NPB101: Endocrine System Lec 1 Part 1
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Endocrine System
Part of our control system
Primarily efferent (motor) pathway
Involves signal factors going into the blood stream
Works with the NS
Homeostasis
is the process by which living organisms maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in external conditions Which is NOT what our Hormones do!
Endocrine System Controls
Growth, development
Metabolism
Stress response & adaptation
Reproductive function
Homeostatic responses
Endocrine Gland
Hypothalamus
Pituitary
Peripheral Endocrine gland axis (Thyroid,adrenal)
HPA
Endocrine Cell/Gland/Tissue
Produces & Secretes Hormones
Endocrine System requires the____ system
Transport
Transport System
transports hormones through blood
Hormone
signal factor that is released by endocrine tissue & it goes into blood & gets transported to target tissue
The ___ factor/hormone is released by ____ tissue
Signal, Endocrine
Classes of Hormones
Water Soluble (hydrophilic) Hormones
Protein/Peptide hormones
often produced as precursors
ex: precursor for insulin is proinsulin
Classes of Hormones
Water Soluble (hydrophilic) Hormones
Amino Acid Derivatives
Classes of Hormones
Lipid Soluble (lipophilic) Hormones
Steroid Hormones
made from cholesterol
Cholesterol is important for:
Sex Hormones: Estrogen
Aldosterone: Kidney Fxn
Cortisol: stress
Cholesterol is not ___ soluble, it needs a transporter to push it into the ___, since ____ is ____ soluble
water, bloodstream, blood, water
There is a protein that ___ onto Cholesterol
holds
Classes of Hormones
Water Soluble (hydrophilic) Hormone
&
Lipid Soluble (lipophilic) Hormone
Amino Acid Derivative
made from a single a.a.
Hydrophilic Hormone is epinephrine—→sympathetic—→fight-or-flight
Lipophilic Hormone is Thyroid
Can’t store ____ Hormones in vesicles because it will ____ out since it’s ____
Steroid, leak, lipophilic
We have to ____ lipid-soluble hormones & then ____ them
synthesize, release
Exception of being released after synthesis
thyroid Hormone (TH)
____ soluble hormones are stored in ____ vesicles & then released
water, secretory
Bioavailability
Hormone needs to be free
Fully functional
Fast activation rate
Removal Rate: eliminate slowly
Activation rate
Slow activation rate of precursor= no bioavailability
Fast= availability
T/F: If you have slow activation of the hormone from the precursor it will affect with. no bioavailability
True, you need fast activation for hormone bioavailability because hormones need to apply their affects to regulate bodily functions
T/F: Albumin is in a bound state and will not affect hormone bioavailability
