NPB101 lectures 42 - 44
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
218 Terms
What is the flow of urine?
Ureters → bladder → urethra
What do the ureters do?
Transport urine from kidneys to bladder
What does the bladder do?
Stores urine until voided form body
What does the urethra do?
Carries urine from bladder to the outside of the body
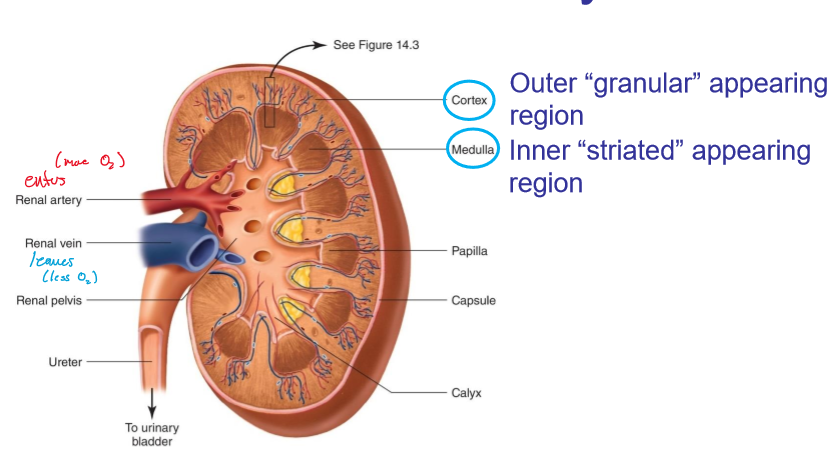
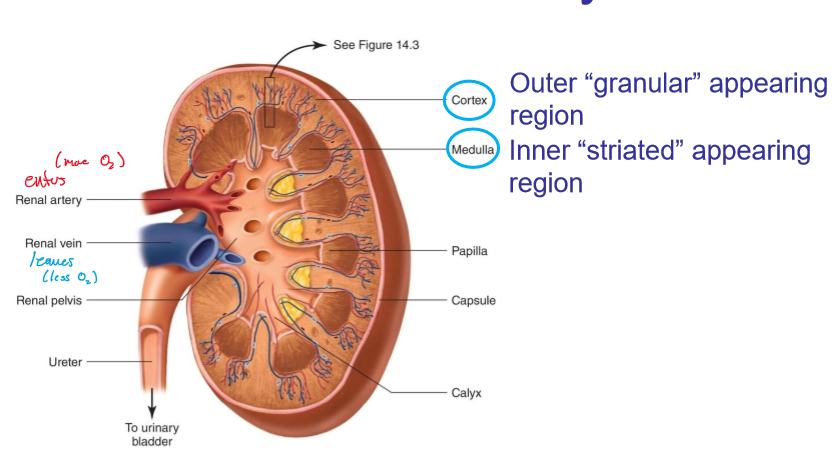
where does blood enter the kidneys?
renal artery
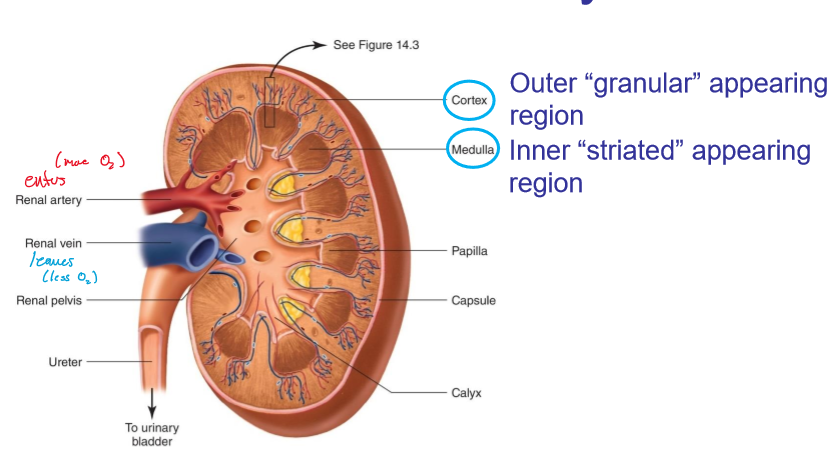
where does blood leave the kidneys?
renal vein
what is the renal artery connected to?
aorta
what is the renal vein connected to?
inferior vena cava
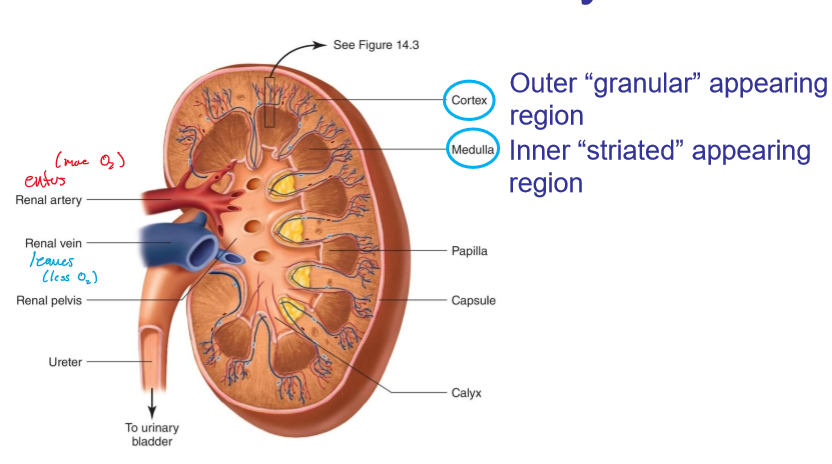
what is a nephron?
The structural and functional units of the kideny
how many nephrons are in each kidney?
over 1 million (~2 million for both)
what is in a neprhon?
a renal corpuscle which contains the glomerulus and a renal tubule
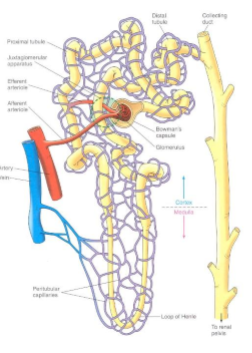
what is a glomerulus?
