ANP 300 Lab 6 - The Skull
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
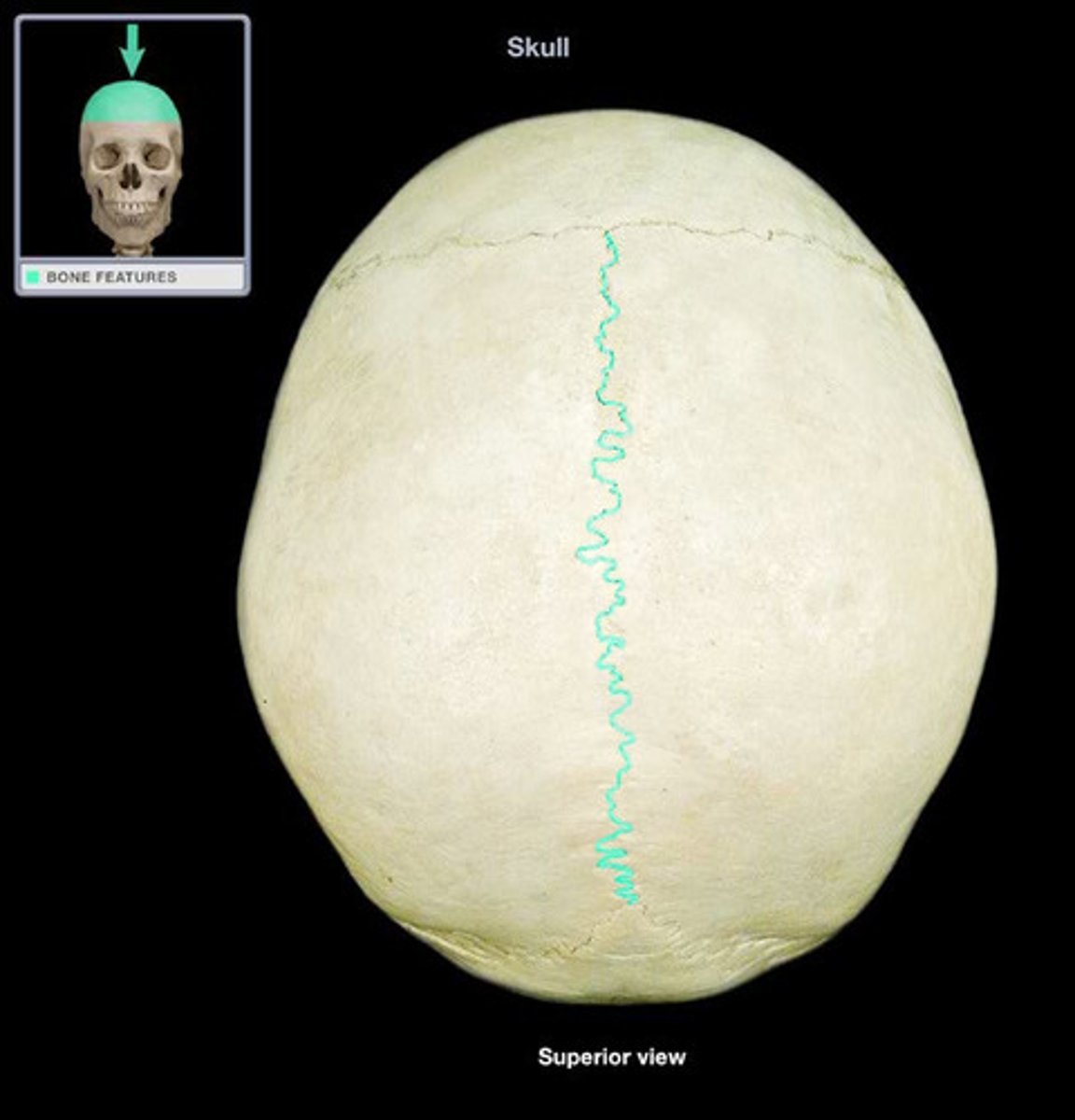
Coronal suture
Fuses frontal and parietal bones
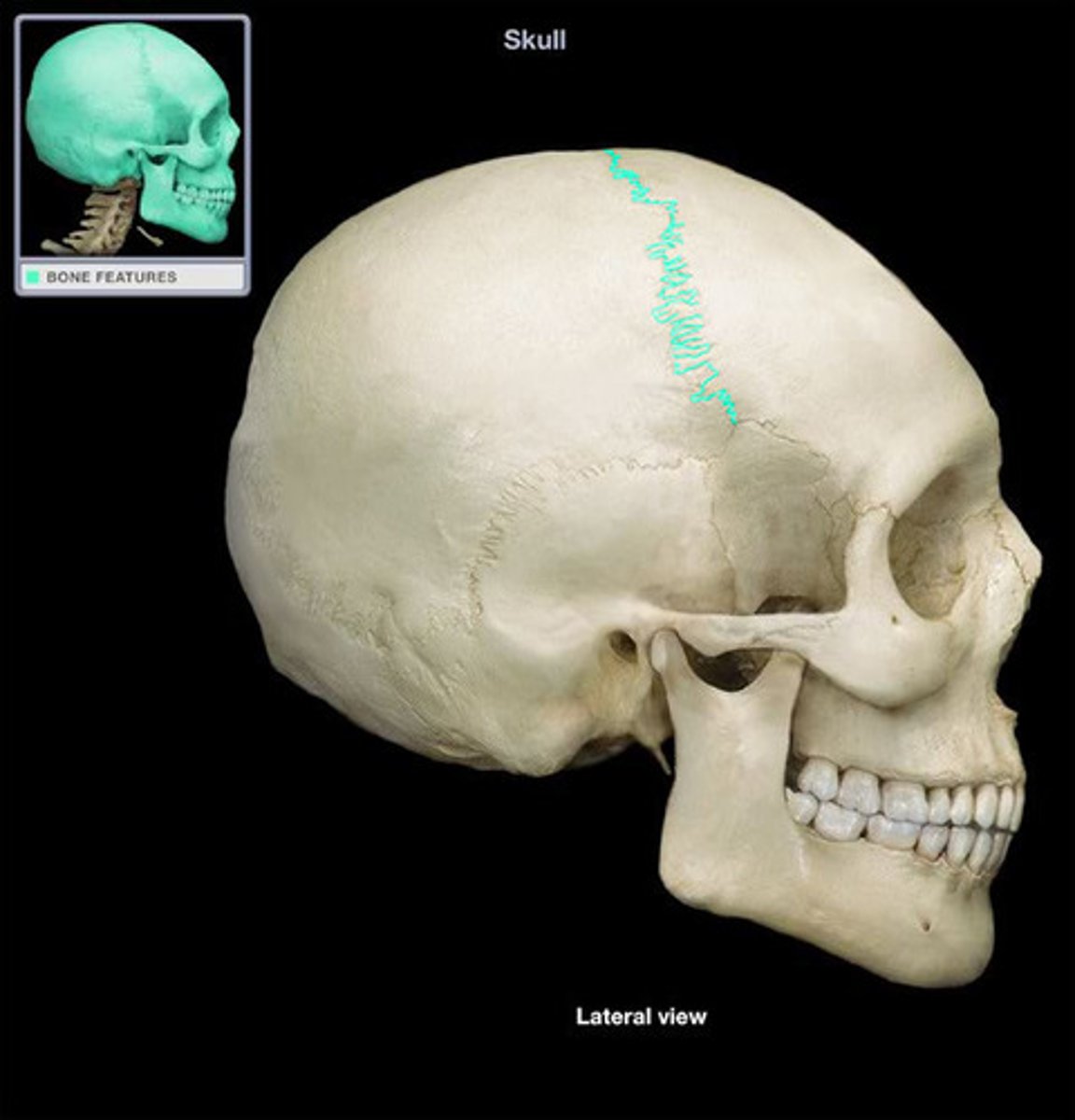
Sagittal suture
Fuses parietals
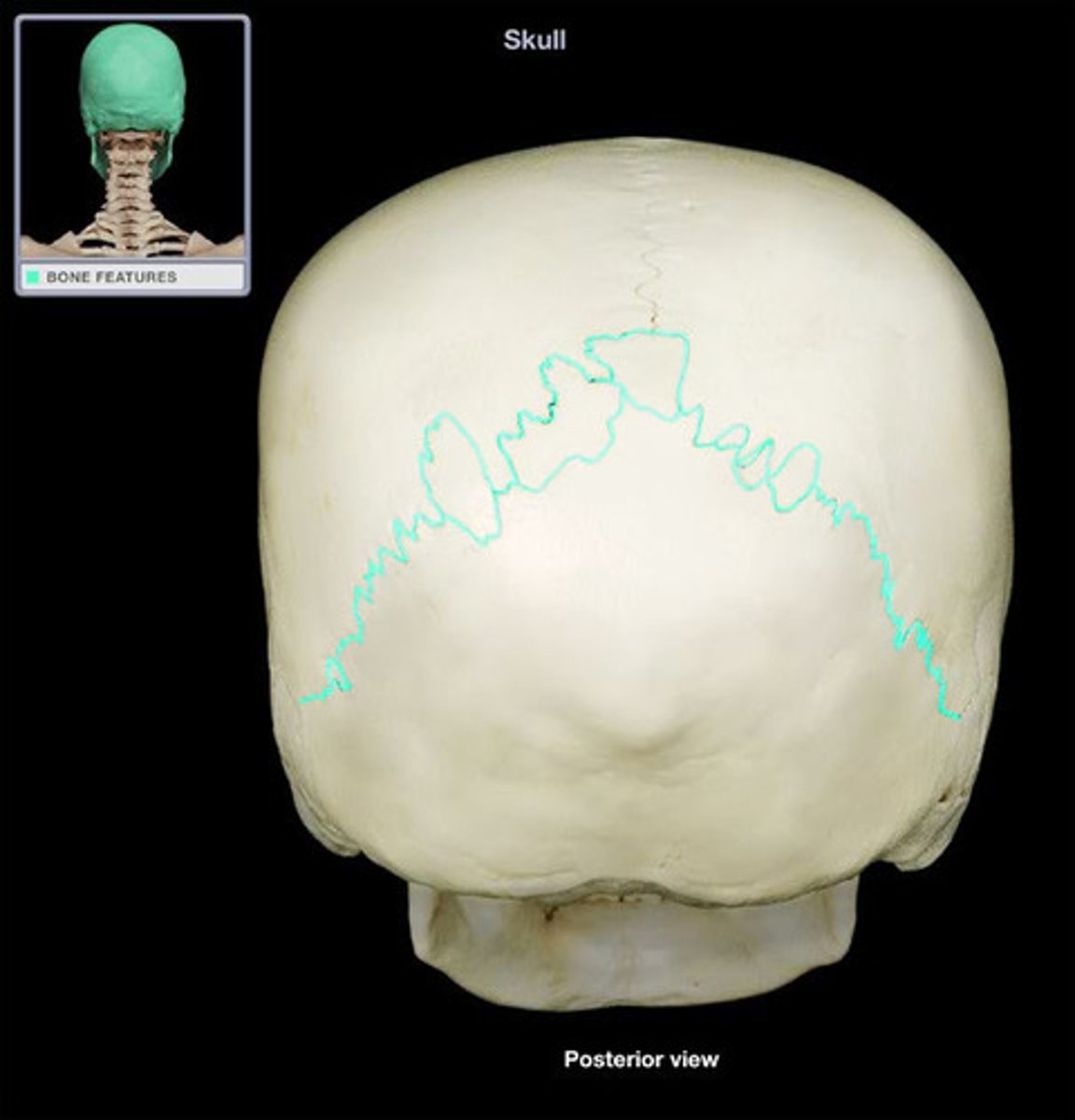
Lambdoid suture
Fuses parietals and occipital
Squamosal suture
Fuses temporal and parietals
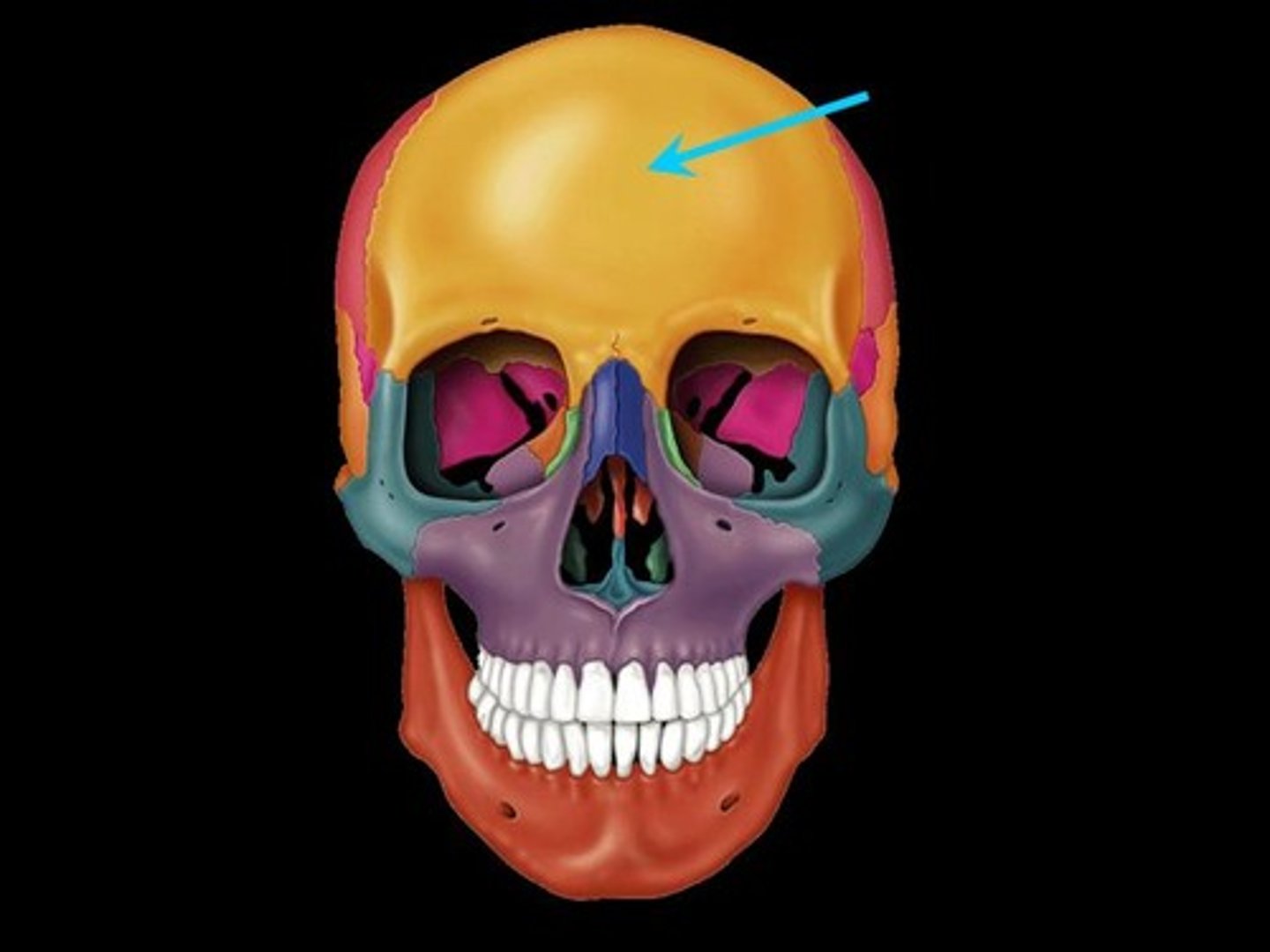
Frontal bone
Forehead
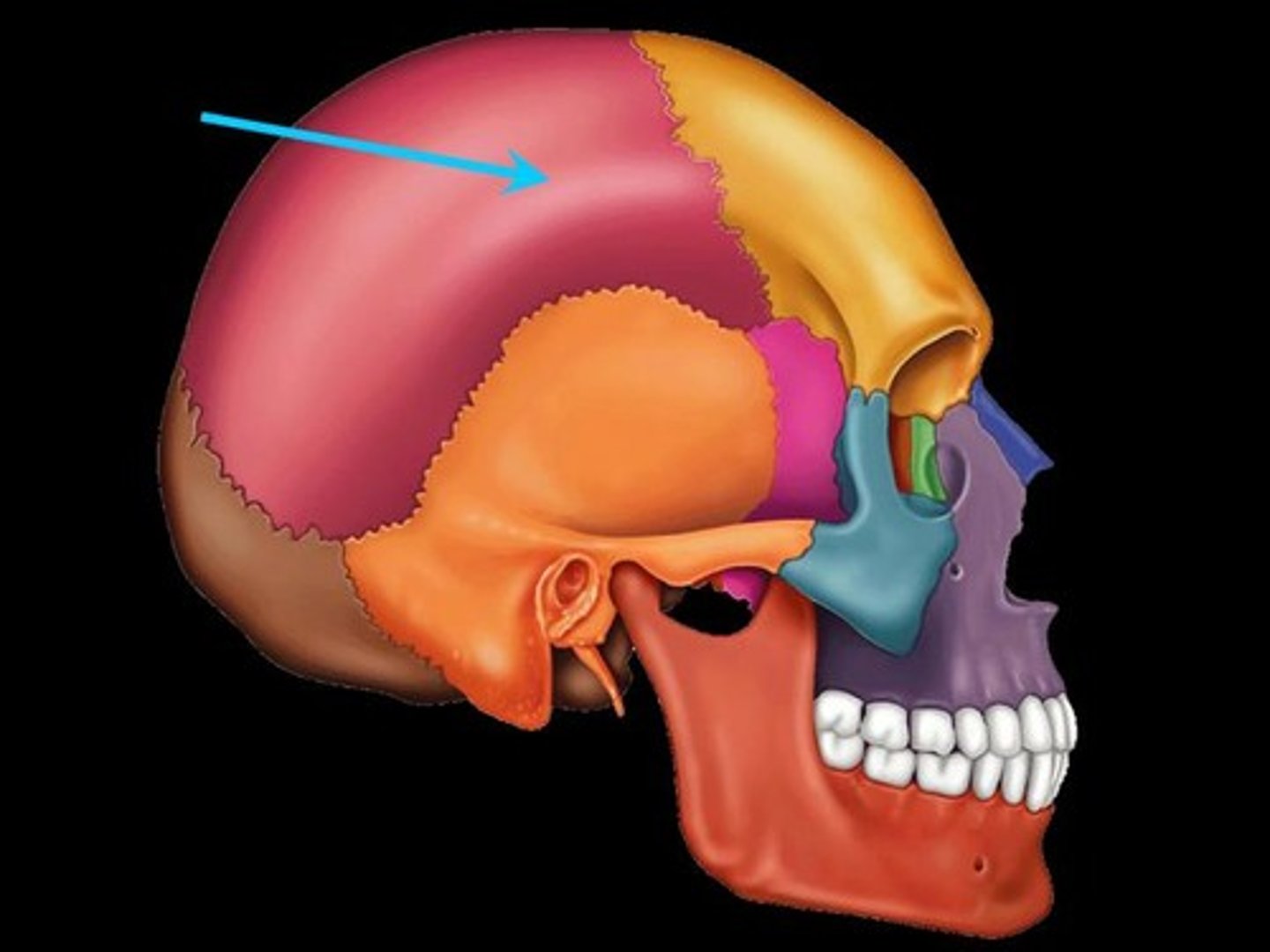
Parietal bones
Superior lateral skull
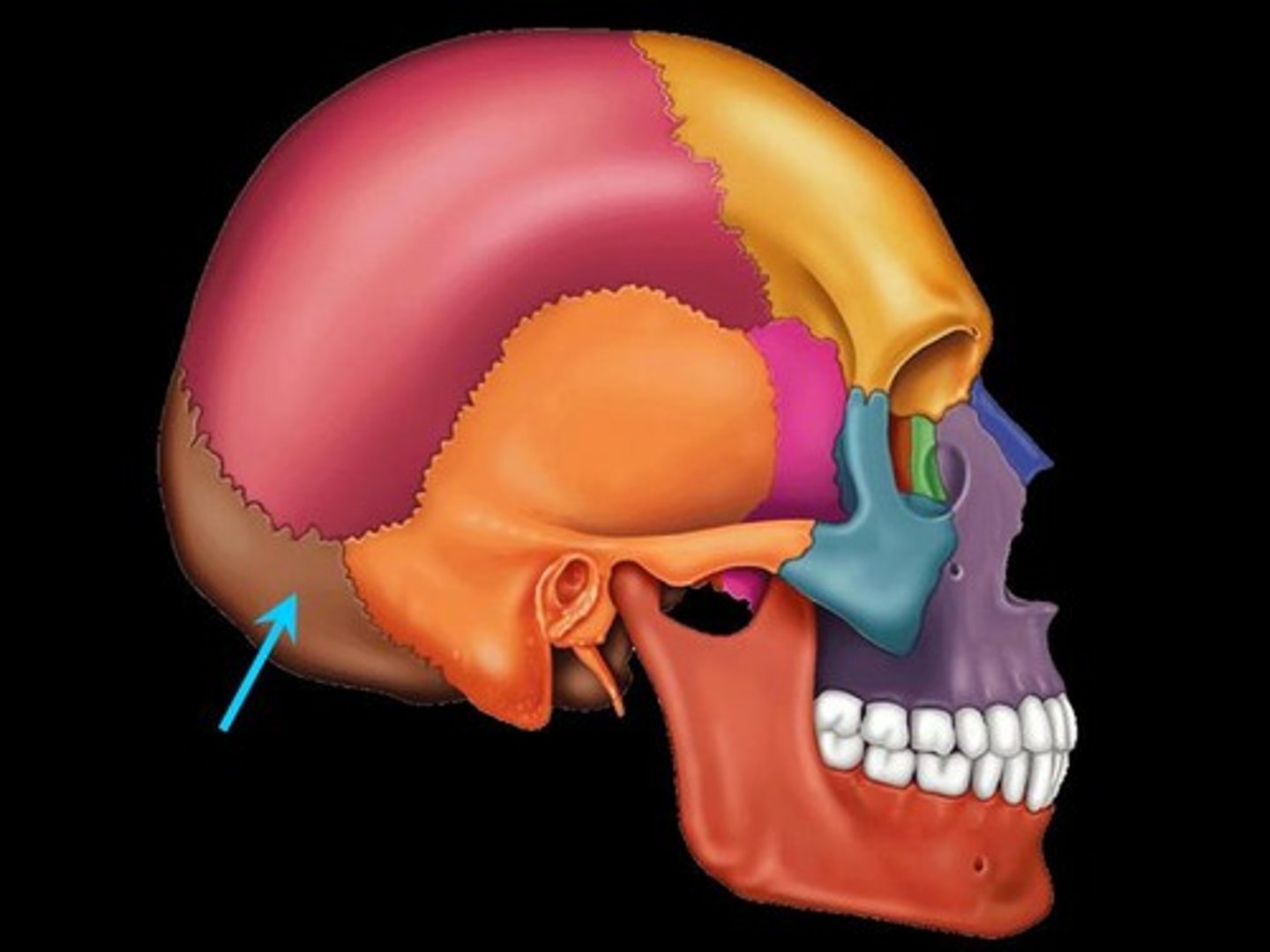
Occipital bone
Posterior bone of the skull
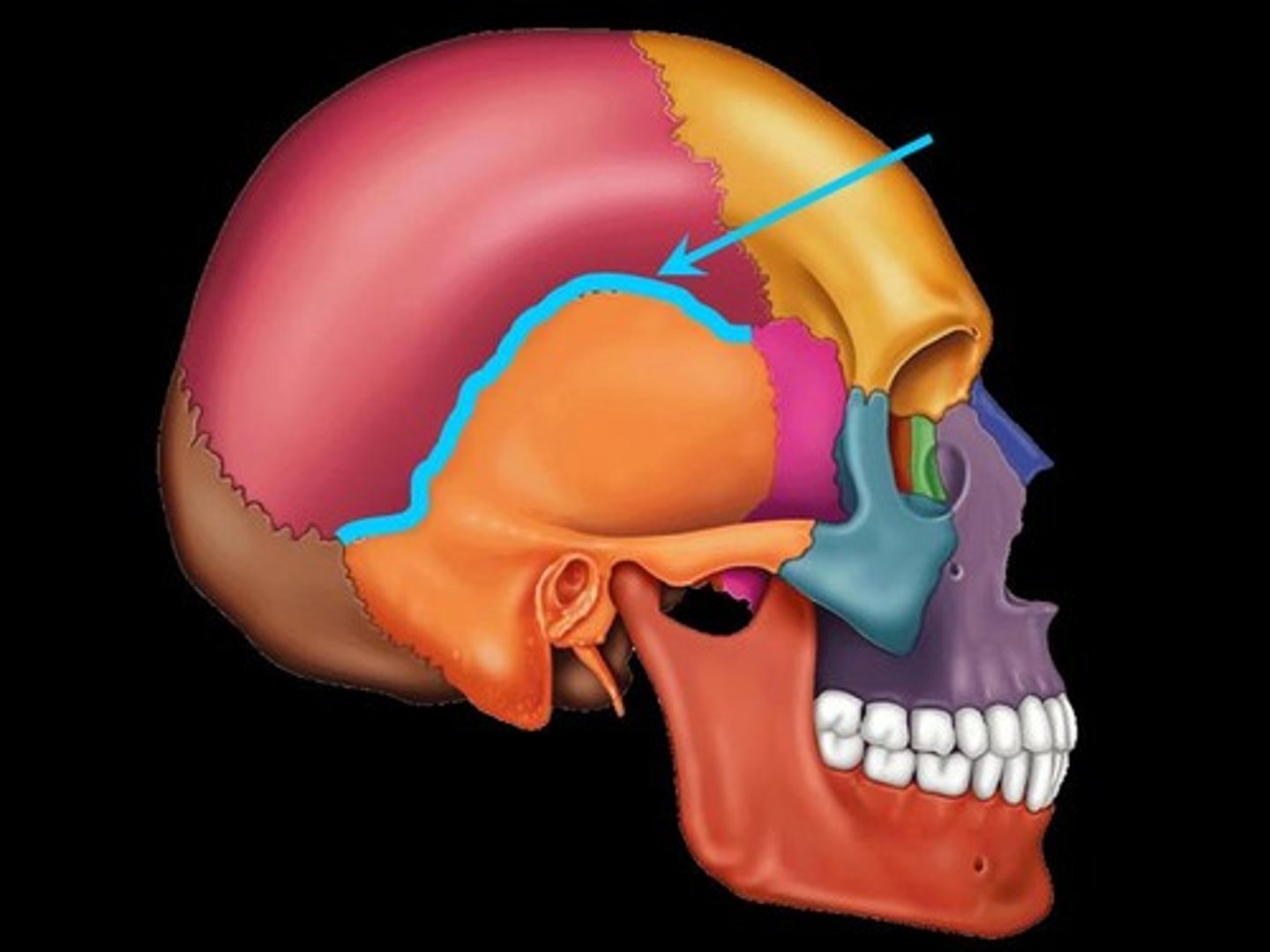
