Unit 6: Human Anatomy
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
Anatomy
Field of study focusing on the physical structure of the body
Physiology
examines the normal functions and activities of these biologic components
Pathophysiology
Study of functional changes that accompany a particular disease or syndrome
Topographic anatomy
Help guide EMT to the locations of the locations of internal features that lie beneath
Anatomic Position
Palms and Feet facing towards you.
Planes of the body
Coronal (frontal) plane
Sagittal (lateral) plane
midsagittal (midline) plane
Transverse( Axial) plane
Coronal (Frontal) Plane
Runs Vertically through the body and divides it into the front and back sections
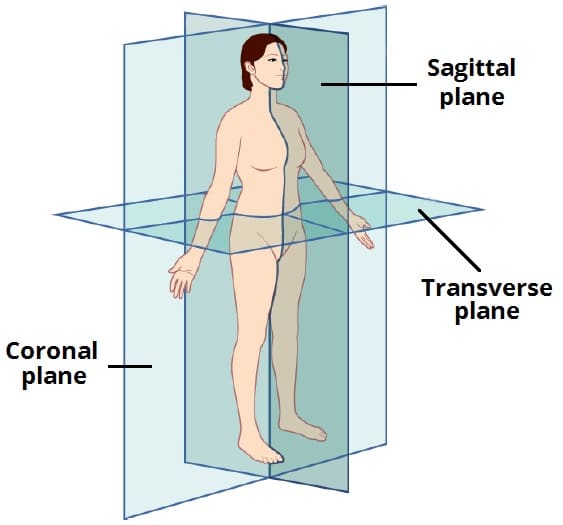
Sagittal (lateral) plane
Also runs vertically, but divides the body into left and right. DOES NOT have to be equal halves
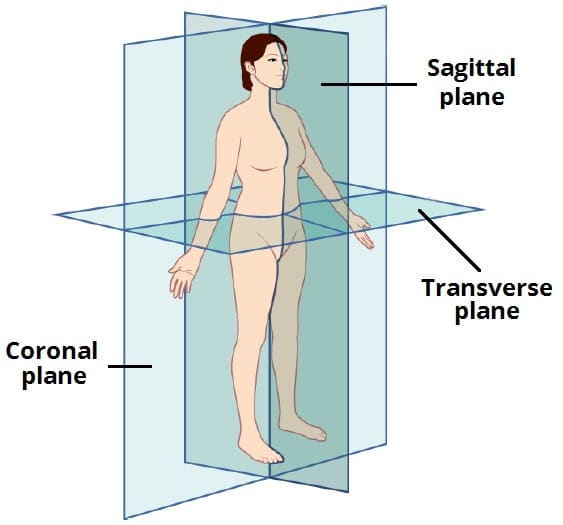
Midsagittal (midline) plane
divides the body into left and right, equal halves. Your nose and umbilicus are found around this midline
Transverse (Axial) Plane
Divides the body horizontally into top and bottom sections
Skeletal System
Provides structural support to bear the body’s weight
Establishes a framework to attach soft tissues and internal organs
Protects vital organs (heart and lungs)
Bone marrow produces red/white blood cells
How many bones are in the human body
206
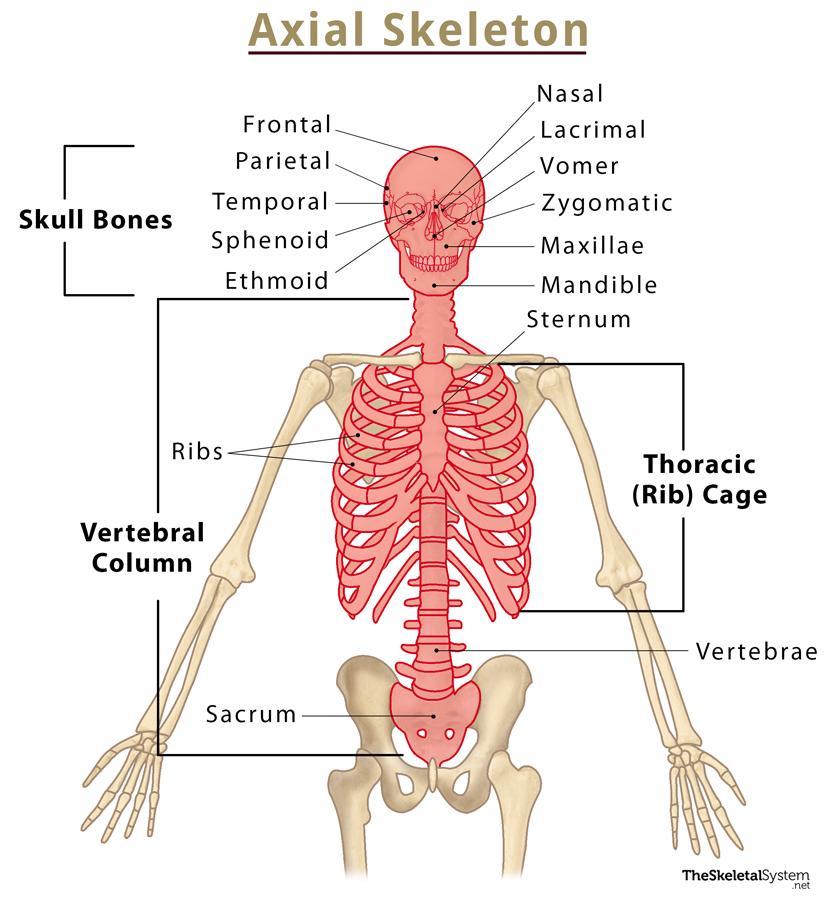
Axial Skeleton
Forms longitudinal axis of the body, from the skull, to the coccyx.