a tuft of capillaries that filters plasma into the tubular component
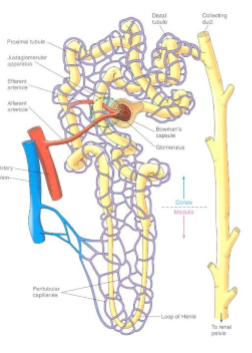
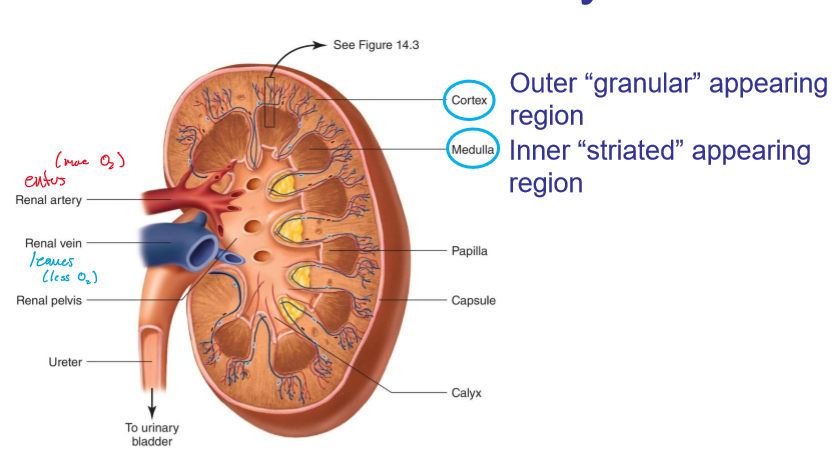
what does the cortex look like in kidneys?
granular
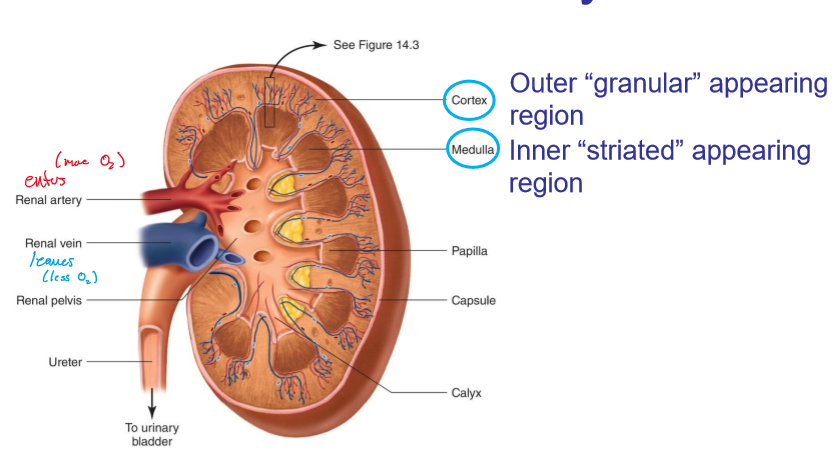
what does the medulla look like?
striated
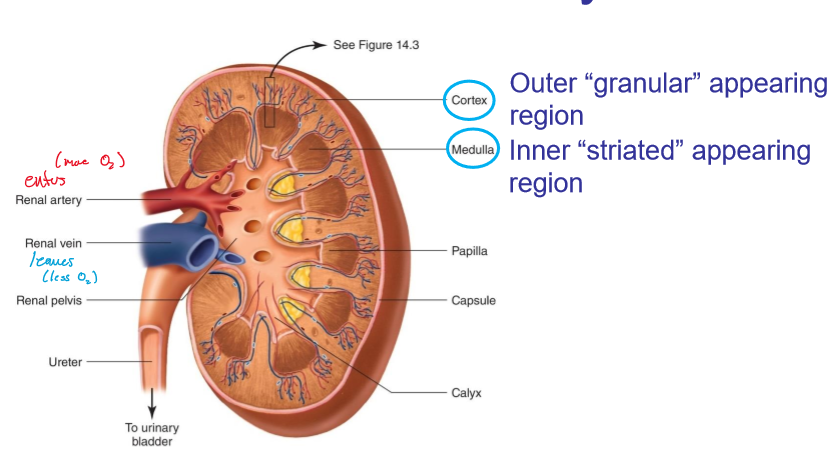
where are the cortex and medulla located, respectively?
outer and inner
what is the renal tubule?
forms a cup shape around the glomerulus (Bowman’s capsule) that collects the glomerular filtrate
each nephron consists of a ______ and ______ component.
Vascular, tubular
what encompasses the vascular component of the nephrons?
Afferent arteriole
Glomerulus
Efferent arteriole
Peritubular capillaries
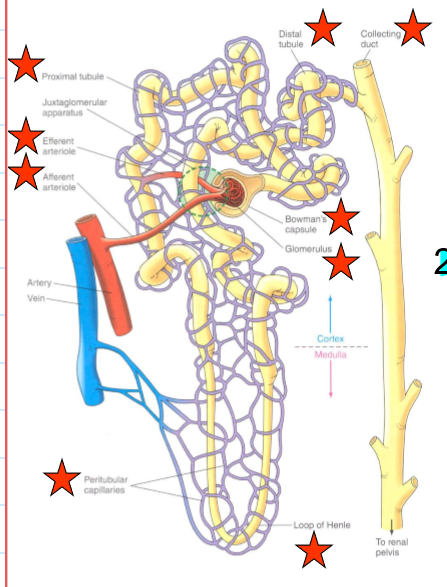
what encompasses the tubular component of the nephrons?
Bowman’s capsule
Proximate tubule
Loop of Henle
Distal tubule and collecting duct
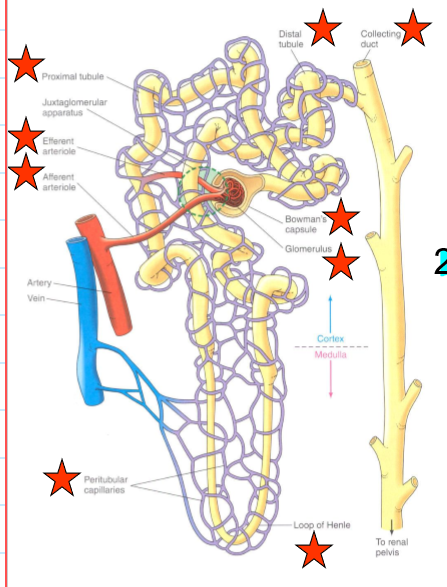
What does the afferent arteriole do?
bring blood to glomerulus
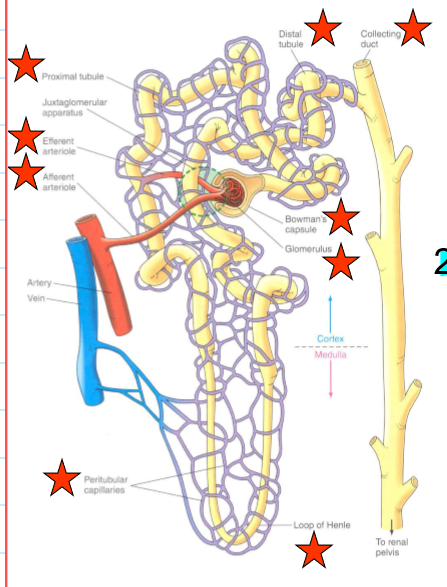
what does the efferent arteriole do?