Temporal bone
Inferior lateral bone of the skull
Jugular foramen
Internal auditory meatus
Carotid foramen
Foramen Lacerum
Where the petrous temporal meets the body of the sphenoid
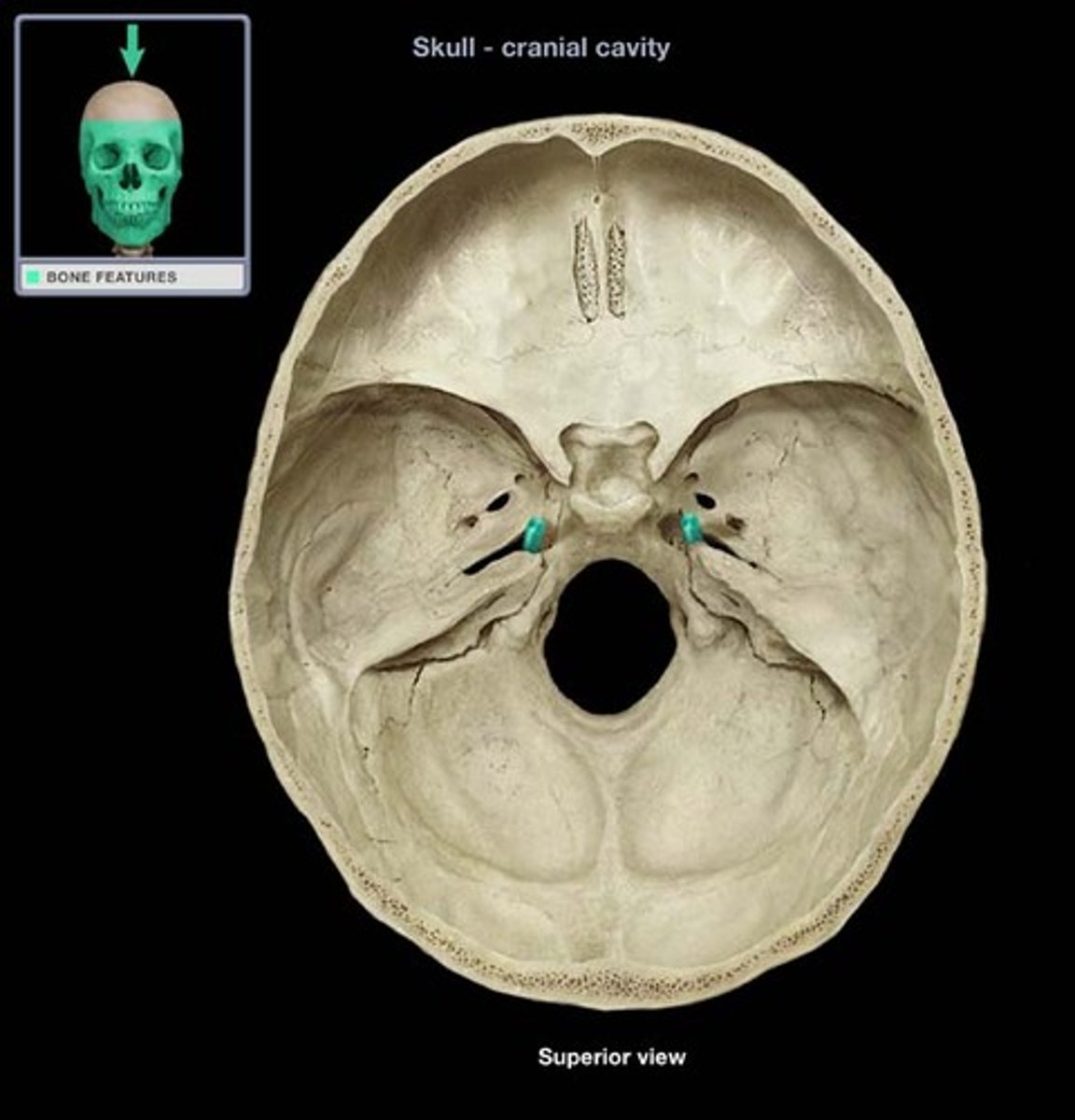
Stylomastoid foramen
Next to the styloid process
Sphenoid
Bat shaped bone embedded in the skull
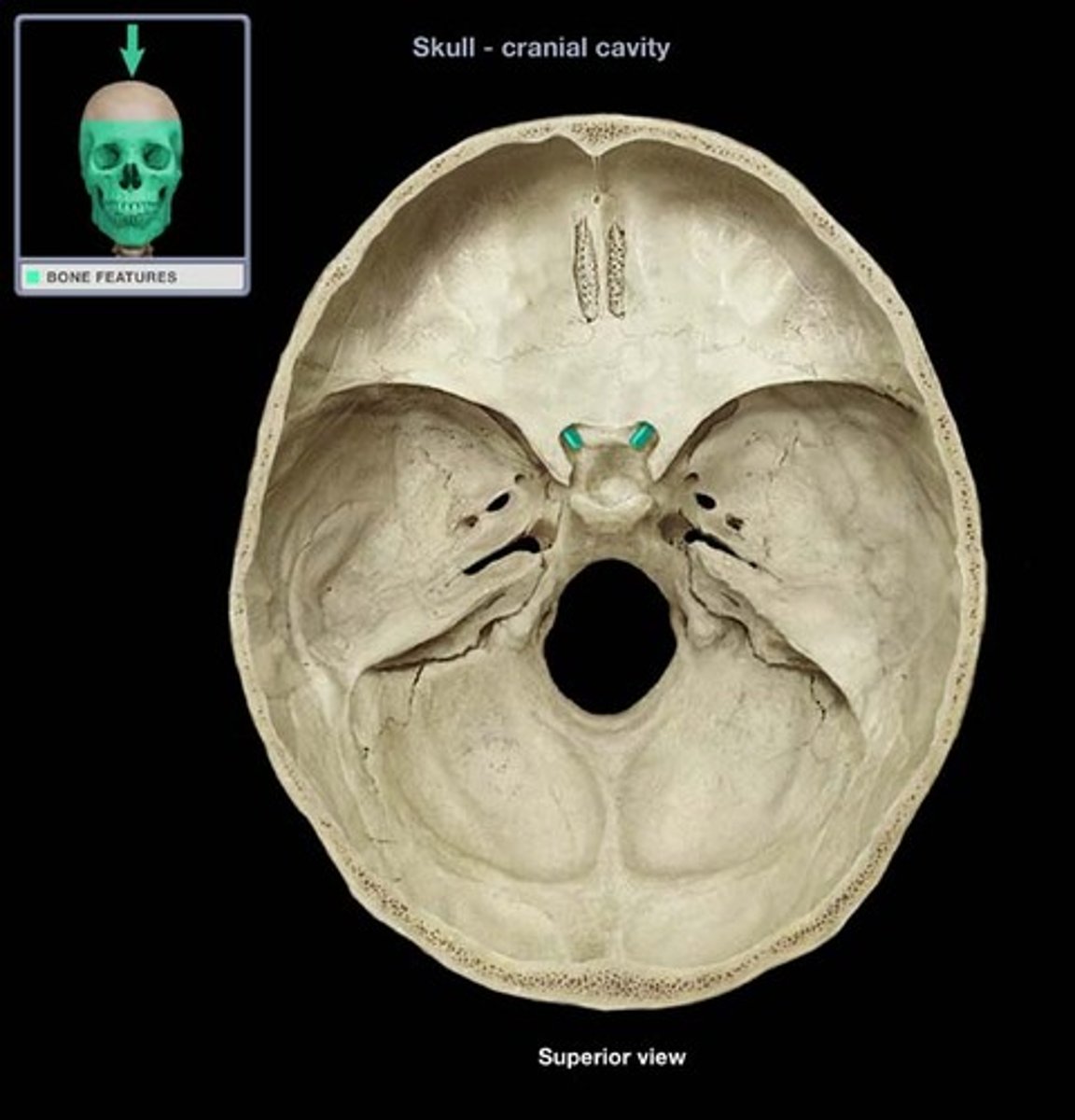
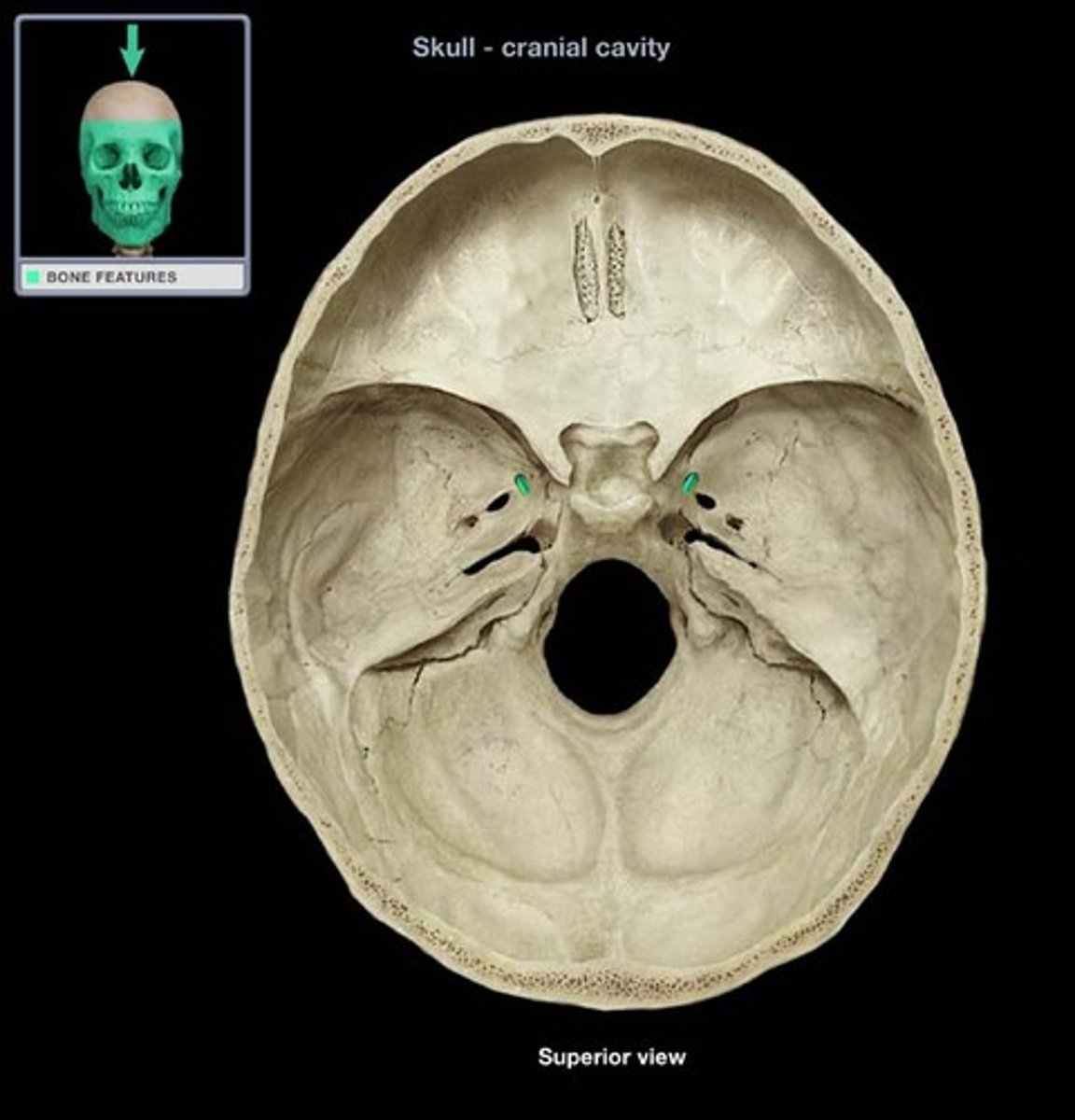
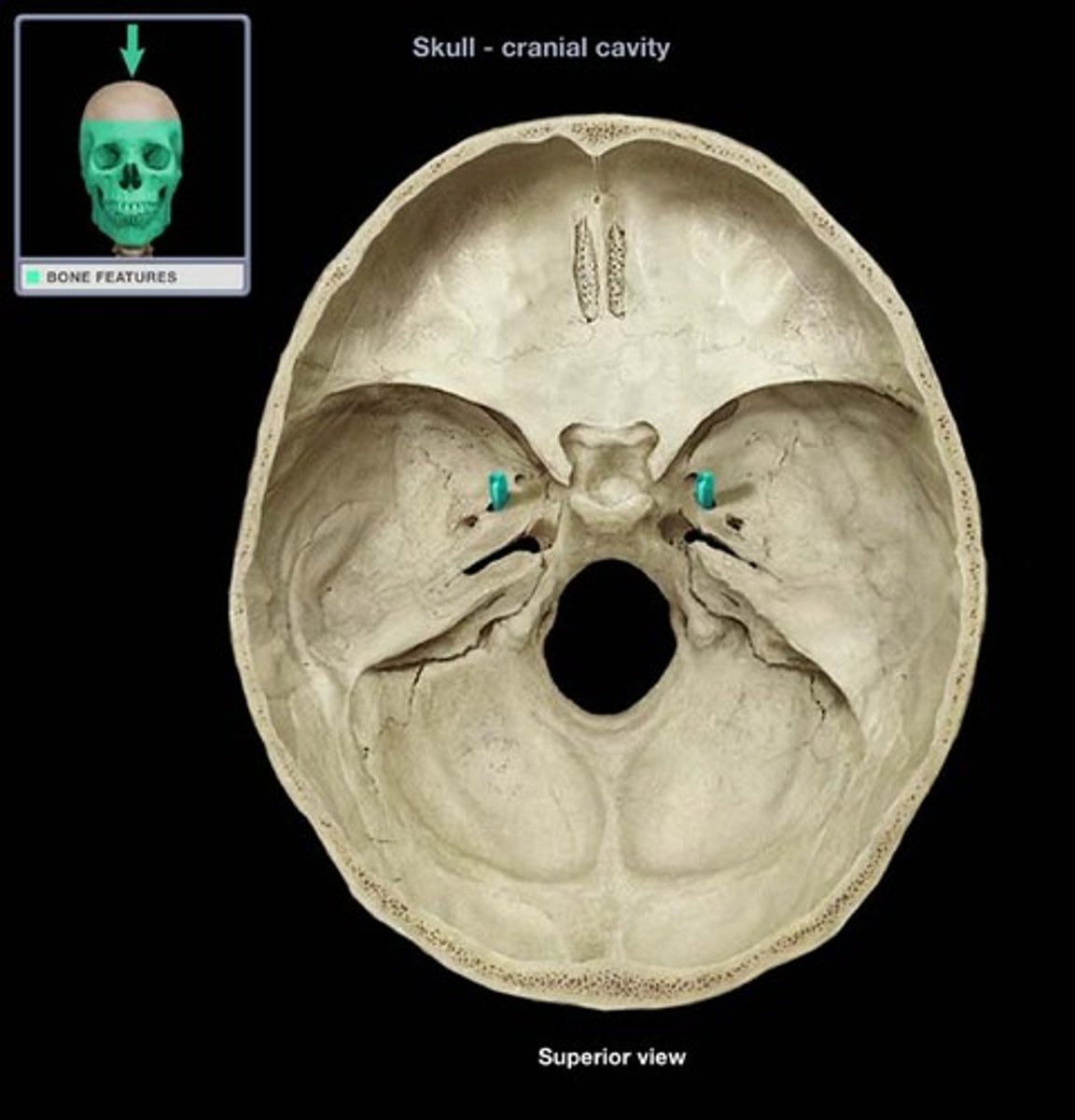
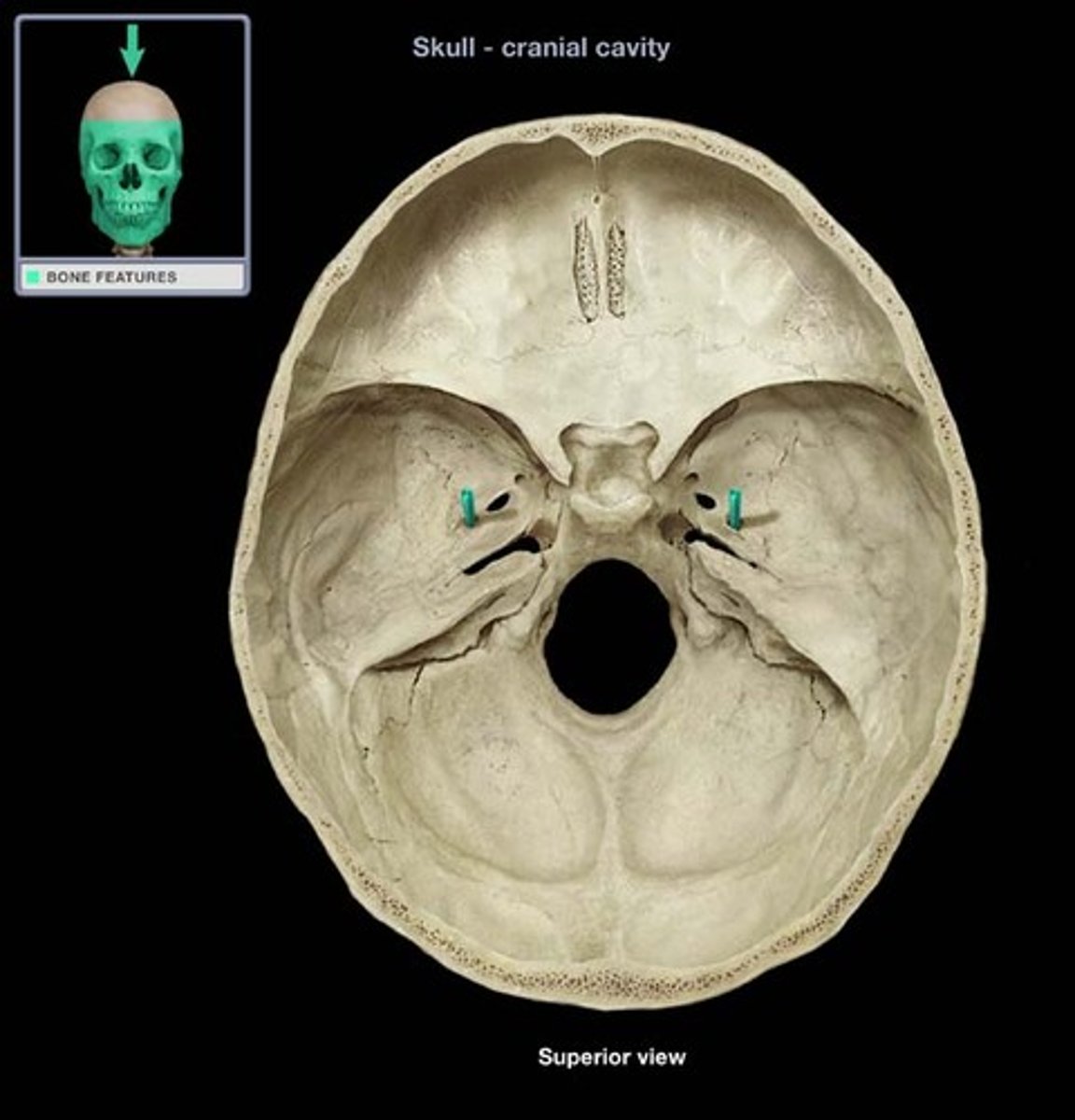
Optic canals
Transmit optic nerves
Superior Orbital Fissure
Separates lesser wing from greater wing
Transmits:
-CN III
-CN IV
-CN VI
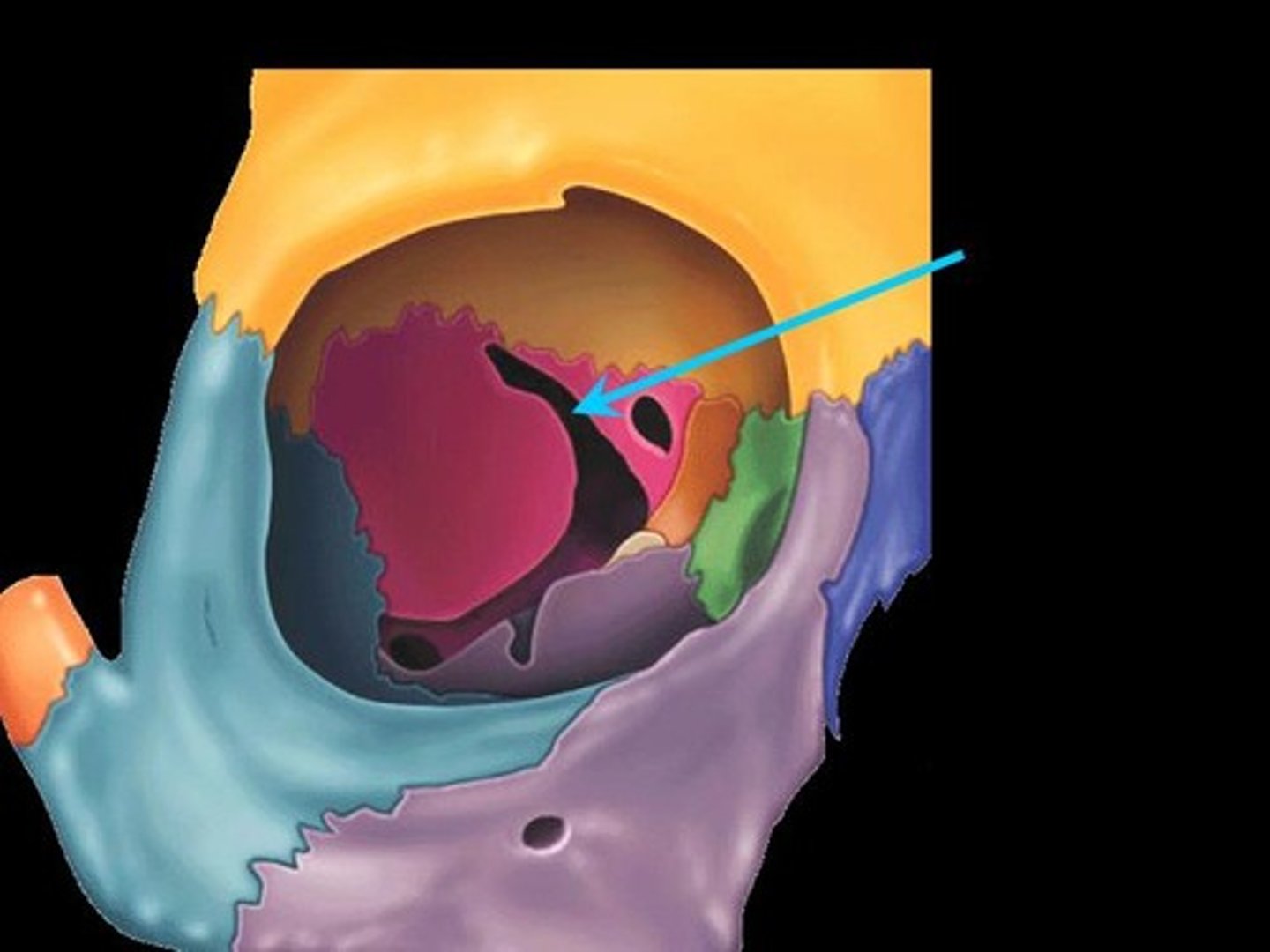
