Geography #2.25: Coral Reefs & Mangrove Swamps
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
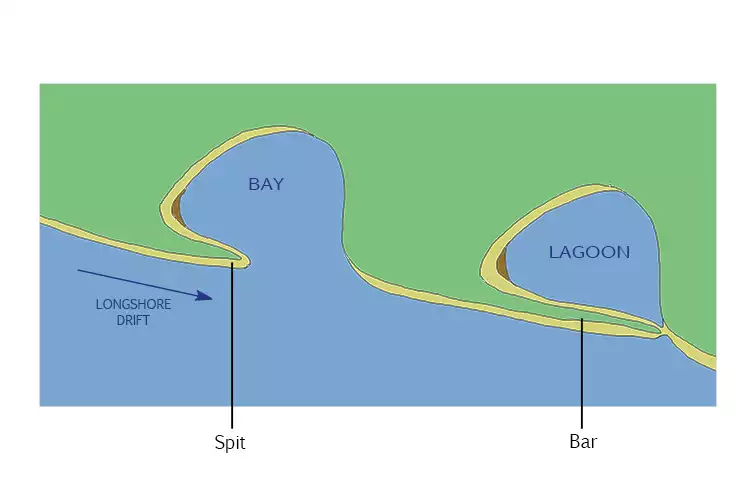
How do lagoons form?
When a sandbar, barrier island, or coral reef separates a shallow body of water from the open sea.

What is a tombolo?
It is a natural landform where a sand or gravel bar connects an island to the mainland or to another island.
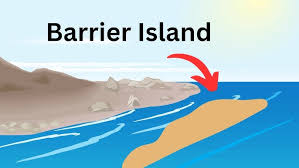
What is a barrier island?
A long, narrow island made of sand that runs parallel to the coast, protecting the shore from waves and storms.
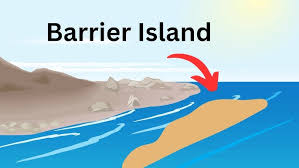
Where do barrier islands form?
Parallel to the coast.

How do barrier islands form?
When waves and currents deposit sand along shallow coastlines.
What is the difference between a barrier island and a bar?
A bar joins two headlands, whereas a barrier island is open at one or both ends.
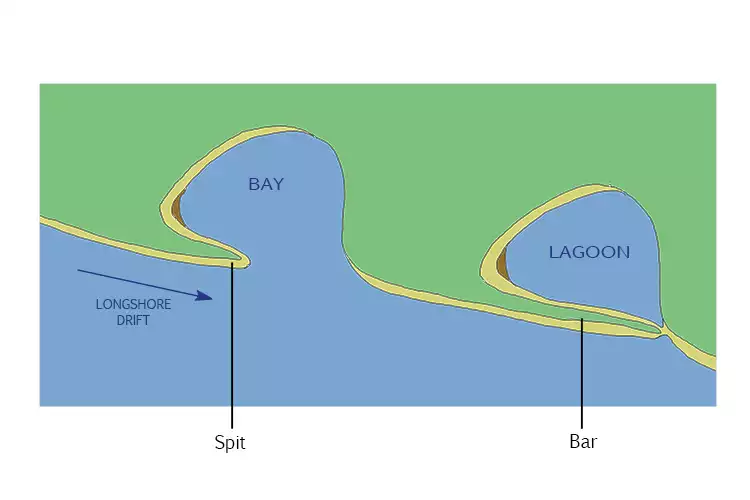
How does a bar form?
When waves and currents move sand or sediment into a ridge.
How do dunes form?
When sand grains are trapped and deposited against an obstacle like rubbish, rocks, or driftwood.
What helps sand dunes form?
Winds and Vegetation

Where do dune ridges form?
They form along coastlines where wind transportation moves sand around and deposit it in ridges.
What is the environment of the sand dunes?
They are dynamic, with changes occurring quickly due to natural forces like wind and water.
Explain the formation of a sand dune.
Windblown sand gathers against obstacles, forming small dunes that grow and align perpendicular to the prevailing wind. Over time, vegetation establishes on the dune ridges, gradually stabilizing them through succession.
What do the first plants or pioneer species have to cope with?
Salinity, Lack of Moisture, Wind, Temporary Submergence by wind blown sand, Rising Sea Levels
What are some examples of these first plants or pioneer species?
Lyme Grass & Sea Couch Grass
How is the sand when the coastal dunes begin?
Little Soil Content & High pH levels or alkaline
What are the characteristics of embryo dunes?
They are very fragile and reach a max height of 1 meter.