carry blood from the glomerulus
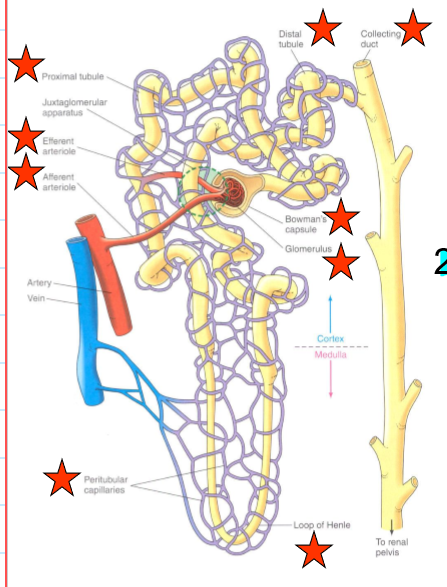
what do the peritubular capillaries do?
supply the renal tissue, and involved in the exchanges with the tubular lumen
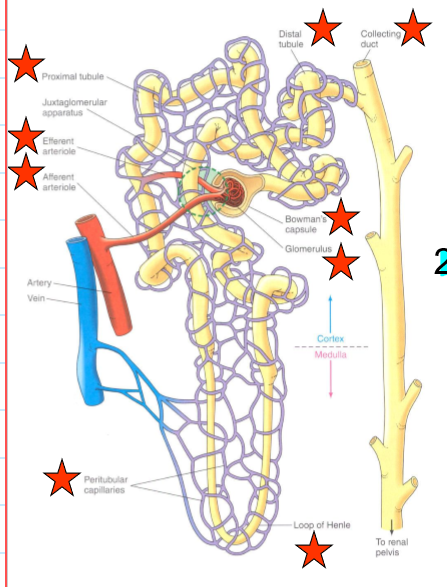
What does the proximal tubule do?
Uncontrolled reabsorption and secretion of selected substance
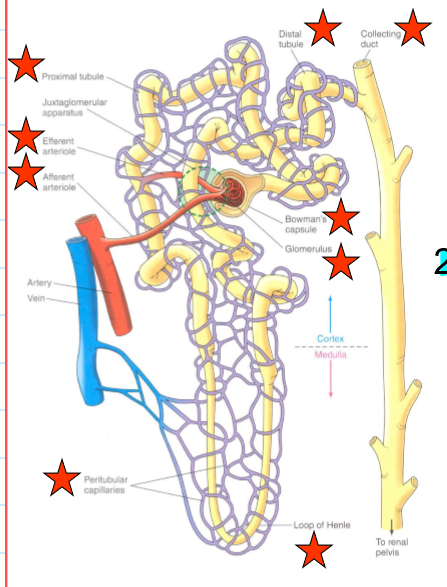
what does the loop of Henle do?
Establishes osmotic gradient that is important for concentrating urine
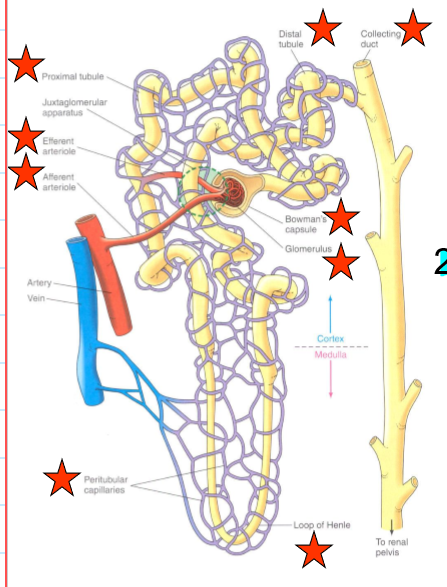
what would happen if the loop of Henle did not exist?
urine would not be concentrated and be mostly water
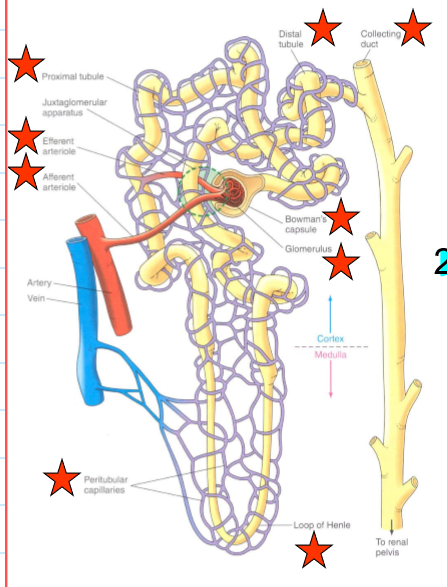
what does the distal tubule and collecting duct do?
variable control of Na+ and H2O reabsorption and K+ and H+ secretion
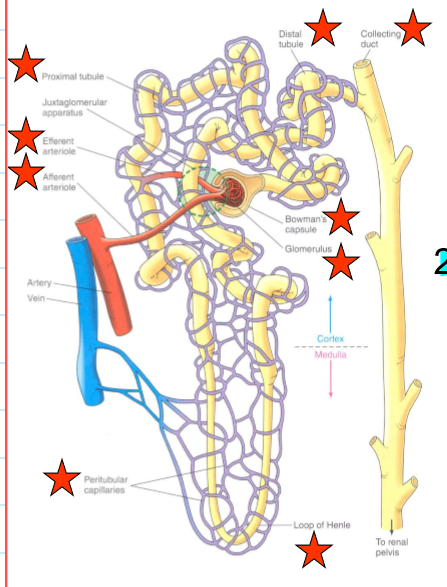
What is the juxtamedullary nephron?
Nephrons found at the border between the cortex and medulla which account for 15% of all nephrons
What are the juxtamedullary nephrons involved in?
It is a long loop of Henle that concentrates urine
What are the cortical nephrons?
Most nephrons that are in the short loop of Henle
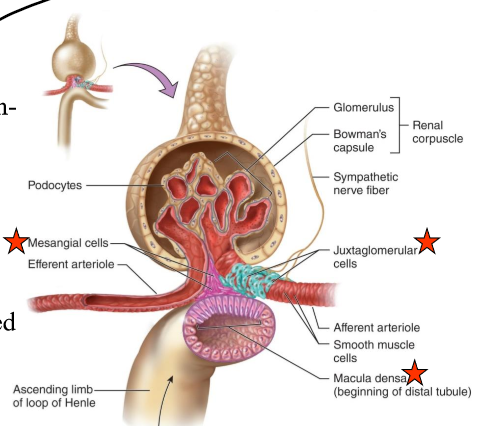
What are podocytes?
Structures of Bowman’s capsule that surround the capillaries
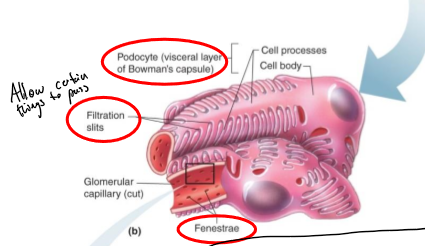
How does blood flow in and out of the glomerulus?