Foramen Rotundum
Just inferior to the medial portion of the superior orbital fissure
Transmits:
-CN V2
Foramen Ovale
Directly behind Foramen Rotundum
Transmits:
-CN V3
Foramen Spinosum
Lateral to Foramen ovale
Transmits:
-Middle meningeal artery
Maxillae
Form floors of orbits and the face below it
Articulates laterally with zygomatic bones
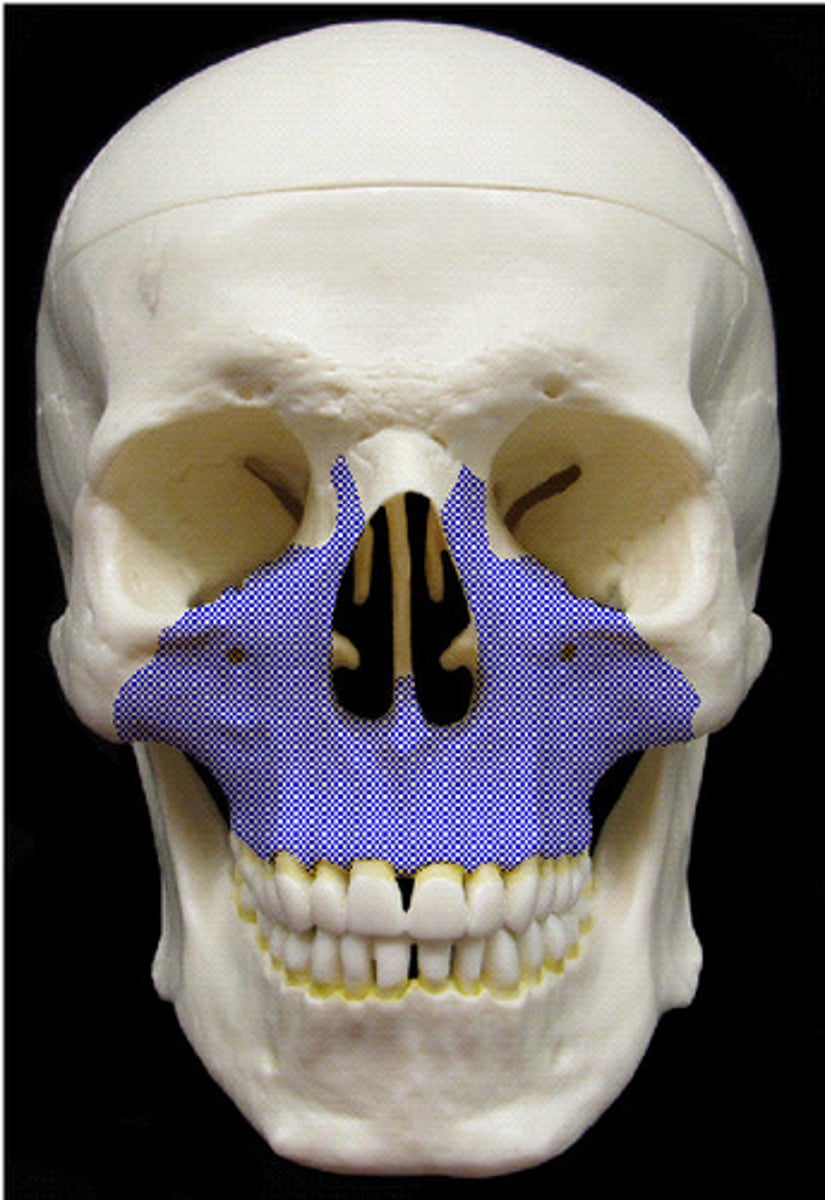
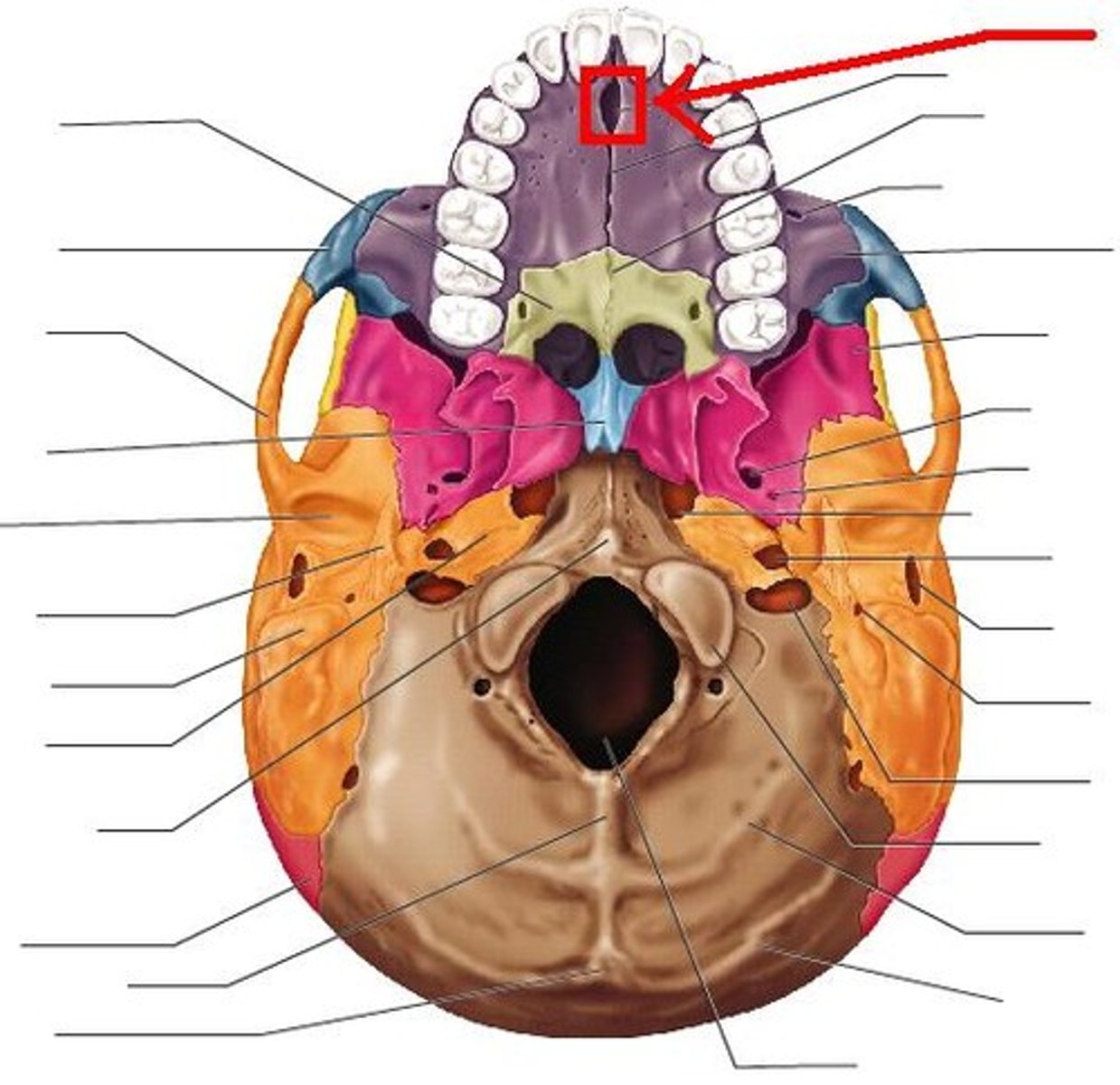
Incisive foramen
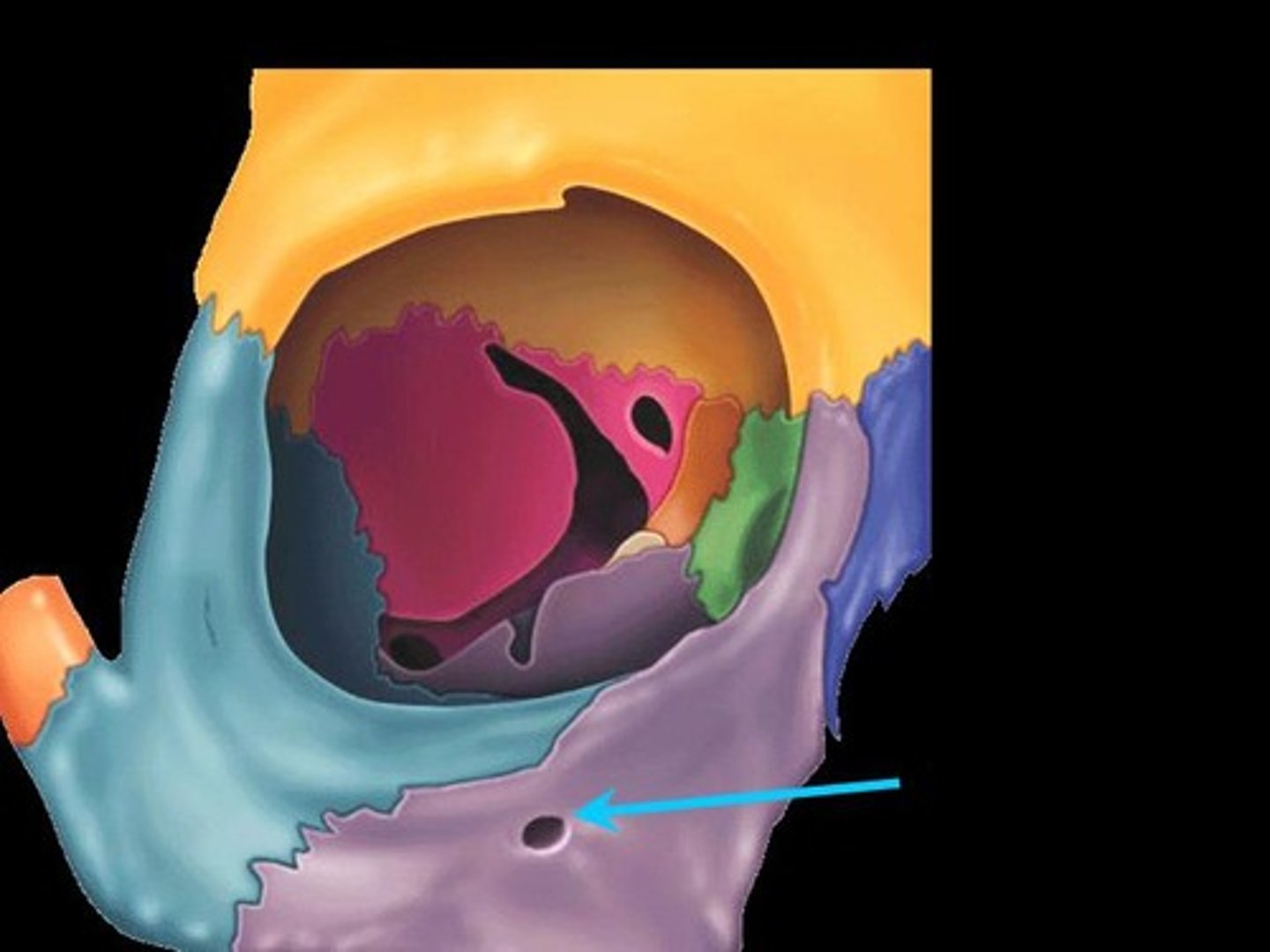
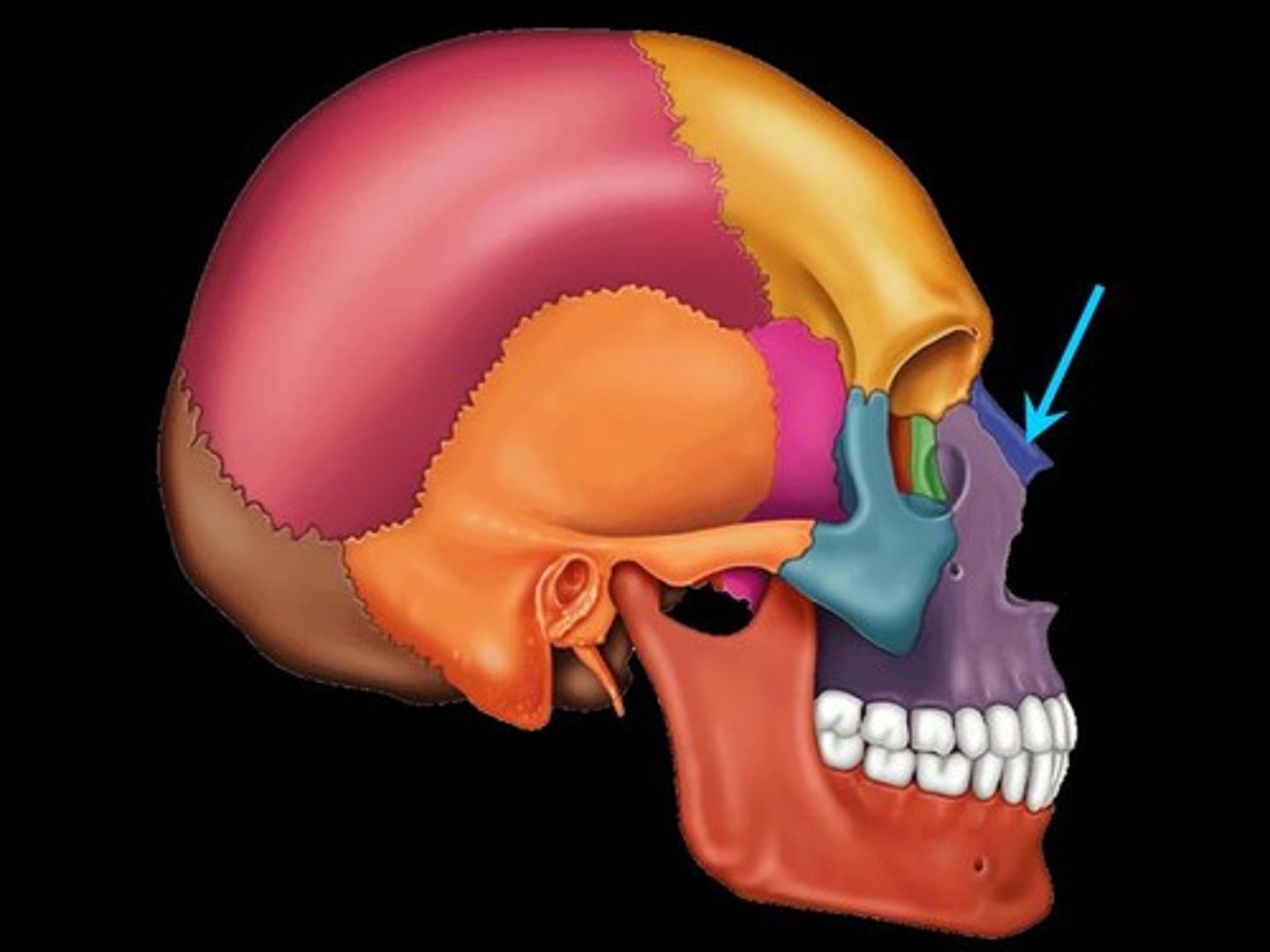
Infraorbital foramen
Right below the inferior margin of the orbit
Nasals
Pair of small bones that articulate superiorly with the