Includes the skull, facial bones, thoracic cage, and vertebral column
Appendicular Skeleton
Joint
Where two bones meet
Names formulated by combining the names of the adjoining bones
Ligaments
Fibrous tissue that connect BONE TO BONE, helping stabilize these joints
Cartilage
Flexible tissue that covers and cushions the ends of articulating bones
Tendons
Tissues that attach bone to muscle, in other joints called symphyses
Joint Capsule
Fibrous sac containing connective tissue that holds together bone ends of a joint
Articular Cartilage
In moving joints, the ends of the bones are covered with a thin layer of cartilage called…
Allows the ends of bones to glide easily instead
Synovial Membrane
Inner lining of the joint capsule
responsible for for making thick lubricant called synovial fluid, which allows bones to glide over each other as opposed to rubbing against each other
Ball-and-socket joint
allows rotation and bending etc. shoulder and hip
Hinge Joints
joints with motion restrcited to flexion(bending) and extension (straightening) ex: elbow, fingers, knees
Skull
Consists of 28 bones containing 3 groups: Cranium, Facial bones, Ear bones
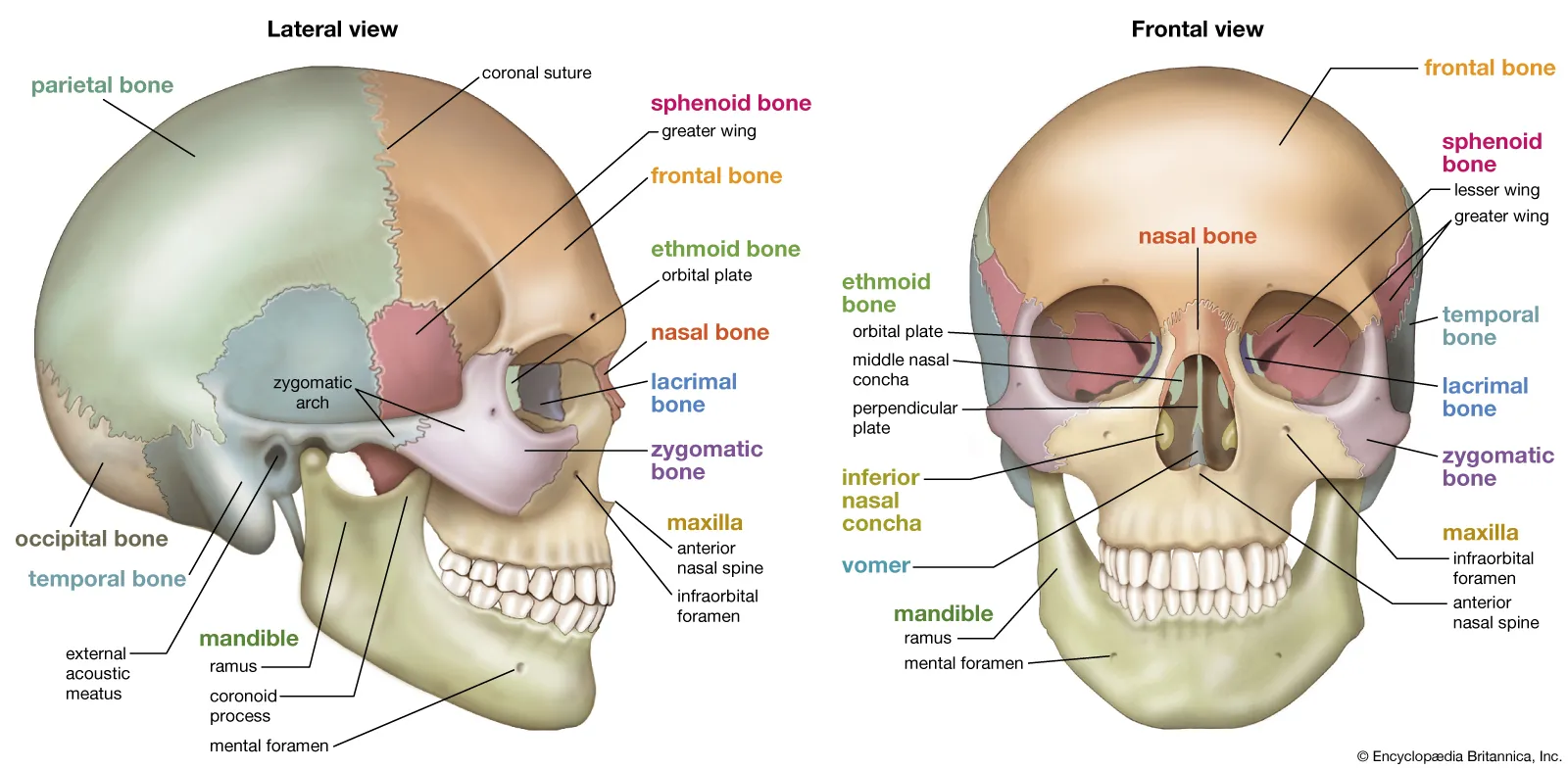
Cranium
Contains Frontal, Temporal, Parietal, and Occipital, Ethmoid, and Sphenoid Bones. Fused together to protect the brain
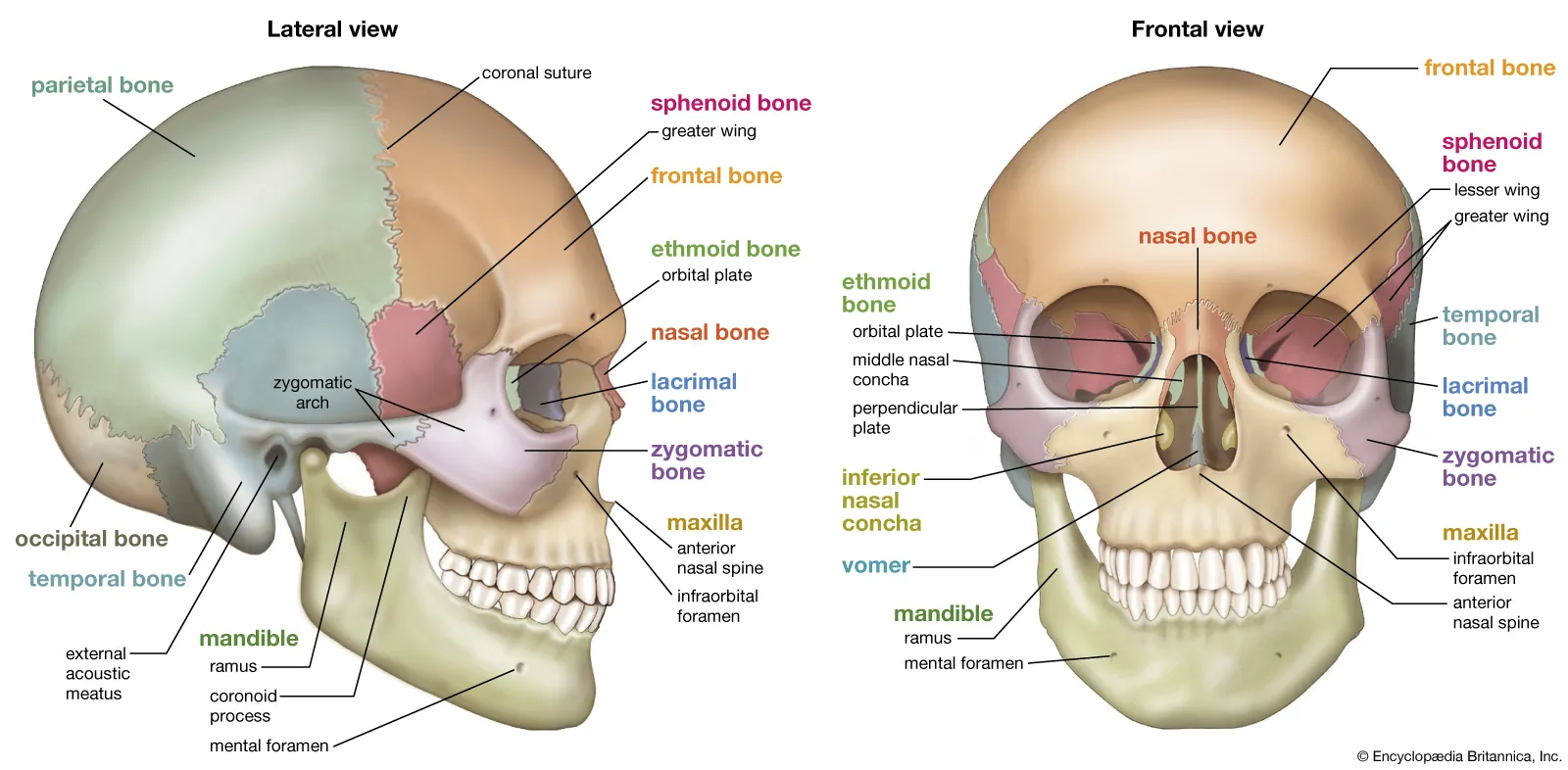
Foramen Magnum
Base of the cranium, large opening, passageway for the spinal cord to connect with the brain and descend into the spinal column
Facial Bones
Maxilla: upper jawbones
Mandible: Lower jaw bones (jawline)
Zygomas: Cheek bones
Orbit: aka eye socket, cavity formed by joining facial bones
Upper third of nose made of short nasal bones that form bridge, rest is flexible cartilage
Vertebral(Spinal) Column
Contains 33 Vertebrae, divided into 5 sections
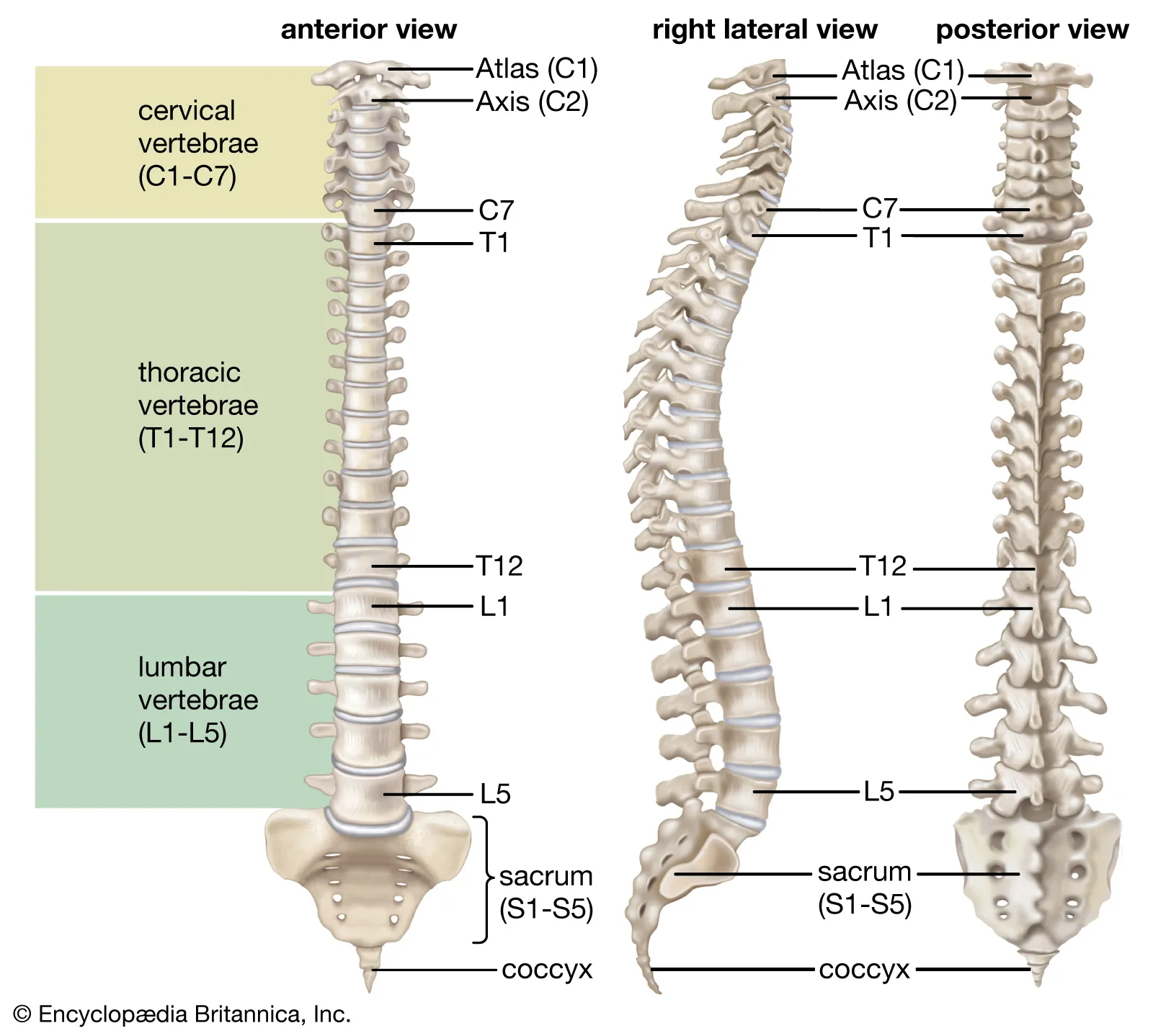
Cervical Spine
First 7 vertebrae (C1 - C7). In the neck. Skull rests on C1, the top being the atlas, and axis, C2
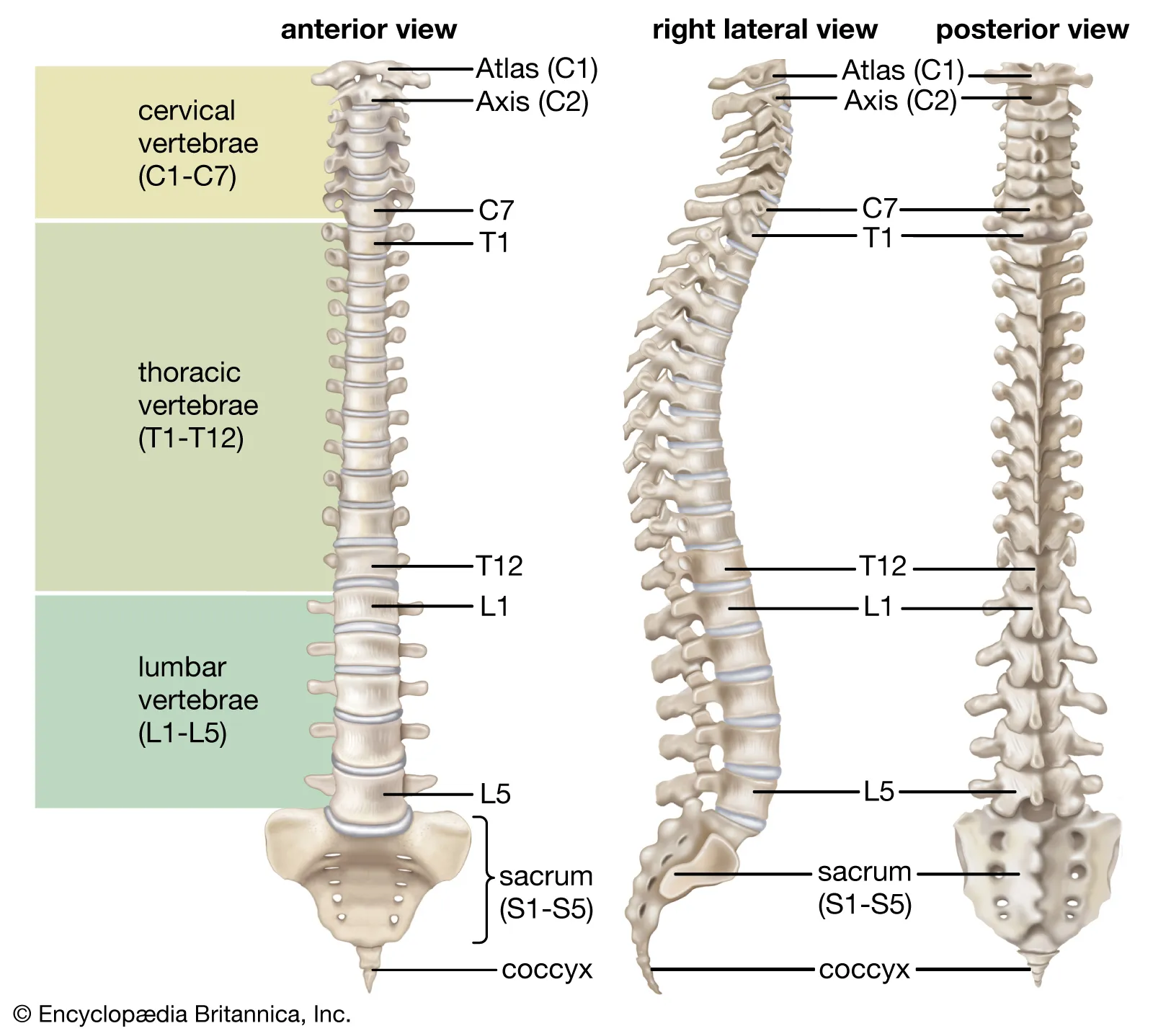
Thoracic Spine
Next 12 Vertebrae. One pair of ribs attached to each of the thoracic vertebrae