In through the afferent arterioles and out through the efferent tubules
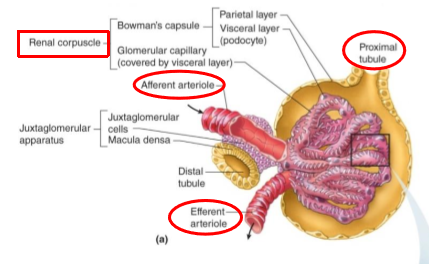
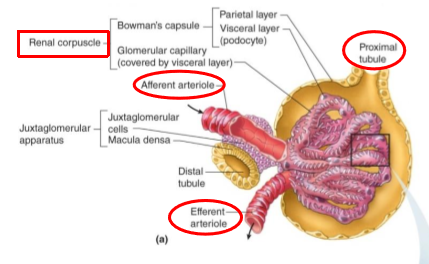
What tubule exits the Bowman’s capsule?
proximal tubule
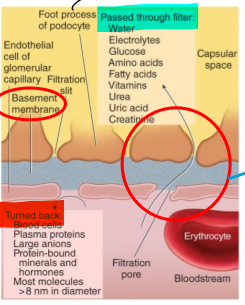
what allows fluid to pass into Bowman’s capsule?
filtration slits
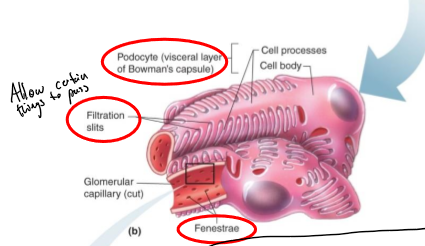
What is special about the capillaries in the glomerulus (glomerular)?
they have an endothelium that is fenestrated to allow filtration between the Bowman’s capsule
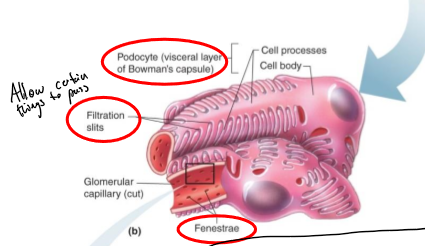
What surrounds the endothelial cells of the capillaries in the glomerulus?
acellular gelatinous layer known as the basement membrane
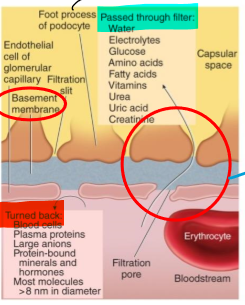
what is the basement membrane?
an acellular gelatinous layer that surrounds the endothelial cells of the capillaries in the glomerulus
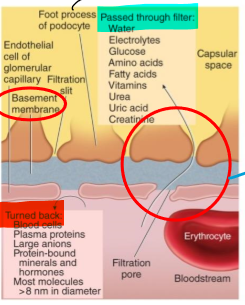
What are the foot processes?
Structures that help filter substances from the basement membrane
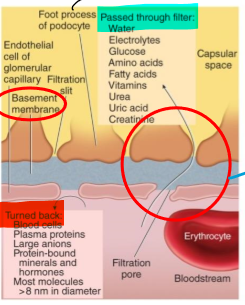
How are substances filtered in blood?
Through capillary pores between endothelial cells (single layer)
Pass through basement membrane and through filtration slits b/w foot processes
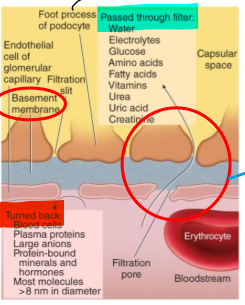
Where is filtrate transferred to once it makes it through the foot processes?
Proximal lumen
What two sets of capillaries are nephrons associated with?
Glomerular and peritubular
What are the glomerular capillaries specialized in?
Filtration, have slits that allow substances to filter out
What are the only capillaries in the body that are fed and drained by an arteriole?
glomerular capillaries
Why are glomerular capillaries special (aside form filtration and being fed and drained by arteriole)?
Blood pressure can be high to push solute out of blood (due to the slits that filter relieving added pressure)
What do the peritubular capillaries do?
Reabsorbs the filtered blood from the renal tubule cells
What do the renal tubule cells do?
Reabsorb most of the filtrate and send it back into blood flow via the peritubular capillaries
What is the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JG)?
Region where the glomerulus and the ascending limb of the loop of Henle are close together
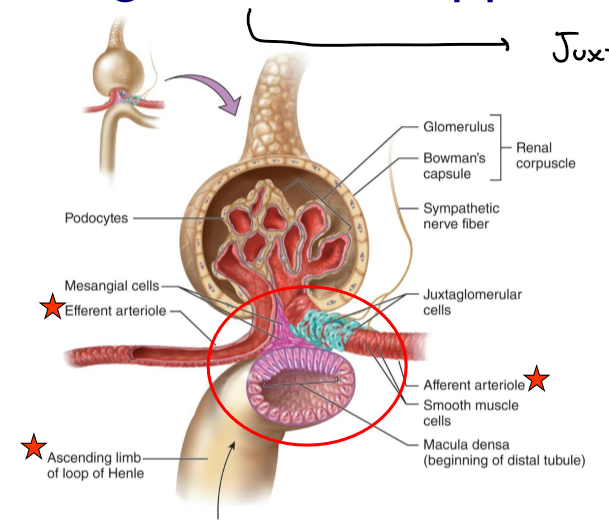
What is in the JG cells?
Specialized smooth muscle cells that have secretory granules which contain hormone renin
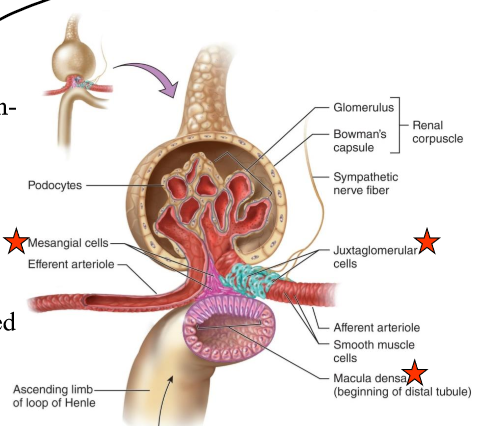
What does renin do?