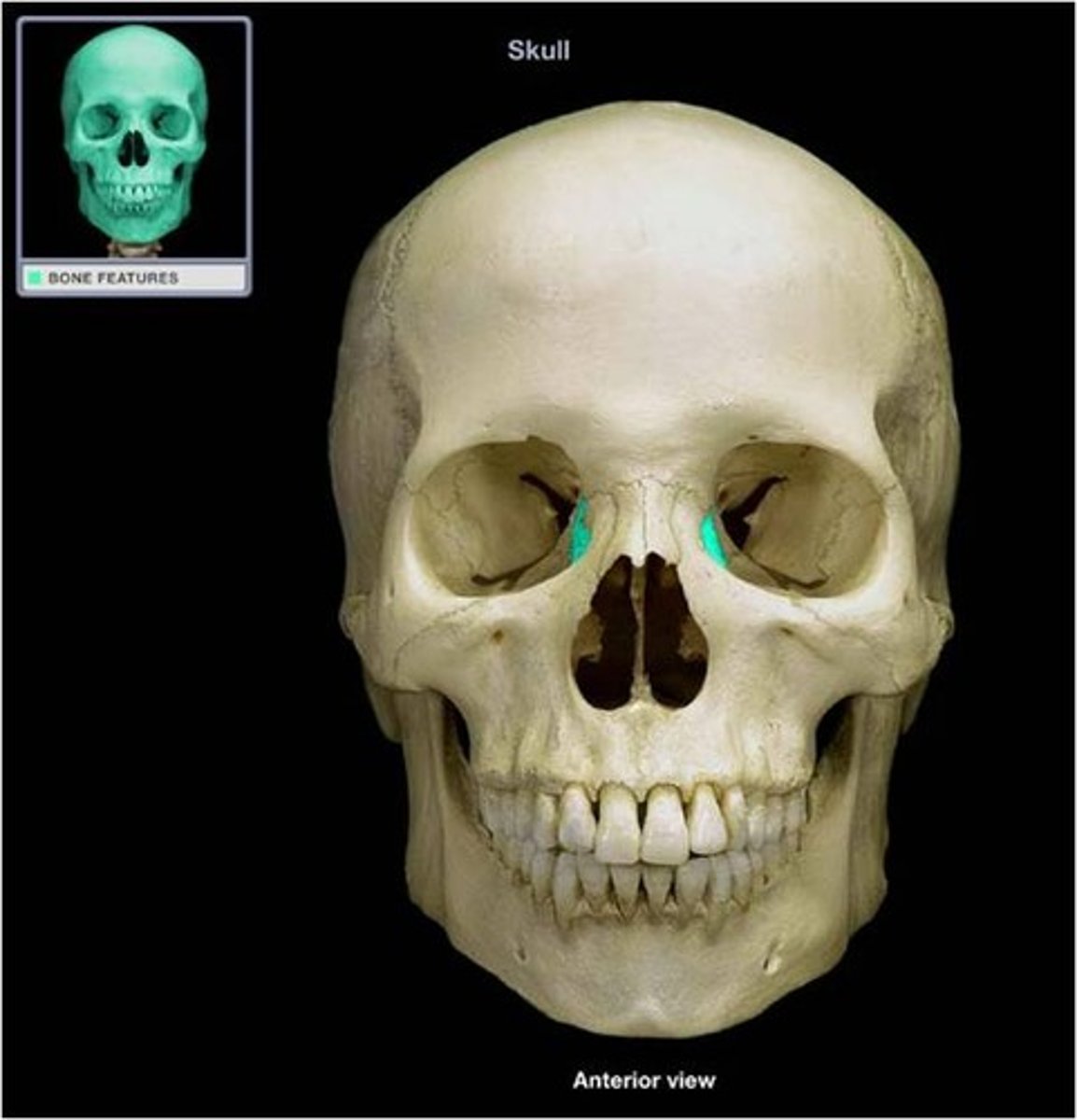
Lacrimals
paired little bones that articulate with the maxillae
Zygomatic
Paired bones that form the prominence of the cheeks
- a thin plate extends posteriorly, articulating with the temporal bone to form the zygomatic arch
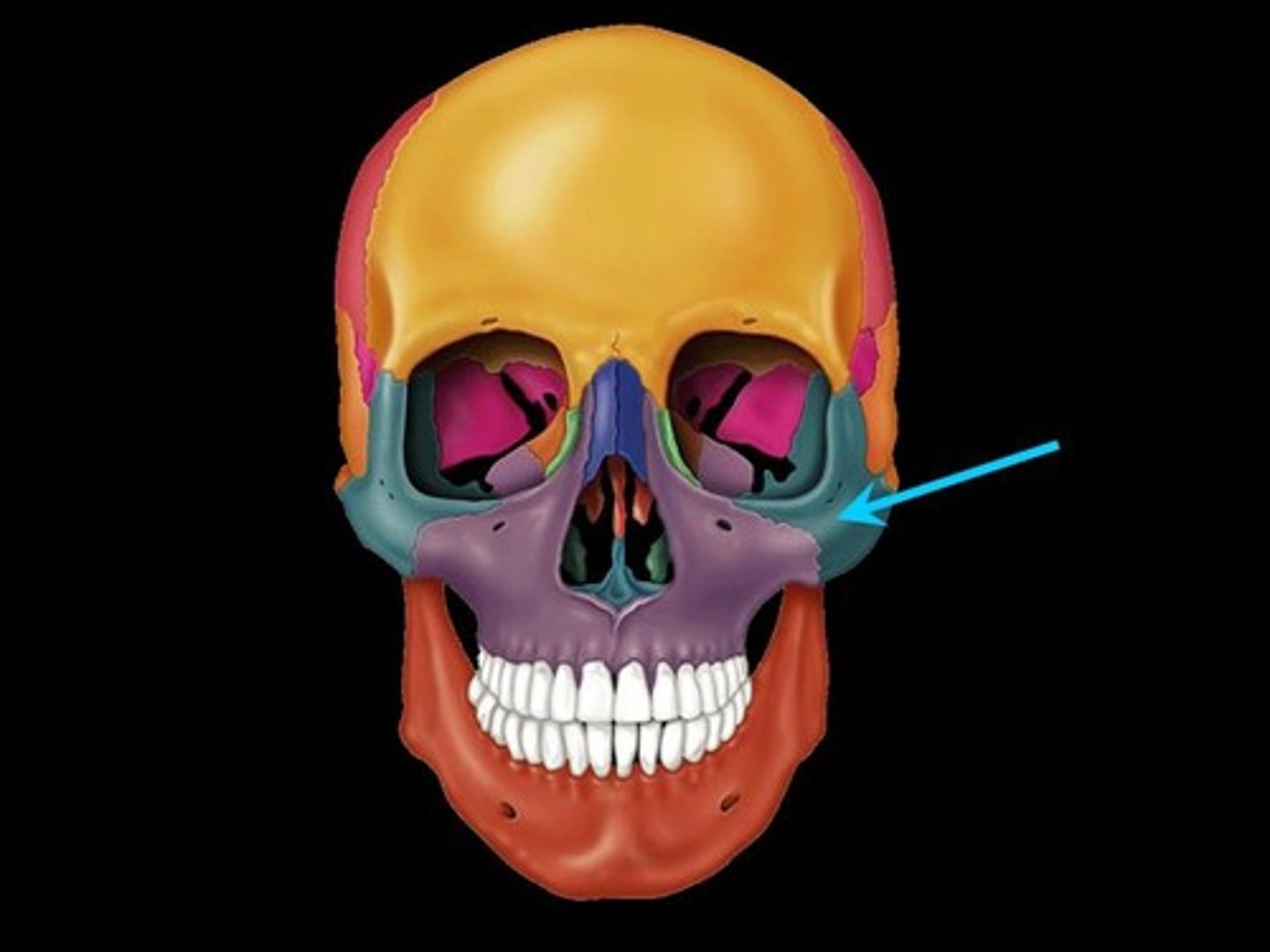
Ethmoid
unpaired box shaped bone
-Contains superior and middle nasal concha
-articulates with septum at the midline
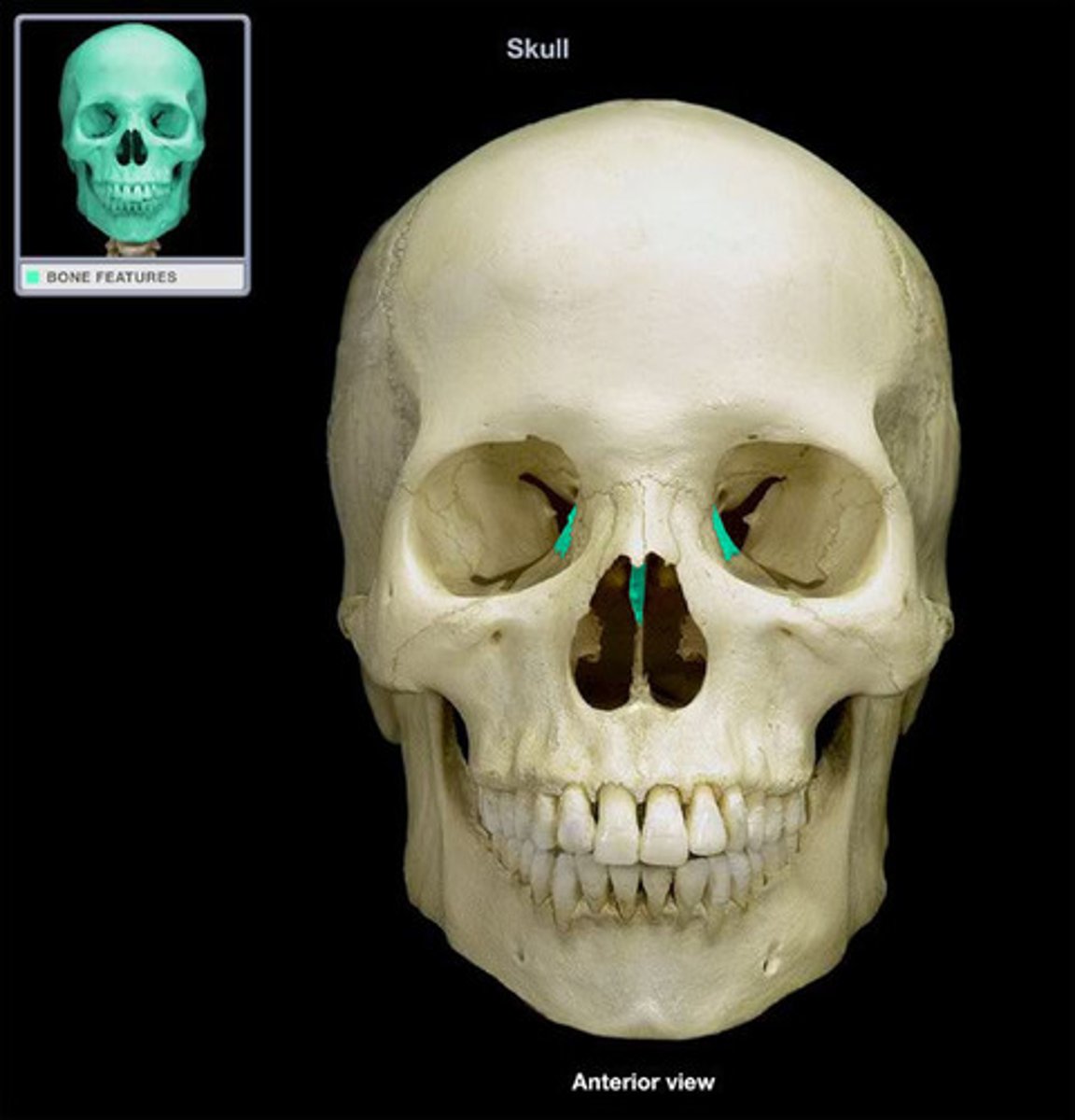
Inferior Nasal Concha
paired small bones that extend along the lateral walls of the nasal cavity just below the middle nasal concha
-Articulate with the maxillae
