ipr 8 communication & nurse pt relationship
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
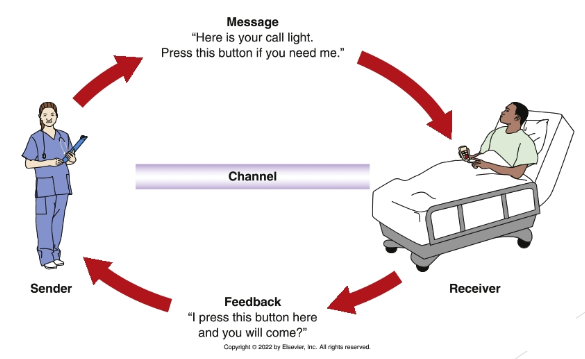
communication process
verbal communication: speaken or written
nonverbal communication: w/o words
gesture, body posture, intonation, general appearance
cultural differences
personal space, eye contact, meaning of words, cultural norms, religious beliefs
best way to ensure understood communication
feedback
close vs open minded question uses
closed: direct questions that answers aren’t necessarily variable
open: need more elaboration
therapeutic touch
signify support to a person when words are hard to find
therapeutic communication technique
general leads: eg. please continue
offering self: eg I'm here for you
encouraging elaboration
giving info
looking at alternatives
summarizing
communicating w hearing impaired
speak distinctly and slowly. don't shout.
face person & get their attention.
short sentences. paraphrase for clarification
maintain a good distance 2 ½ - 4 ft
watch for nonverbal feedback.
communicating w an aphasic patient
difficulty expressing / understanding language
speech therapist can help
communication boards/ writing
speak slowly & give time to respond. 1 question at a time
communicating w older adults
assess for hearing and visual deficits
give time for elders
wait for answer before answering another q
obtain feedback
communicating w children
eye level. calm, friendly voice
parent in room when possible
short simple sentences & demonstrations
allow child to handle equipment
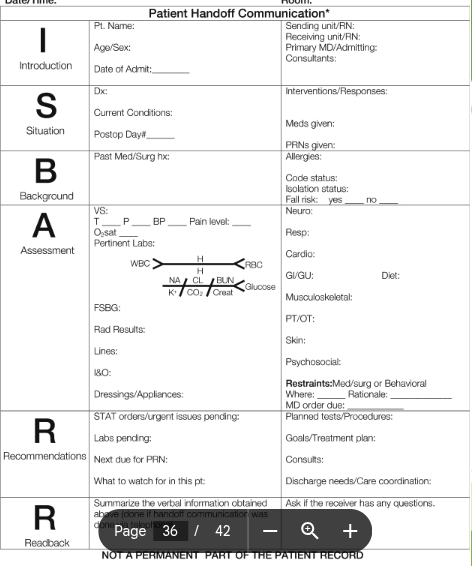
end-of-shift report
walking rounds. audiotape. computerized sheets. ISBAR-R
ISBAR-R
aka sbar
introduction
situation
background
assessment
recommendations
readback
should be specific
telephoning primary are providers
have pt data on hand. lab data, vital signs, I&o, meds recieved, allergies
keep chart handy
prepare a concise problem statement. document cal & response
laissez-faire leader
allows team members to function independently
does not attempt to control the team and offers little direction