Raise blood pressure
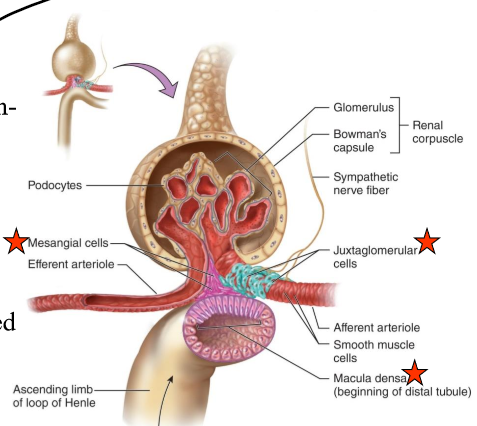
JG cells are _____-receptors that sense ______ in the afferent arteriole.
mechano-, blood pressure
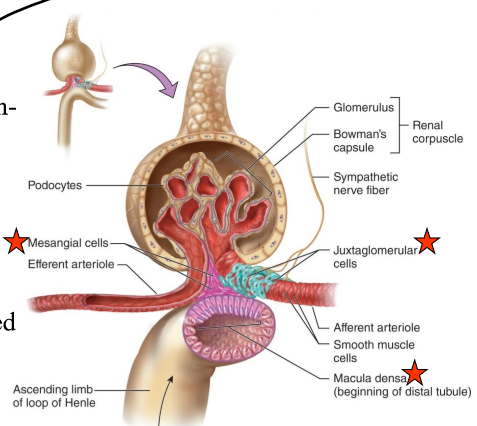
What are the macula densa?
Group of tall, closely-packed cells that are adjacent to the granular JG cells
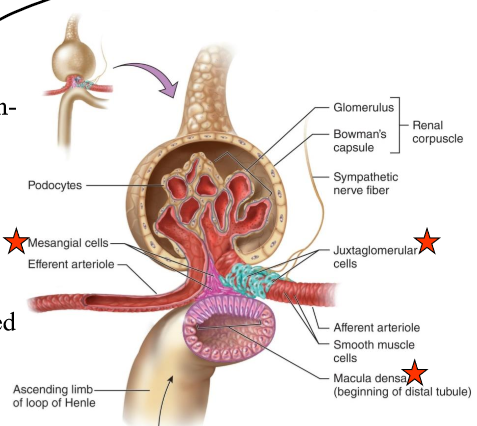
The macula dense are _____-receptors that respond to _______.
chemo-, changes in the NaCl content of the filtrate
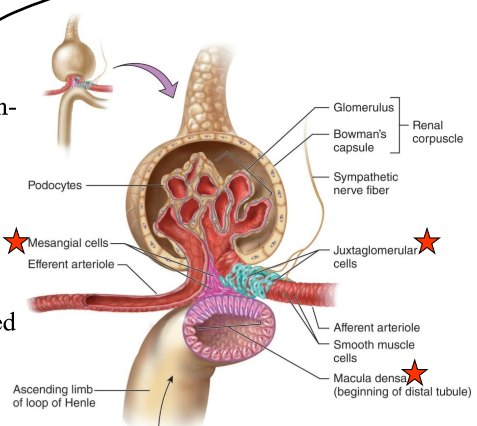
What do the smooth-muscle like mesangial cells do?
Engulf the macromolecules that get hung up during filtration to “clear clogs”
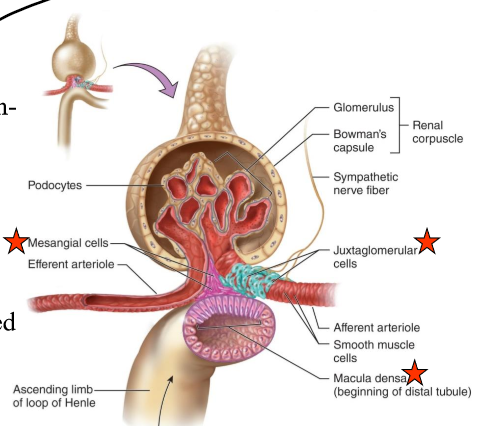
What is in the arteriolar wall of the granular (JG) cells?
Enlarged smooth muscle cells that have secretory granules that secrete renin
What is the basic renal process?
Glomerular filtration
Non-discriminant filtration of protein-free plasma
Tubular secretion
Selective movement of nonfiltered substances
Tubular reabsorption
Selective movement of filtered substances
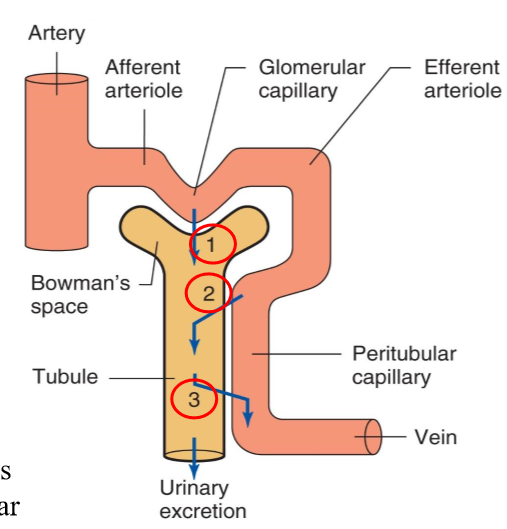
What does glomerular filtration entail?
Non-discriminant filtration (not RBCs) of protein-free plasma from the glomerulus into Bowman’s capsule (1)
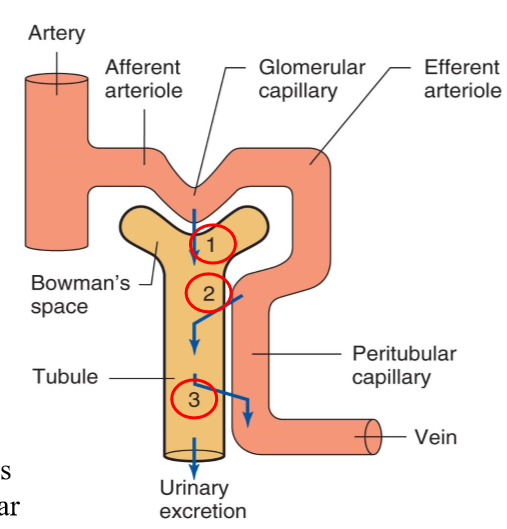
What does tubular secretion entail?
Selective movement of nonfiltered substances from the peritubular capillaries into the tubular lumen (2)
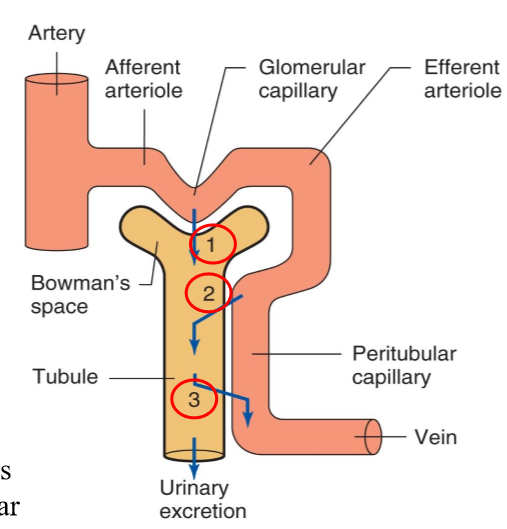
What does tubular reabsorption entail?