False, Albumin in bound state means its unavailable & will affect hormone bioavailability
T/F: If the removal rate is fast this will be good for hormone bioavailability
False, If you can remove a hormone fast with removal rate this will not be great for bioavailability, because we will have less time to absorb hormone
Bloodstream has to ___ hormones to particular ____ & the targets have to have the hormone ___
carry, targets, receptor
T/F: So if a patient has cardiovascular issues it will have problems with driving blood to tissues, the hormone will still get there
False, If a patient has cardiovascular issues where it has problems driving blood to tissues, the hormone will not still get to the blood because the bloodstream carries the hormone to the blood to a particular target and without the blood the hormone cant go anywhere
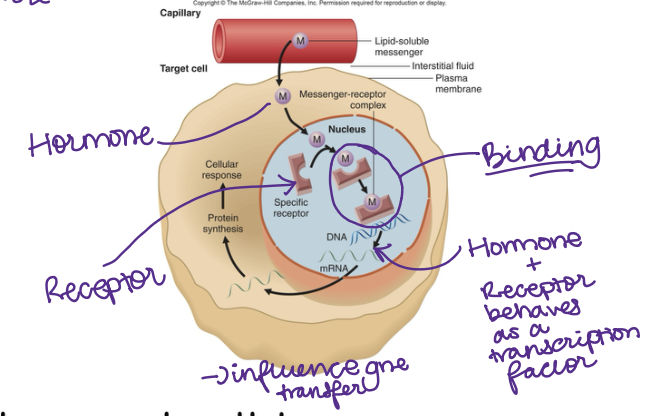
The Plasma Membrane bound receptors will bind to the ____ soluble hormones like peptide hormones
water
The Receptor will bind to the ___, inside the____
Hormone, cell
Hormone & Rector behave as a _____ factor
transcription —→ it can dec or inc transcription
Plasma-Membrane Associated Receptors
Receptor is stuck in the PM
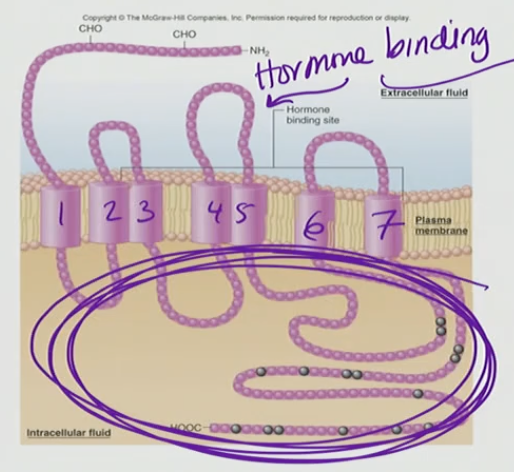
Intracellular part of the Hormone binding
interacts with G-protein (a type of signal transduction protein)
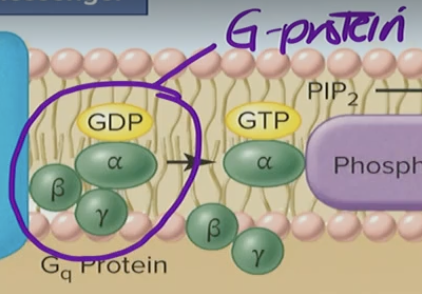
G-Protein
has beta, alpha, gamma, subunits stuck together with a GDP
Alpha subunit
turns on a signal process
Left go of GDP and binds to GTP which activates it
Transducing effect of hormone (1 hormone) —→ binding that allows activation of intracellular enzymes

T/F: In the presence of a hormone: The hormone doesn’t bind to G-protein, but bind to receptor
True, this occurence of a hormone binding to the receptor itself & not the G-Protein is because the hormone can be a steroid hormone, which initiates signaling with a recptor
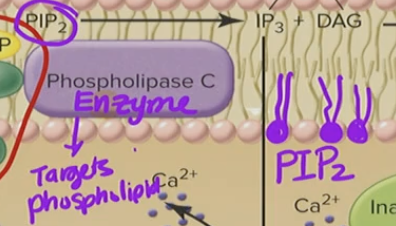
Phospholipase C Beta (PLC-β)
Targets a phospholipid (PIP2) & chops it up —→ 2nd messenger
G-Protein _____ PLC-β which then ____ PIP2
activates, targets
When you ___ PIP2 it creates the molecule ___
target, IP3
T/F: IP3 is a secreting hormone
False, IP3 is a second messenger
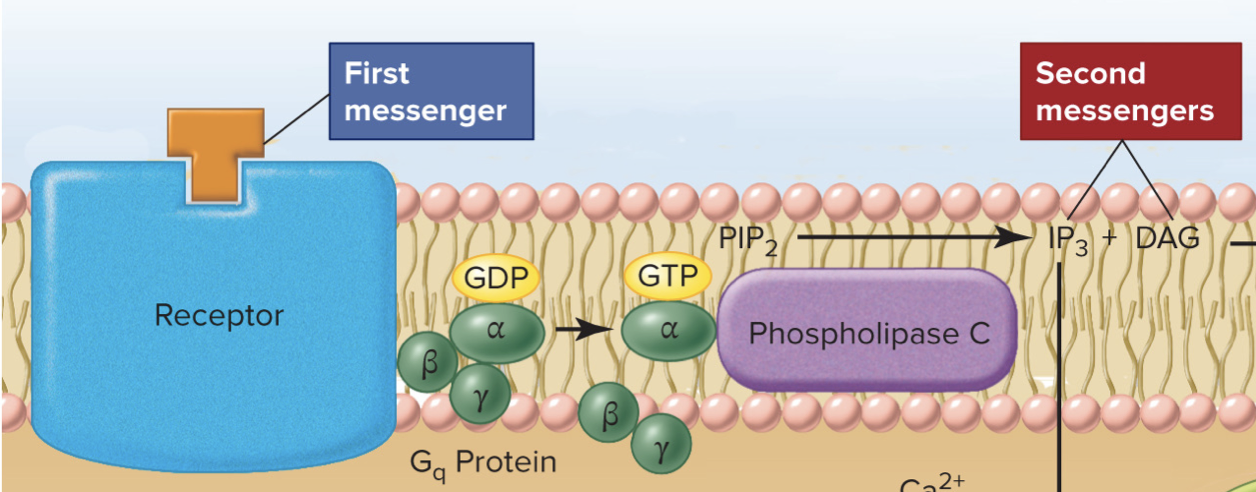
So the alpha betta gamma subunit are together with GDP due to G protein, but then alpha subunit activates intracellular when bound to GTP which then activates PLC-B which then targets PIP2 and creates IP3, IP3 is a second messenger that then triggers release of Ca2+
Dimerization
Identical receptors w/intrinsic built inside
Why do Dimerization?