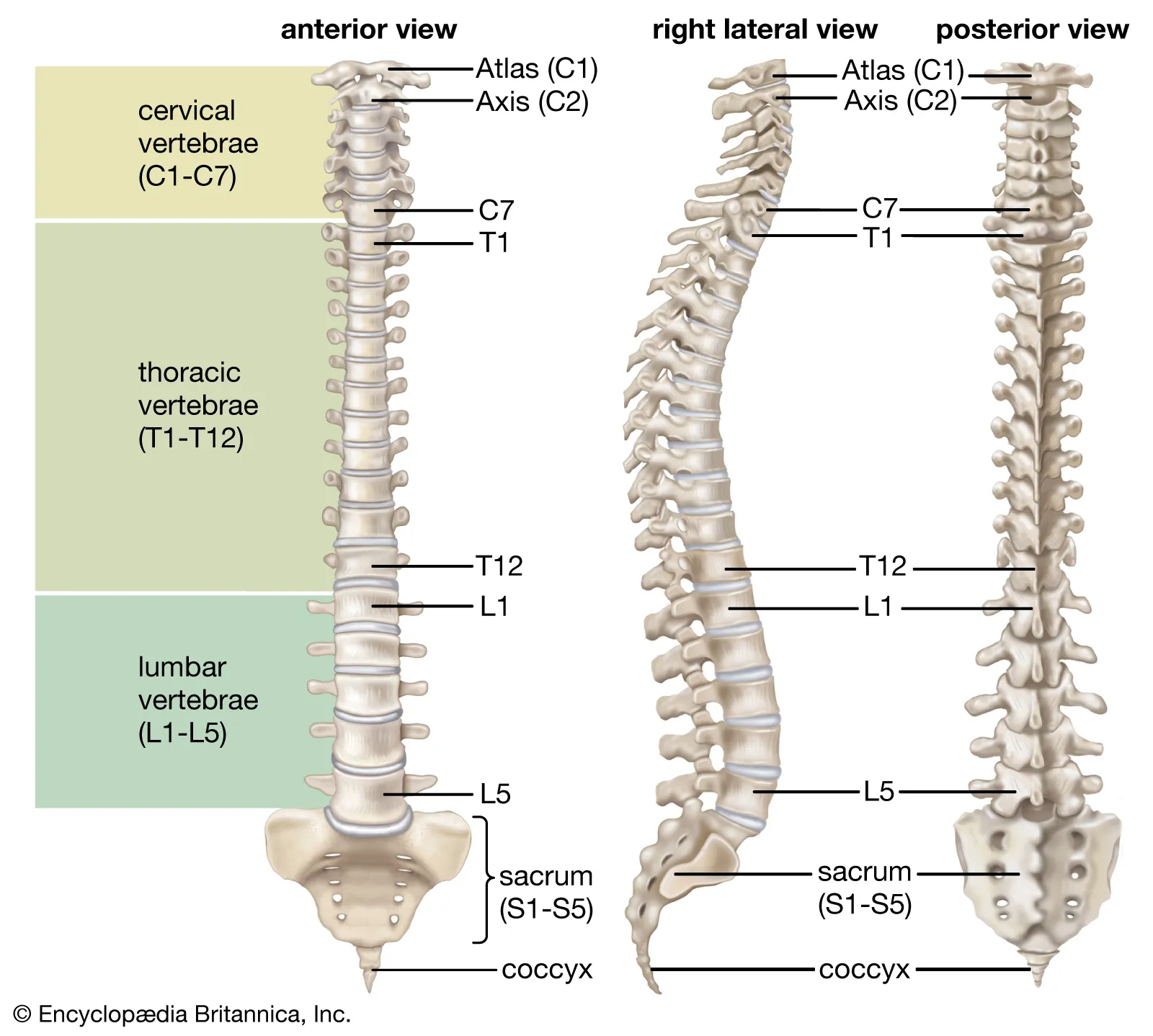
Lumbar Spine
Next 5 Vertebrae after Thoracic
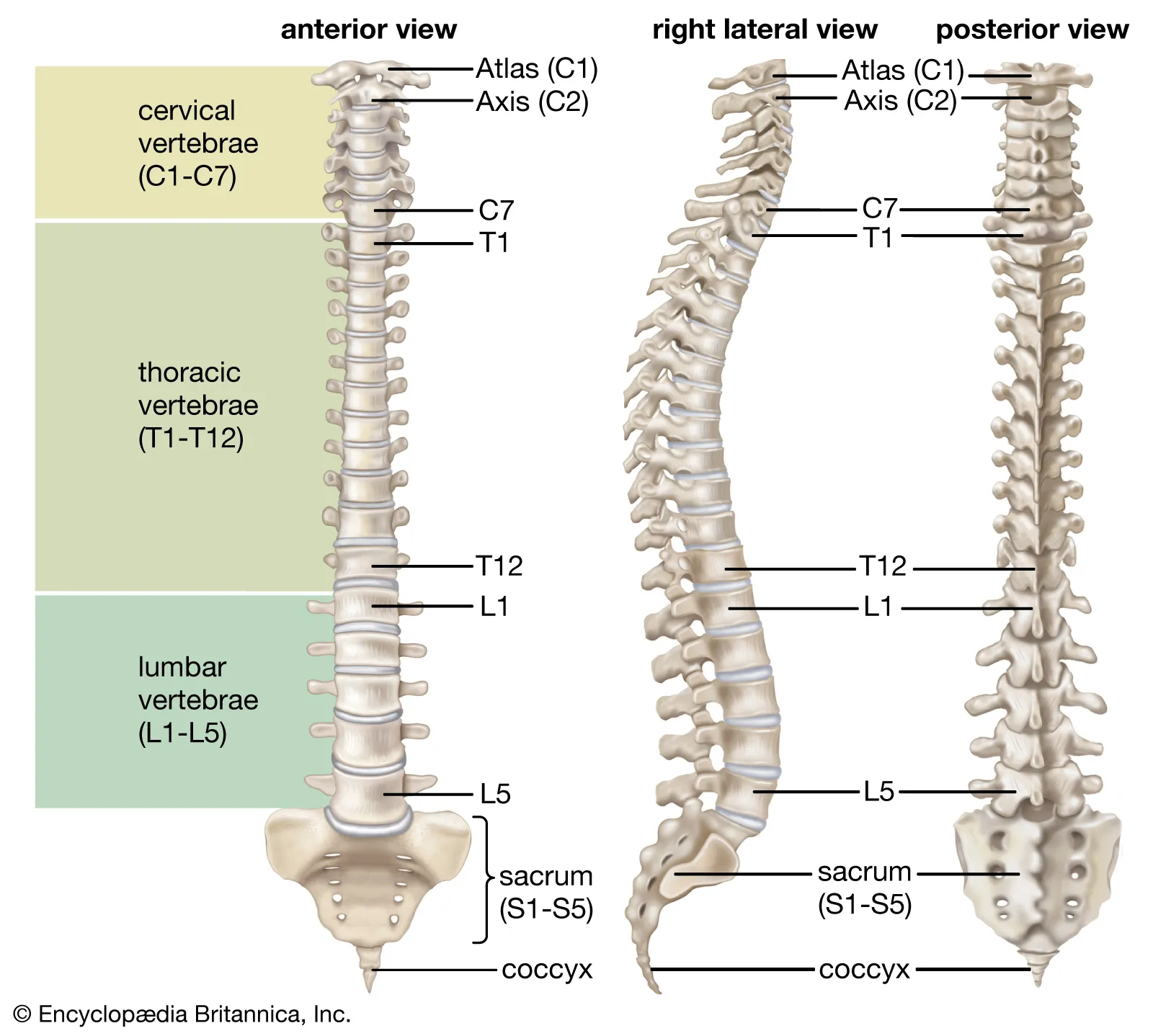
Sacrum
Five sacral vertebrae are fused together to form one bone. Joins the iliac bones of the pelvis via strong ligaments at the sacroiliac joints
Coccyx
Last four vertebrae fused together to form coccyx
Intervertebral disks
Vertebrae are connected by ligaments and the gaps between the vertebrae are occupied by cushioning, shock absorbing structures called…
Thorax
aka chest, contains heart, lungs, esophagus, and great vessels (aorta, and venae cavae)
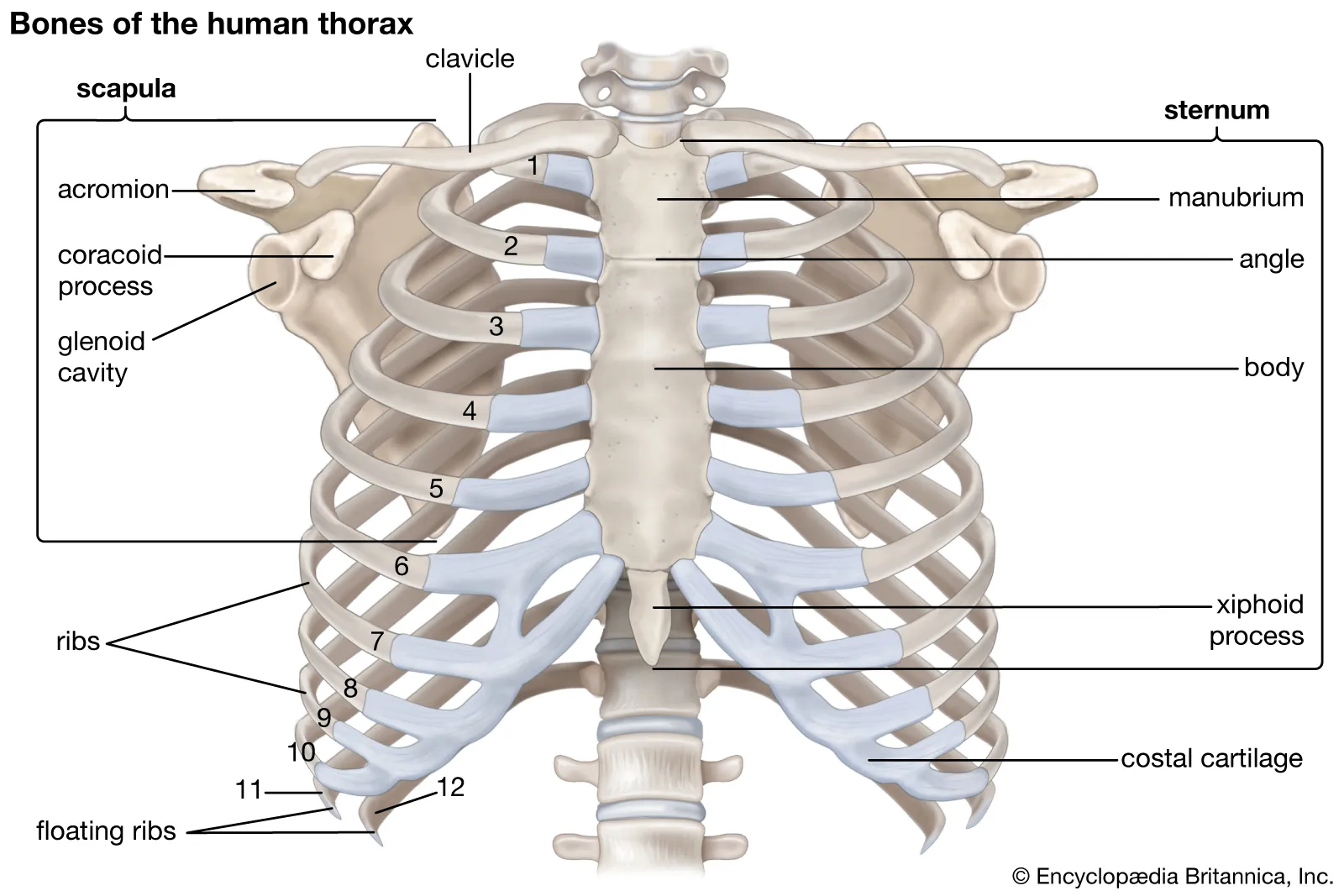
Sternum
Midline of the anterior surface of the chest, Three main parts:
Manubrium, body, xiphoid process
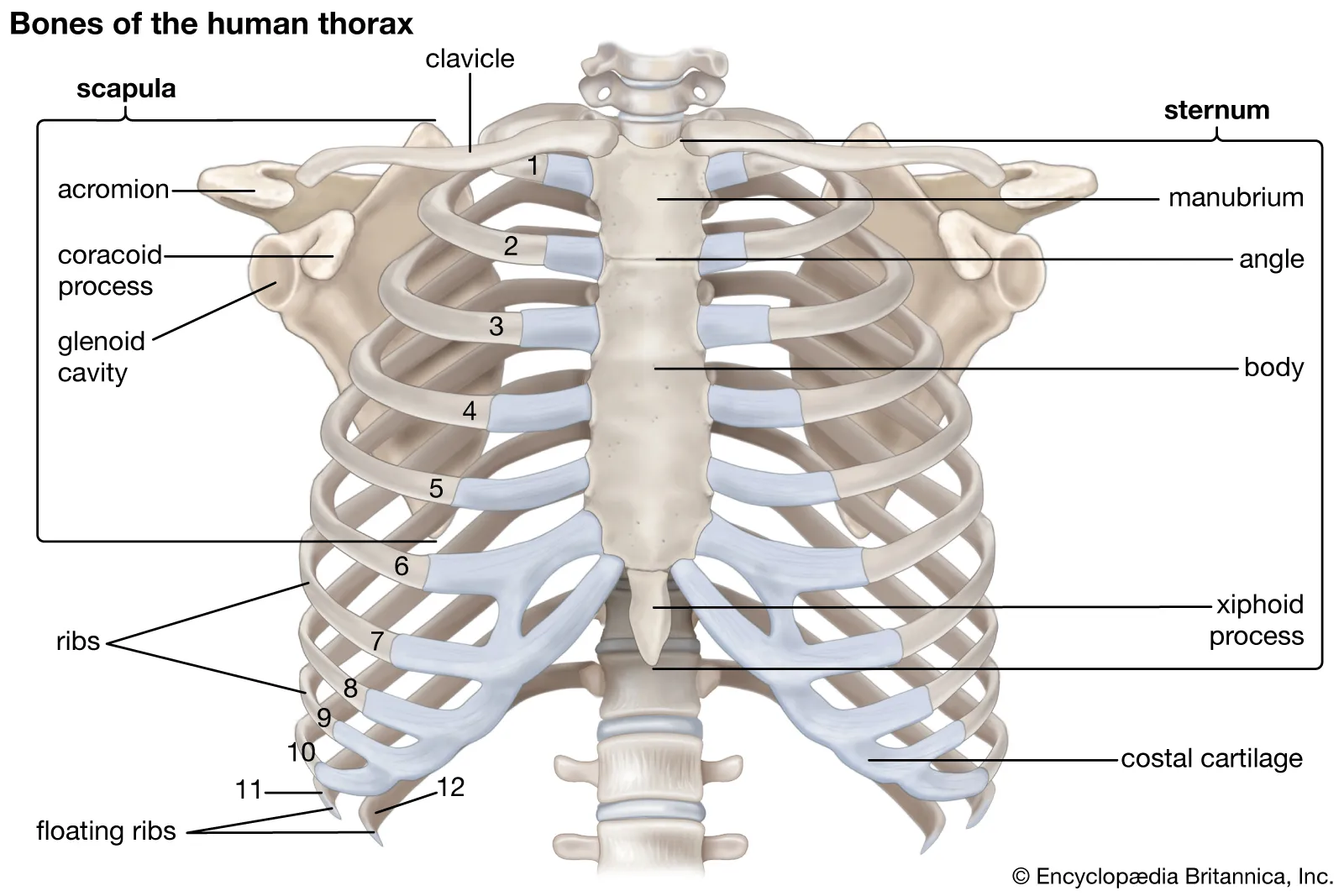
Manubrium
Upper most part of the sternum. Superior edge of manubrium forms a landmark called the sternal notch
Sternal Body
Middle, largest part of the sternum
Xiphoid Process
Inferior tip of the sternum. Cartilaginous Structure
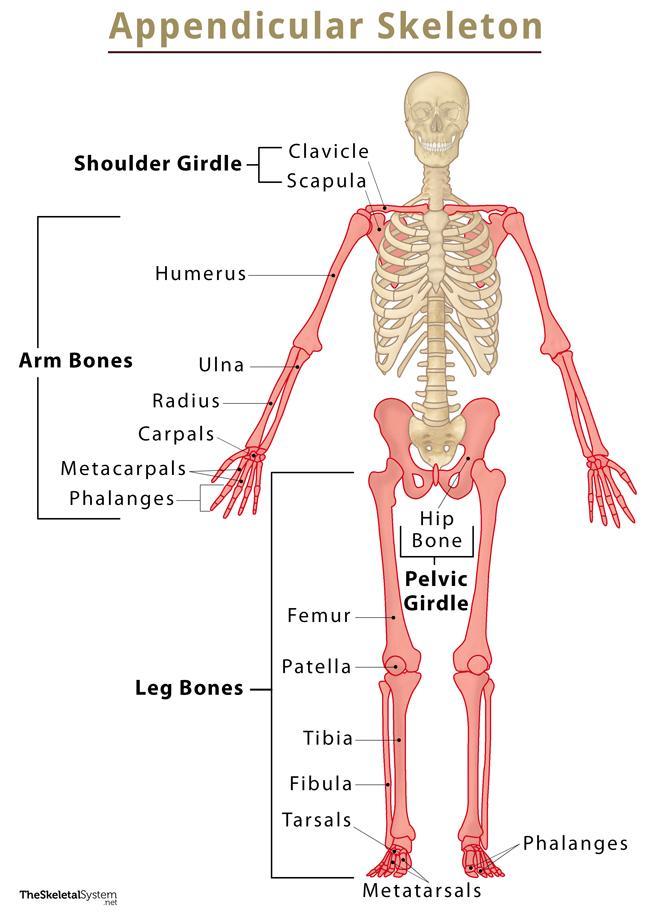
