OB -chapter 4 values, attitudes, work behaviour
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Power distance
extent to which unequal power and hierarchy are accepted in society
Uncertainty Avoidance
degree to which people are uncomfortable with ambiguity and uncertainty.
ex. in Greece (high uncertainty avoidance), firms may have strict policies and resist change. In contrast, in Sweden (low uncertainty avoidance), employees might welcome flexible roles and innovative approaches.
Individualism vs. Collectivism
Whether people view themselves as independent individuals or part of a group
Cultural distance
extent to which two cultures differ in values, norms, and practices.
Cultural intelligence.
The capability to function and manage well in culturally diverse environments.
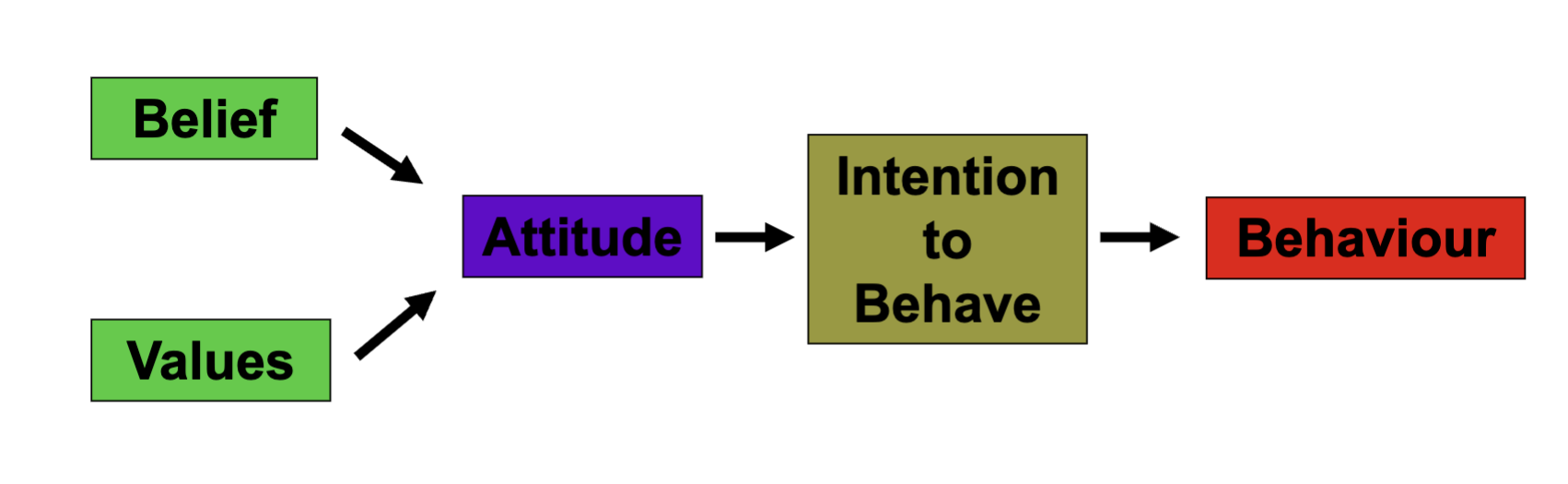
Attitude
fairly stable evaluative tendency to respond consistently to a specific object, person, situation, or group
It comes from beliefs and values, influences behavior, but isn’t always shown in actions.
Affective Events Theory
Events at work influence the emotions (affect) we experience.
.● Peaks & Ends are very important.
EVENT: Health benefits cut EMOTION : � Anger � ATTITUDE : Lower Job Satisfaction
Discrepancy theory
job satisfaction arises when there is a match (or mismatch) between the job outcomes a person wants and the outcomes they believe they actually receive
Distributive fairness
Fairness that occurs when people receive the outcomes they think they deserve from their jobs
Equity theory
Job satisfaction depends on how fairly people think they are treated compared to others—comparing their own inputs (effort, skills) and outcomes (pay, recognition) to others’
ex. If you work hard (input) but see a coworker getting the same pay with less effort, you may feel unfairly treated and dissatisfied.
Procedural fairness
Fairness that occurs when the process used to determine work outcomes is seen as reasonable.
ex. If two employees apply for a promotion and only one gets it, the other might still feel satisfied if the selection process was transparent and based on clear criteria.
interactional Fairness
Fairness that occurs when people feel they have received respectful and informative communication about an outcome.
Disposition
Some people are naturally more or less satisfied with their jobs due to stable personality traits
Emotional contagion
tendency for moods and emotions to spread between people or throughout a group.
ex. If one team member is super positive and energetic, others may start to feel and act more upbeat too.
Emotional labour
Requirement for people to conform to emotional “display rules” in their job behaviour in spite of their true mood or emotions.
Organizational citizenship behaviour (OCB).
Voluntary, informal behaviour that goes beyond job requirements and contributes to organizational effectiveness
ex. Helping: A busy coworker still takes time to help you learn new software.
Affective commitment
employee’s emotional attachment to, identification with, and involvement in their organization. People with strong affective commitment genuinely want to stay because they feel connected and loyal to the organization.
Continuance commitment
is based on either the costs that would be incurred in leaving an organization (e.g., losing a pension) or a lack of suitable job alternatives. People with high continuance commitment stay with an organization because they have to.
ex. no job
Normative commitment
is based on ideology or a feeling of obligation to an organization. People with high normative commitment stay with an organization because they think that they should do so.
ex. they gave me this i should stay
Job Satisfaction
Global: Overall satisfaction
Facet: Satisfaction with specific aspects (e.g., pay, coworkers, tasks)
Common Measures
Job Descriptive Index (JDI)
Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire (MSQ)
Organizational Justice Theory
Three Methods of Distribution
Equity – Based on contribution/performance
Equality – Everyone gets the same
Need – Based on individual need
Different types of justice
Distributive Justice –Focus on the rewards, materials, punishments which are divided amongst employees
Example: Two employees who perform equally receive the same bonus.
Procedural Justice – Focus on how the rewards, materials, punishments arerdistributed in the organization
Example: The company follows a clear and consistent process for deciding promotions.
Interactional Justice – Concerns the fairness of interpersonal treatment during decision-making or communication between supervisors and subordinates.
Example: A manager respectfully explains the reasons for denying a raise.
Consequence of commimtent
High Affective Commitment (AC) → High performance
High Continuance Commitment (CC) → Low performance
High CC + Low AC → Very poor performance
imdpediment to change