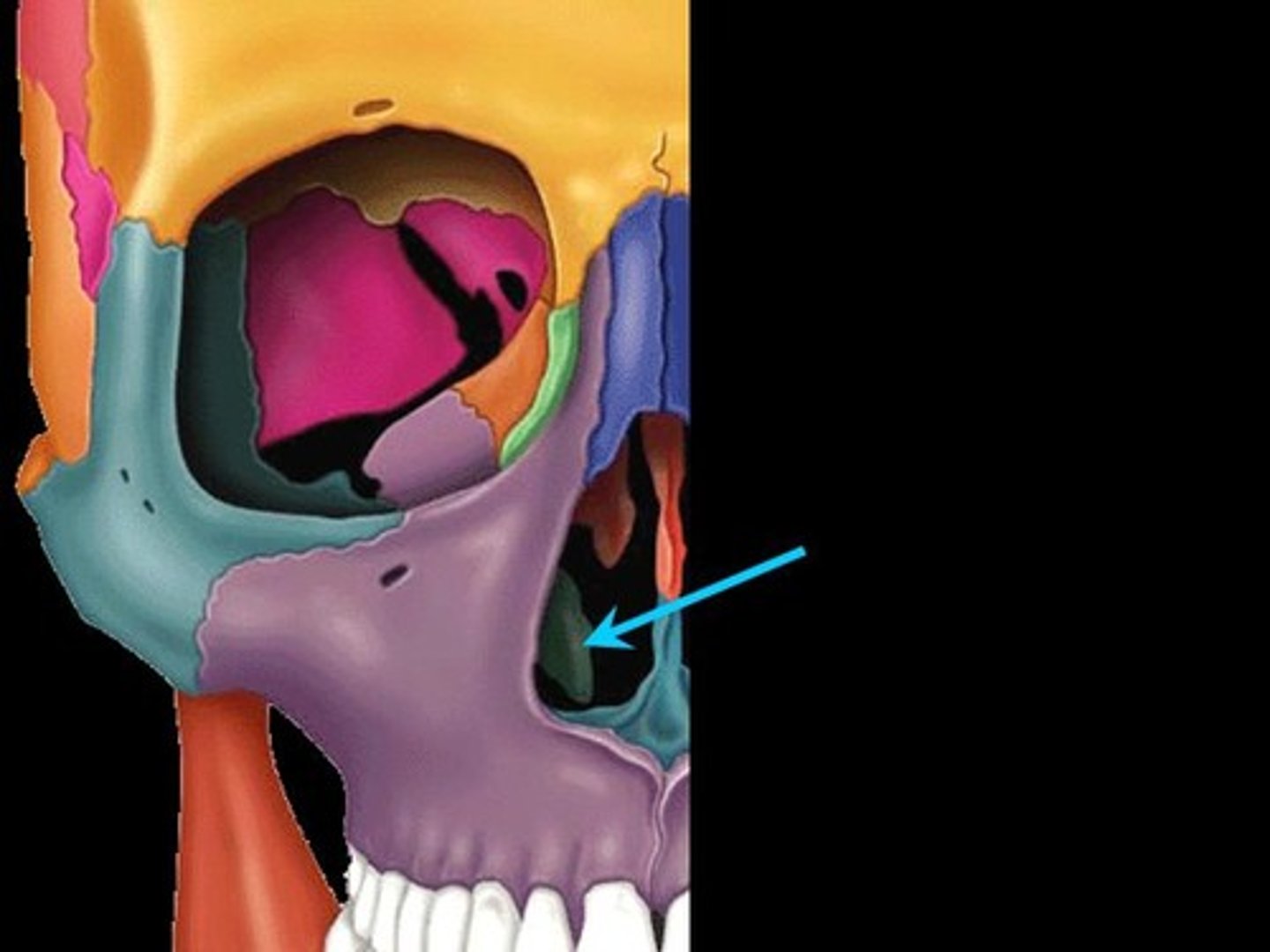
Vomer
Thin unpaired bone that forms part of the midline of the nasal septum.
-Articulates inferiorly with the maxillae
-Articulates superiorly with the ethmoid and sphenoid
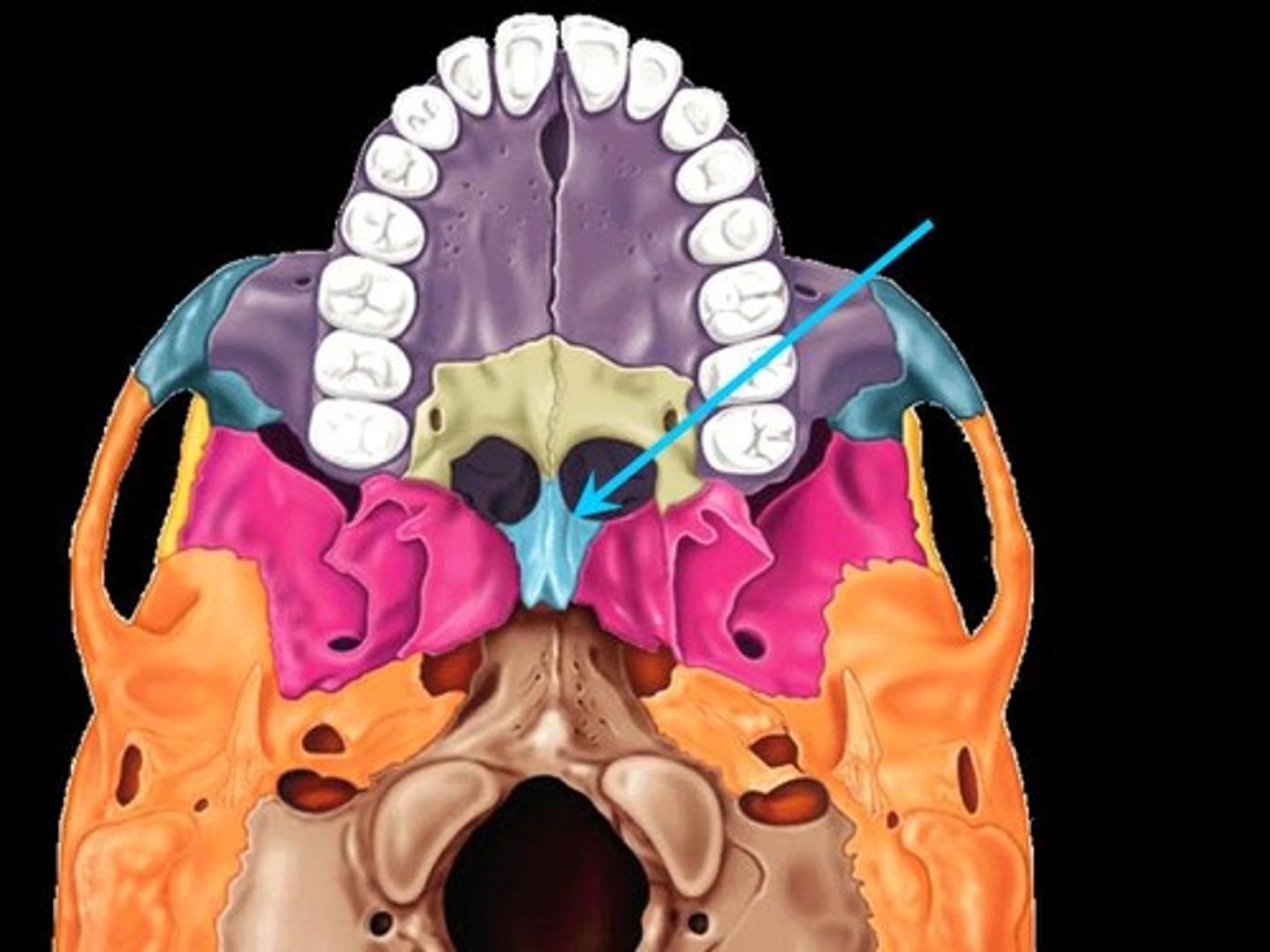
Palatines
Paired, L-shaped small bones, with vertical and horizontal plates
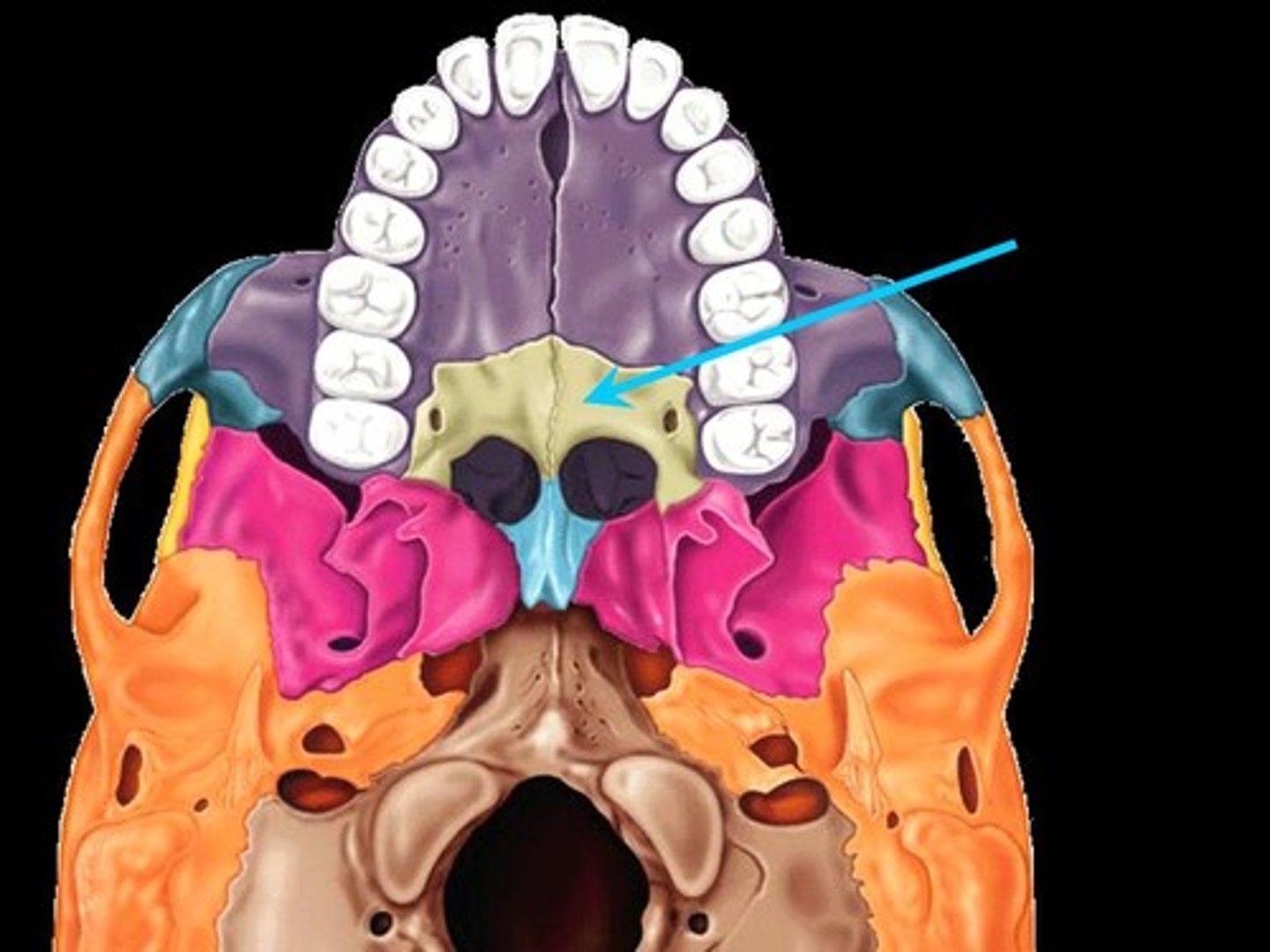
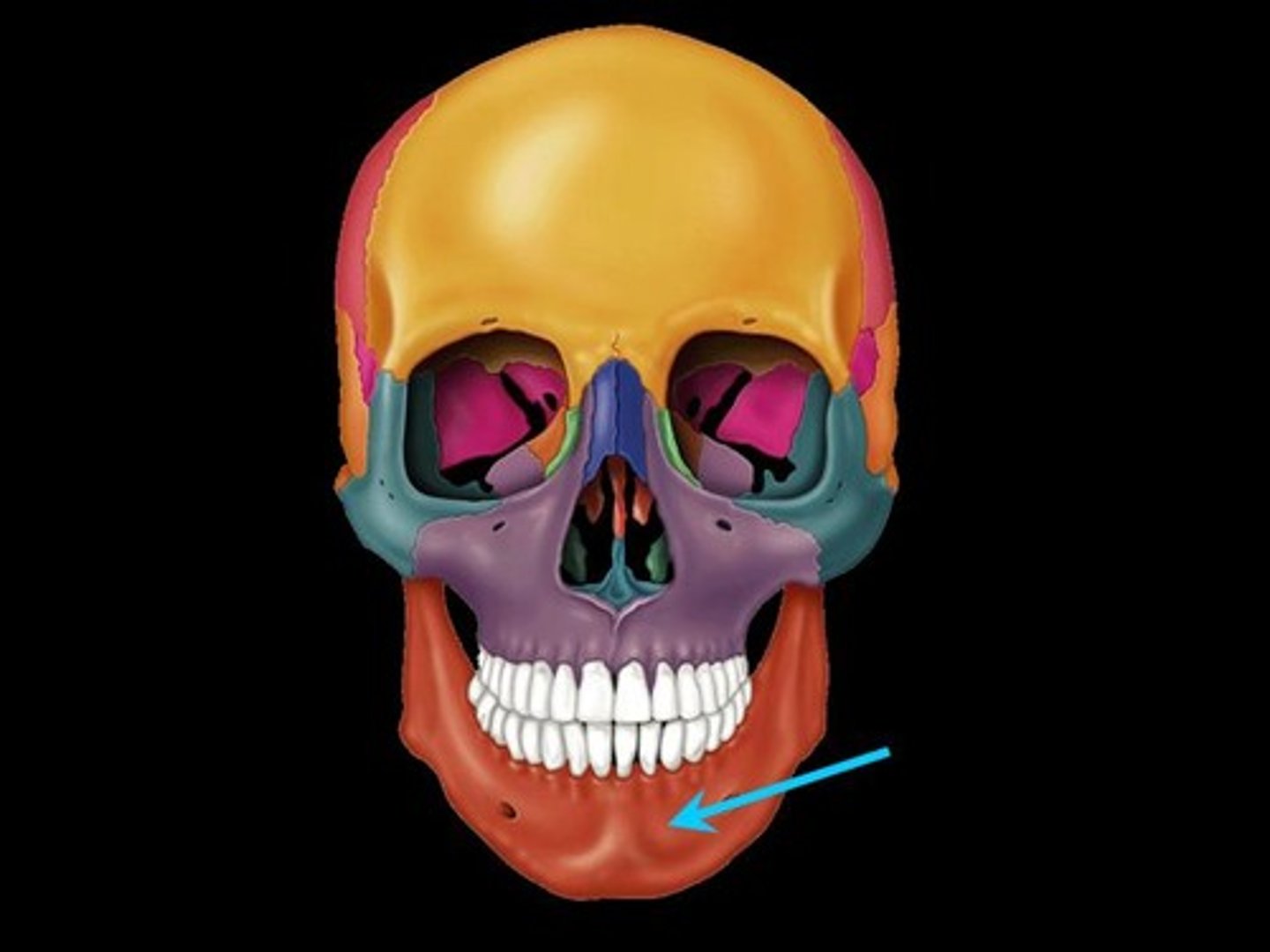
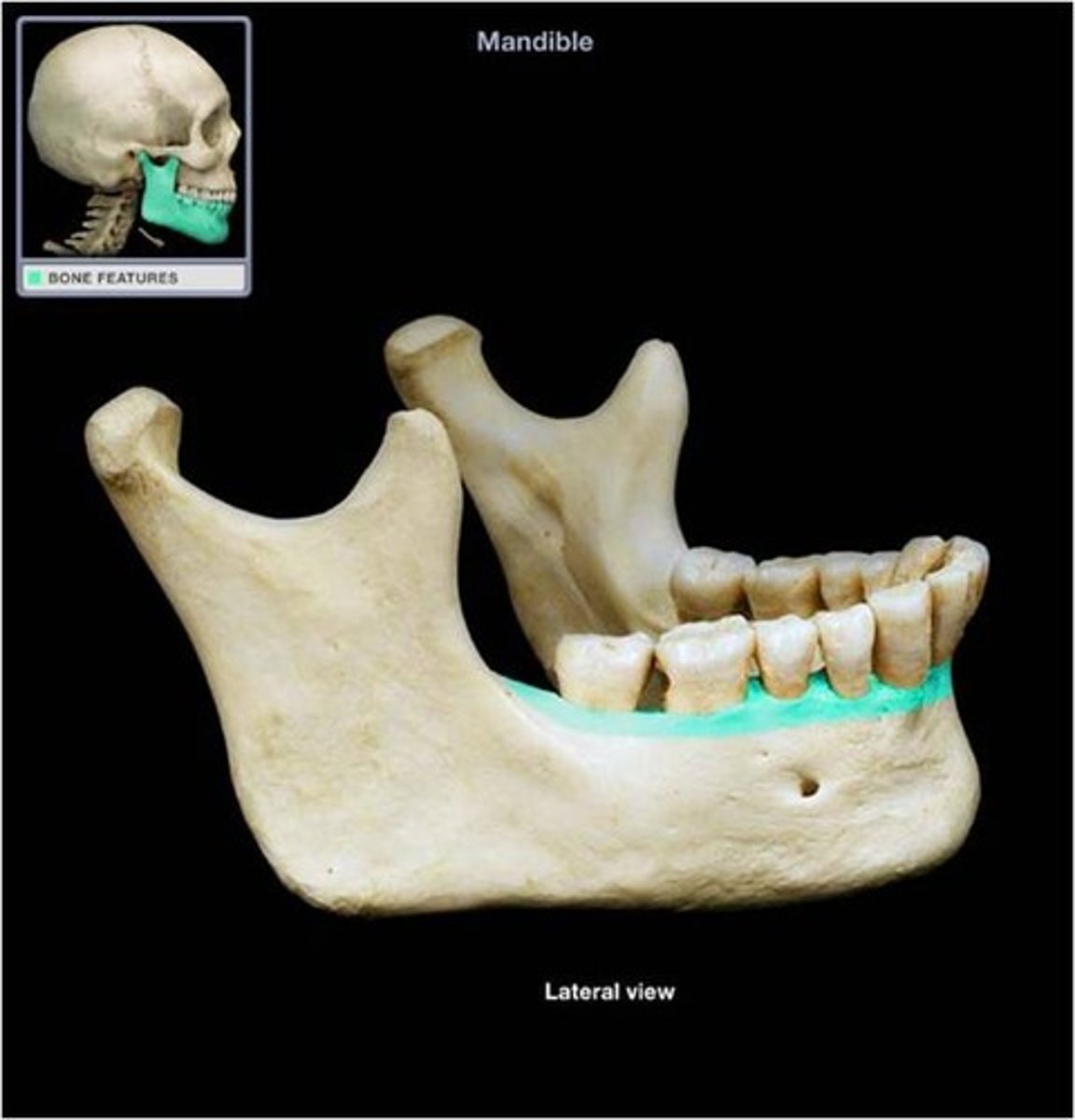
Mandible
Lower jaw
-Contains roots with alveolar processes
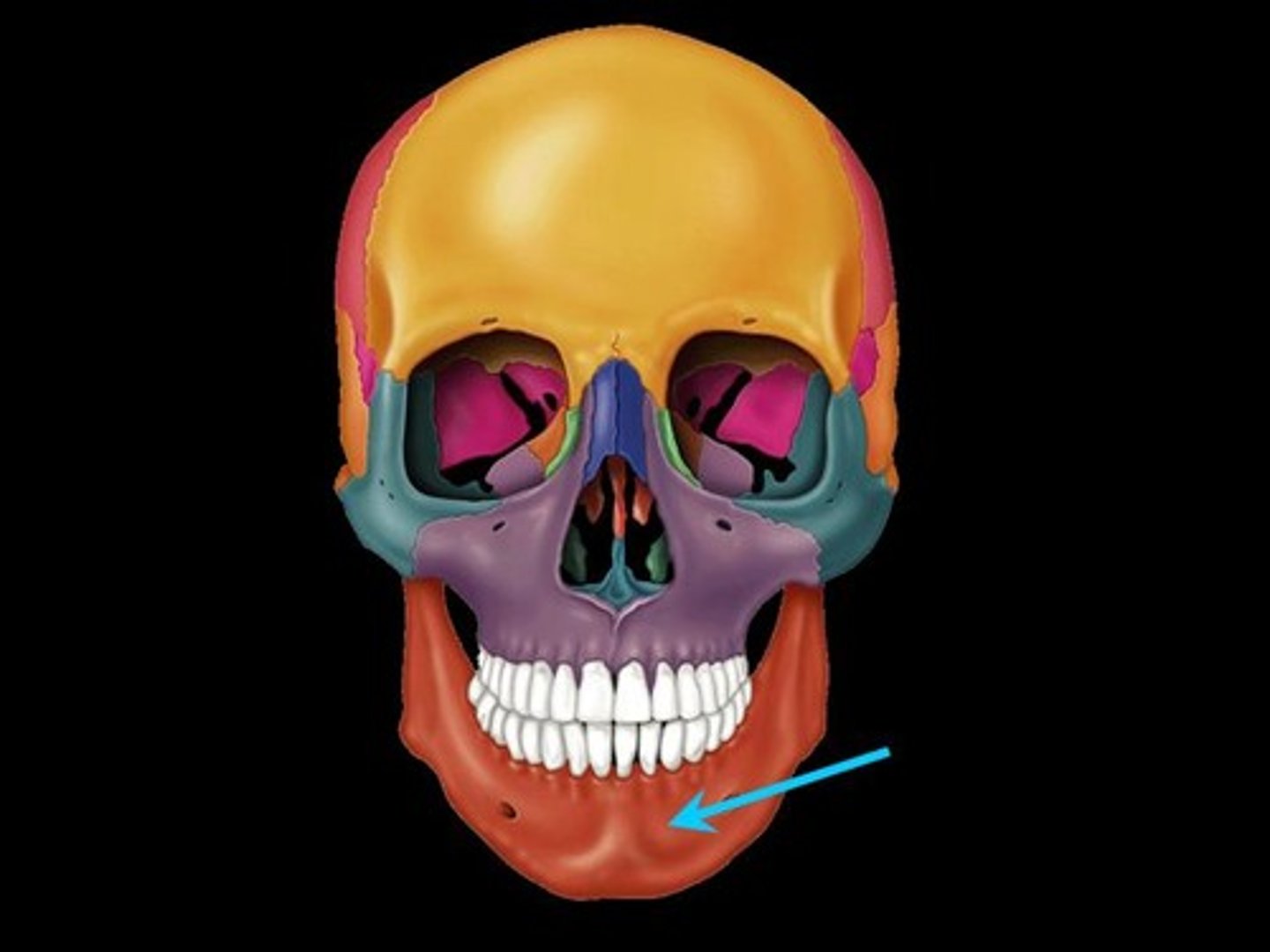
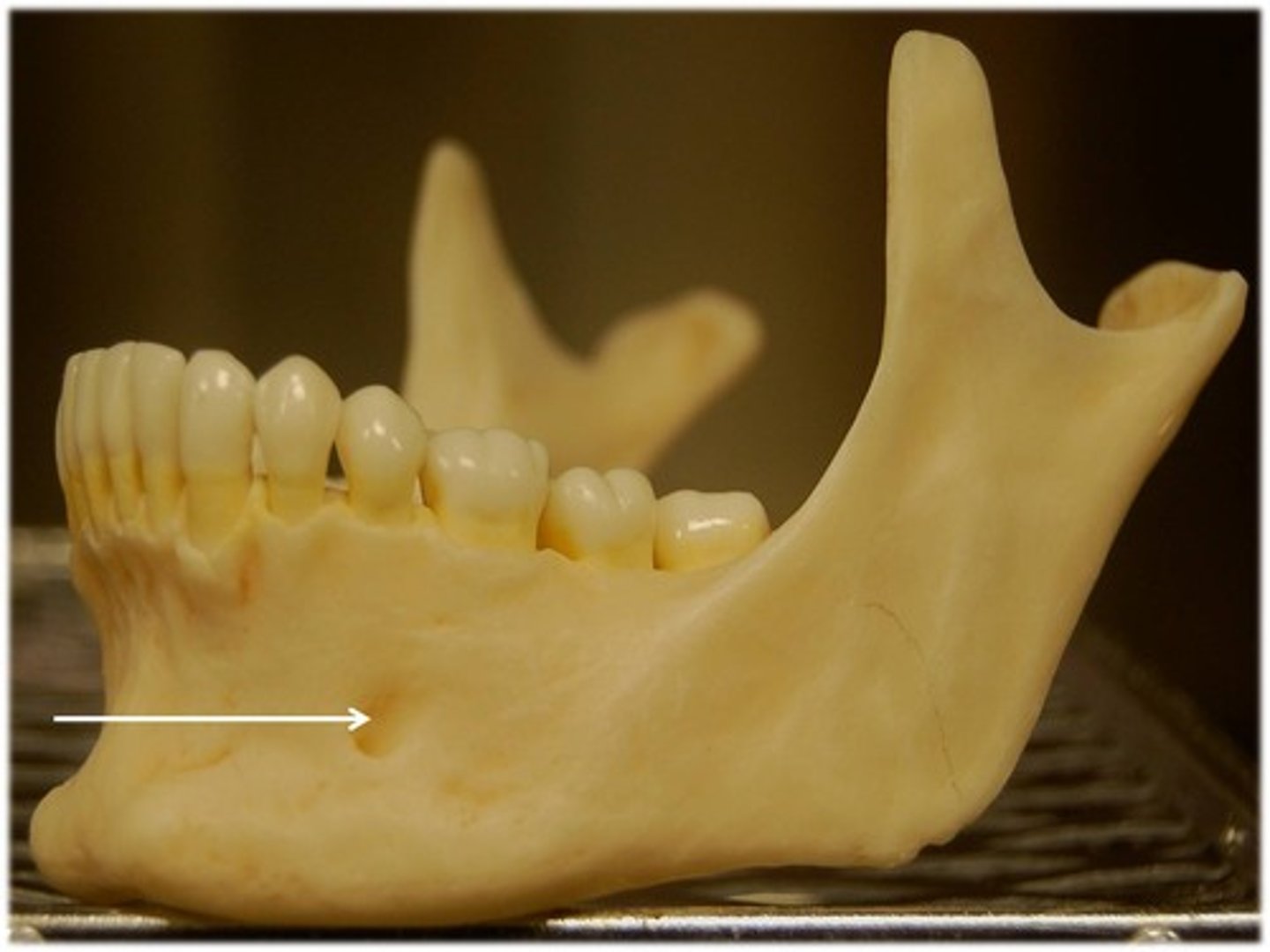
Mental foramen
-transmits CN V
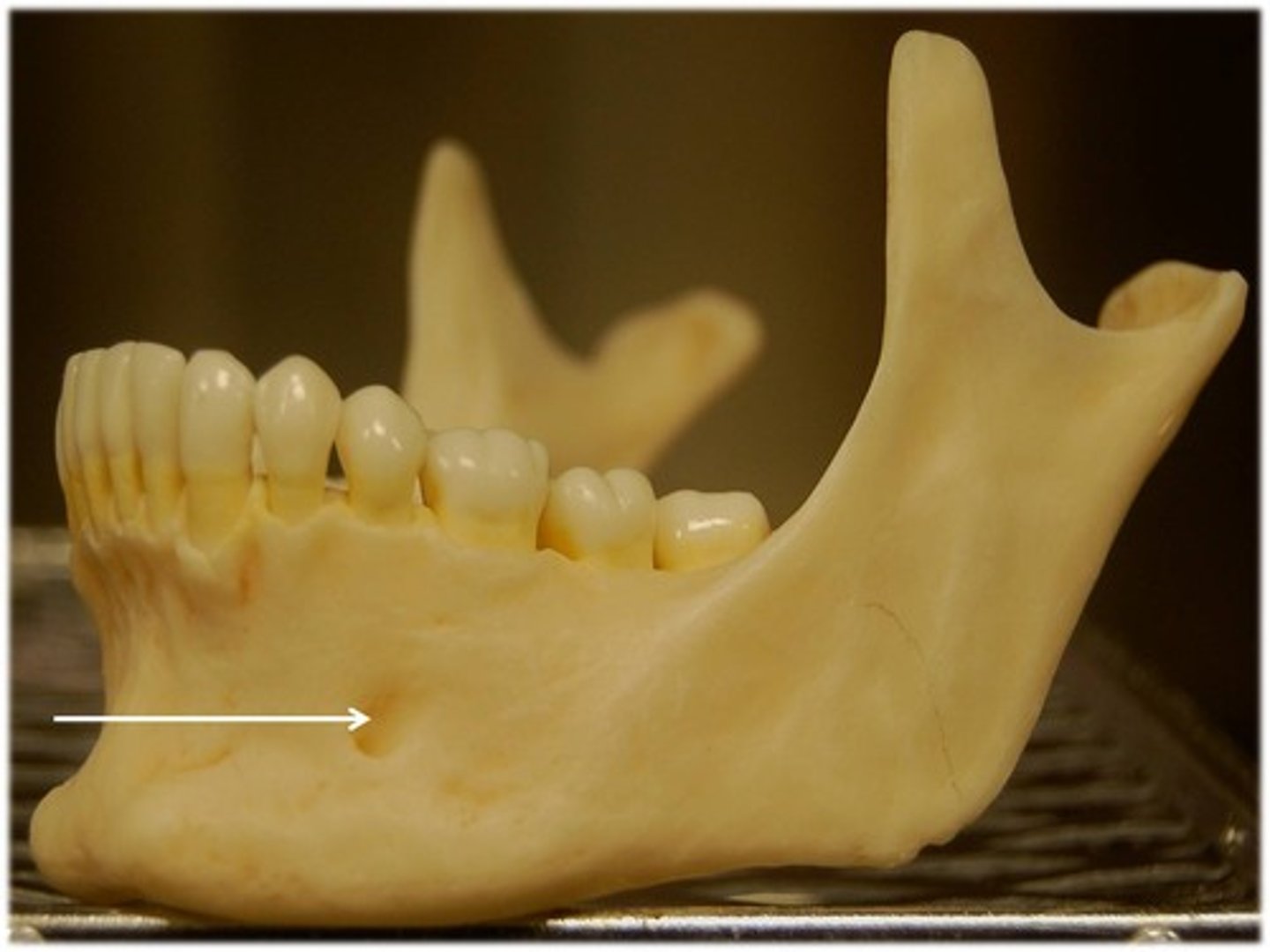