What is one function of fore dunes?
They give some protection against the prevailing wind which allows other species of plants, like the Marram Grass, to grow.
How do the Marram Grass stabilize the dune?
With its roots system and hard structure
How does these plants help the dunes?
They add organic matter, they make the dunes more hospitable for future plants.
What forms in the dune slack?
A microclimate; a small area with its own unique weather conditions.
What is the height of a fore dune?
Max height is 5 meters
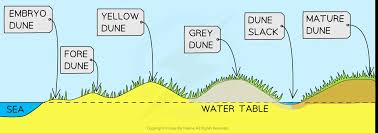
What is the height of a yellow dune?
Max height is 8 meters
Do yellow dunes stay yellow?
They begin with a yellow color but darkens organic material adds humus to the soil.
Do plants like the Marram grass still dominate the vegetation in the Yellow Dunes?
They do, but more delicate flowering plants and insects are found in the dune slacks.

What are dune slacks?
Low, wet areas between sand dunes, often in depressions, providing a sheltered habitat for plants and insects that thrive in moist conditions.
How much is a yellow dune exposed?
20%
What is the height of a yellow dune?
It does not exceed over 8 meters
What are the most oldest and stable dunes?
Mature Dunes
How far away are mature dunes from the shore?
Several Hundred Meters or More
The soil of mature dunes can support?
A variety of flora and fauna such as oak trees and alders
What is the final stage of coastal dune succession?
Mature dunes, known as the climax community stage
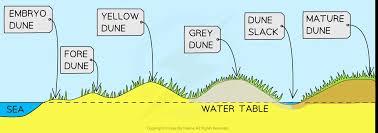
What is the order of coastal dune succession?
Embryo, Foredunes, Yellow Dunes, Grey Dunes, Dune Slacks and then Mature Dunes
What is a coastal dune succession?
It is the gradual process by which sand dunes develop and evolve over time, forming distinct zones that host different plant and animal communities.
How do embryo dunes form?
They form by the accumulation of sand, often trapped by small obstacles like shells, pebbles, or driftwood.
How is the vegetation of embryo dunes? What grows there?
Pioneering plants, like Lyme Grass & Sea Crouch Grass. These plants are salt-tolerant, hardy, and adapted to withstand harsh, windy conditions.
How do fore dunes form?
They start as embryo dunes but as more sand accumulates, they grow into foredunes.

What is the vegetation of foredunes or yellow dunes? What grows there?
Marram grass. Its roots help hold the sand in place, and it grows quickly when covered by blowing sand, which helps strengthen the dunes.
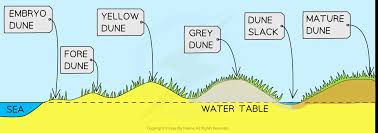
What are some characteristics of yellow dunes or foredunes?
They are yellow due to the sand and have minimal organic matter.
How do grey dunes form?
They form as vegetation stabilizes the dunes, accumulating organic matter, and the soil gradually becomes more fertile.
What is the vegetation of grey dunes? What grows there?
Marram grass declines as new plants like shrubs and bushes establish. These dunes are called "gray" because organic material darkens the sand.
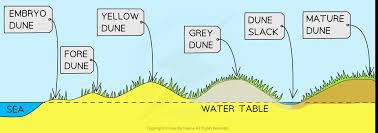
What are some characteristics of grey dunes?
They are more stable and have more developed soil and are called "gray" because organic material darkens the sand.

What are dune slacks? How do they form?
They are low, wet areas between sand dunes that form when the land dips close to the water table, allowing water to collect and creating a moist environment.
How is the vegetation of a dune slack? What grows there?
Water-tolerant plants such as rushes, sedges, and reeds grow here.

What are some characteristics of a dune slack?
They are wet and often serve as habitats for amphibians and other species adapted to moist environments.
What are mature dunes? How do they form?
They are stable, older dunes. They form when sand becomes stable over time, allowing soil to develop and support more complex plants like shrubs and trees.
What is the vegetation of a mature dune? What grows there?
Oak trees, alders and other more permanent vegetation grow there.

What is a salt marsh?
A coastal ecosystem in between land & open water that is flooded and drained by saltwater brought in by the tides.
How does a salt marsh start?
When mud and silt are deposited along a sheltered part of the coastline.

What is a coastal salt marsh?
A coastal ecosystem found between land and open salt water or brackish water that is regularly flooded by the tides.
How does a salt marsh begin?
A salt marsh begins when mud and silt are deposited along a sheltered part of the coastline.

