Biochemistry-Chapter 4: Amino Acids and the Peptide Bond
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Chemistry of Amino Acids
~at pH =7, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated, and the amino group is protonated
~can polymerize to form peptides/proteins (result of having two different functional groups
~all amino acids have the S configuration at the alpha carbon with the exception of cysteine (R)
~L amino acids are the ones incorporated into living systems; few times D amino acids are used
zwitterion
A molecule that contains charges, but is neutral overall. Most often used to describe amino acids
Nonpolar hydrophobic side chains
glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine, proline
Aromatic side chains
phenylalanine, tryptophan
Polar, uncharged
serine, threonine, cysteine, asparagine, glutamine, tyrosine
acid side chains (-) charged
aspartic acid, glutamic acid
basic amino acids (+) charged
lysine, arginine, histidine
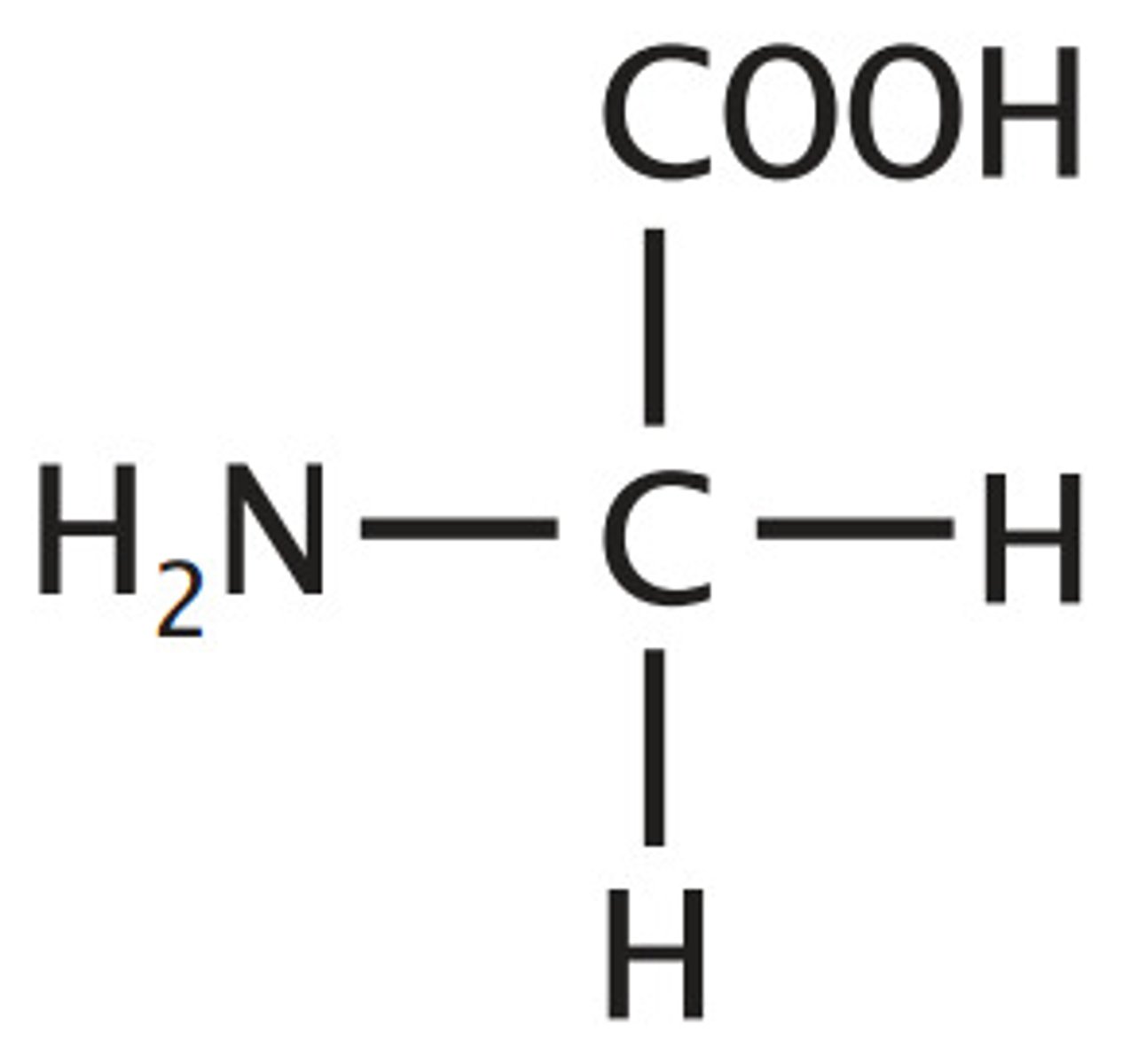
Glycine
Gly, G
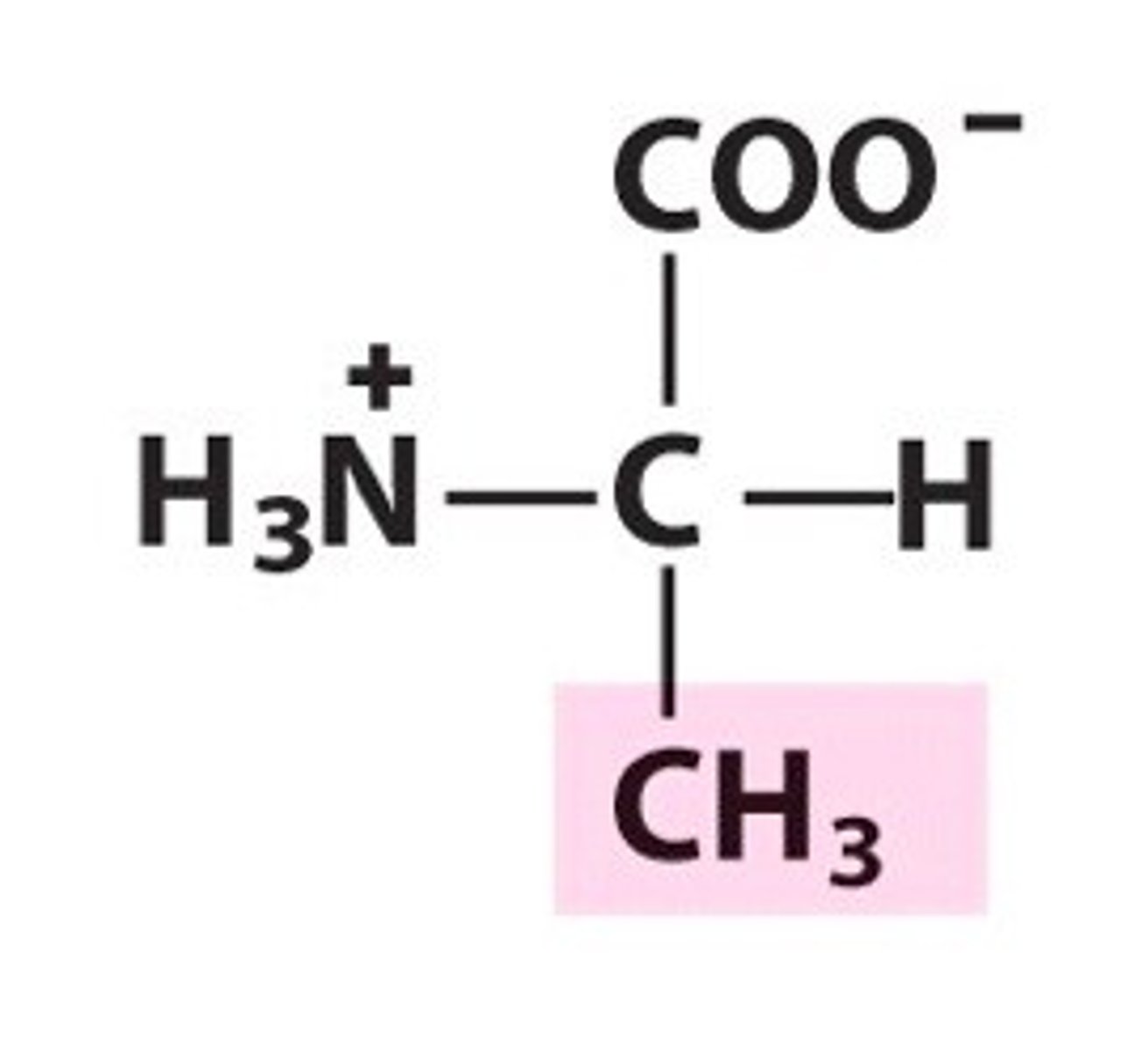
alanine
Ala, A
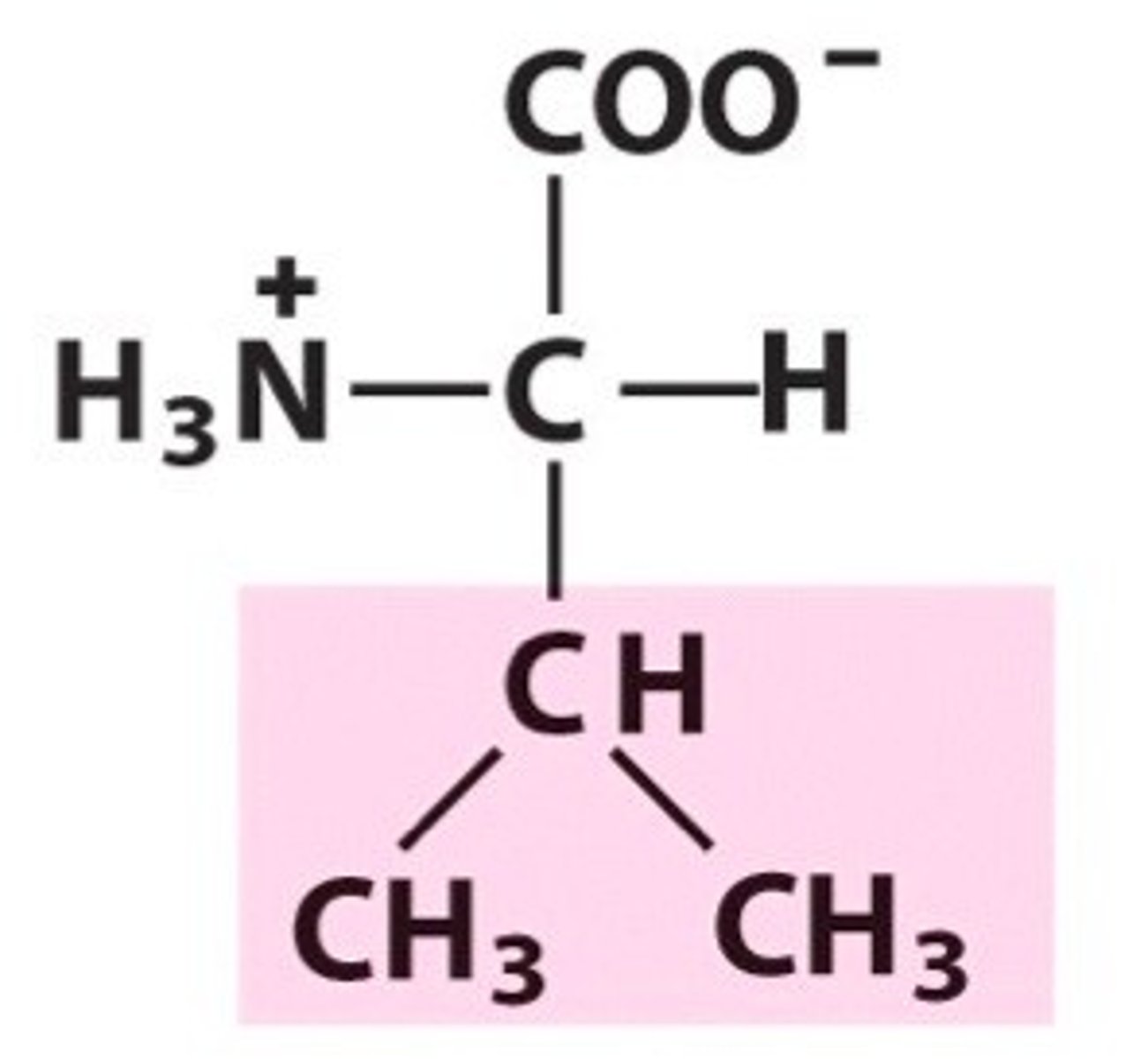
Valine
Val, V
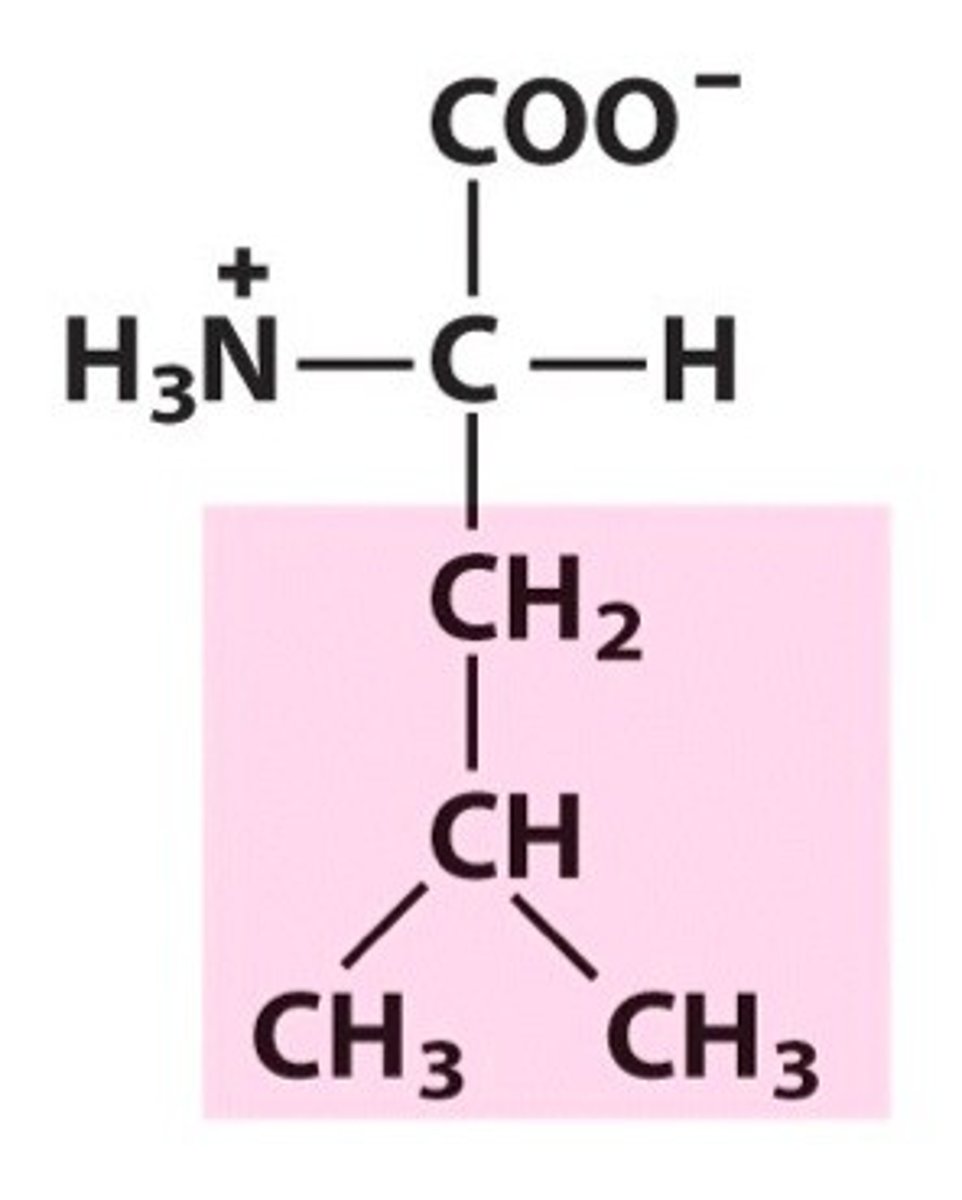