Mandibular foramen
-Path that inferior alveolar nerves enter the mandible through
Name the three parts of the Temporal bone
Squamous portion, Petrous portion, Tympanic ring
Mastoid process
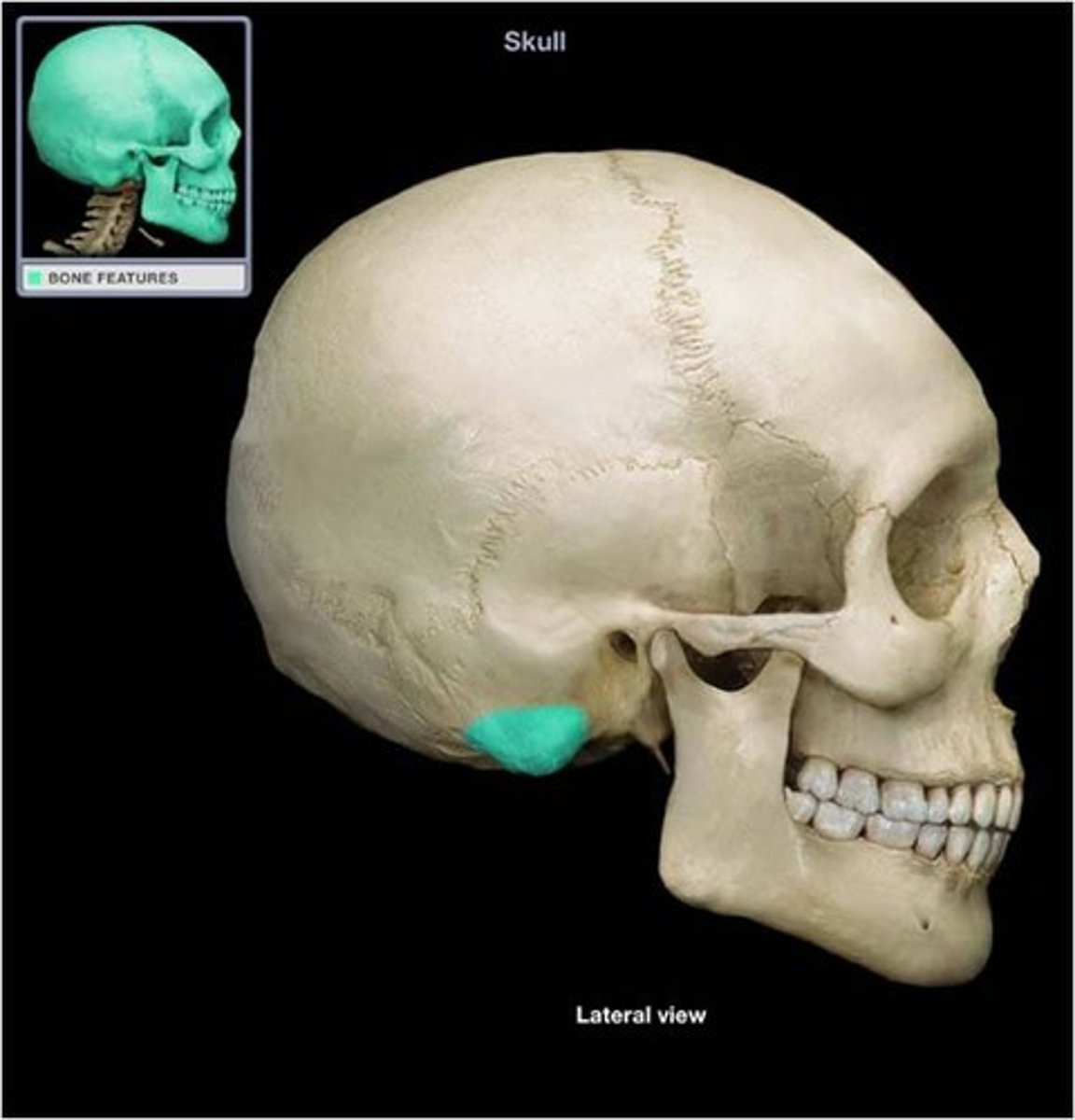
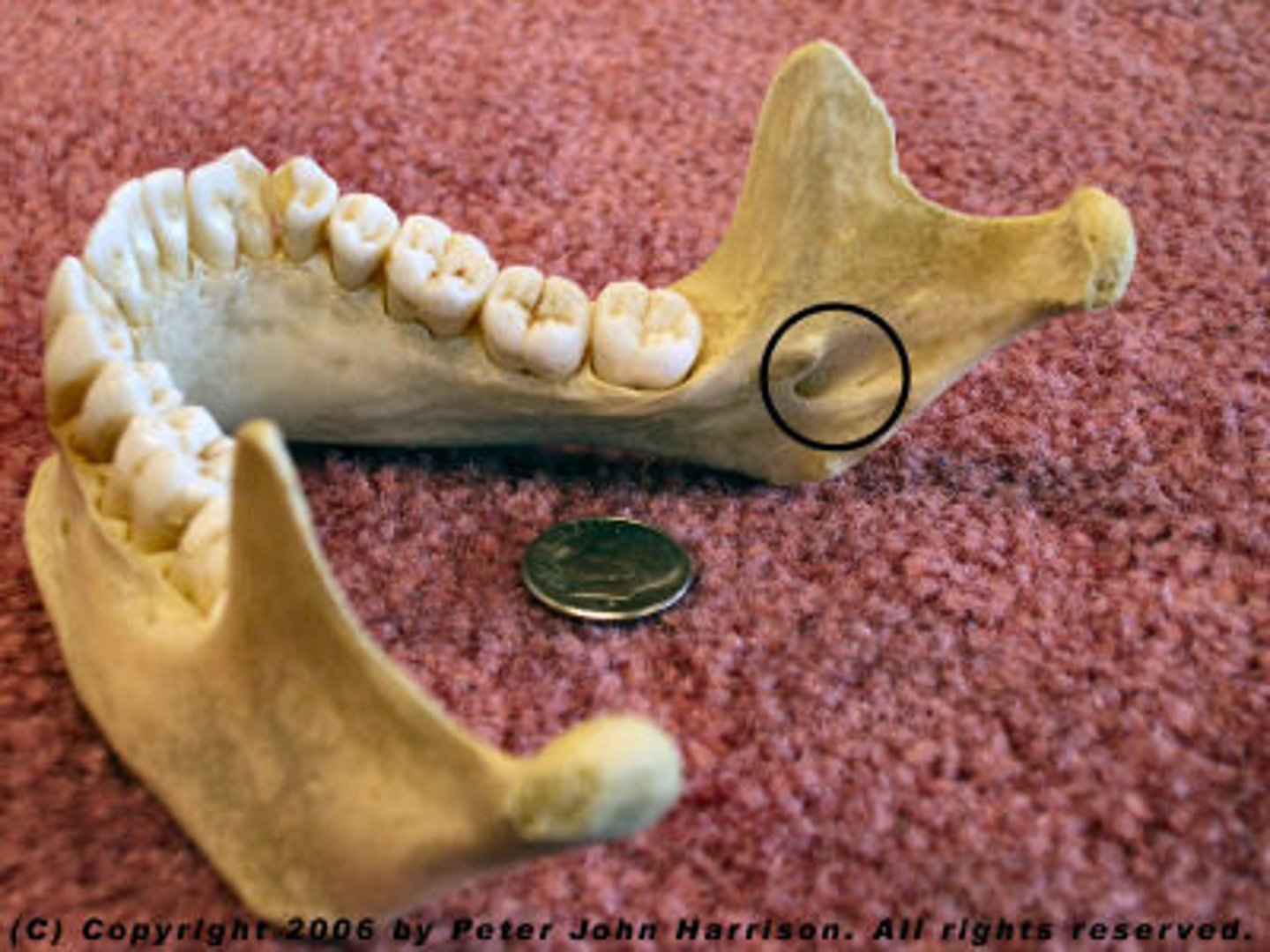
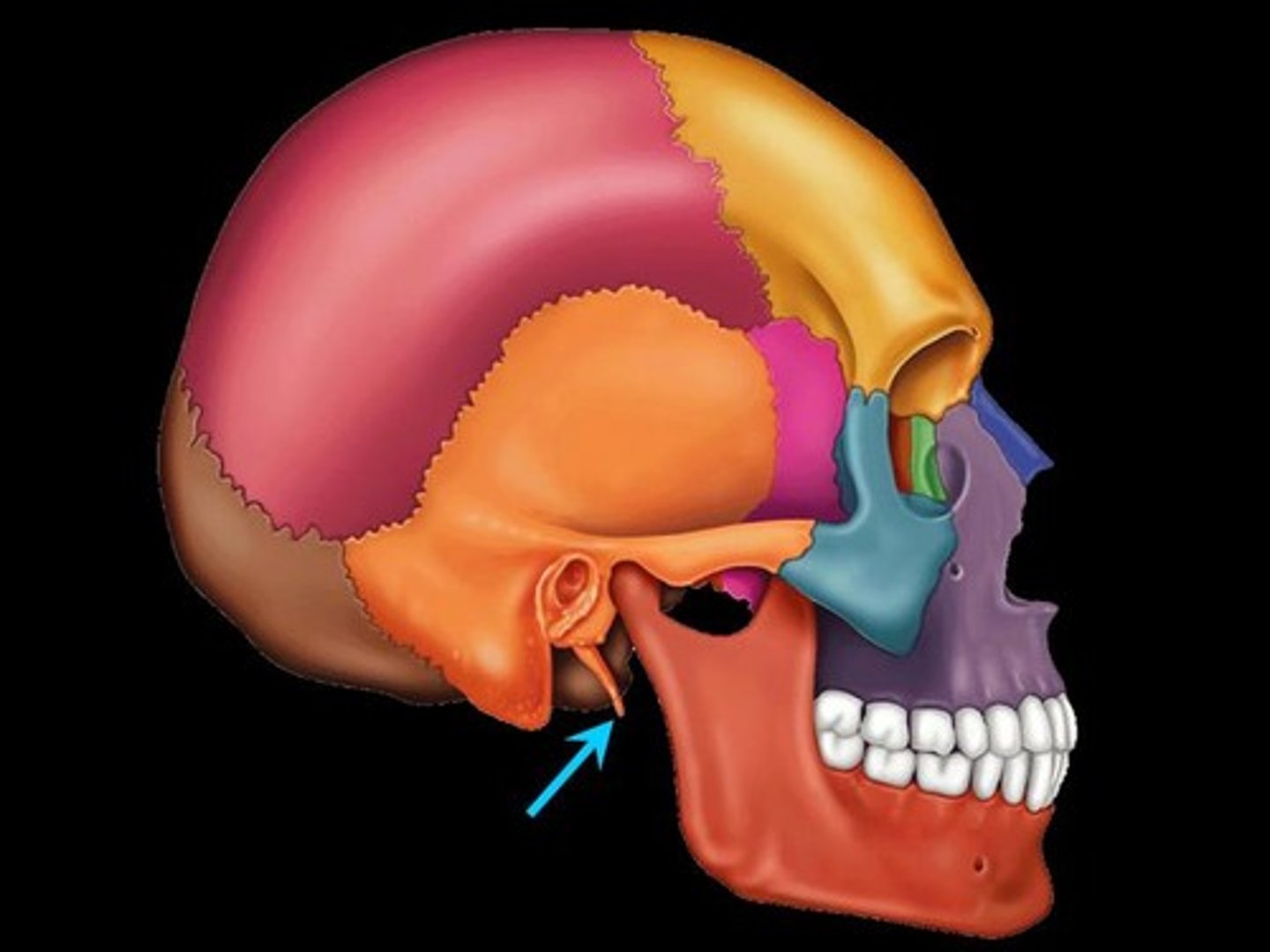
Styloid process
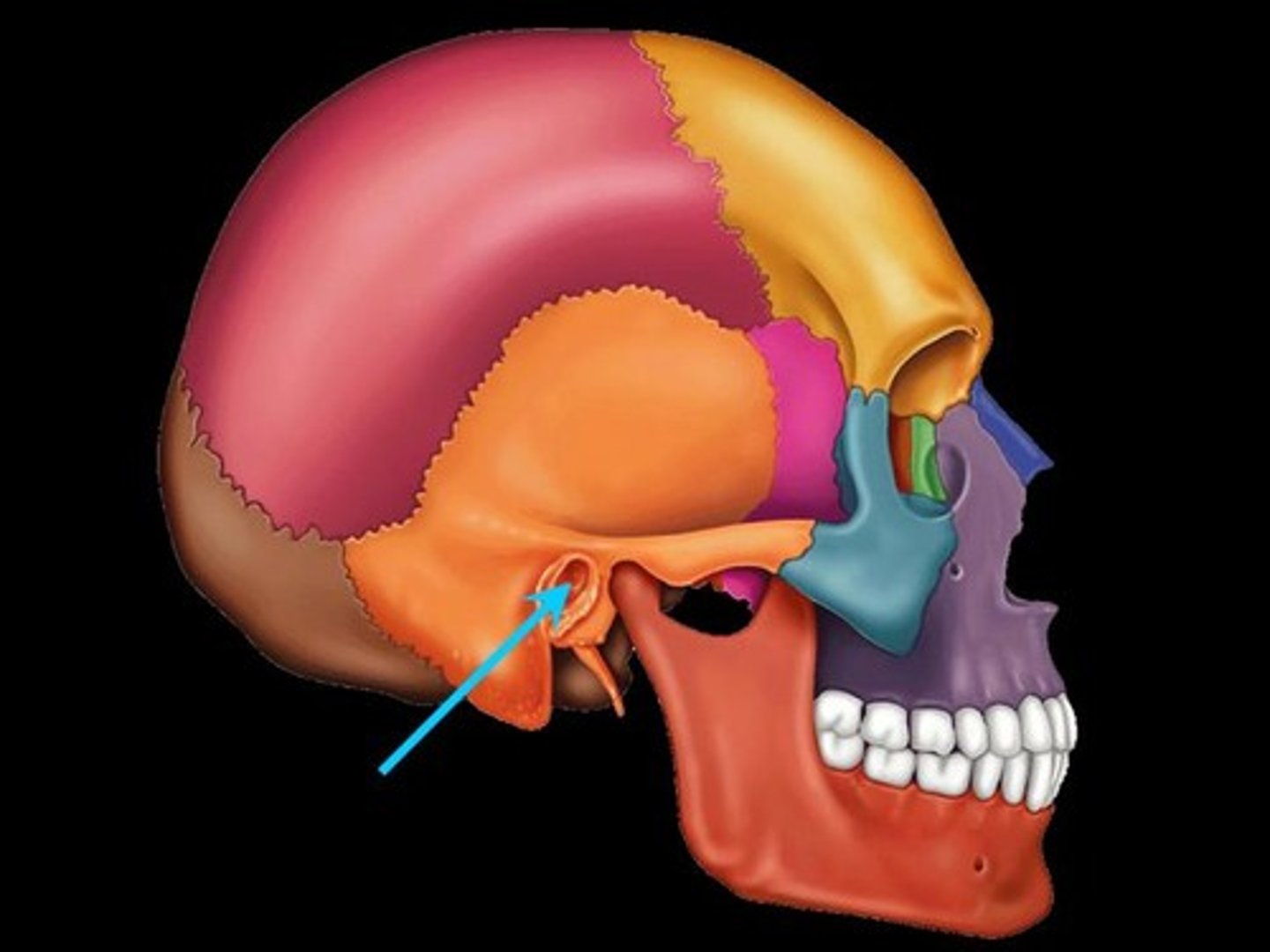
External auditory meatus
Foramen lacerum
-Associated bones: temporal and sphenoid
-Transmits: CN VII
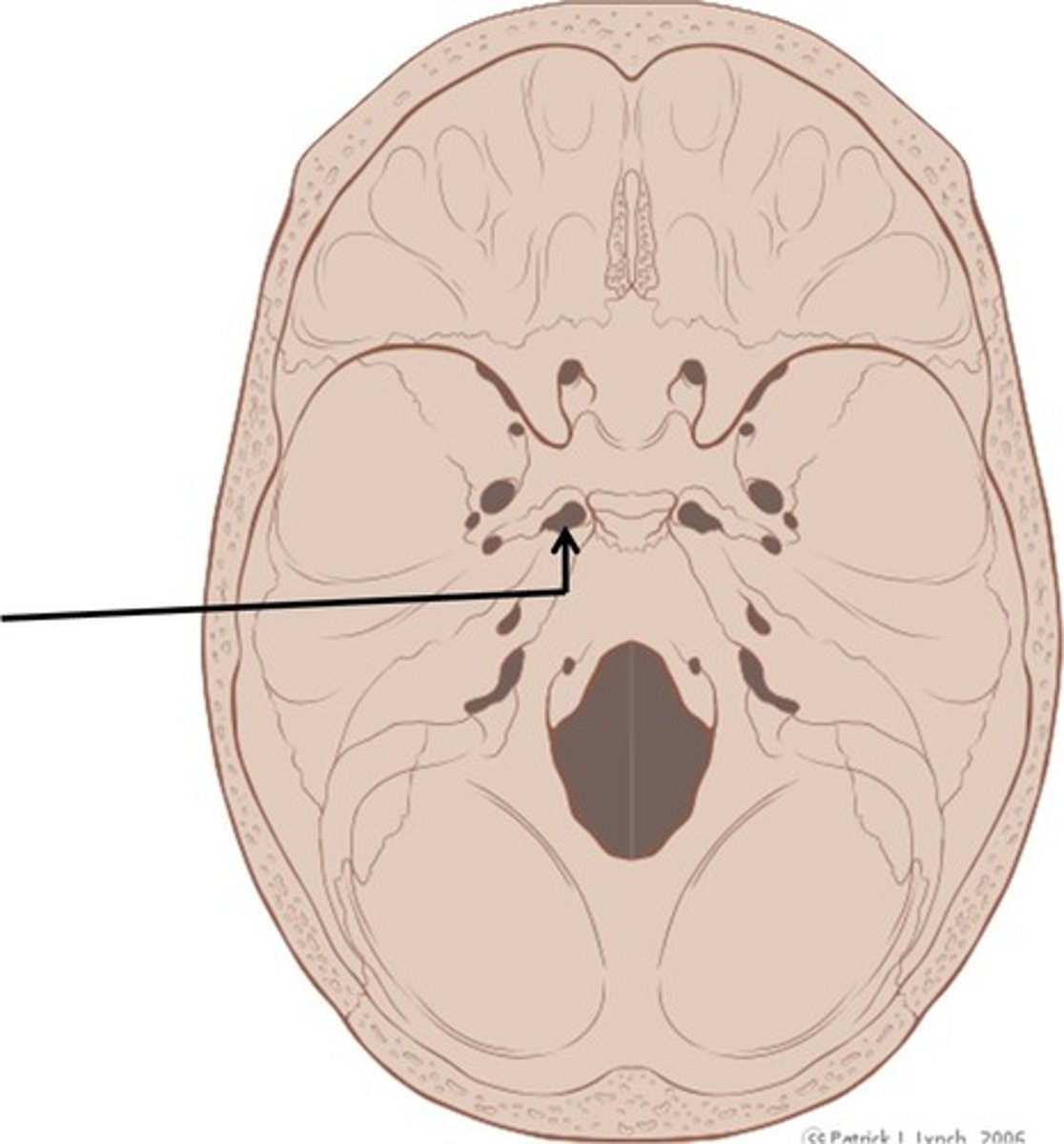
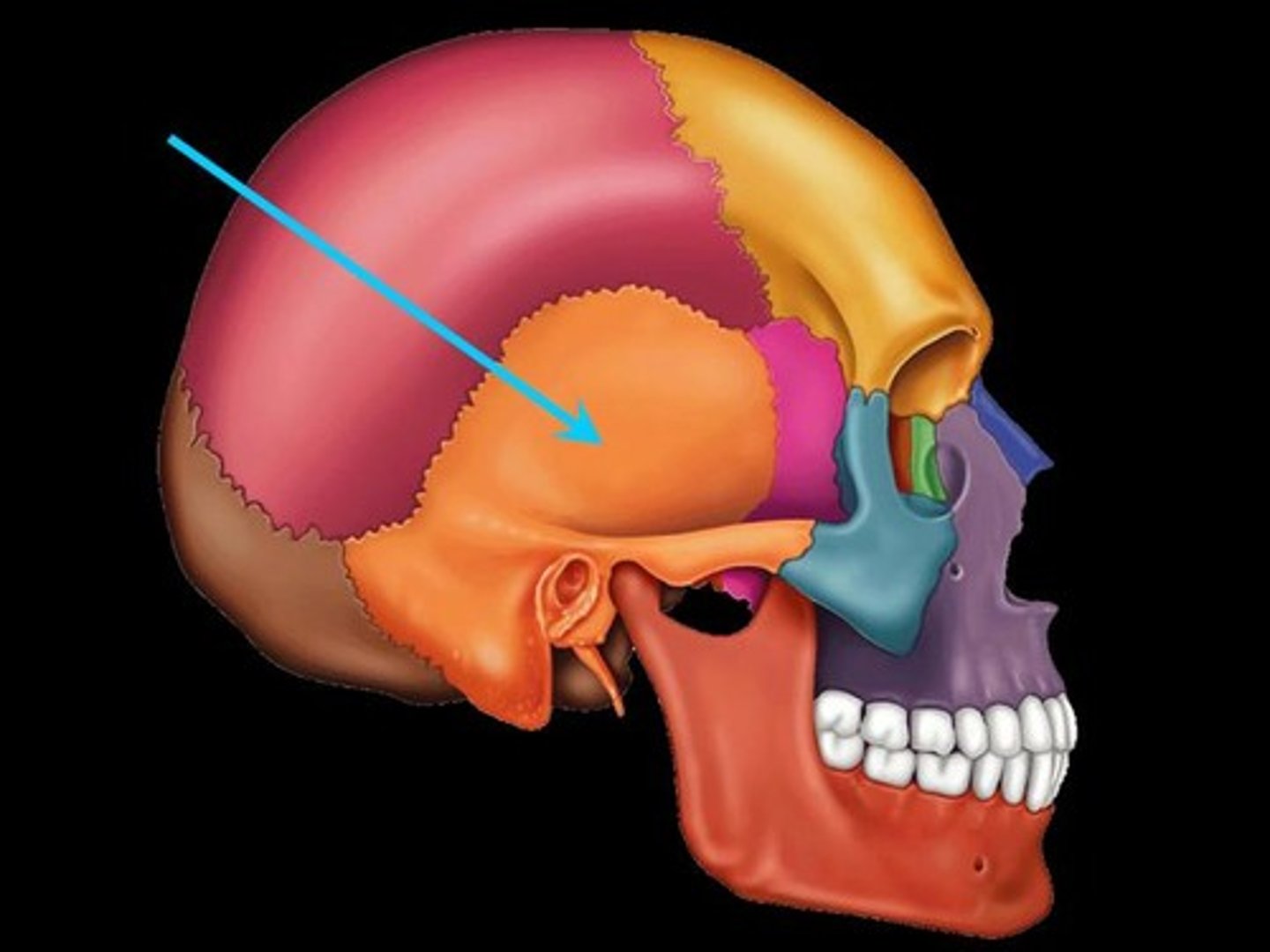
Jugular Foramen
-Associated bones: Temporal and Occipital
Transmits:
-CN, 9,10 and 11
-Internal Jugular