What role do plants play in the development of salt marshes?
Plants help to stick mud particles together and trap more sediment, making the mudflats more stable.
What is the ecological significance of salt marshes?
Salt marshes are important habitats for various species such as worms, fish, and birds, providing nursery areas and food sources.
What is the term for the process of mudflats and salt marsh development over time?
Succession.
Name two types of birds that rely on salt marshes for roosting.
Curlew and Godwits.
What are some threats to salt marsh habitats?
Rising sea levels, erosion, pollution, farming, housing development.
What is one function of salt marshes regarding wave action?
They can reduce the force of waves hitting sea walls.
Which animals may graze on the upper parts of the salt marsh?
Farm animals.
What happens to mudflats during high tide?
They are covered by the sea, providing a habitat for feeding birds.

What is the primary vegetation type found in salt marshes?
Low growing vegetation with narrow channels between.
How do sediment deposits contribute to the development of salt marshes?
Sediment deposits help to build up stable mudflats which allow vegetation to grow.
What types of water can a salt marsh be found adjacent to?
Salt water or brackish water.
How does human activity impact salt marshes?
Human activities can lead to pollution, disturbance, and land claims that threaten salt marsh habitats.

What unique plants are often found in salt marshes?
Plants that can cope with saline conditions and periodic flooding. Like, Saltwort & Bullrush.
Which crustaceans are often found in the channels of salt marshes?
Crabs.
What is 'coastal squeeze' in relation to salt marshes?
The loss of salt marsh habitat due to rising sea levels and human development.
What ecological role do wading birds fulfill in salt marshes?
They find food and nesting sites there.
How do seasonal changes affect salt marshes?
They can alter the availability of food and habitat for wildlife.
What are the primary sources of pollution threatening salt marshes?
Oil, sewage, fertilizers, and waste dumping.
What adaptation helps salt marsh plants survive?
They can tolerate high salt levels and withstand being underwater.
What is 'colonization by Cord Grass'?
It refers to the process where Cord Grass becomes established in salt marsh habitats.

How do mudflats begin to stabilize over time?
Through the accumulation of sediment and growth of vegetation.
Why are salt marshes crucial for fish populations?
They act as nursery areas, providing safe habitats for young fish.
What do mudflats and salt marshes provide for birds during high tides?
They provide areas to roost and rest.
What happens to sediment held in sheltered waters like harbors?
It settles out and builds up, leading to the formation of mudflats.
How does wave energy affect the deposition of sediment in coastal areas?
Lower energy waves allow for greater deposition of sediments.
Why are salt marshes considered unique ecosystems?
Many plants and animals found there are not found elsewhere.

What is a key characteristic of salt marsh vegetation?
It consists of blocks of flat low-growing plants.
Which factors can lead to erosion of salt marshes?
Rising sea levels and human interference.
How can salt marshes serve as a natural defense?
By reducing the impact of waves on coastal structures.
What role do worm species play in salt marshes?
They contribute to the nutrient cycling and aeration of the sediment.
What is the significance of narrow channels in salt marshes?
They provide pathways for water flow and habitats for various organisms.
How does the presence of salt marshes benefit crustacean populations?
They offer refuge and feeding grounds.
What is one way humans can help protect salt marsh habitats?
By reducing pollution and limiting coastal development.
What type of marsh evolves from mudflats over time?
Salt marshes.
How does the health of a salt marsh ecosystem impact bird populations?
Healthy marshes provide food and nesting habitats for birds.
What are two critical ecological functions provided by salt marshes?
Nutrient cycling and habitat support for wildlife.
What happens to sediment during the colonization by plants in a salt marsh?
The sediment is trapped and stabilized by the plants.
What is the importance of sea defenses in relation to salt marshes?
They can impact the natural processes of sediment deposition.
What type of animals are termed as 'waders' in the context of salt marshes?
Birds that feed in shallow water or on mudflats.
What type of grasses are often characteristic members of salt marsh ecosystems?
Cord Grass.
How do salt marshes contribute to biodiversity?
By providing unique habitats for specialized plants and animals.
What forms coral reefs and atolls?
Coral reefs and atolls are formed through the build-up and compression of the skeletal structures of tiny marine animals called polyps.
Where are living corals typically found in coral reefs?
Living corals are found in the upper and outer part of the coral reef only.
What material do corals use to build their structures?
Coral structures are made out of calcium carbonate.
What temperature range do coral reefs thrive in?
Corals cannot tolerate water temperatures below 18°C but grow best at 22°C-25°C.
What do corals need for photosynthesis?
Corals need light for photosynthesis due to the algae called zooxanthellae that live in their tissues.
At what depths are corals generally found?
Corals are generally found at depths of less than 25m where sunlight can penetrate.
What is the salinity range that corals need to survive?
Corals need salty water to survive, ranging from 32-42 percent saltwater.
List one factor at a local level that helps coral development.
Wave action provides well-oxygenated, clean water, helping coral development.
What happens to corals if they are exposed to air for too long?
Corals cannot be exposed to air for too long or they will die.