Selective movement of filtered substances from the tubular lumen into the peritubular capillaries (concentrates our urine and gives us stuff we NEED for our body) (3)
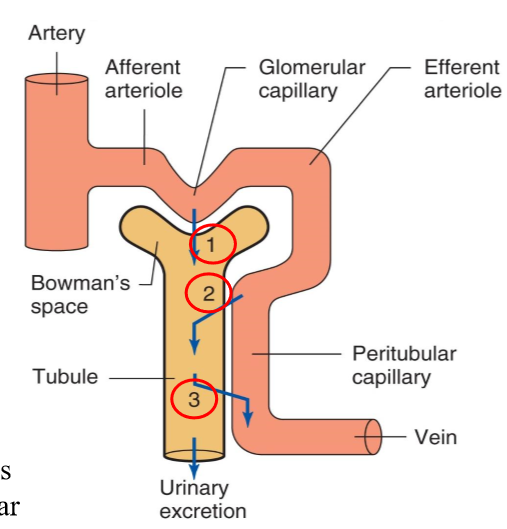
What percentage of plasma that enters the glomerulus is NOT filtered?
80%, it leaves through the efferent arteriole
What percentage of plasma that enters the glomerulus is filtered?
20%
Appx. how many liters of glomerular filtrate is formed each day?
180
What is the average plasma volume?
2.75 liters
Of the 180 liters of plasma filtered each day, how many liters are reabsorbed?
178.5
What is Glomerular filtration?
Passive process by which hydrostatic pressures force fluid and solutes through a membrane
Why is the glomeruli in the kidney a much more efficient filter than other capillary beds in the body?
Filtration membrane is a large surface area and very permeable to water and solutes
Glomerular pressure is higher (~55 mmHg), so they produce 180L/day vs. 34L/day formed by other beds
What needs to stay in the plasma during filtration so as to maintain osmotic pressure?
plasma proteins
What should you not see in your urine?
blood or protein (protinuria)
What is the cause of blood cells or proteins in the urine?
Problem with the filtration membrane, common in untreated diabetes and hypertension
What is the glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
volume of filtrate formed each minute
What affects the GFR?
Volume of surface available, filtration membrane permeability, and net filtration pressure (NFP)
(T/F) GFR is directly proportional to NFP.
True
Is NFP subject to autoregulation?
Yes
What happens if the afferent arteriole is constricted or efferent is dialated?
Pressure in the glomerular capillary is decreased and GFR is decreased
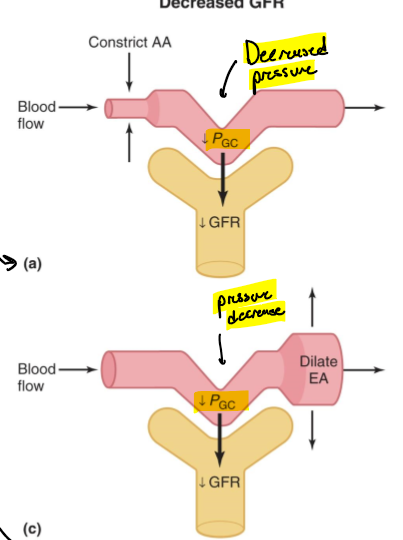
What happens if the afferent arterioles are dilated or the efferent is constricted?
Pressure in the glomerular capillary is increased and so if GFR
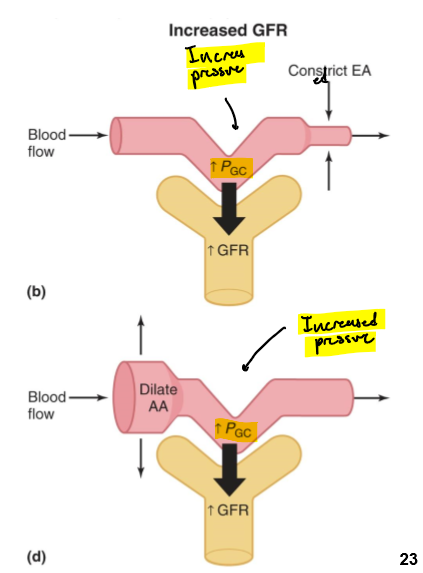
WHat 2 mechanisms can adjust GFR?
Sympathetic control
Baroreceptor reflex
Autoregulation
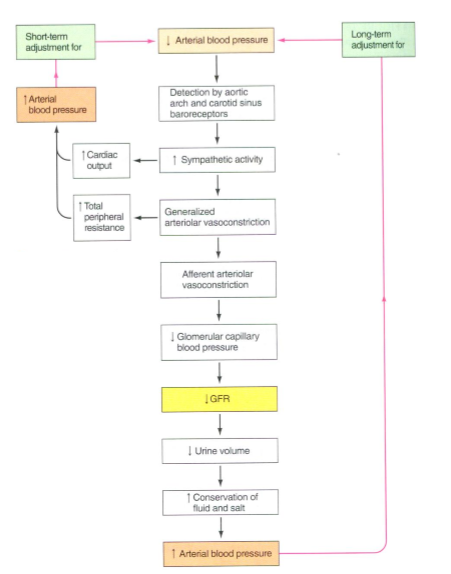
How does the baroreceptor reflex help control GFR?
-Arterial carotid sinus and aortic arch baroreceptors detect rises and falls in BP
-Send signals to cardiovascular control center, which adjusts levels of sympathetic activity
What is an example of how the baroreceptor reflex works?
Hemorrhage decreases plasma volume
BRs detect drop in BP
Cardiovascular control center coordinates increase in sympathetic activity
Increases cardiac output and total peripheral resistance
Decreases GFR to maintain plasma volume
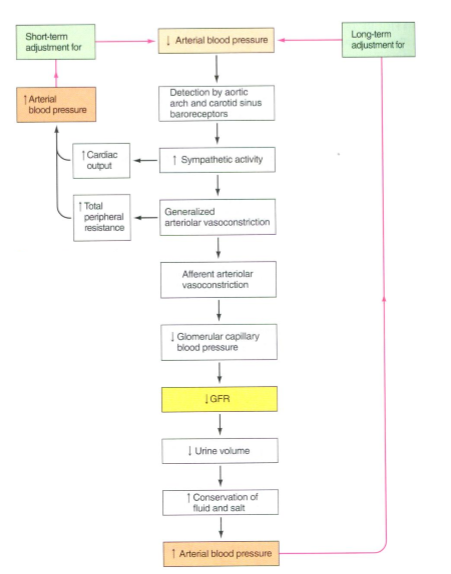
What is another effect that decreased GFR has?
decreased urine volume and an increase of conservation of fluids and salts
What does the autoregulation of GFR do?
Helps maintain a constant blood flow into the glomerular capillaries by changing the caliber of the afferent arterioles (constriction/relaxation)
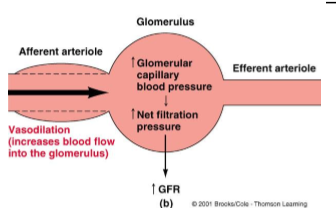
What is an example of how GFR is regulated by autoregulation?