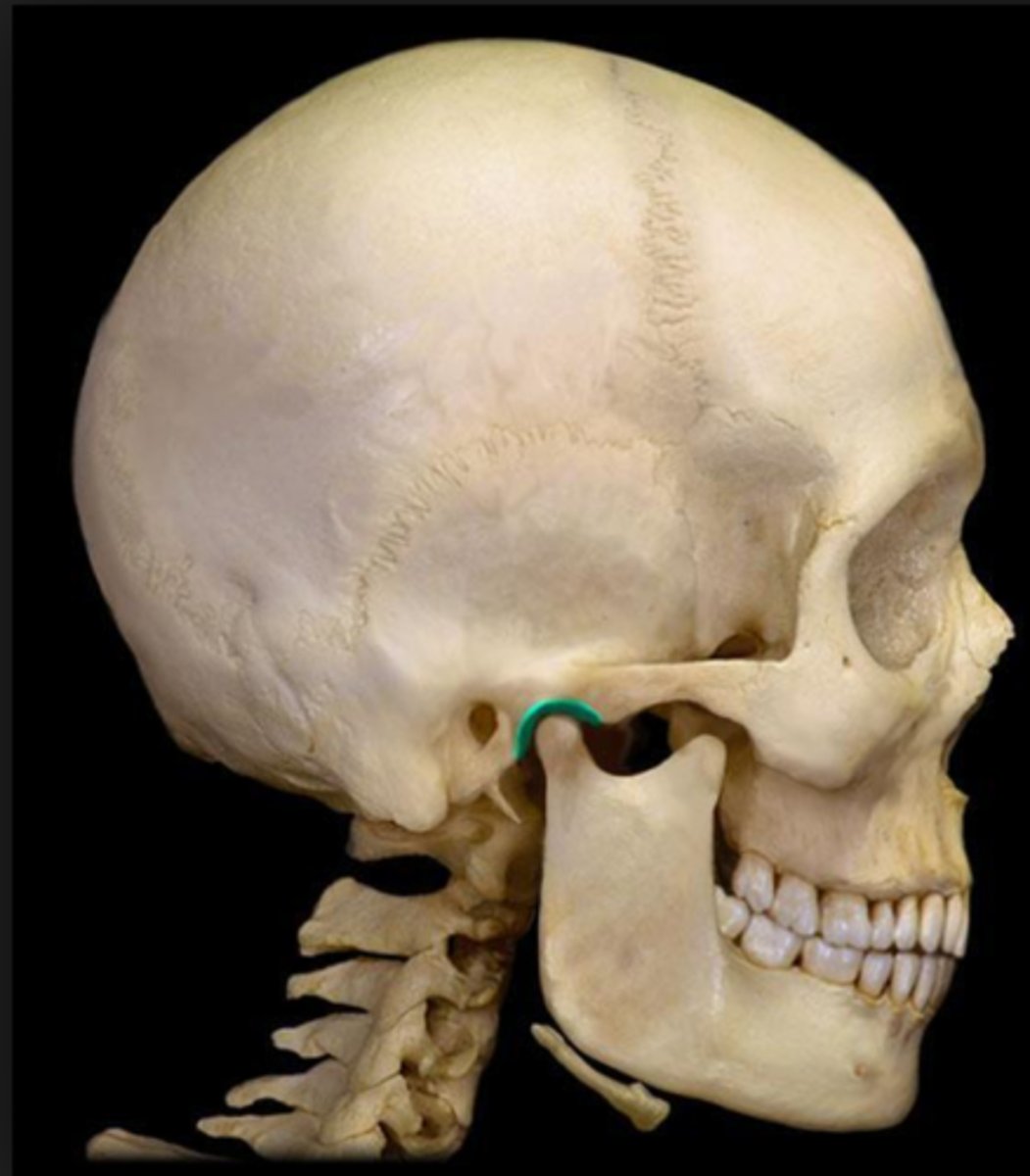
Glenoid Fossa
Articulates temporal bone with Mandible
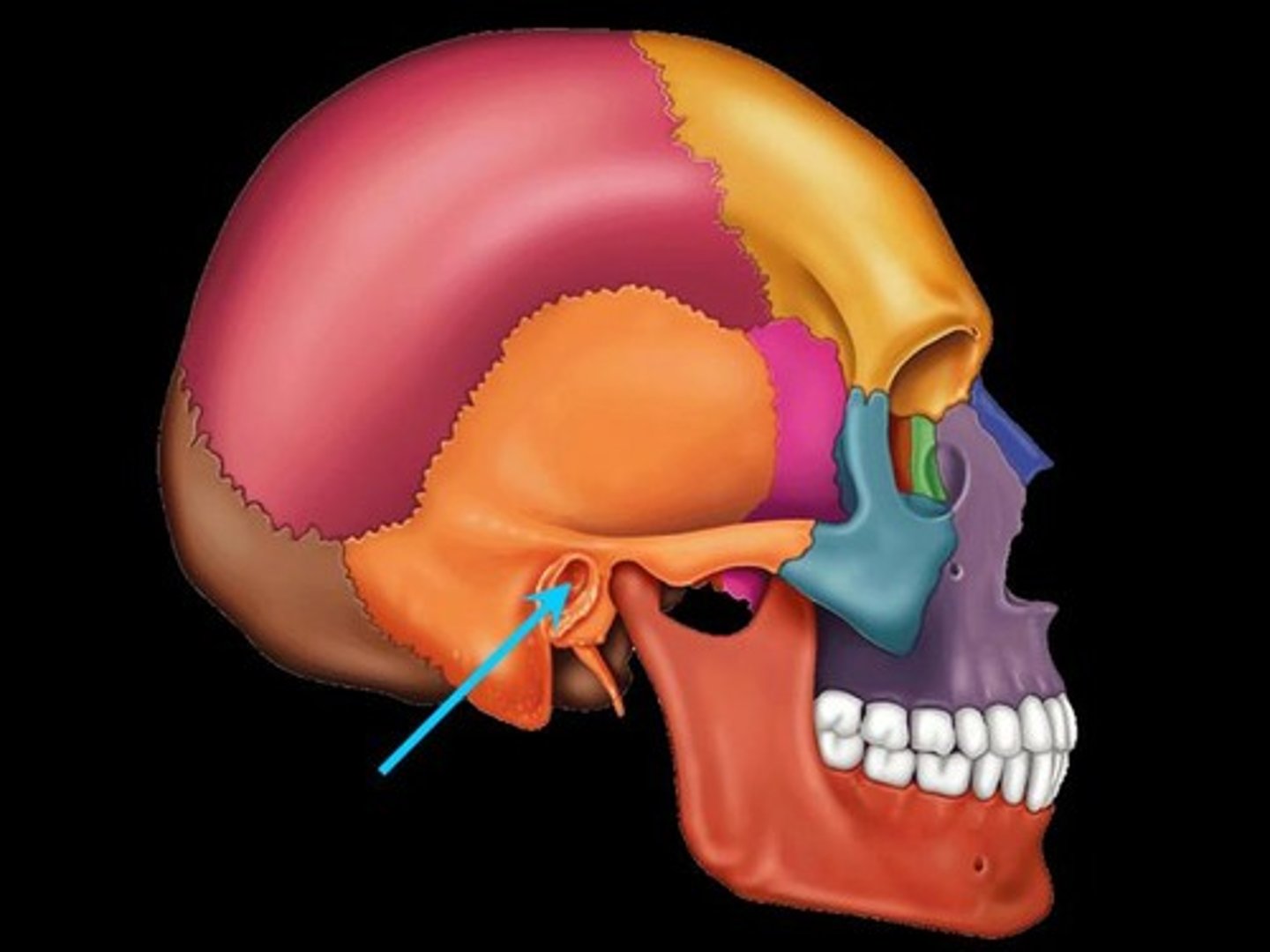
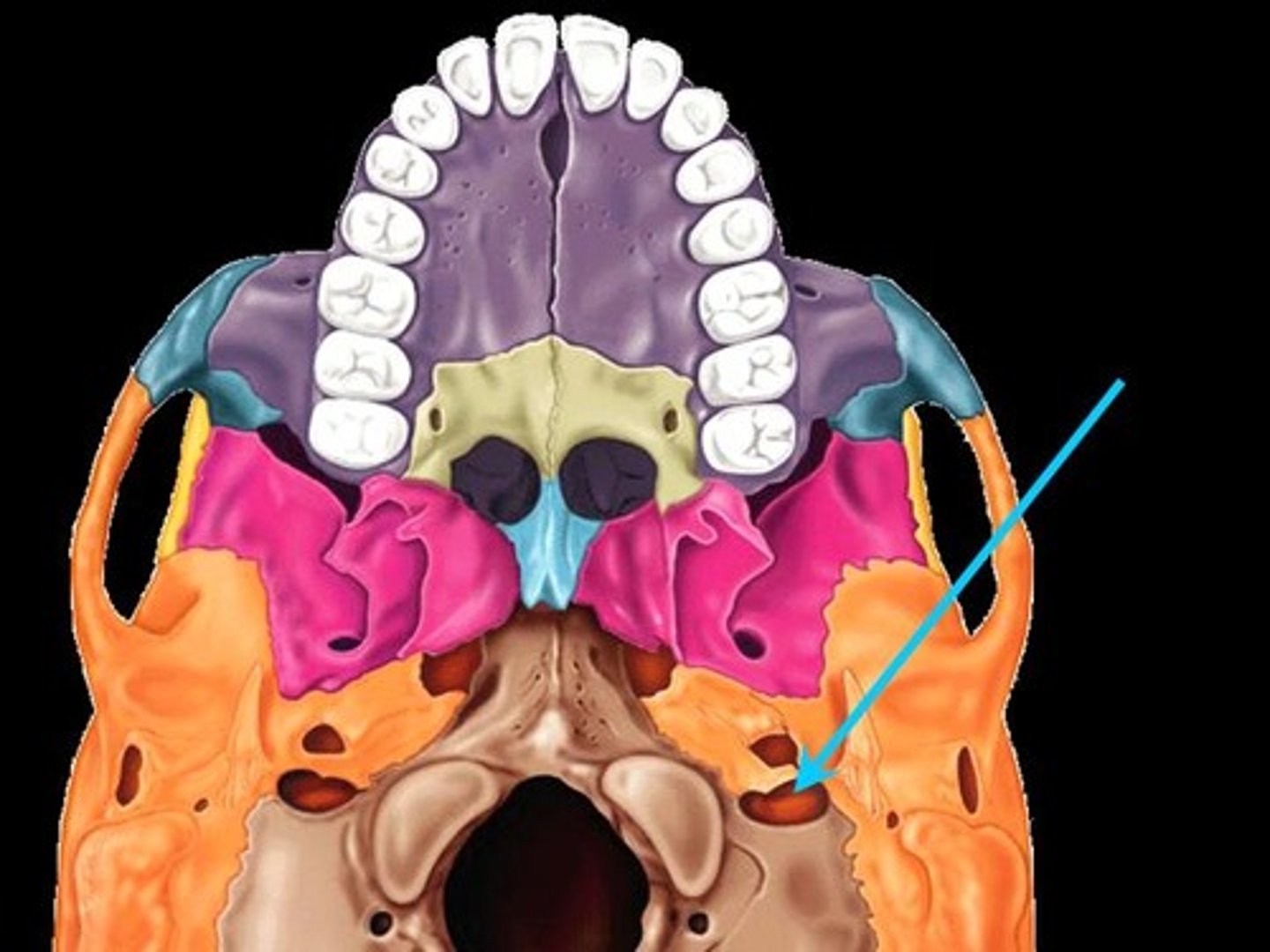
Stylomastoid Foramen
Associated bones: Temporal
Transmits: CN VII(facial nerve)
Zygomatic process
Bridge between zygomatic's and temporal bone
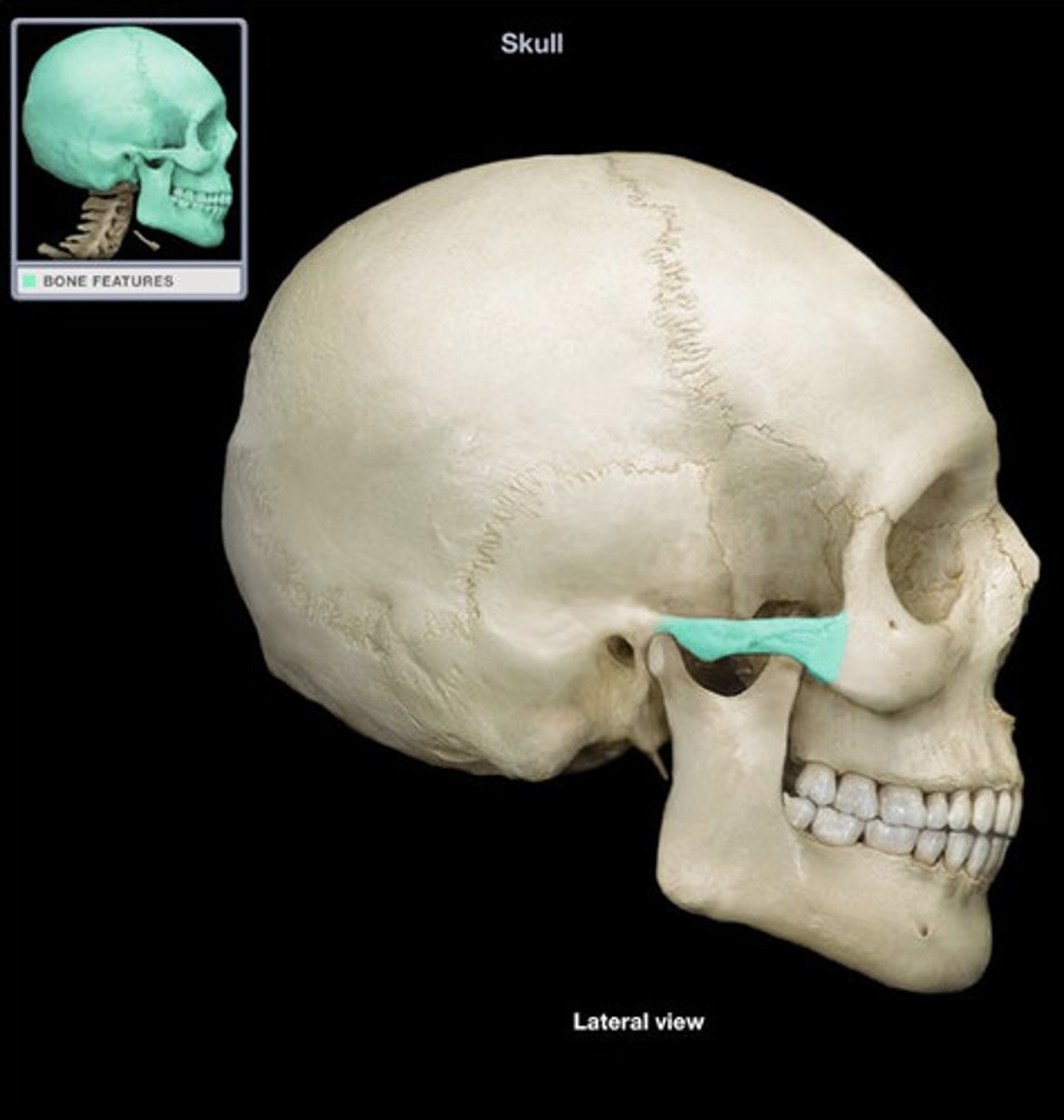
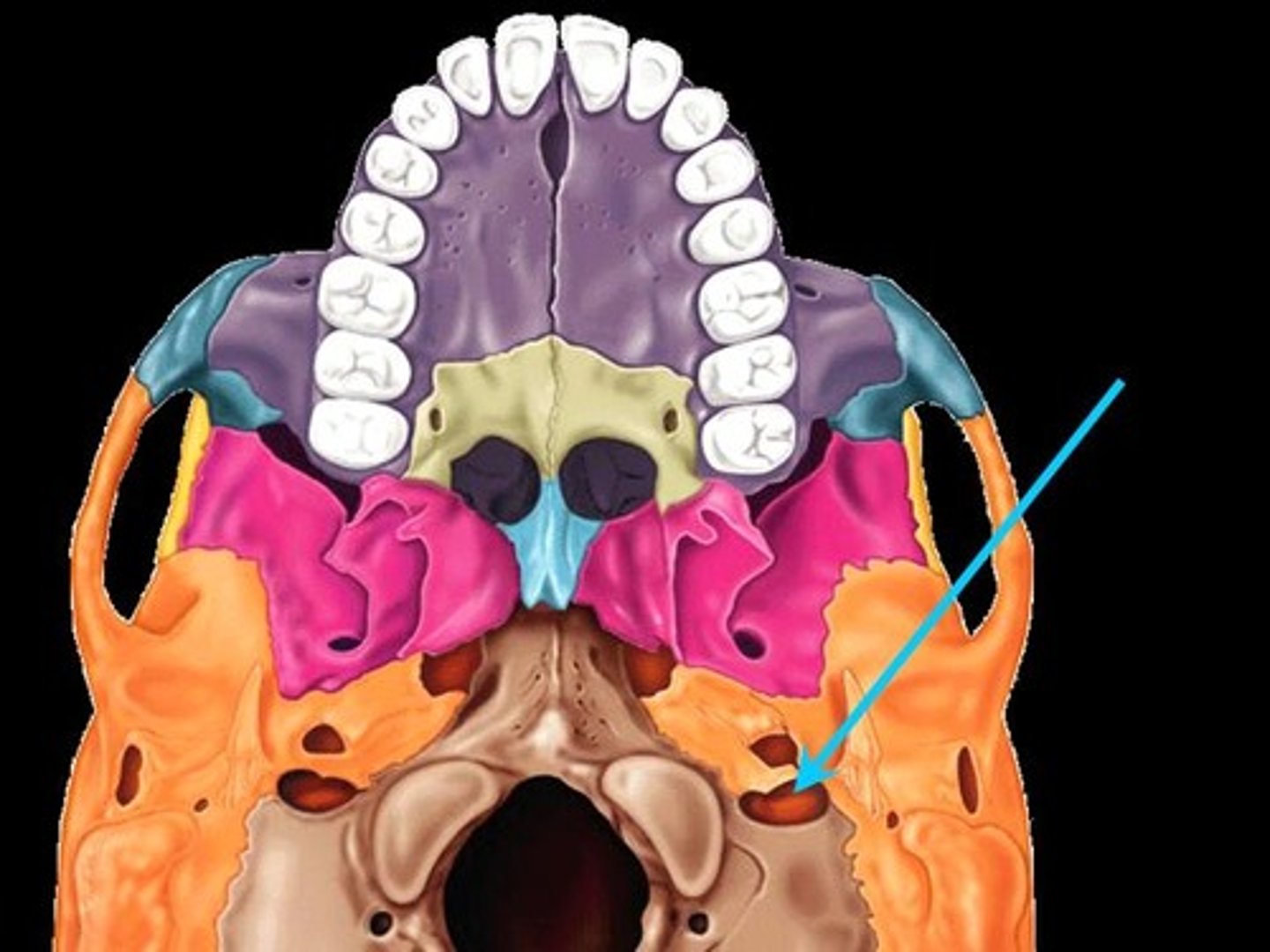
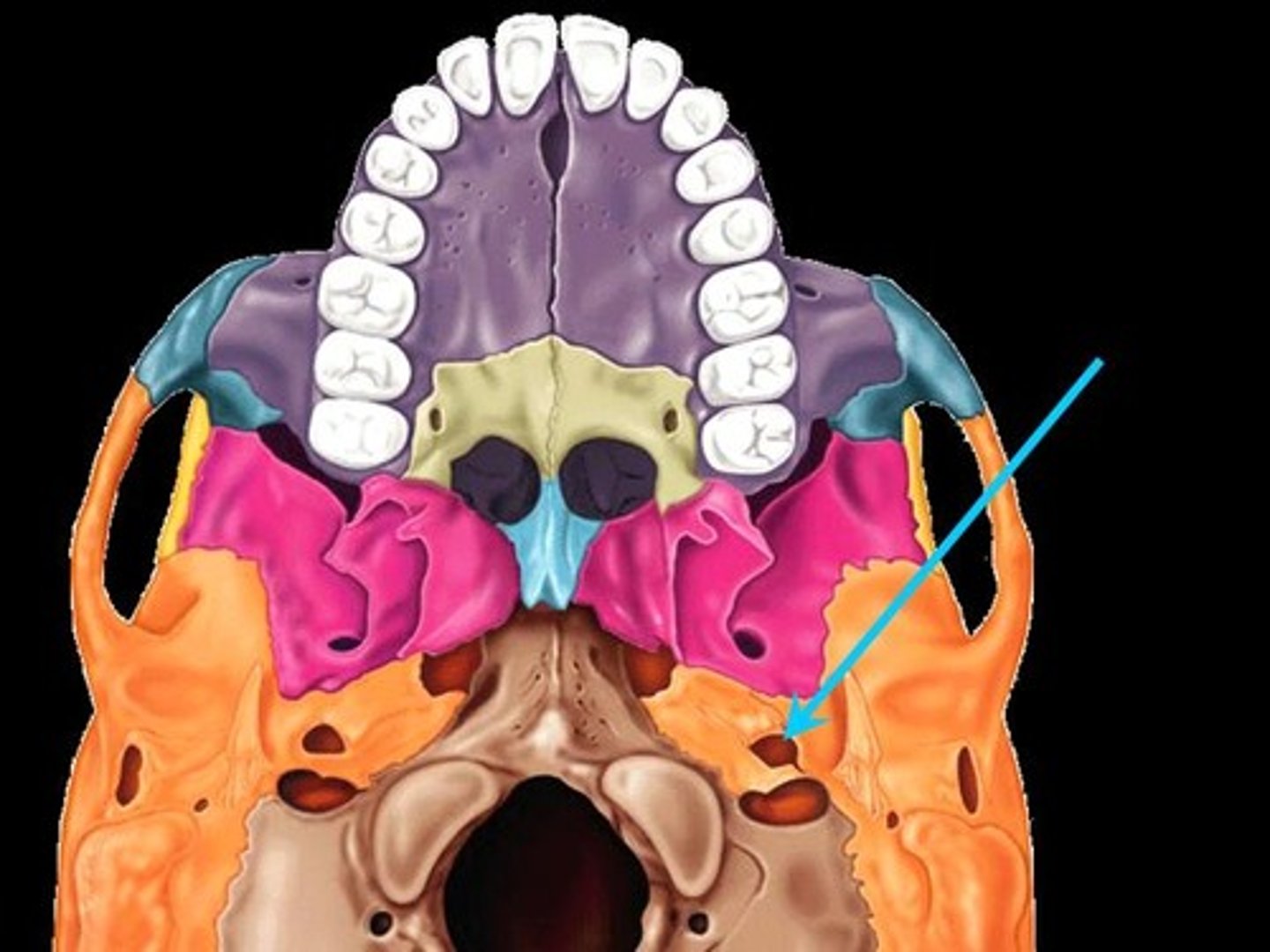
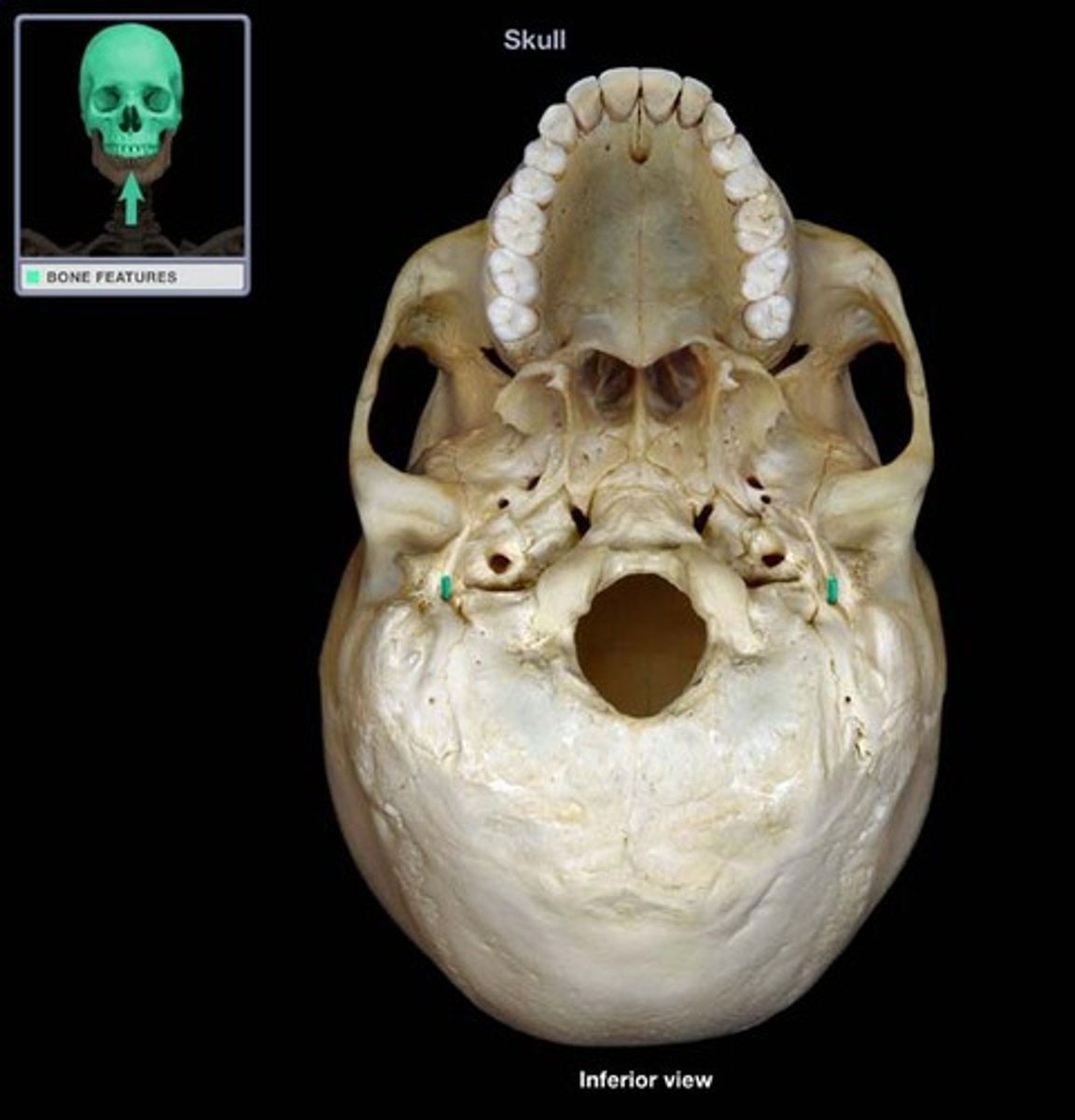
Carotid Foramen
Associated bones: Temporal
Transmits: Internal Carotid artery
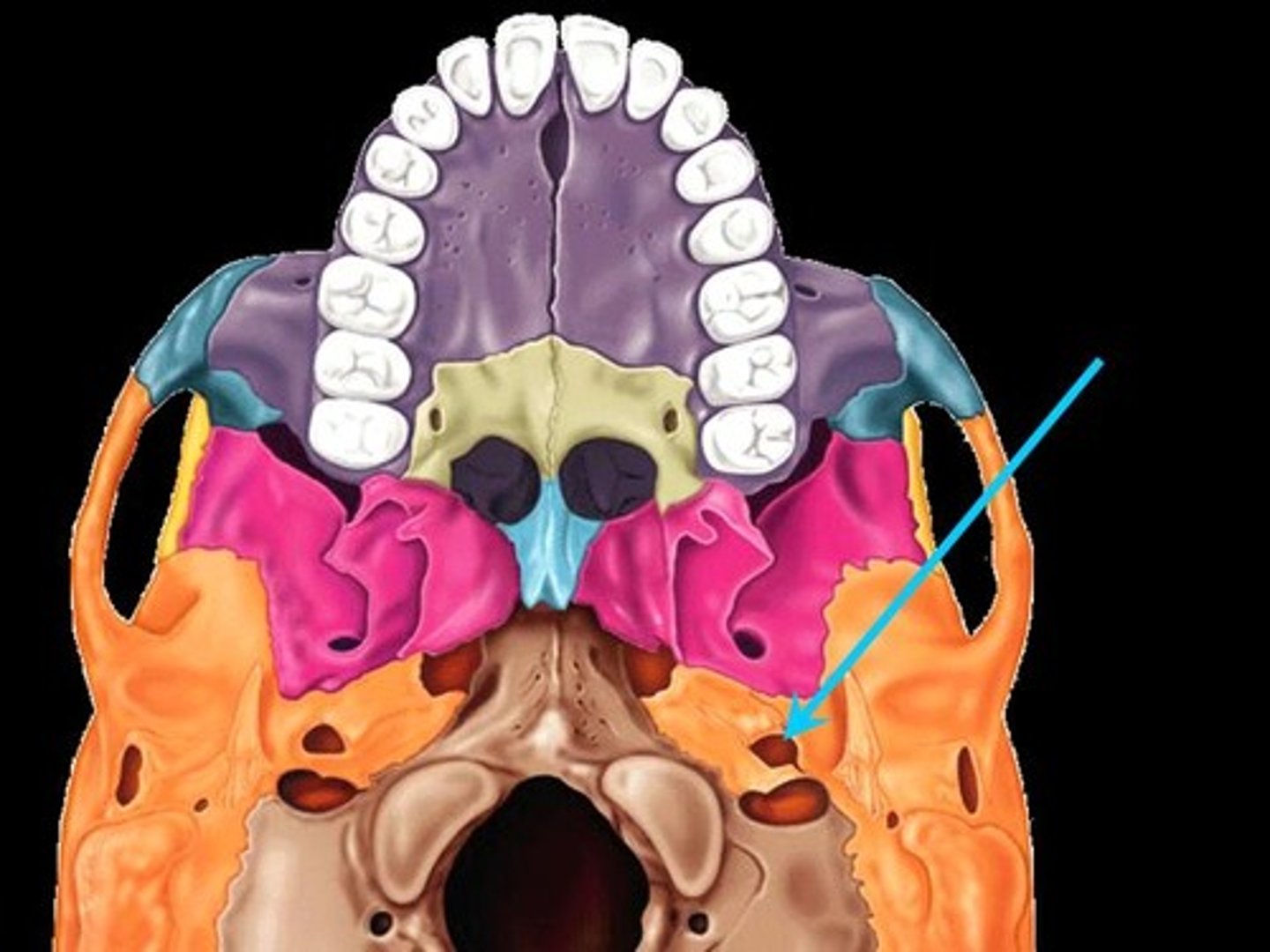
Where us the middle inner ear located?