Leucine
Leu, L
Isoleucine
Ile, I
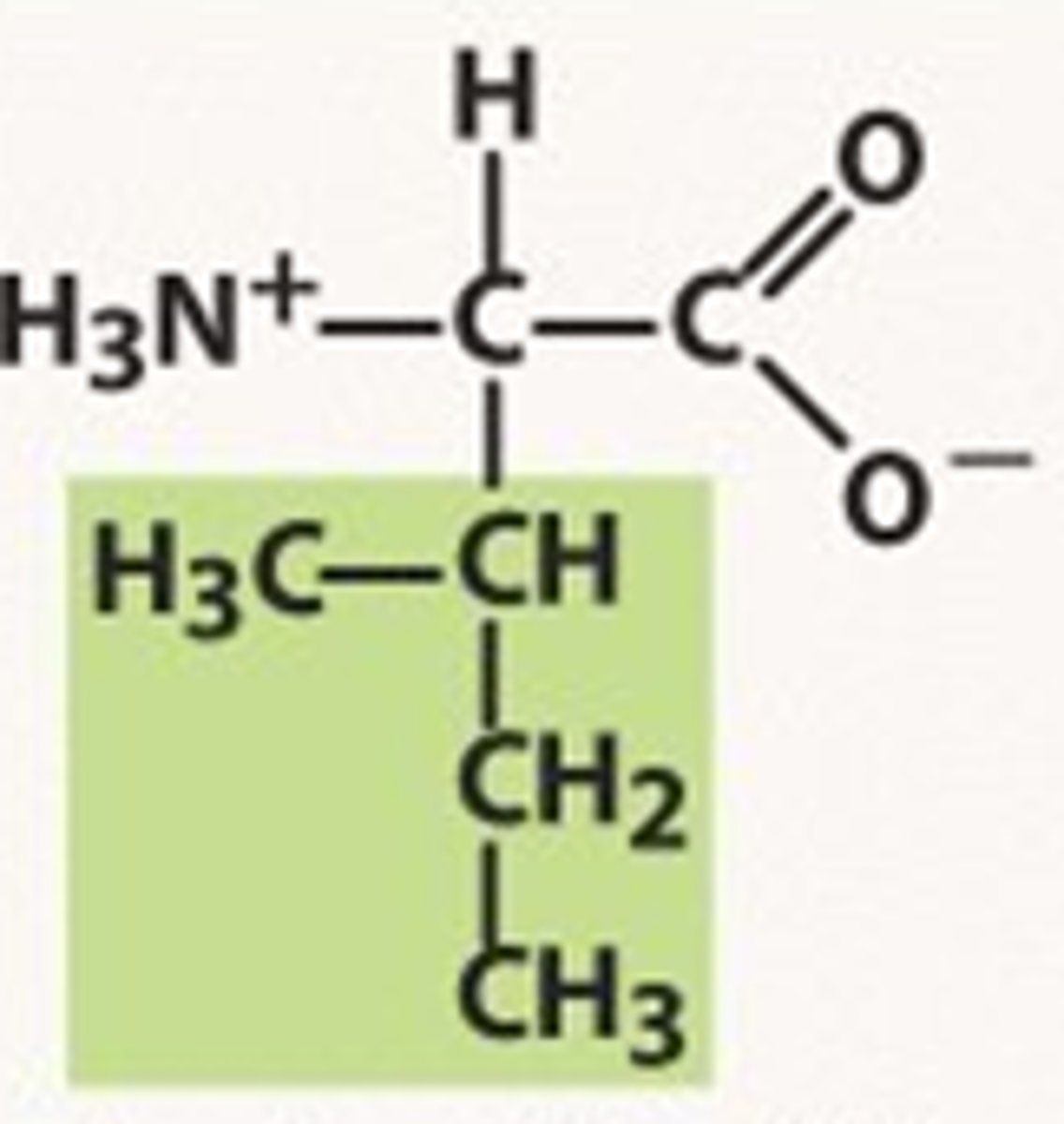
Methionine
Met, M
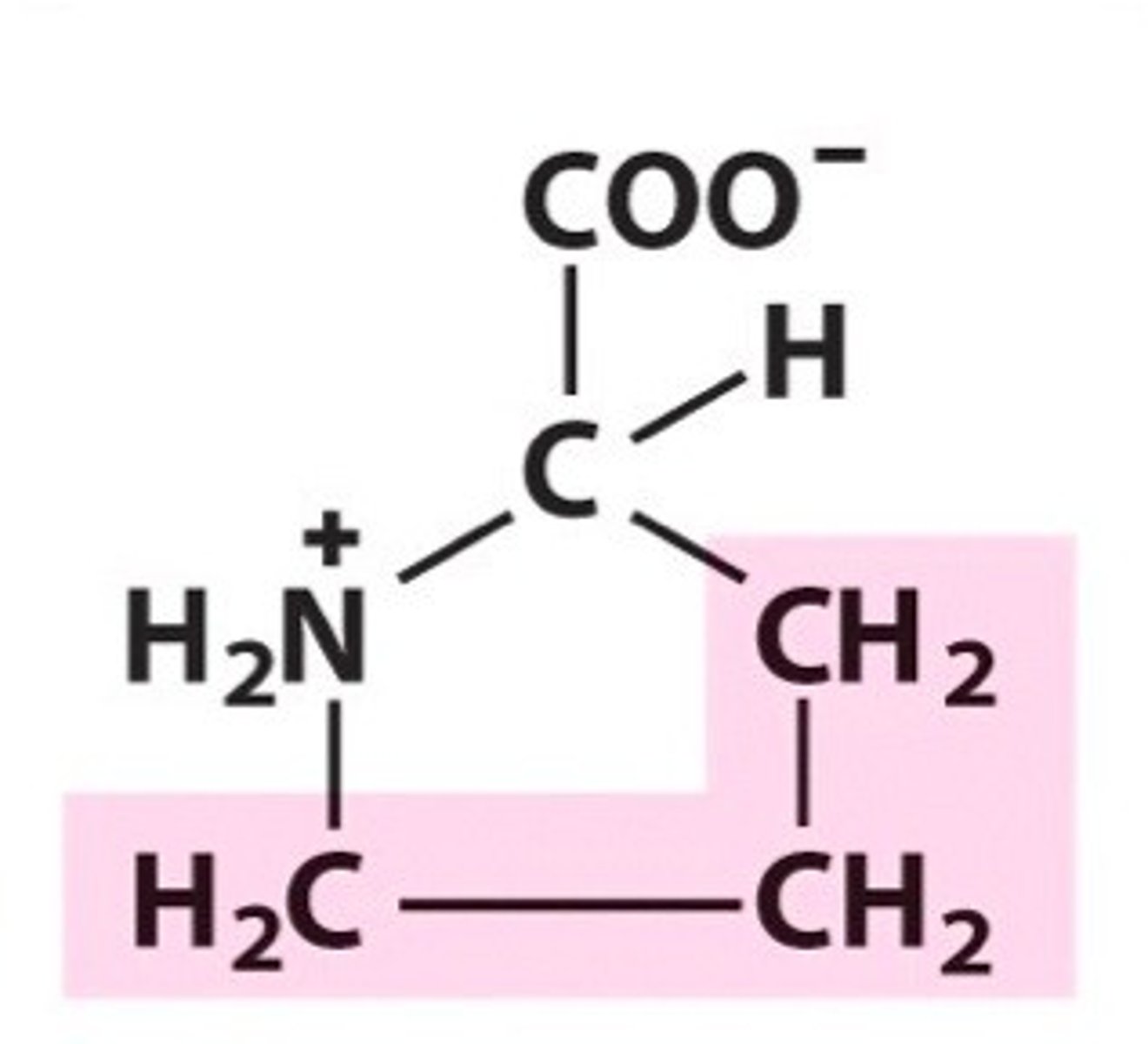
Proline
Pro, P
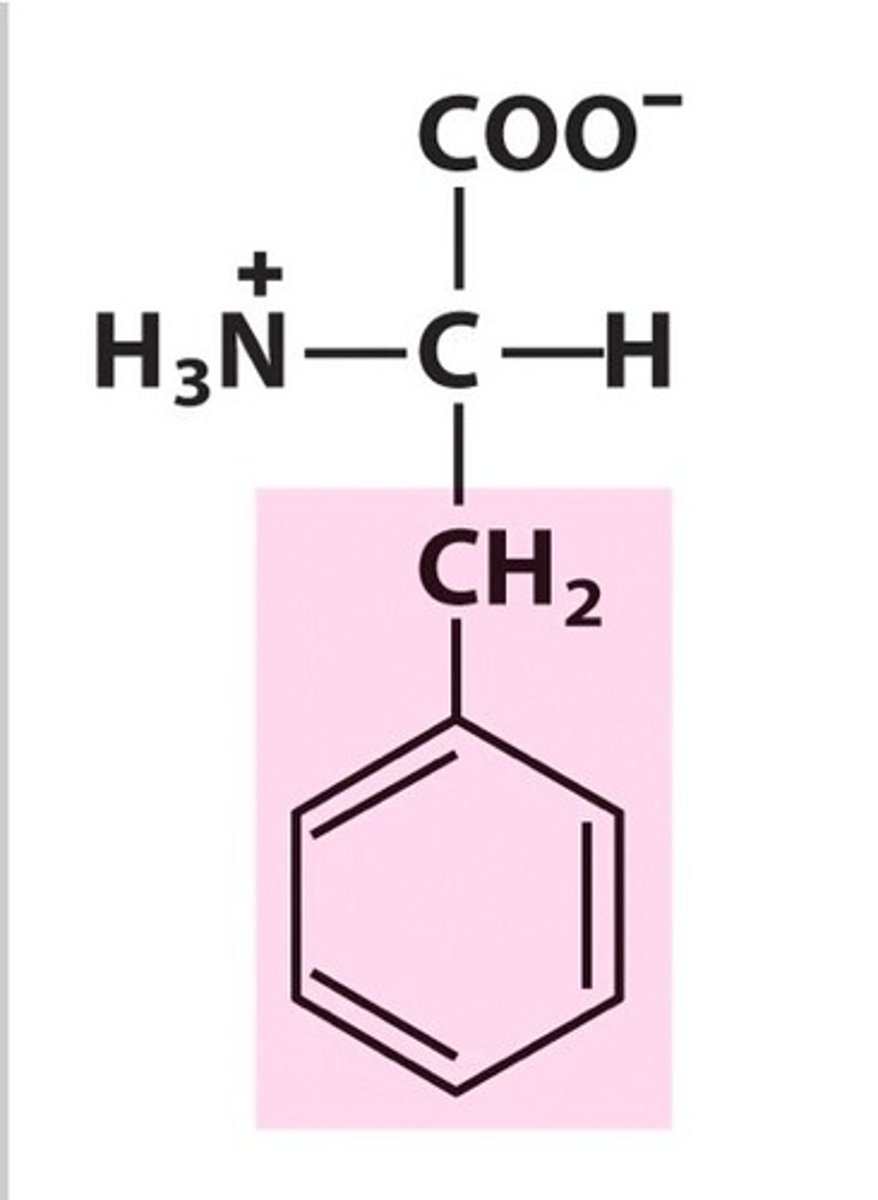
Phenylalanine
Phe, F
Tryptophan
Trp, W
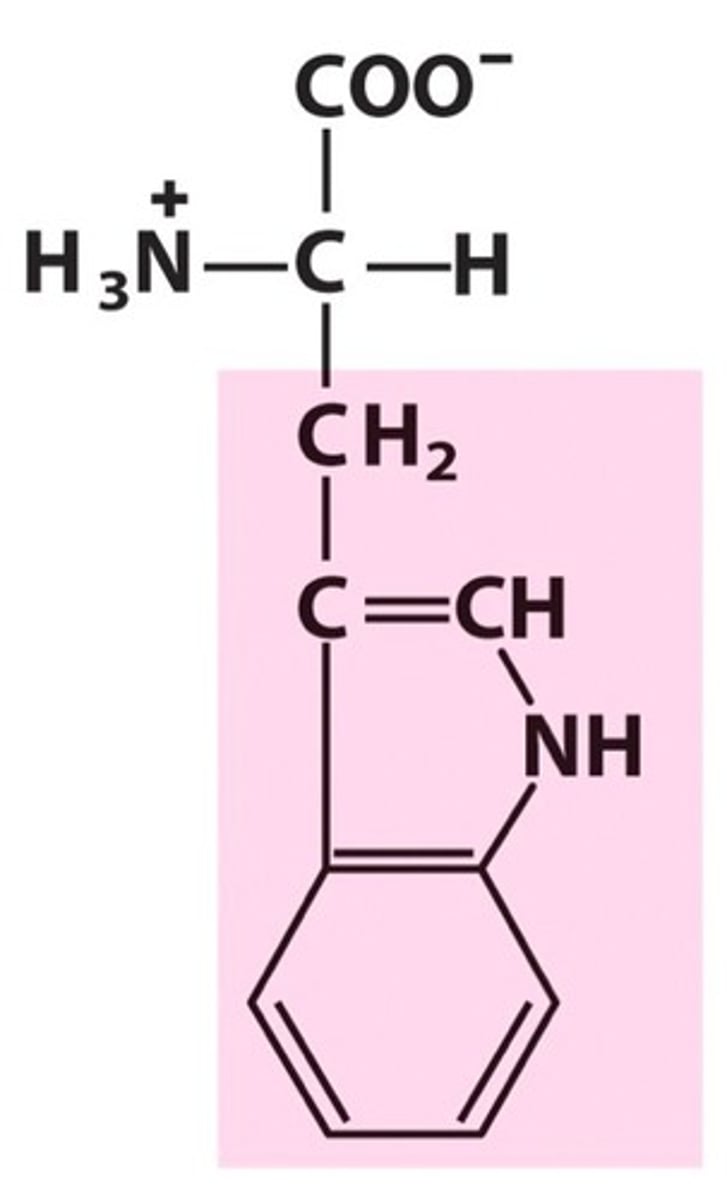
Serine
Ser, S
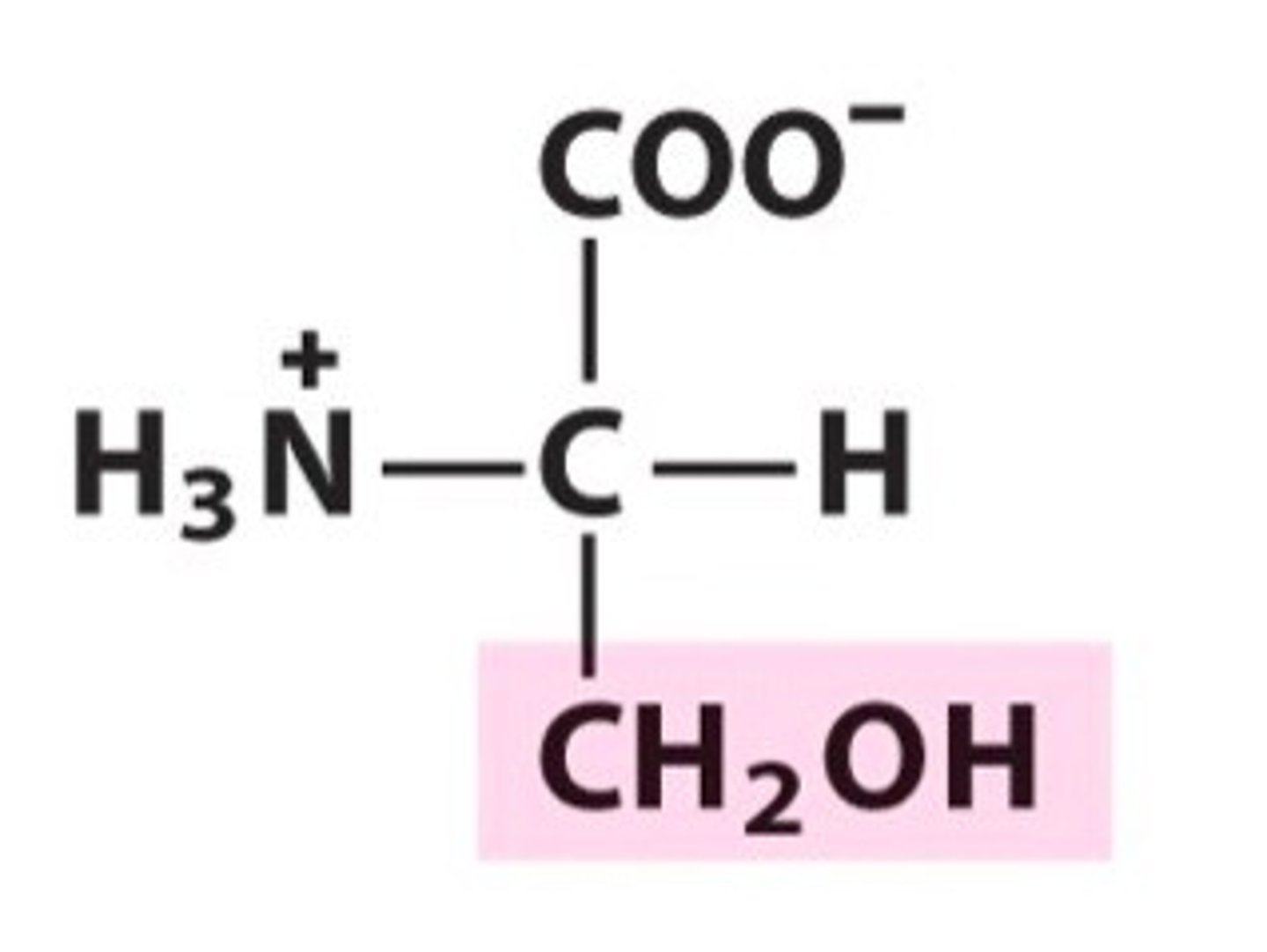
Threonine
Thr, T
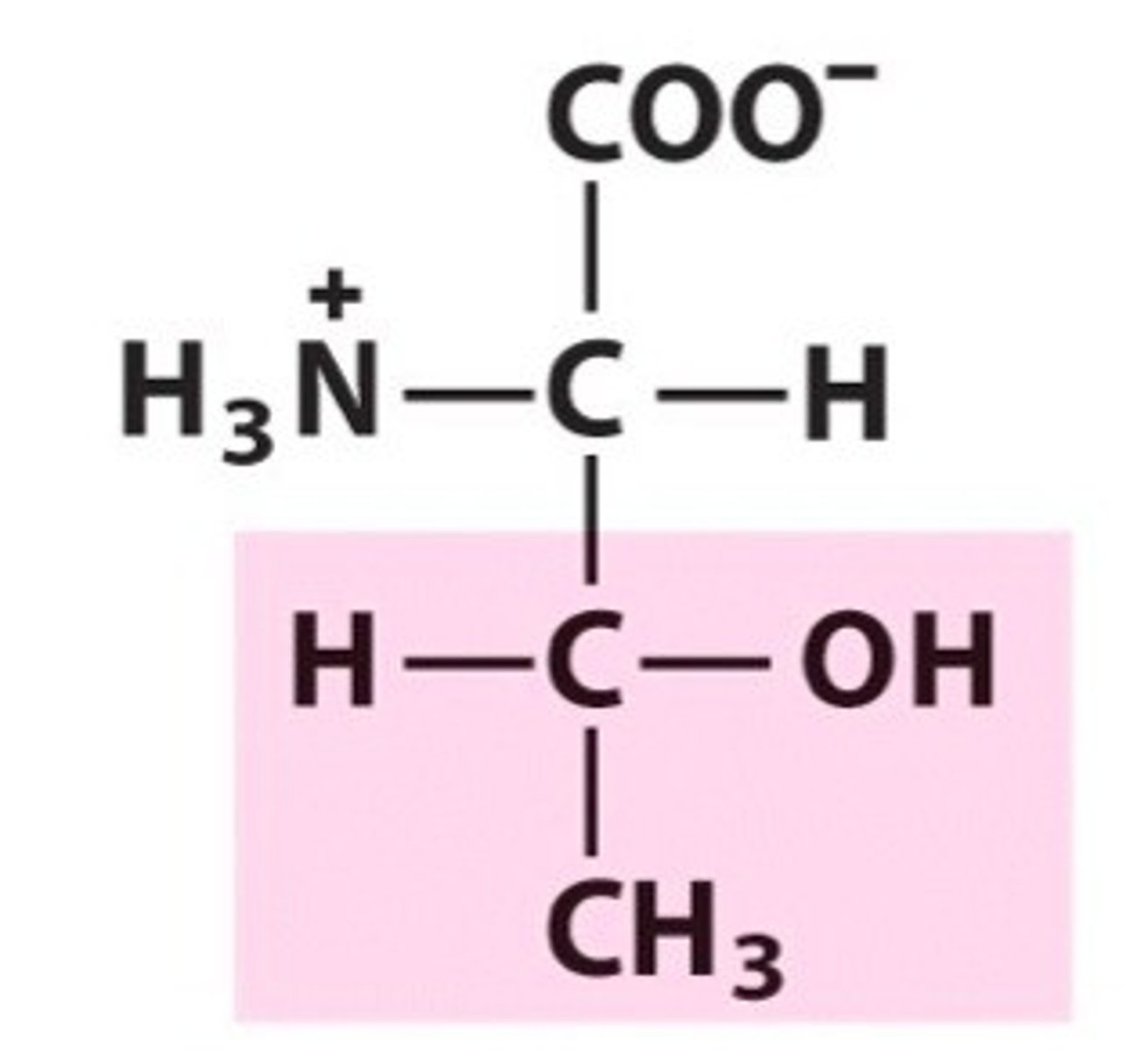
