FIN 4250 Vocabulary
0.0(0)Studied by 3 people
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:17 PM on 9/29/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
1
New cards
Multinational corporations (MNCs)
firms that engage in some form of international business
their managers conduct international financial management and intend to maximize value of the MNC
their managers conduct international financial management and intend to maximize value of the MNC
2
New cards
agency problem
conflict of goals between a firm's managers and shareholders
3
New cards
comparative advantage
allows firms to penetrate foreign markets
4
New cards
imperfect market
conditions where factors of production are somewhat immobile
costs and other restrictions affect the transfer or labor and other resources used for production
costs and other restrictions affect the transfer or labor and other resources used for production
5
New cards
product cycle theory
a firm first becomes established in its home market, where information about markets and competition is readily available
6
New cards
international trade
conservative approach that can be used by firms to penetrate markets (by exporting) or to obtain supplies at a low cost (by importing)
7
New cards
licensing
arrangement whereby one firm provides its technology (copyrights, patents, trademarks, or trade names) in exchange for fees or other considerations
8
New cards
franchising
arrangement, one firm provides a specialized sales or service strategy, support assistance, and possibly an initial investment in the franchise in exchange for periodic fees, allowing local residents to own and manage the specific units
9
New cards
direct foreign investment (DFI)
direct investment in foreign operations
10
New cards
joint venture
business that is jointly owned and operated by two or more firms
11
New cards
acquisitions of existing operations
firms frequently acquire other firms in foreign countries as a means of penetrating foreign markets
acquisitions represent DFI because MNCs directly invest in a foreign country by purchasing the operations of target companies
acquisitions represent DFI because MNCs directly invest in a foreign country by purchasing the operations of target companies
12
New cards
domestic valuation model
purely domestic firm, does not engage in any foreign transactions
n = number of future periods in which cash flows are received
E(CF..) = denotes expected cash flows to be received at the end of period t
k = weighted average cost of capital and required rate of return by investors and creditors that provide funds to the MNC
n = number of future periods in which cash flows are received
E(CF..) = denotes expected cash flows to be received at the end of period t
k = weighted average cost of capital and required rate of return by investors and creditors that provide funds to the MNC
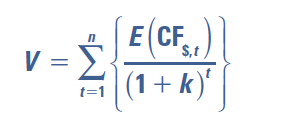
13
New cards
multinational valuation model
deals with multiple currencies
CFj,t = amount of cash flow denominated in a particular foreign currency j at the end of period t
Sj,t = exchange rate at which the foreign currency can be converted to dollars at the end of period t
CFj,t = amount of cash flow denominated in a particular foreign currency j at the end of period t
Sj,t = exchange rate at which the foreign currency can be converted to dollars at the end of period t
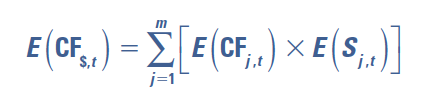
14
New cards
uncertainty surrounding MNC cash flows
exposure to international economic conditions
exposure to international political risk
exposure to exchange rate risk
exposure to international political risk
exposure to exchange rate risk
15
New cards
foreign exchange market
allows for the exchange of one currency for another
16
New cards
foreign exchange dealers
serve as intermediaries in the foreign exchange market by exchanging currencies desired by MNCs or individuals
17
New cards
spot market
market where foreign exchange transactions is for immediate exchange
18
New cards
spot rate
exchange rate at which one currency is traded for another in the spot market
19
New cards
interbank market
where trading between banks occurs
20
New cards
bid price
buy quote of currency
21
New cards
ask price
sell quote of currency
22
New cards
bid/ask spread
difference between the bid and ask prices and meant to cover the costs associated with fulfilling requests to exchange currencies
= (ask rate - bid rate) / ask rate
= (ask rate - bid rate) / ask rate
23
New cards
factors that affect bid/ask spread
order costs
inventory costs
competition
volume
currency risk
= f(+order costs, +inventory costs, -competition, -volume, +currency risk)
inventory costs
competition
volume
currency risk
= f(+order costs, +inventory costs, -competition, -volume, +currency risk)
24
New cards
direct quotations
quotations that report the value of a foreign currency in dollars
number of dollars per unit of other currency
= 1/indirect quotation
number of dollars per unit of other currency