Upper Extremities
arms, extend to pectoral girdle (shoulder), clavicle, scapula. Also includes Pelvic girdle (hip bones (coxae) sacrum, coccyx). Each coxa is formed by fusion of ilium, ischium, and pubis.
Pubic Symphysis
Cartilage joining left and right pubic bones, limiting movements in these two bones
Acetabulum
where the pelvis articulates with the femur
Lower Extremities
Includes femur, tibia, fibula, femoral head, greater trochanter, lesser trochanter, patella, ankle and foot (calcaneus, talus)
Skeletal system Physiology
gives body shape
storage of calcium
protects organs
creation of blood cells
Muscle
Form of tissue facilitating movements. Three tyoes: skeletal, smooth, cardiac
Skeletal Muscle
attaches to bones, makes up for bulk of the human mass
Smooth Muscle
Found within blood vessels, and the intestines
when are tummy growls, it’s the smooth muslces vibrating in the intestine
Cardiac Muscle
In the heart. Unique because it generates its own electrical impulses
Muscoskeletal Physiology
Production of heat (shivering = muscles generating heat to maintain homeostasis)
Protects organs
Respiratory System
set of organs responsible for breathing, or respiration, and gas exchange. Includes lungs, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, larynx nose, mouth
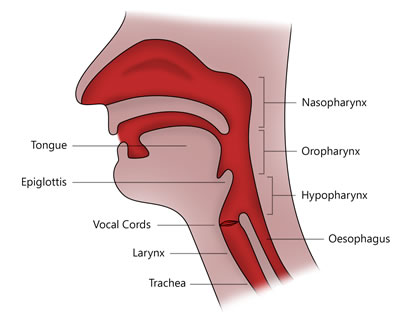
Upper Airway
Located anteriorly at the middle: Goes in order:
Nasopharynx: Upper section of pharynx connecting the nasal cavity
Oropharynx: back of the throat, form soft palate to the U-Shaped hyoid bone
Laryngopharynx
Larynx (voice box)
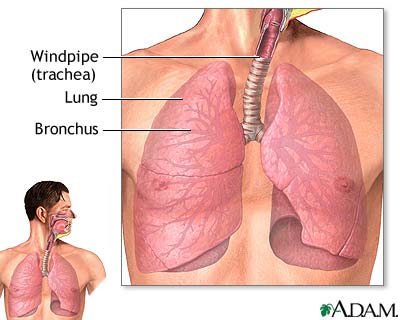
Lower Airway
Includes:
Trachea: wind pipe
Bronchiol Tree(main stem bronchi and bronchioles)
Alveoli
Lungs
Gas exchange
Occurs in alveoli (alveolar sacs) exchanged between lungs and bloodstream. Walls of alveoli contain blood vessels carrrying CO2 from the blood and body, and exchanges O2 from the lung.
Mechanics of breathing
The lungs must expand and relax. Several muscles are involved in the making of this. Diaphragm is the primary muscle. It acts both as a voluntary and involuntary muscle. Other muscles involved are the intercostals, neck muscles, abdomen
Inhalation: when you inhale, the diaphragm and intecostals contract, moves slightly down, enlarging the thoracic cage. As the volume of chest cavity increases, air rushes into the lungs (negative pressure)
Exhalation: muscles relax, all dimesnsions of thorax decrease, ribs/muscles return to normal position
Respiratory System physiology
function is the provide body with o2 and eliminate CO2. Also ventilation and respiration
Ventilation
the movement of air between the lungs and the environment, requires chest rise and fall.
Respiration
Process of gas exchange. Exchange allows for body to control pH of blood
Chemical control of breathing
Brain—specifically brain stem— Nerves in area act as sensors for level in CO2 in bloos and spinal fluid. Cells are constantly working to eliminate CO2 to regulate acid-alkaline balance of body. The medulla oblonogata, which stimulates the phrenic nerve, sends a signal to the diaphragm to increase rate of contraction.