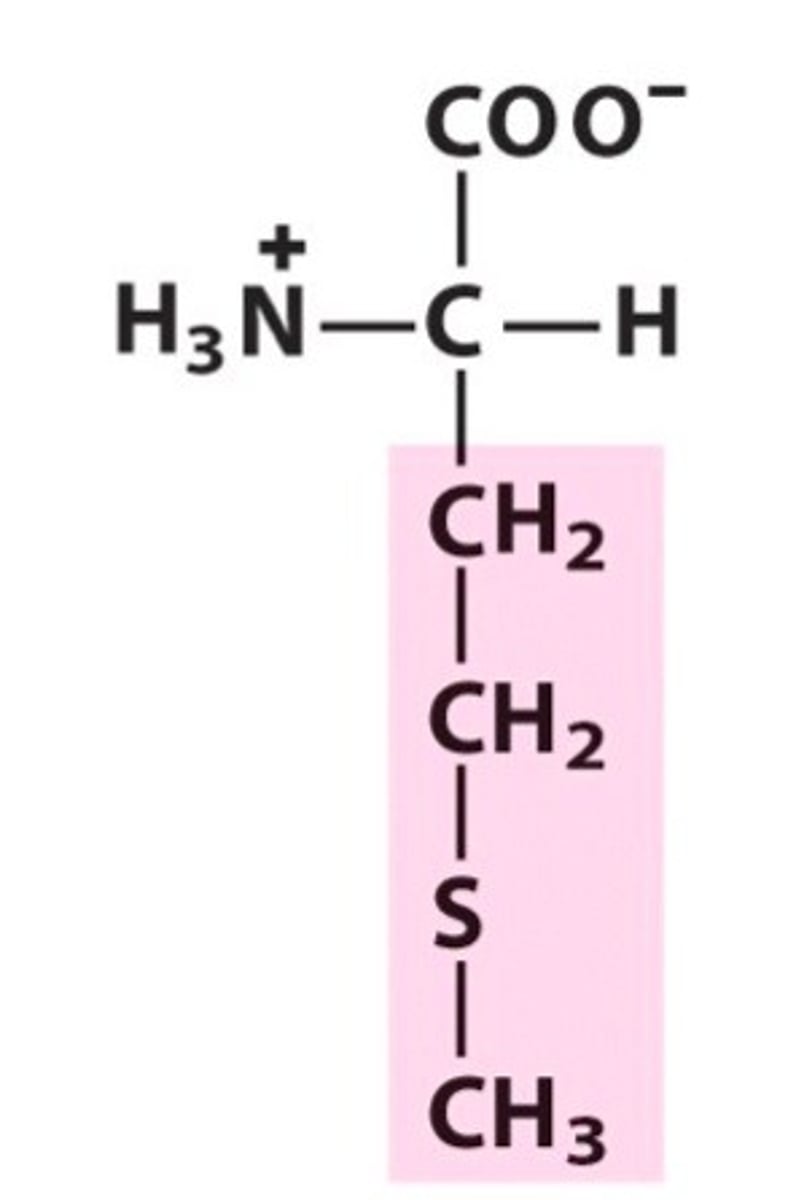
Cysteine
Cys, C
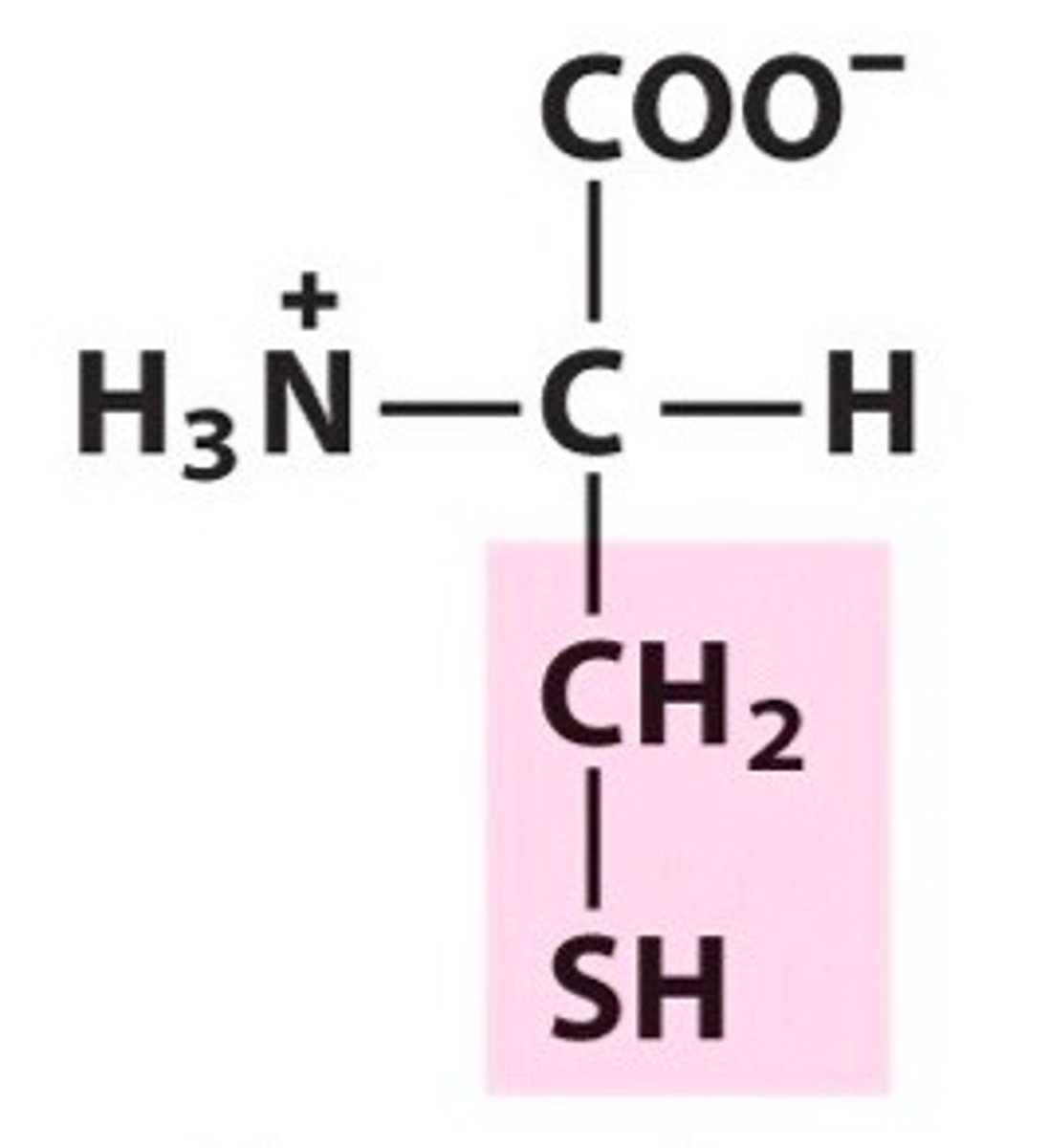
Asparagine
Asn, N
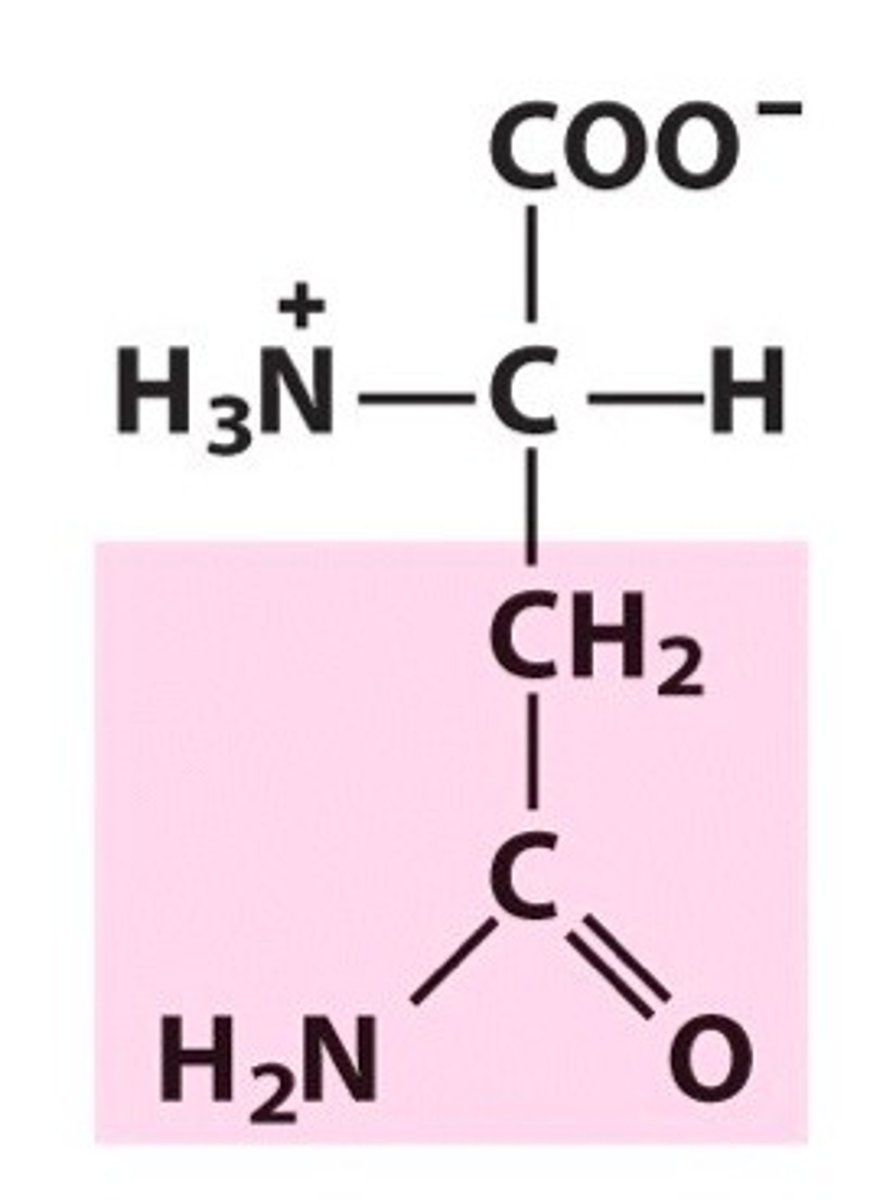
Glutamine
Gln, Q
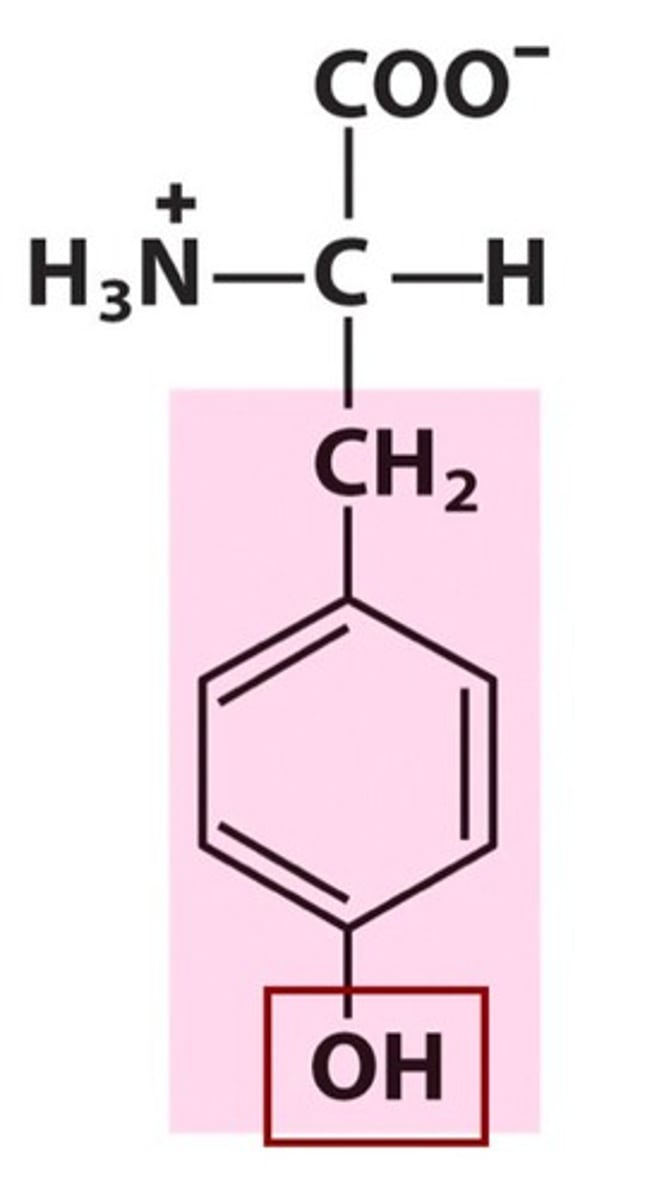
Tyrosine
Tyr, Y
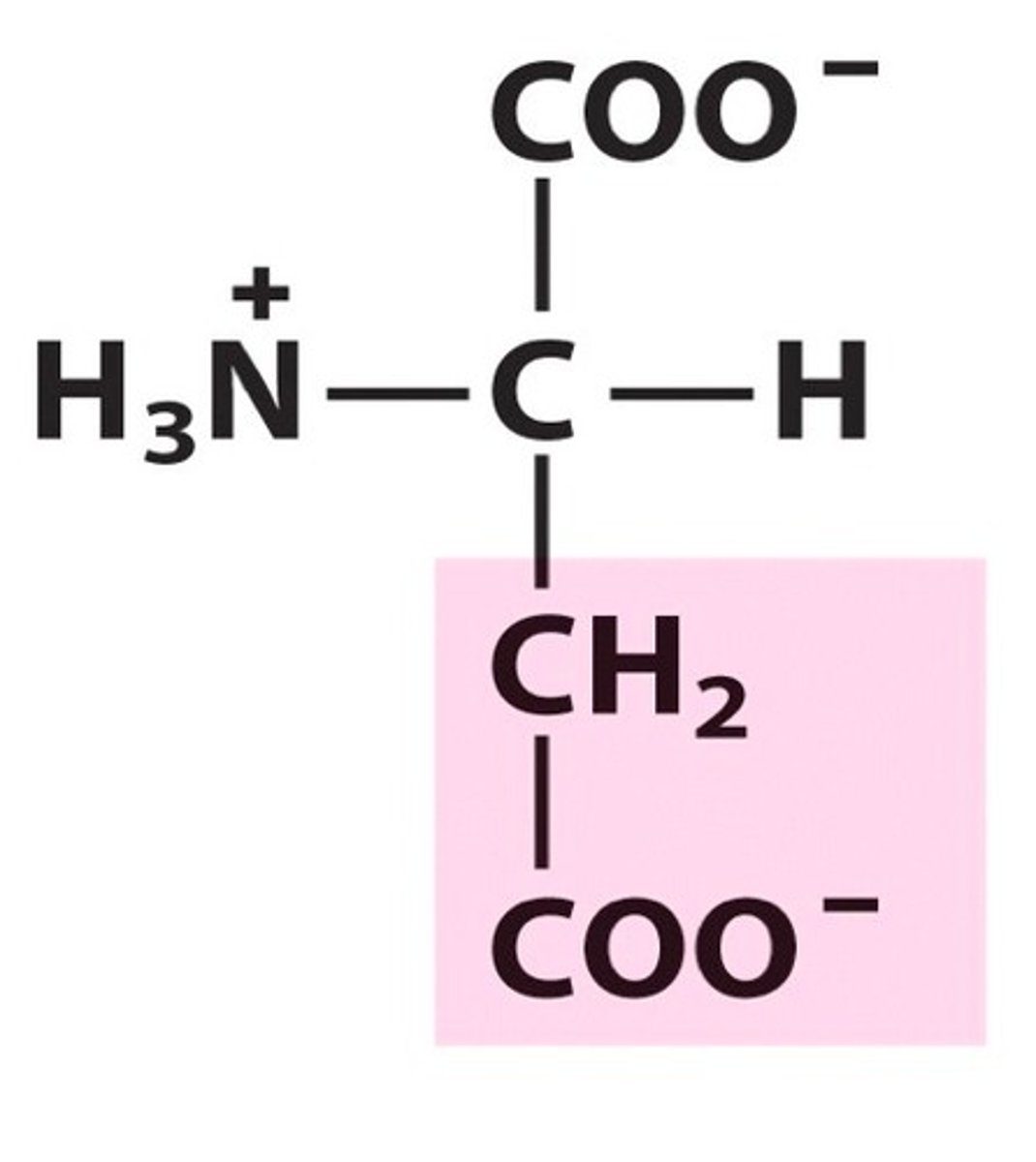
Aspartic Acid
Asp, D
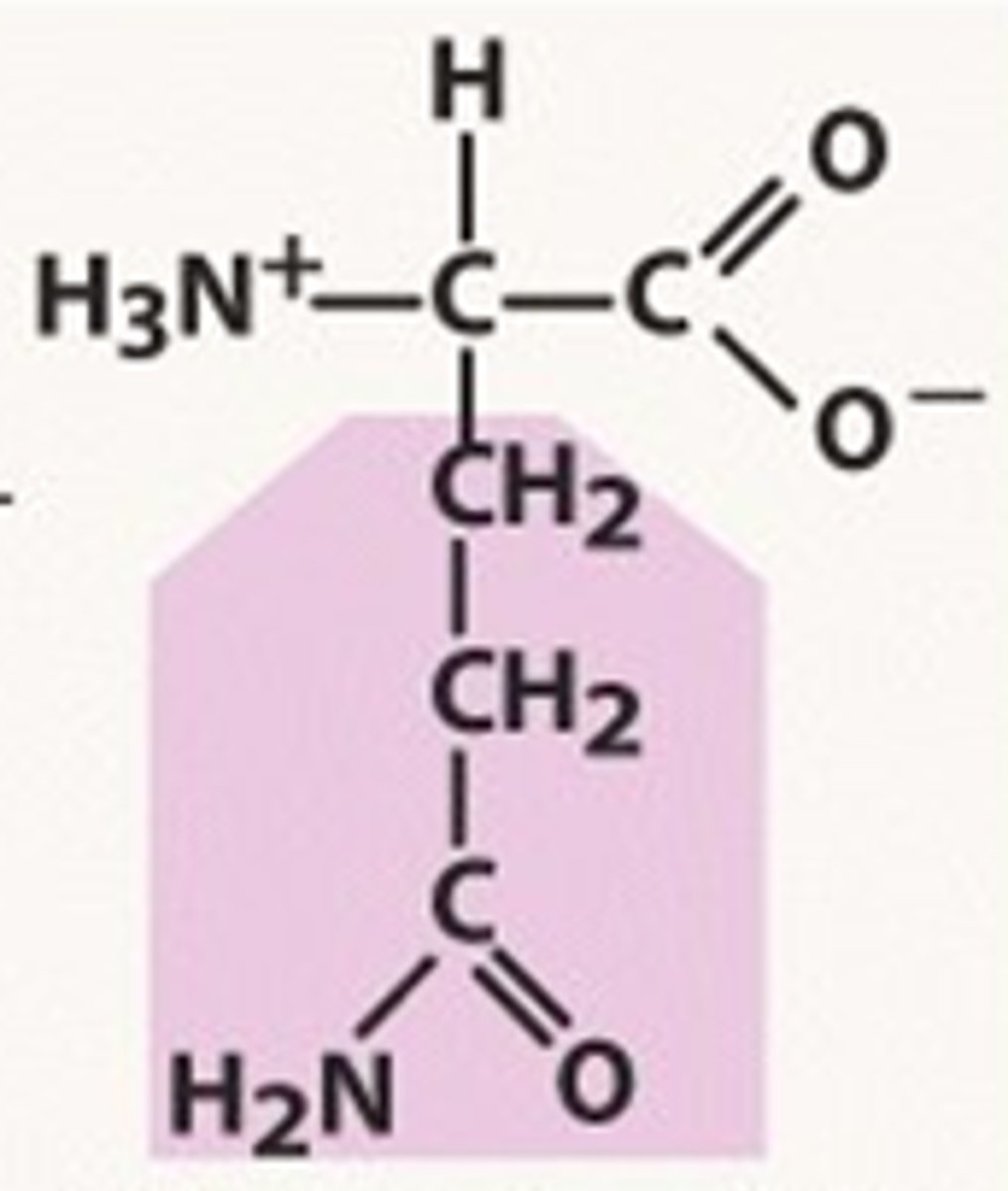
Glutamic Acid
Glu, E