Decrease in arterial BP
Decrease in GFR
Afferent arteriole vasodilates
Increases glomerular capillary BP
Increases net filtration pressure
(T/F) The sympathetic nervous system can override the autoregulation of GFR.
True
What are the mechanisms for autoregulation of the GFR?
Myogenic mechanism
Tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism
What is the myogenic mechanism?
Common property of vascular smooth muscle by which contraction occurs automatically to increased stretch and vice versa.
What does the tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism invovle?
The JG apparatus
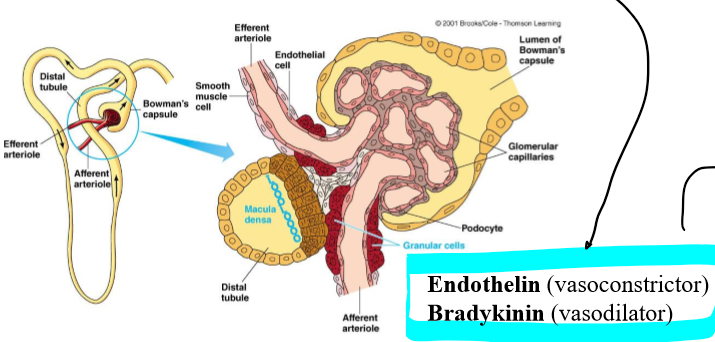
What do the Macula densa cells do?
Detect changes in rate fluid is flowing as indicated by NaCl content of filtrate
Release local acting vasoactive chemical
Endothelin (vasoconstrictor)
Bradykinin (vasodilator)
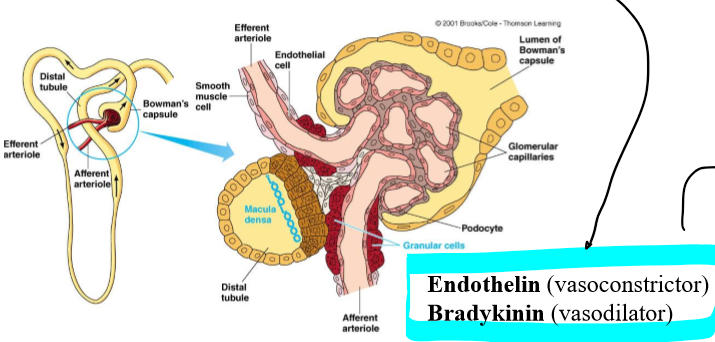
In the autoregulation of glomerular filtration, what does an increase in arterial BP cause?
increase driving pressure into glomerulus
increase glomerular capillary pressure
In the autoregulation of glomerular filtration, what does an increase in driving pressure into the glomerulus and an increase in glomerular capillary pressure cause?
increased GFR
In the autoregulation of glomerular filtration, what does an increased GFR cause?
increase rate of fluid flow through tubules, which increases stimulation to maca densa cells to release vasoconstrictive chemical
In the autoregulation of glomerular filtration, what does increased vasoconstrictive chemicals do?
decrease blood flow to the glomerulus and returning the glomerular capillary pressure and GFR to normal
(water/sodium) is reabsorbed in greater percentages.
Sodium (99.5)
When does tubular reabsorption happen?
As soon as filtrate enters tubule cells
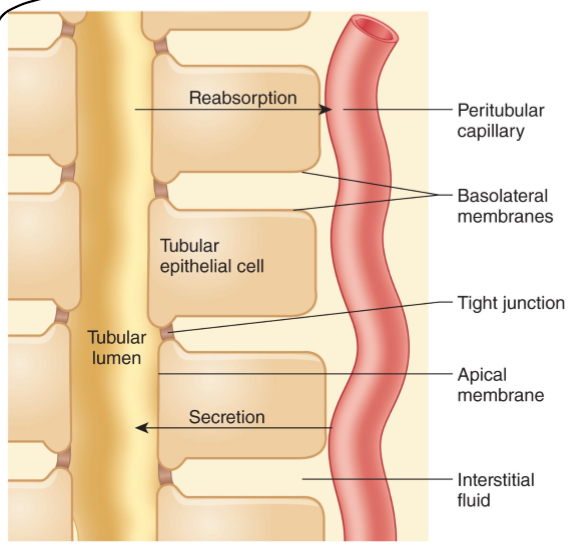
What is paracellular transport?
Transport between cells as mediated by tight junctions (mainly ions)
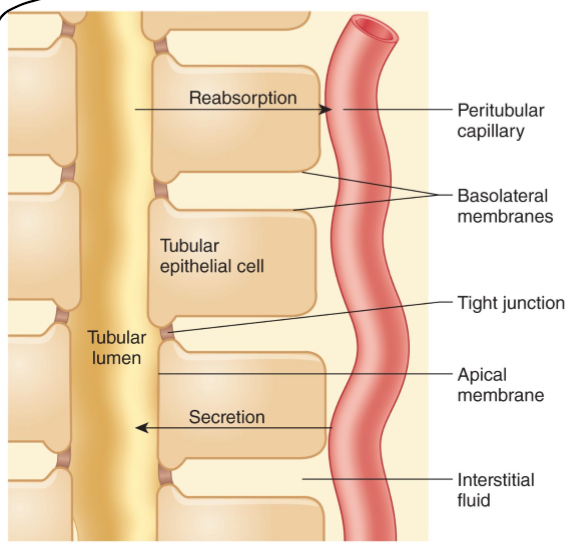
(T/F) transport in the tubular reabsorption happens only via simple diffusion.
False, it can be active (requires energy) or passive (no energy required)
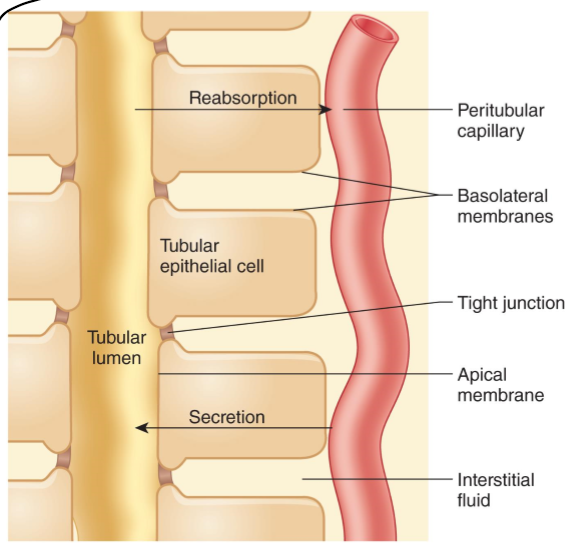
What is transcellular transport?