Hypoxic Drive
Body’s backup system to control respiration. When oxygen drops, areas in the brain, walls of the aorta, and the carotid arteries act as oxygen sensors
The Pons
Another area in brainstem that controls breathing. Helps augment respirations during emotional or physical stress.
Comparisons of respiratory system in children, infants, and adults
Anatomy:
Children have a smaller and less rigid system
Smalled larnyx, trachea and cricoid cartiliage
This makes it easier for obstruction in children
Smaller chest in children, meaning they relied more on diaphragm
Respitory Rate:
children and infants breath faster than adults
Signs that an infant or child not breathing normally
Muscle retractions, in which muscle is working extra hard
Nasal flaring
S=Seesaw retractions, in which sides of chest alternate contractions
Grunting
Adult lung capacity
Usually 6,000 mL
Normal respiratory Rates
Adults: 12-20 Breaths per min
Children: 12-30 BPM
Infants: 30-60 BPM
Tidal Volume
amount of air moved in or out of lung in a single breath, generally 500 mL in adults
Inspiratory Reserve volume
deepest breath you can take after normal breath
Expiratory reserve volume
maximum air pushed out after normal breath
Residual Volume
Gas remaining in lungs after exhalation
Dead Space
Portion of respiratory system that has no alveoli, little gas exchange. When you ventilate a patient, with any device, you create more dead space, gas must fill the device before it can be moved into the patient
Minute Volume
amount of air moves in and out of lung in 1 minute
Minute Volume = Respiratory rate x Tidal Volume
Scenario where minute volume is essential
Patient presents with normal rate of 20 breaths per min. However, chest is barely moving, little air movement out of mouth.
Even though respiratory rate is normal, amount of air being moved in inadequate. MV is too low
Characteristics of Normal Breathing
Appear easy
Normal rate and depth
Regular rhythm or pattern of inhlation
Clear, audible breath sound
Regular rise and fall'\
Movement of abdomen
Inadequate Breathing in adults
Labored breathing, or significant use of acessory muscles in chest, neck, abs.
Breathing much slower, or faster
Muscle retractions above clavicles, between ribs, below rib cage, especially in children
Pale of blue skin
Cool, damp (clammy) skin
Tripod position (hands on knees)
Agonal Gasps
Patient in cardiac arrest may appear to be breathing, gasping breaths. Respiratory signal in brain still send signals to breathing muscles.
These patients need artifical ventilation, and most likely chest compressions
Circulatory System
Contains capillaries, veins, arteries. System that delivers blood to the body
Systemic Circulation
circuit in the body. Carries oxygen-rich blood from left ventricle through the body, back to the right atrium. Blood passes through tissue and organs giving up oxygen and nutrients and retaining CO2 and waste
Pulmonary circulation
In the lungs. Gives up O2 and retains CO2
Circulation
Right side of the heart receives blood from the veins of the body, blood enters the superior and inferior vena cava into atrium and to ventricle through tricuspid valve. When the right ventricle contracts, blood goes through the pulmonary arteries from the pulmonary vein, and goes to the lungs.
Left side of the heart receives oxygenated blood from the lungs from the pulmonary veins. Goes to atrium through mitral valve, into the ventricle. The ventricle contracts, the blood goes through the aortic valve to the aorta and throughout the body.
Chordae tendineae
thin bands of fiborous tissue that attach to the valves in the heart and prevent them from inverting
Normal Heartbeat i adults
Adults: 60/100 BPM resting
Athletes: 45/60 BPM resting
Stroke Volume
Amount of blood moved in 1 beat
Cardiac Output
Amount of blood moved in one minute
CO= HR x SV
Electrical Conduction System in the heart
Depolorization: electrical changes on the surface of the cell goes from positive to negative
Repolarization: Resting state to postive charge
Electrical impulse starts high in the atria, in the sinoatrial Node, then travels to the atrioventricular node, producing smooth flow of electricity
Arteries
Carry all blood from the heart to all tissues of the body.
Branch into smaller arterioles, and then into capillaries
Contract to accommodate loss of blood and increase in blood pressure
Middle layer called tunica media
Main one in body is aorta
Capillaries
Fragile divisions of the arterial system that allow contact between the blood and the cells of the tissues
Veins
Once oxygen depleted blood passes through the network of capillaries, moves into venules.
Blood returns to the heart via larger network of veins (superior and inferior vena cavae)
Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR)
Resistance to blood flow within all blood vessels except the pulmonary vessels.
Effects of Blood vessel diameter on the blood
Constricted blood vessel: Decreased size of container, increase in pressure within container
Normal: equal
Dilated Blood Vessel: Increased size of container, decrease pressure within container
Spleen
Located under rib, in upper left quadrant of abdomen. As blood cells degrade, this filters it out by digesting it. Hemoglobin is recycled
Blood Pressure
Force circulating blood against wall of arteries.
systolic: when the left ventricle contracts, pumping blood into aorta, pressure during this time
Indicates heart pumping effectiveness ad indicates blood available in the heart
Diastolic: pressure in arteries when ventricle is relaxed
Indicates adequate cardiac relaxation and pressure in the arteries between heartbeats. Also indicates amount of blood within blood vessels.
Measured in mmHg
Perfusion
circulation of blood in an organ or tissue
Hypoperfusion
Organs, tissues, and cells no longer adequately supplied with oxygen or right amount of blood
Can effect the whole body leading to shock
Mean Arterial Pressure
The average arterial pressure during systole and diastole
Hydrostatic Pressure
occurs as fluid pushes against the vessel walls to force fluid out of the capillary
Oncotic Pressure
opposing force and occurs because proteins in the blood plasma cause water to be pulled into the capillaries due to diffusion
Functions of Blood
Fights Infection: White Blood Cells
Transports Oxygen: Red Blood Cells
Transports Carbon Dioxide: Plasma
Controls pH (Buffer): Within Plasma
Transports wastes and nutrients: Plasma (water)
Clotting (Coagulation): platelets and clotting factors in the plasma
Alpha-Adrenergic Receptors
found in the blood vessels. When stimulated, blood vessels constrict, increasing blood pressure
Beta-Adrenergic Receptors
Beta-1: Located in the Heart: cause heart to increase its rate and squeeze harder with each contraction, increasing cardiac output
Beta-2: Located in Lungs. Causes the bronchi to dilate, allowing more air to be inhaled and exhaled, allowing more oxygen to enter cells of the body.
Central Nervous System
Control center of the body, containing brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
Nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord that link CNS to various organs throughout the body
Can be split into somatic and autonomic nervous systems