1.2 Classification of Smart Materials
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
What is a smart material?
Smart material are materials whose physical properties change in response to an input or change in the environment, such as electricity, pressure, temperature or light. Many products utilise smart materials, often bringing benefits such as increased safety and/or ease of use.
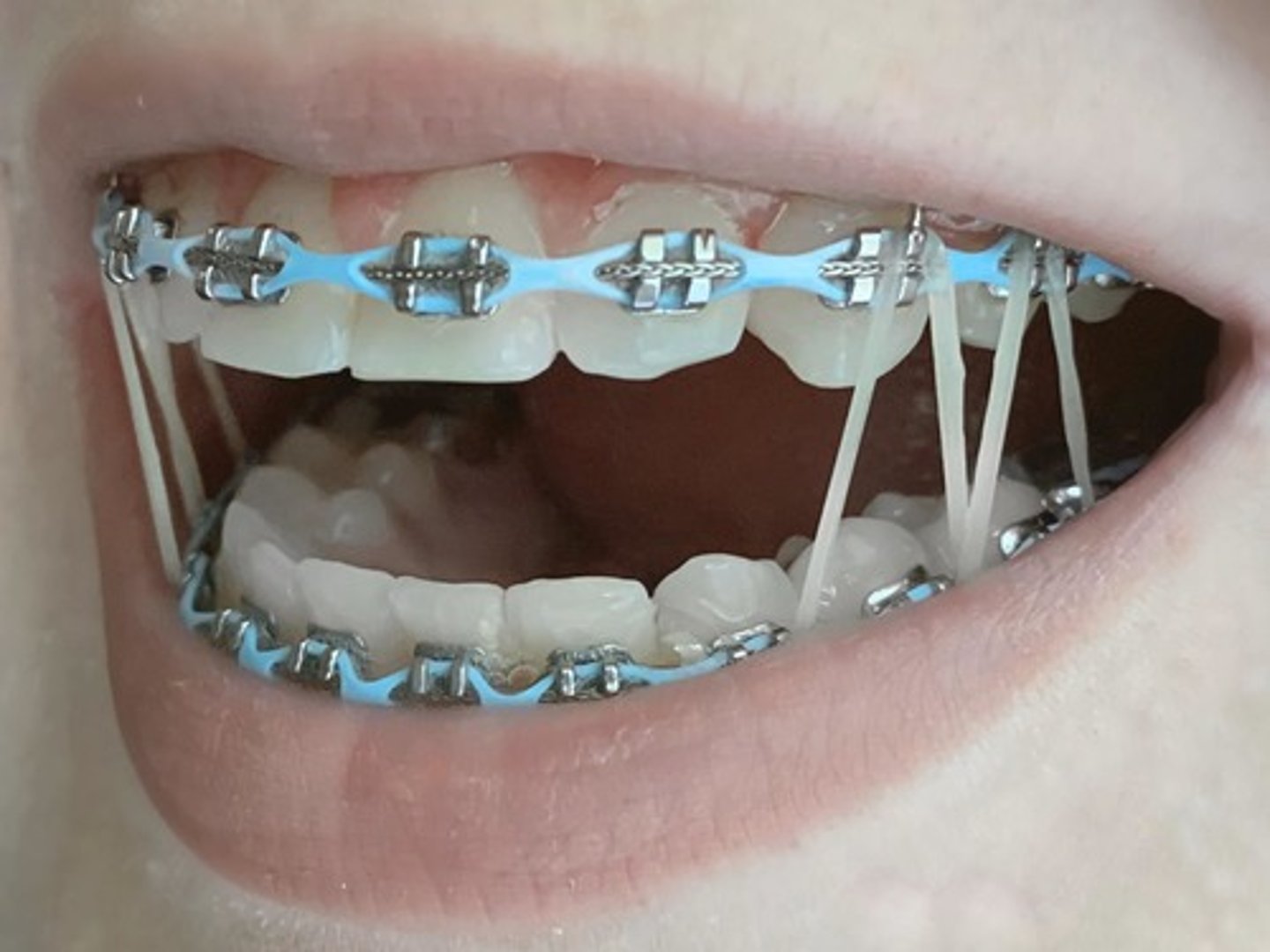
SMAs, e.g. nitinol
Changes shape in response to a change in temperature or electrical input.
For example, nitinol wire in dental braces changes length in response to a change in temperature.
Dental braces, self-closing windows, aeroplane wing flaps, bioengineering such as stents, bone plates and screws,
Thermochromic pigment
Changes colour in response to temperature change.
Room thermometers, medical thermometers for children, bath water thermometers, colour change mugs and kettles, food packaging to indicate food is hot to eat or cool for drinks, baby feeding spoons, battery charge indicator strips.