when dimerization occurs the protein kinase becomes active through cross phosphorylation and then the protein kinase will phosphorylate intracellular targets
T/F: There will be a delay in gene expression
True, There will be a delay because protein synthesis pathways take tons of minutes before you see a change in protein levels
Up-regulation
Increase in number of receptors
Down-Regulated
Decrease responsiveness
Permissiveness
To be responsive, it needs the exposure to another hormone before expose to the one hormone
The effect of Hormone _#_ requires the presence and action of Hormone _#_
1, 2 (adipose tissue needs to be (pre-treat) exposed to thyroid before responding to EPI
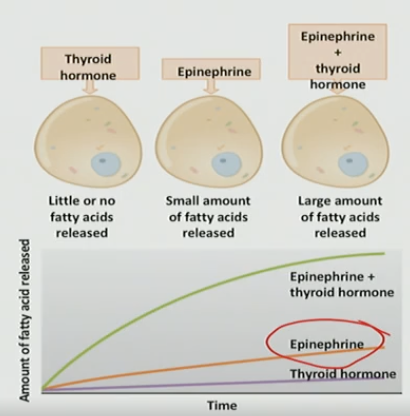
Syngerism
The combined effect of two hormones is greater than their individual effects
Antagonist
opposite effects (one rises & one falls)
Humoral (blood fluidity) Regulation
Altering liquid levels of hormones around our blood
Neural Regulation
Nueronal output that talks to glandular tissue & then alters levels of hormones (epinephrine)
Hormonal Regulation
variety of hormones being regulated
Neurons live in the _____ because its responsible for maintaining ____
hypothalamus, homeostasis
Oxytocin
mothering instinct
T/F: the Posterior Pituitary makes hormones
False the Posterior Pituitary stores the hormones, while the Anterior Pituitary is actually making the hormones
Tropic Hormones
Induce hormone release by another endocrine gland—- TROPIC
Can also cause growth —TROPHIC AFFECT
The ____ pituitary contains all trophic hormones that allow ____
Anterior, growth
Cortex
outside of something liek cerebral cortex —→ outside of cortex
Anterior Pituitary Hormones
F: FSH
A: ATCH
T: TSH
P: Prolactine
I: LH
G: GH
What is controlling/regulating these Anterior Pituitary Hormones?
The Hypothalamus
The Hypothalamic ___ and ____ hormones
releases and inhibits
__1__ comes out of hypothalamus and stimulates release of __2_ then __2__ talks to thyroid gland and causes release of __3__
TRH,TSH, TH
___ causes the release of ___
CRH, ACTH
Which hormone has the biological affect H1, 2, or 3?
Hormone 3 has the affect as Hypothalamus send hormone signal to anterior pituitary that then release/stimulates hormone to endo gland and the adrenal gland then porduces hormone 3 that carries that biological affect, H3 then goes bacjk to the brain and inhibits secretion from anterior pituitary
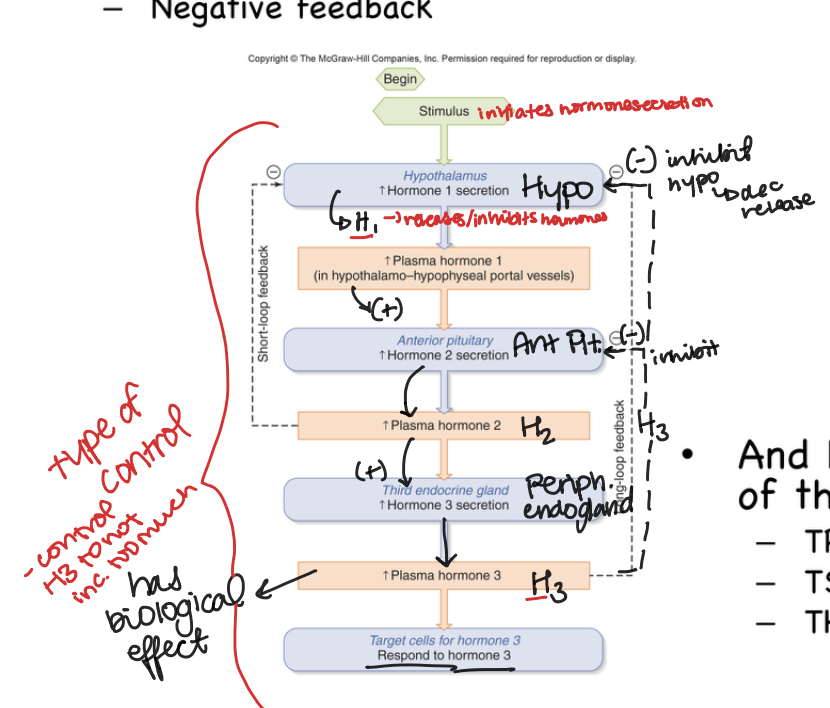
Negative Feedback
Hormone number 1 gets releases from hypothalamus to anterior pituitary and then the Anterior pituitary sends hormone 2 to endo gland and the endlo gland releases the biological affect in shape of Hormone 3 and then H3 gets send back to brain (anterior pituitary) and that inhibits release and then it inhibits release of hormone 1 from hypothalamus