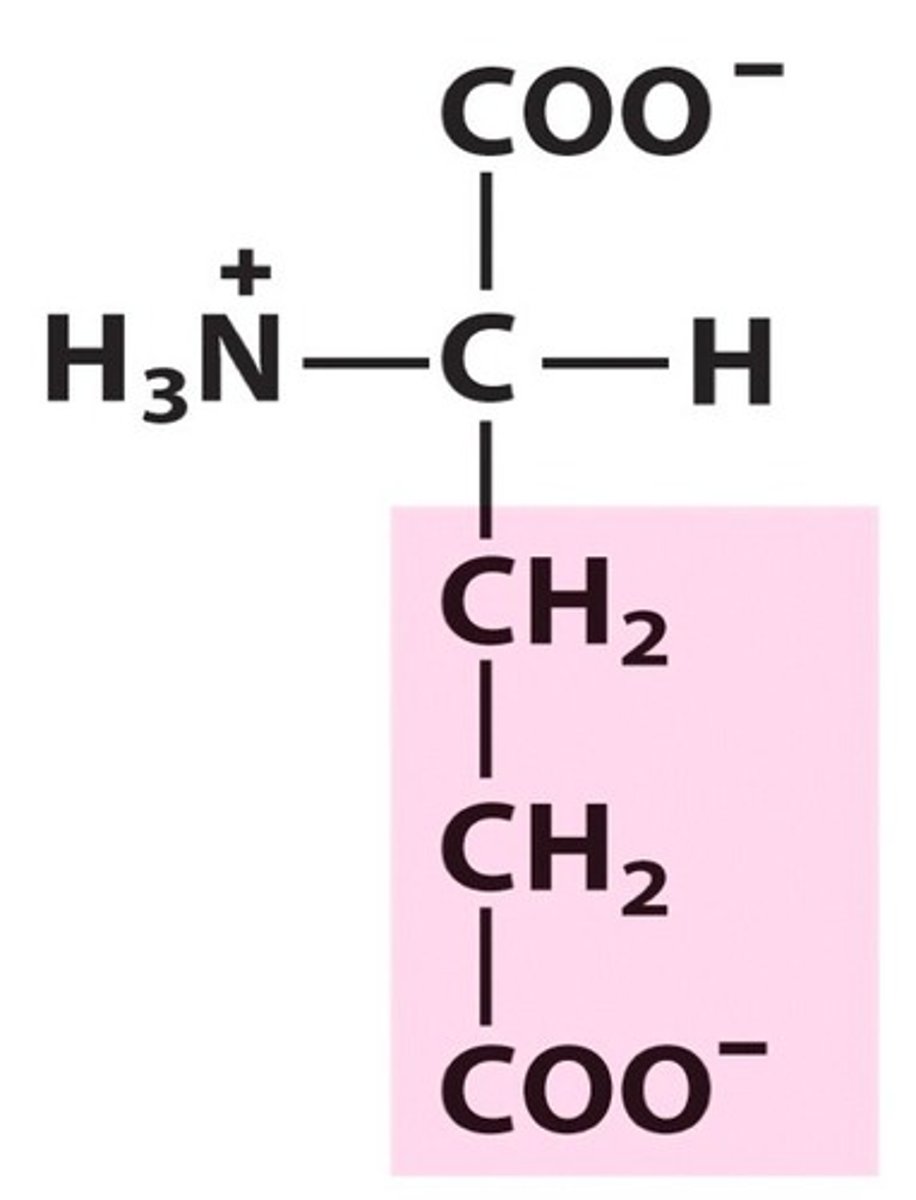
Lysine
Lys, K
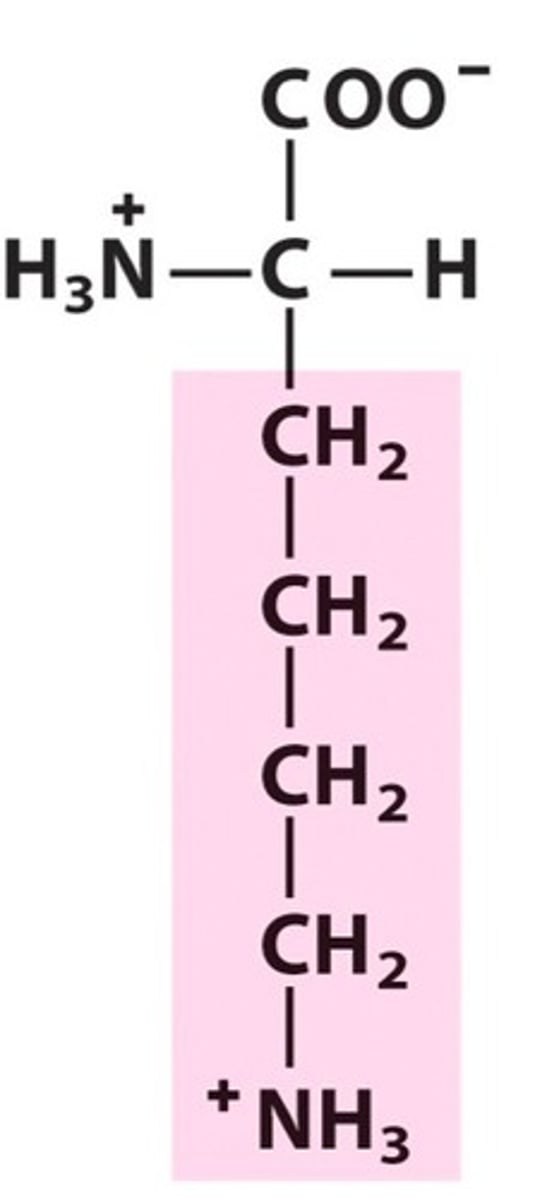
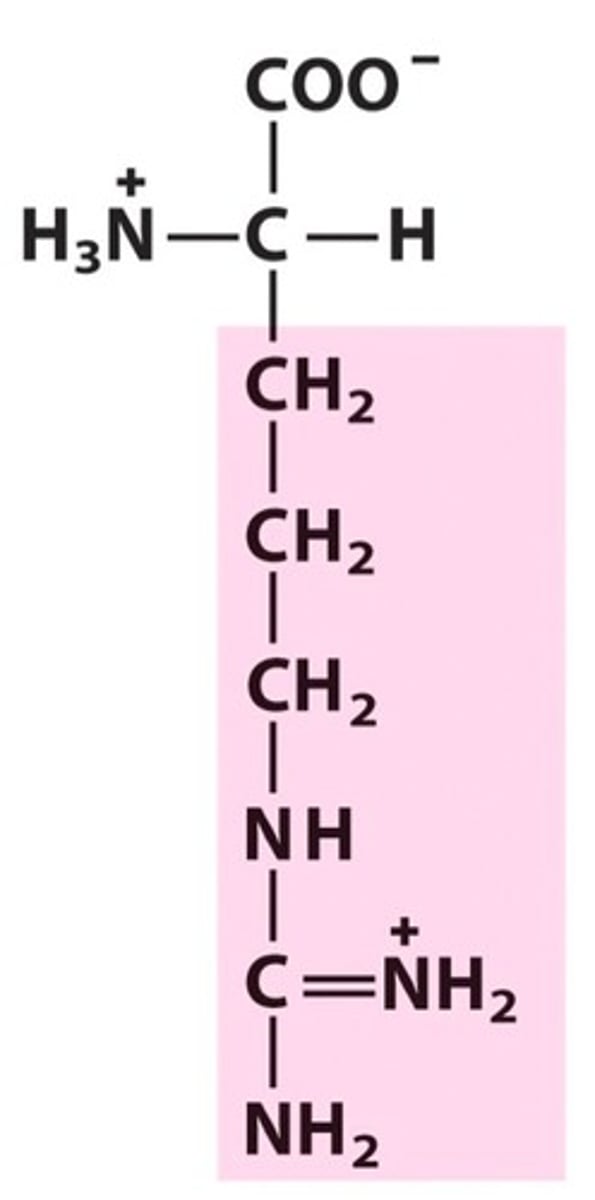
Arginine
Arg, R
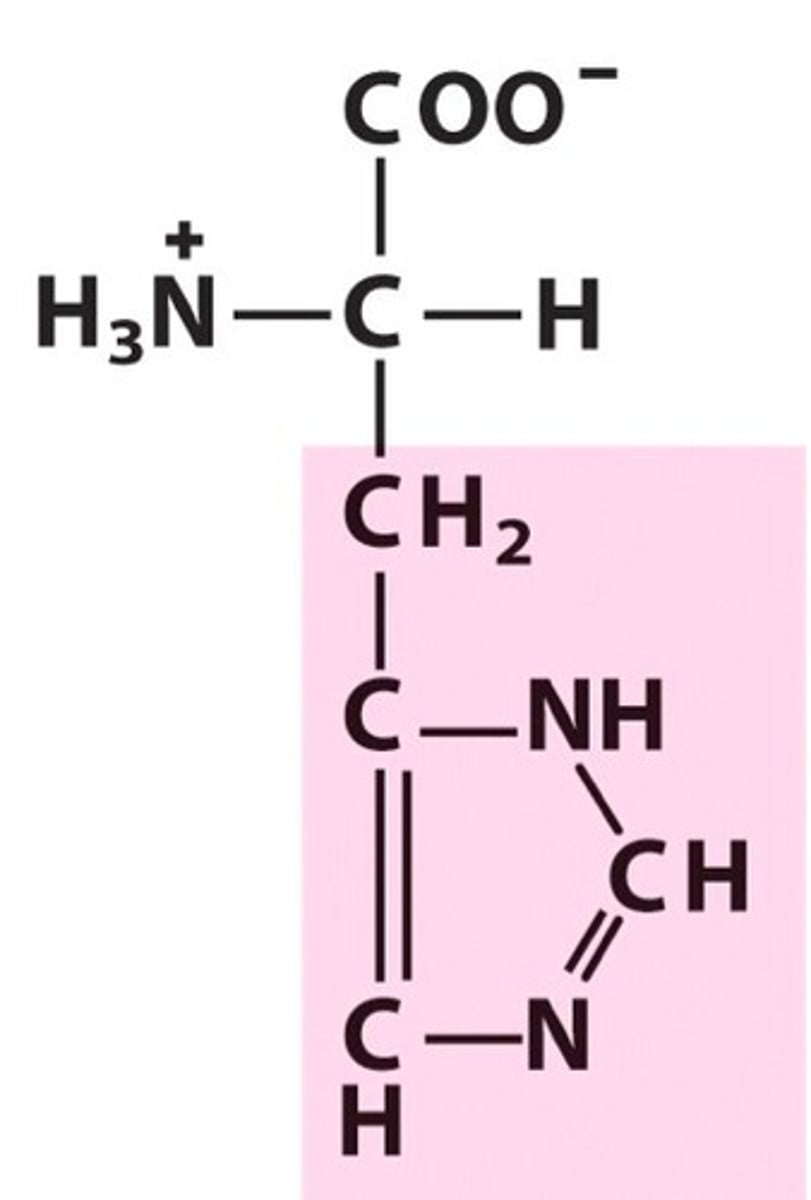
Histidine
His, H
Acid-Base Chemistry
~weak acids and weak bases
~degree of dissociation of H+ depends on pH
~all have 2 ionizable groups, but some have more than 2 (2 pkas)
Stereochemistry
~all but glycine have stereocenter at alpha position
~natural amino acids are L configuration
~no correlation to R/S system or direction; plain polarized light is rotated
~based on comparison to D and L glyceraldehyde
~all but one amino acid of L configuration are S (cysteine is the exception since its R)
Protein structure
~unbranched, linear polymers of amino acids
~the repeat unit is amide nitrogen, alpha carbon with side chain, and carbonyl carbon
trans-configuration
~limits the rotation between amide nitrogen and carbonyl carbon
~all peptide bonds have resonance structures giving double bond character to amide
peptide
short polymer of up to 12 amino acids
dipeptide
two amino acids
tetrapeptide
four amino acids
oligopeptides
12-20 amino acids
polypeptides
greater than 20 amino acids