Phosphorescent pigment
Absorbs light energy during the day and "re-emits" the light energy when it is dark.
Fire exit signs, glow in the dark products such as adhesive stars, masks, night lights, watch hands.
Photochromic pigment
Changes colour with light intensity.
Welding goggles, reactive spectacle lenses. security markers that show under UV light.

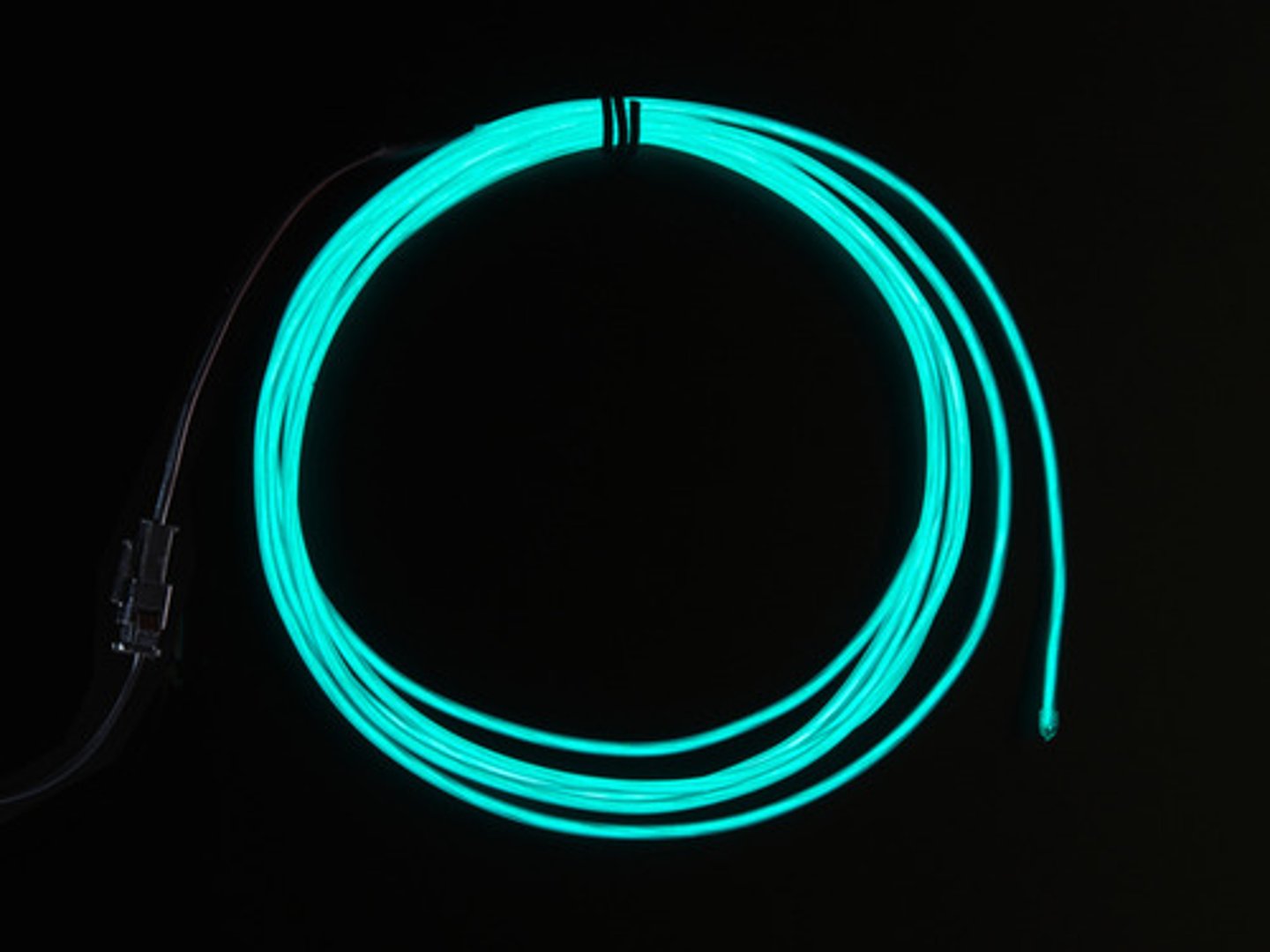
Electroluminescent wire
Thin copper wire coated in a phosphorescent material which glows in response to an alternating current.
Glow bracelets, interweaving for clothing, home decoration, outdoor decorative lighting.

Piezoelectric material
Gives off a small electrical charge when deformed.
Increases in size (up to 4 per cent) when an electrical current is passed through it.
Airbag sensors in cars, lighters for barbecues, vibration damping in tennis racquets, musical greetings cards, pressure sensors
