the 2 ways local communication occurs
-Autocrine signals
-Paracrine signals
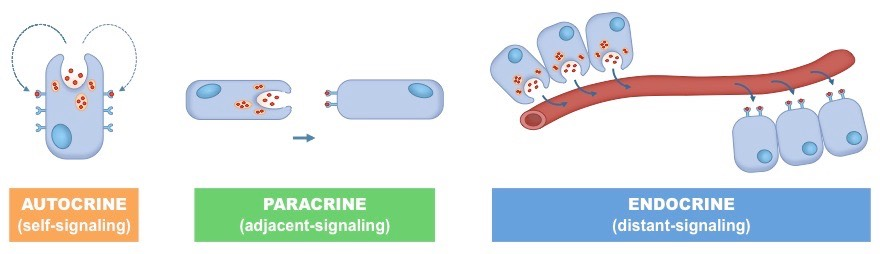
What are autocrine signals
Act on the same cell that secreted them
Ex. Immune cells do this
What are paracrine signals
Secreted by one cell and diffuse to adjacent cells as long as the the target cell have the receptors for that particular messenger
How does the peripheral nervos system illicit long distance communication between cells
Via neurotransmitters, released at axon terminals
Ex. Acth and norepinephrine
What are neurotransmitters
Chemicals secreted by neurons that diffuse across a small gap to the target cell
What are neurohormones
Chemicals released by neurons int the blood for action at distant targets
Usually derived from neurally derived tissue as opposed to endocrine tissue
Ex. Epinephrine released by specialized neural tissue in adrenal glands
What do membranes do
-Separate material between the intercellular fluid and extracellular fluid
-Allow exchange of material between ICF and ECF
Why is transport across membranes important
-Allows us to obtain oxygen and nutrients while also getting rid of waste products
Non-polar molecules are ______ transported across the membrane
Easily trasnported
Via simple diffusion
Ex. O2, CO2, Fatty acids
Ions and polar molecules are normally _________ across the membrane
Normally not transported across the membrane
They need help
Ex. Glucose, Proteins, Na+
Is K+ higher in concentration in the ICF or ECF
ICF
Is Na+ higher in concentration in the ICF or ECF
ECF
Is Ca2+ higher in concentration in the ICF or ECF
ECF
Is Cl- higher in concentration in the ICF or ECF
ECF
True or False
Amino acids and proteins are positively charged and have a higher concentration in the ECF
False
Amino acids and proteins are negatively charged and have a higher concentration in the ICF
What factors determine the direction of transport
Chemical Forces
Electrical Forces
Both= Electrochemical forces
Describe Passive transport
- Spontaneous
-Downhill movement (simple diffusion)
-High to low concentration
Describe Active transport
-Needs energy (ATP) to happen
-Not spontaneous (requires pumps)
-Uphill movement
-Against the concentration gradient (Low to high)
What is the chemical driving force based on
Concentration gradients
Moves molecules from high concentration to low concentration
What 2 factors does the direction of the electrical driving force depend on?
1) polarity of the cell
2) charge on the particle
Does the ICF have more anions or cations?
anions
- has a negative charge
Does the ECF have more anions or cations?
cations
- has a positive charge
What is the equation for the total force?
chemical + electrical forces
If the forces act in the same direction, what is the equation of the magnitude?
magnitude = chemical + electrical force
If the forces act in the same direction, what direction will the force be?
the same direction of each force
If the forces act in the opposite direction, what is the equation of the magnitude, and what direction will the force be?
magnitude = larger force - smaller force
If the forces act in the opposite direction, what direction will the force be??
of the stronger force
True or false: an ions equilibrium potential is a membrane potential in which the electrical force = the chemical force
true
If Vm = Ex, then force =?
force = 0
What do you need to determine which force is larger?
an ions equilibrium potential
What direction does the electrochemical force follow? (How do you know which way an ion will move across the membrane?)
It will favour the force which will bring the membrane to the equilibrium potential
- It will move in the direction that will lead to Vm = Ex
If a chemical gradient existed, under which conditions would a particle not be transported across a membrane even if it is permeable to that particle?
when the electrical force is equal to, but opposite in direction to the chemical force
true or false: an ions equilibrium potential is a membrane potential in which the electrical force and chemical force act in opposite directions
true
true or false: equilibirum is achieved when the Vm is equal to the equilibirum potential
true
What creates a membrane potential?
1) ion concentration gradients between ECF and ICF
- difference in charge
2) selectively permeable cell membrane
What are the 2 principles of the elctrical driving force?
1) opposites attract
2) like charges repel
chemical force + electrical force = ?
electrochemical force
What should you consider when determining the direction of the electrochemical force for a particular ion?
1) the membrane potential
2) the equilibrium potential
3) direction of the chemical and electrical forces
What is the equilibrium potential of an ion?
the membrane potential at which the ions movement will be at equilibirum
- 0 flux
What is permeability
Determines what moves in and out of cell
Cell membranes are selectively permeable
Selective permeability restricts materials based on:
- Size
-Molecular shape
-Electrical charge
-Lipid solubility
What is bulk flow
-Type of Transport process
-Movement of fluids (gases and liquids)
-Uses pressure gradients
Ex. Blood through circulatory system (blood has dissolved solutes and blood cells)
Describe other forms of transport
Diffsuion
Protein mediated transport
Vesicular transport (vesicle)
True or False:
Diffusion will continue until equilibrium is reached
True
True or False
If a system is already at equilibrium, there is no concentration gradient, thus diffusion cannot occur
True
Describe Passive Transport
- Spontaneous
-No cell E required
-Downhill movement
What are the types of passive transport
- Simple diffusion
-Facilitated diffusion (protein structure facilitates movement)
-Diffusion through channels (Channels that have pores which allow movement of ions to travel through)
True or False
Simple diffusion uses membrane proteins
False