Into and out of the cell
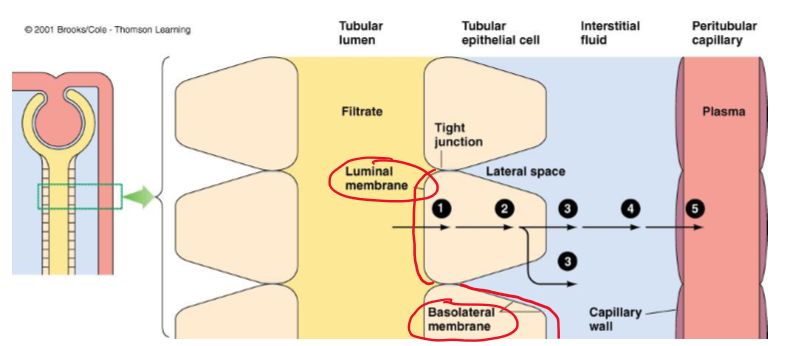
Throughout its entire length, the tubule is _____ layer thick.
one

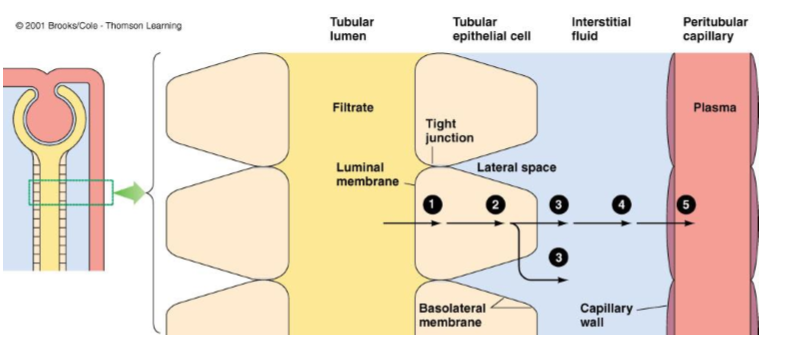
What do tubular epithelial cells have?
Luminal and basolateral membrane
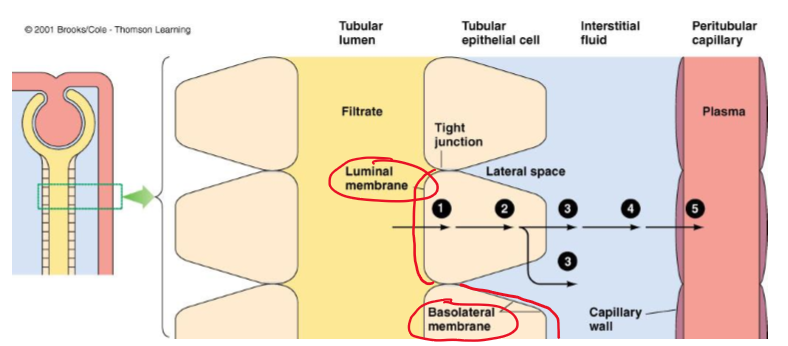
What do the adjacent cells form?
tight junctions
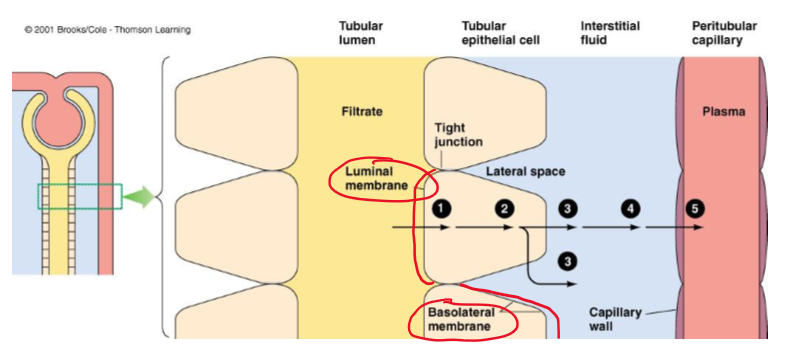
What fills the gaps in (lateral spaces) in between epithelial cells?
interstitial fluid
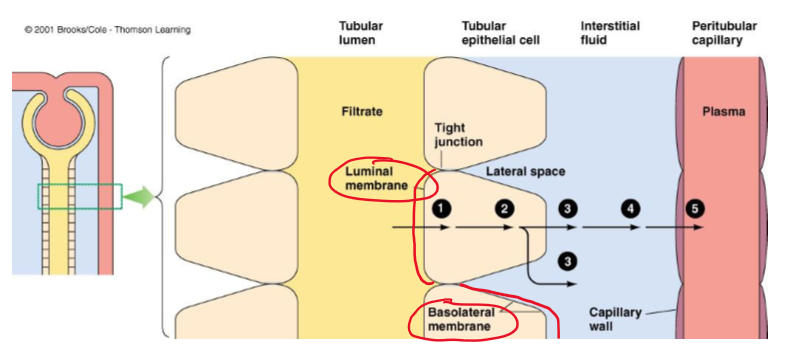
What is the gap between epithelial cells called?
lateral spaces
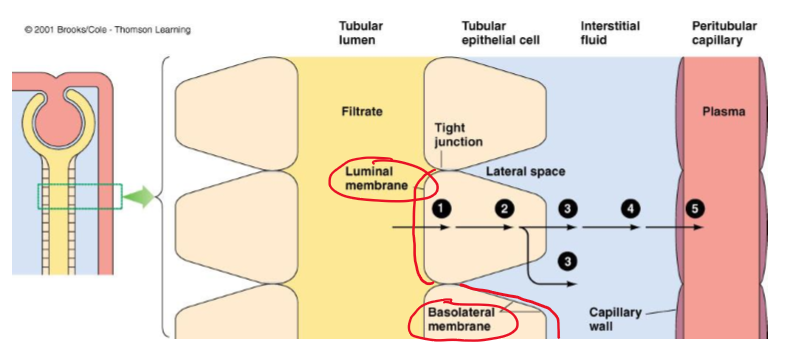
(Most/few) materials (except _____) must pass through the cells to leave the tubular membrane and enter the blood.
Most, water
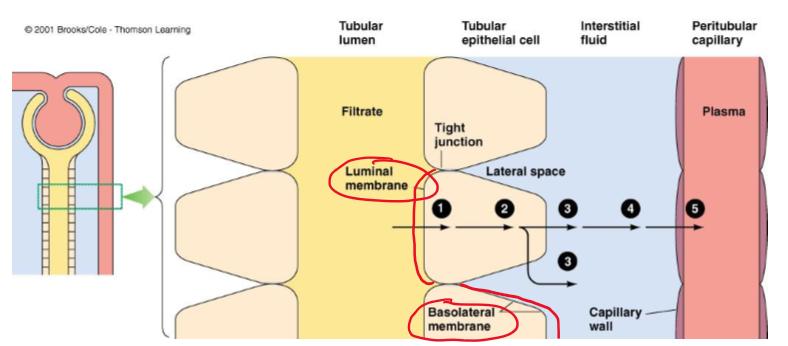
What 5 barriers must a substance cross in transcellular transport in tubular reabsorption?
Luminal membrane of the tubular cell
Cytosol of the tubular cell
Basolateral membrane of the tubular cell
Interstitial fluid
capillary wall