= 1/indirect quotation
25
New cards
indirect quotations
quotations that report the number of units of a foreign currency per dollar
= 1/direct quotation
= 1/direct quotation
26
New cards
cross exchange rate
The amount of one foreign currency per unit of another foreign currency
Found using foreign exchange quotations
Found using foreign exchange quotations
27
New cards
forward contract
an agreement between an MNC and a foreign exchange dealer that specifies the currencies to be exchanged, the exchange rate, and the date at which the transaction will occur
28
New cards
forward rate
the exchange rate specified in the forward contract, at which the currencies will be exchanged
29
New cards
forward market
market in which forward contracts are traded
over-the-counter market, the main participants are the foreign exchange dealers and the MNCs that wish to obtain a forward contract
over-the-counter market, the main participants are the foreign exchange dealers and the MNCs that wish to obtain a forward contract
30
New cards
currency futures contract
specifies a standard volume of a particular currency to be exchanged on a specific settlement date
31
New cards
futures rate
the exchange rate at which an entity can purchase or sell a specified currency on the settlement date in accordance with the futures contract
32
New cards
currency call option
provides the right to buy a specific currency at a specific price (strike price or exercise price) within a specific period of time
33
New cards
currency put option
provides the right to sell a specific currency at a specific price within a specific period of time
34
New cards
eurodollars
The dollar deposits in banks in Europe (and on other continents)
35
New cards
Asian money market
accommodates dollar-denominated bank accounts
36
New cards
London Interbank Offer Rate (LIBOR)
currency's money market is highly influenced
interest rate most often charged for short-term loans between banks in international money markets
interest rate most often charged for short-term loans between banks in international money markets
37
New cards
international money market securities
When MNCs and government agencies issue debt securities with a short-term maturity
(one year or less) in the international money market
(one year or less) in the international money market
38
New cards
syndicate
join together
39
New cards
foreign bond
an international bond issued by a borrower foreign to the country where the bond is placed
40
New cards
parallel bonds
currency denominating each type of bond is determined by the country where it is sold
41
New cards
eurobonds
bonds that are sold in countries other than the country whose currency is used to denominate the bonds
42
New cards
American depository receipts (ADRs)
certificates representing bundles of the firms stock
43
New cards
depreciation
decline in currency's value
44
New cards
appreciation
increase in currency value
45
New cards
percent change in foreign currency value
S = spot rate
S t-1 = spot rate at earlier date
S t-1 = spot rate at earlier date

46
New cards
real interest rate
adjusts the nominal interest rate for inflation
= nominal interest rate - inflation rate
= nominal interest rate - inflation rate
47
New cards
forward contract
an agreement between a corporation and a financial institution (such as a commercial bank) to exchange a specified amount of a currency at a specified exchange rate (called the forward rate) on a specified date in the future
48
New cards
non-deliverable forward contract (NDF)
often used to hedge currencies in emerging market
agreement regarding a position in a specified amount of a specified currency, a specified exchange rate, and a specified future settlement date
agreement regarding a position in a specified amount of a specified currency, a specified exchange rate, and a specified future settlement date
49
New cards
currency futures contracts
contracts specifying a standard volume of a particular currency to be exchanged an a specific settlement date
- used to hedge foreign currency positions
- used to hedge foreign currency positions
50
New cards
currency call option
grants the right to buy a specific currency at a designated price within a specific period of time
51
New cards
exercise price/strike price
price at which the owner is allowed to buy the currency
- desirable when one wishes to lock in a maximum price to be paid for a currency in the future
- desirable when one wishes to lock in a maximum price to be paid for a currency in the future
52
New cards
factors affecting currency call option premiums
spot price relative to strike price
length of time before the expiration date
volatility of the currency
length of time before the expiration date
volatility of the currency
53
New cards
currency put option
the right to sell a currency at a specified price (strike price) within a specified period of time
- owner of put option is not obligated to exercise the option
- owner of put option is not obligated to exercise the option