petrous portion
Greater and lesser wings
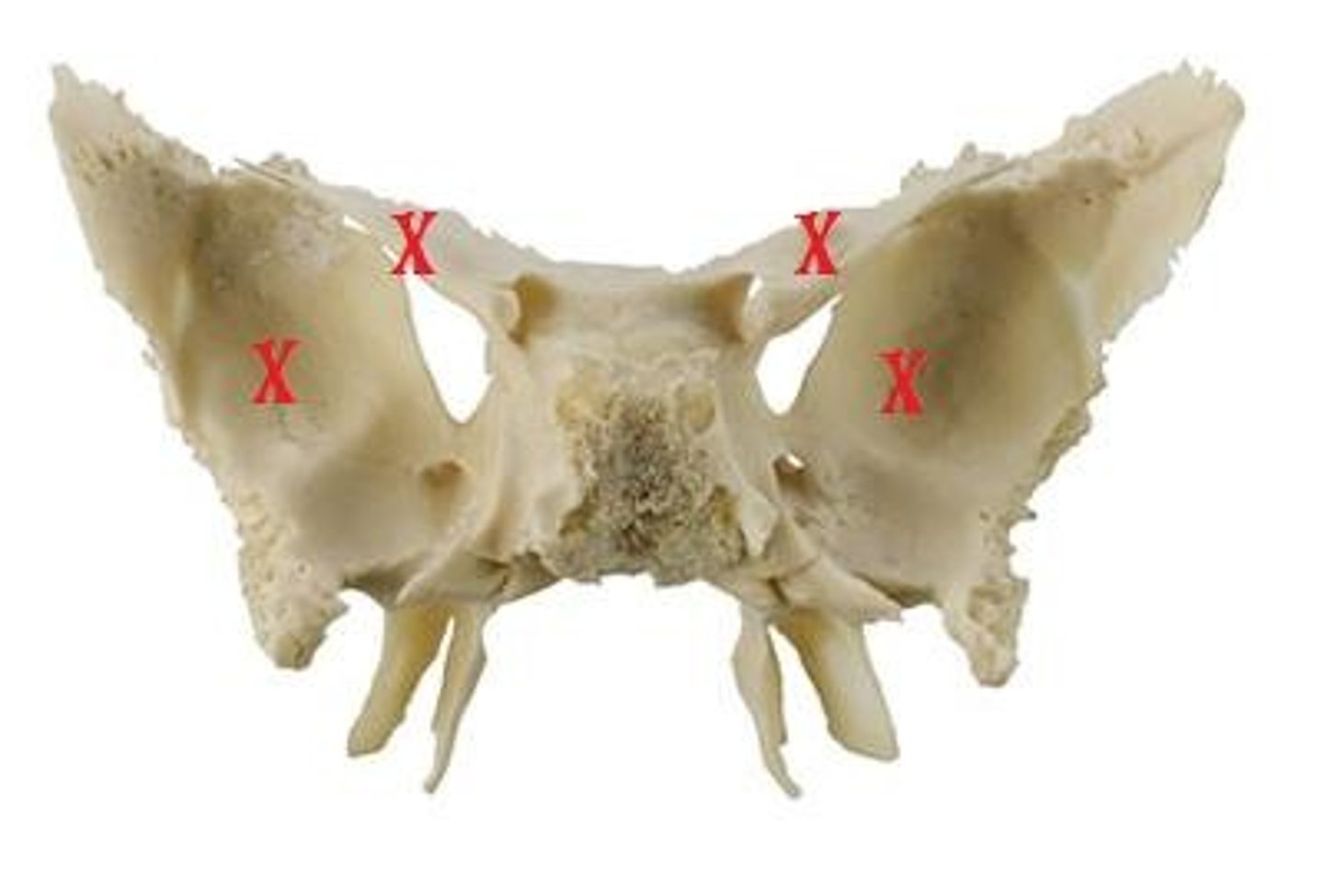
Medial and lateral pterygoid plates
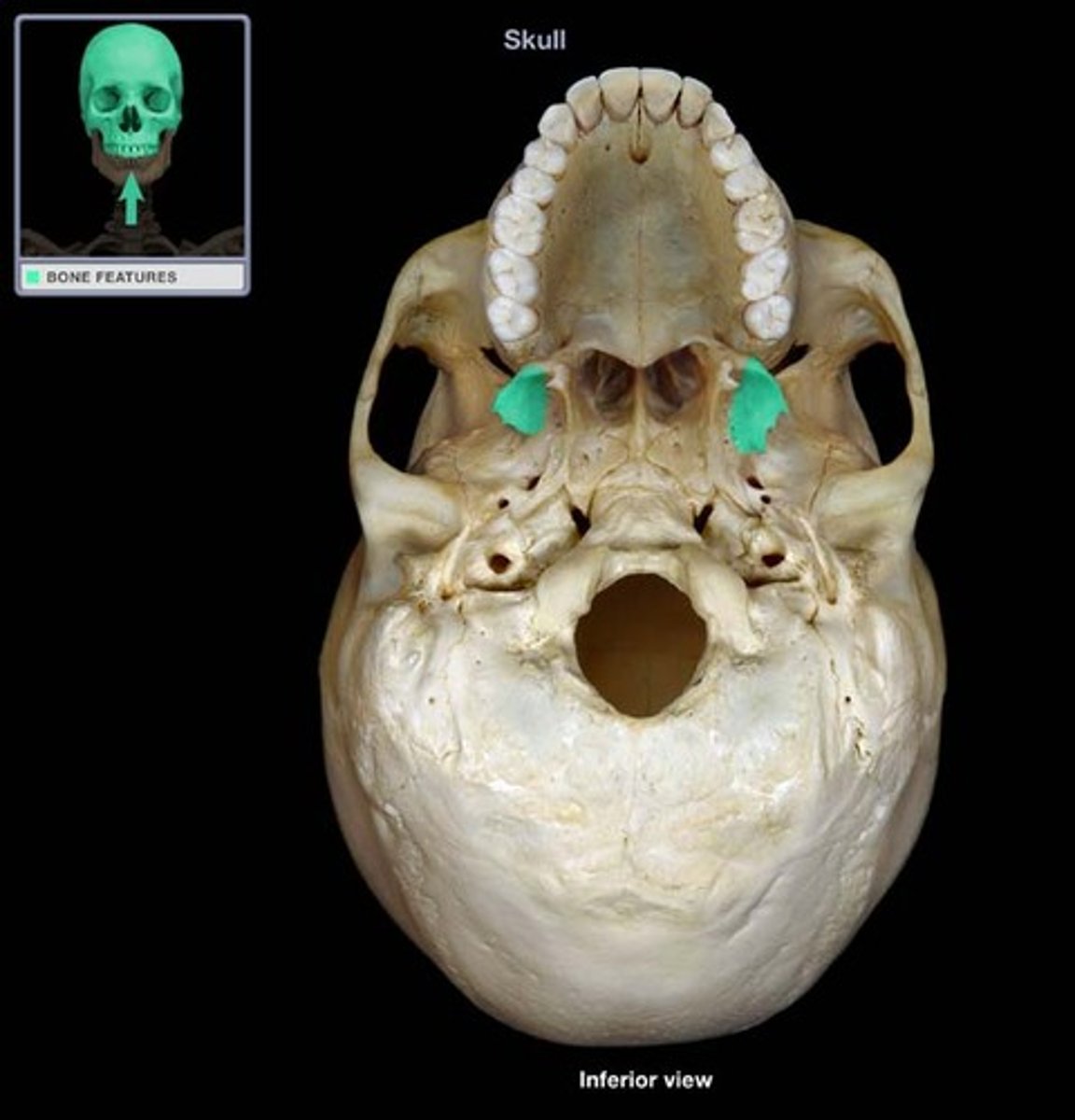
Foramen rotundum
Associated Bones: sphenoid bone
Transmits: Maxillary V2
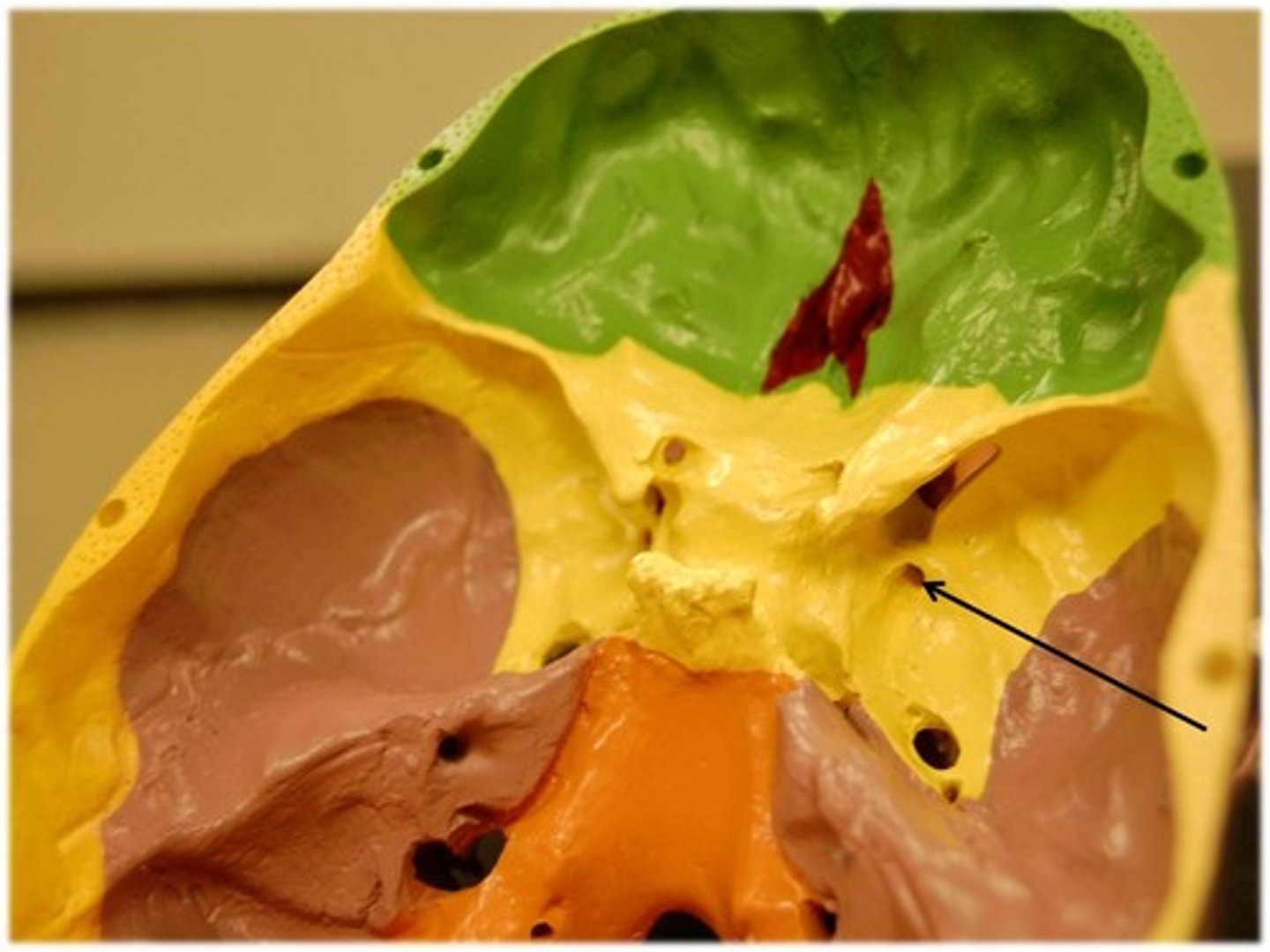
Foramen spinosum
Associated bones: Sphenoid bone
Transmits: middle meningeal
Sella Turica
Medial superior portion of sphenoid
Superior orbital fissure
Associated bones: Sphenoid(B/t greater and lesser wings)
Transmits: CN 3,4,5 and 6
Foramen ovale
Associated bones: Sphenoid
Transmits: V3
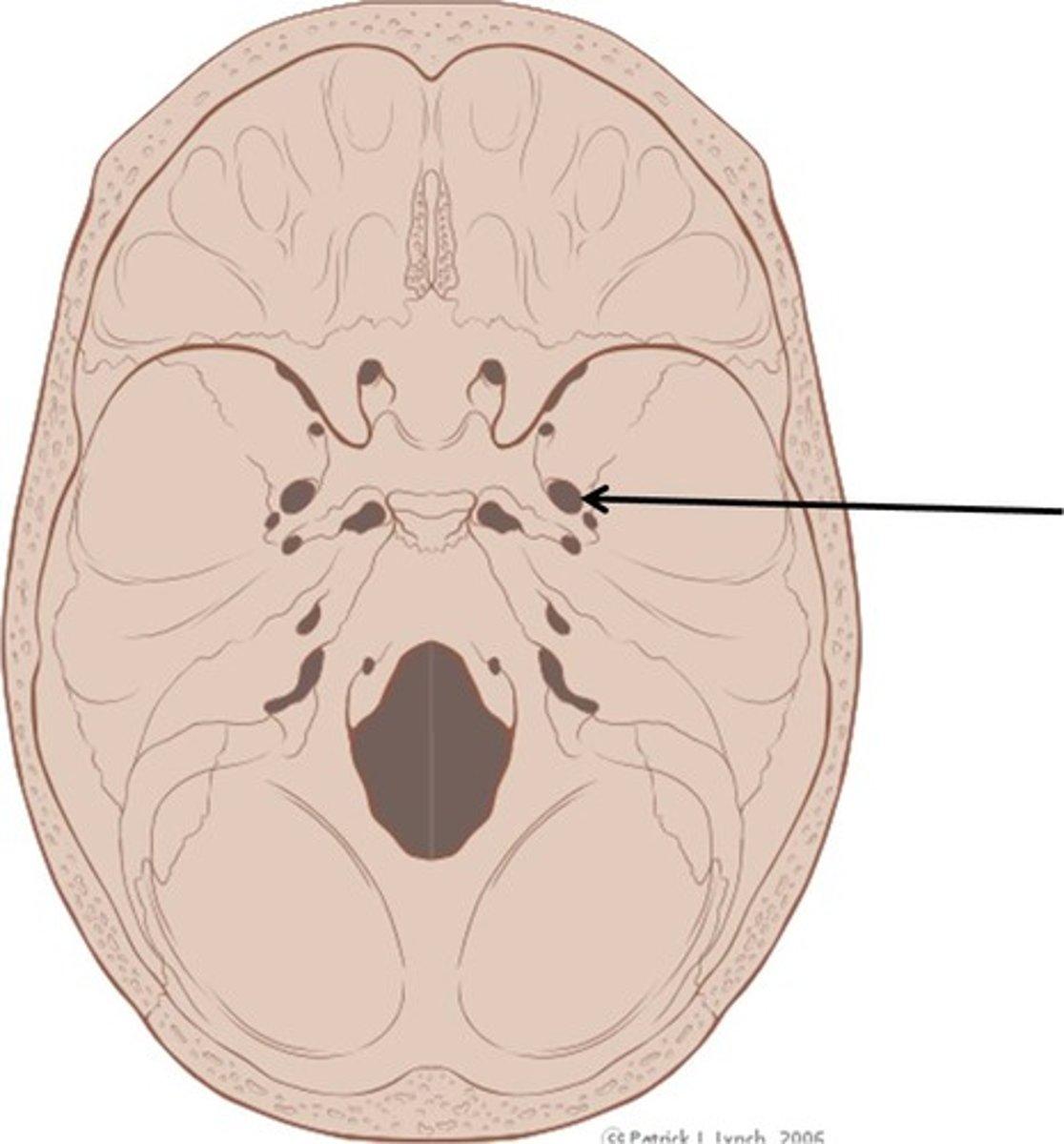
The superior and middle conchae are part of which bones?
Ethmoid
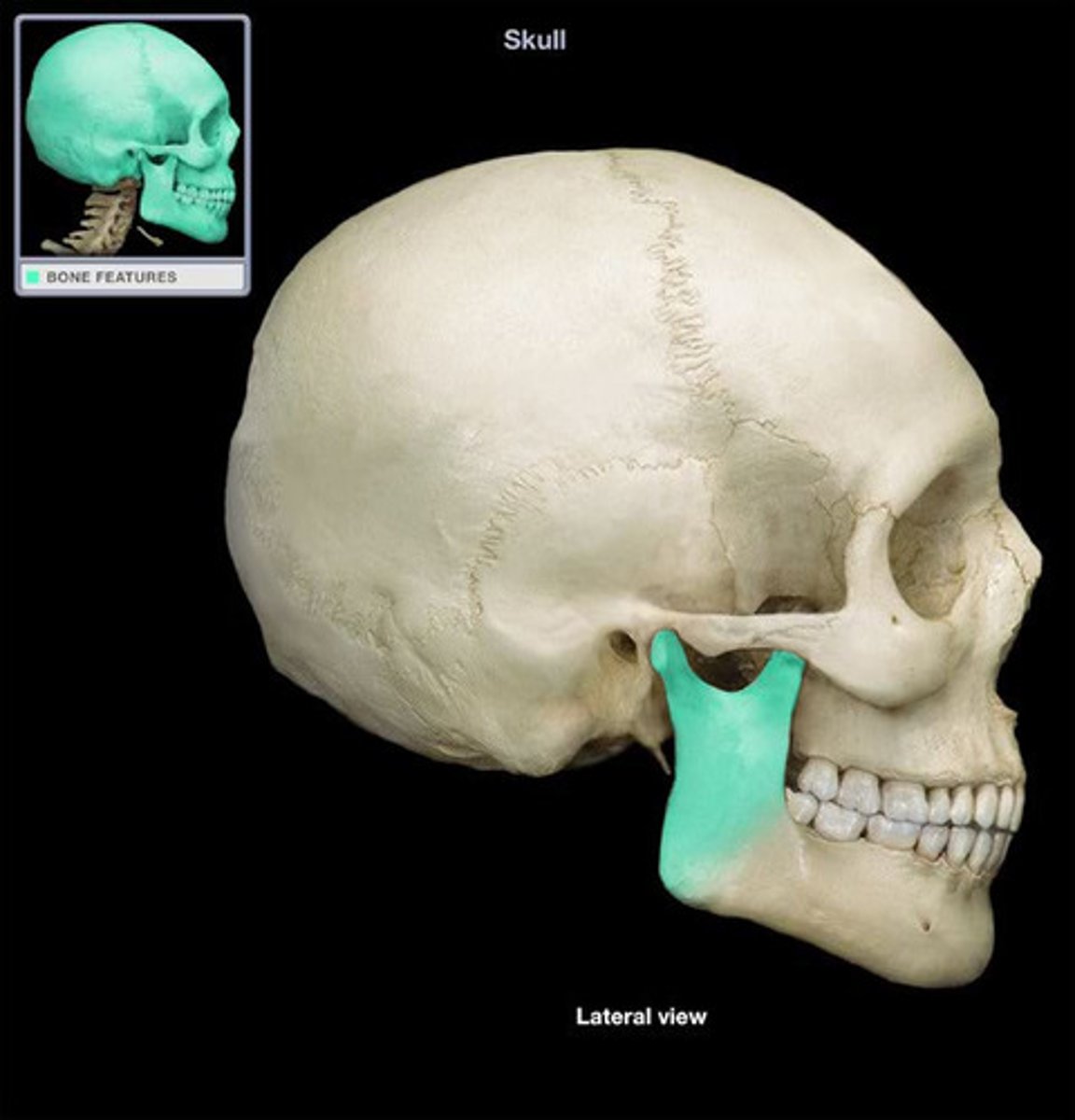
Mandible body
Mandible ramus
Mandible coronoid process
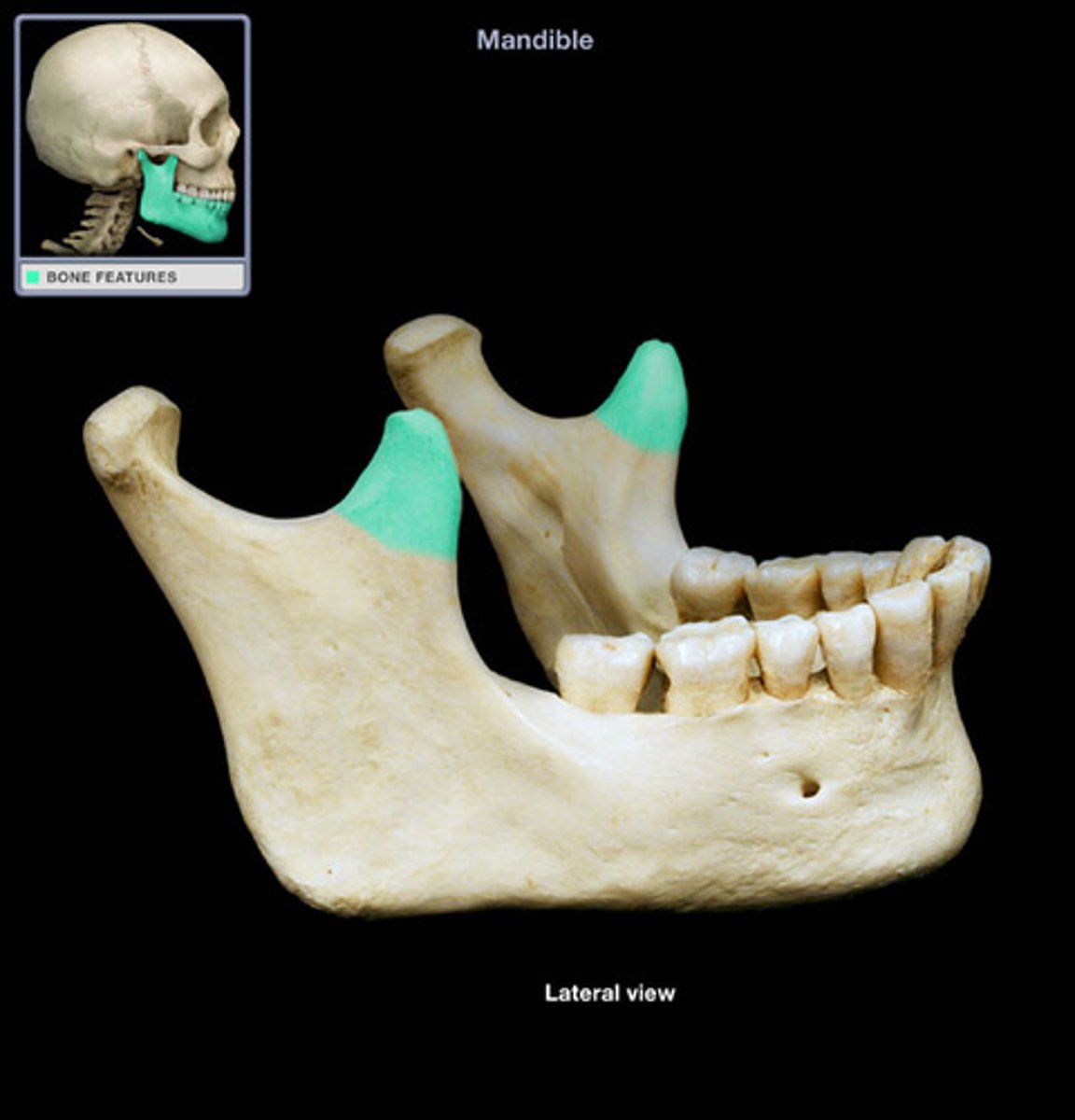
Mandibular condyle
Articulates with glenoid fossa
Mental protuberence
Mental foramen
Alveolar process
Mandibular foramen
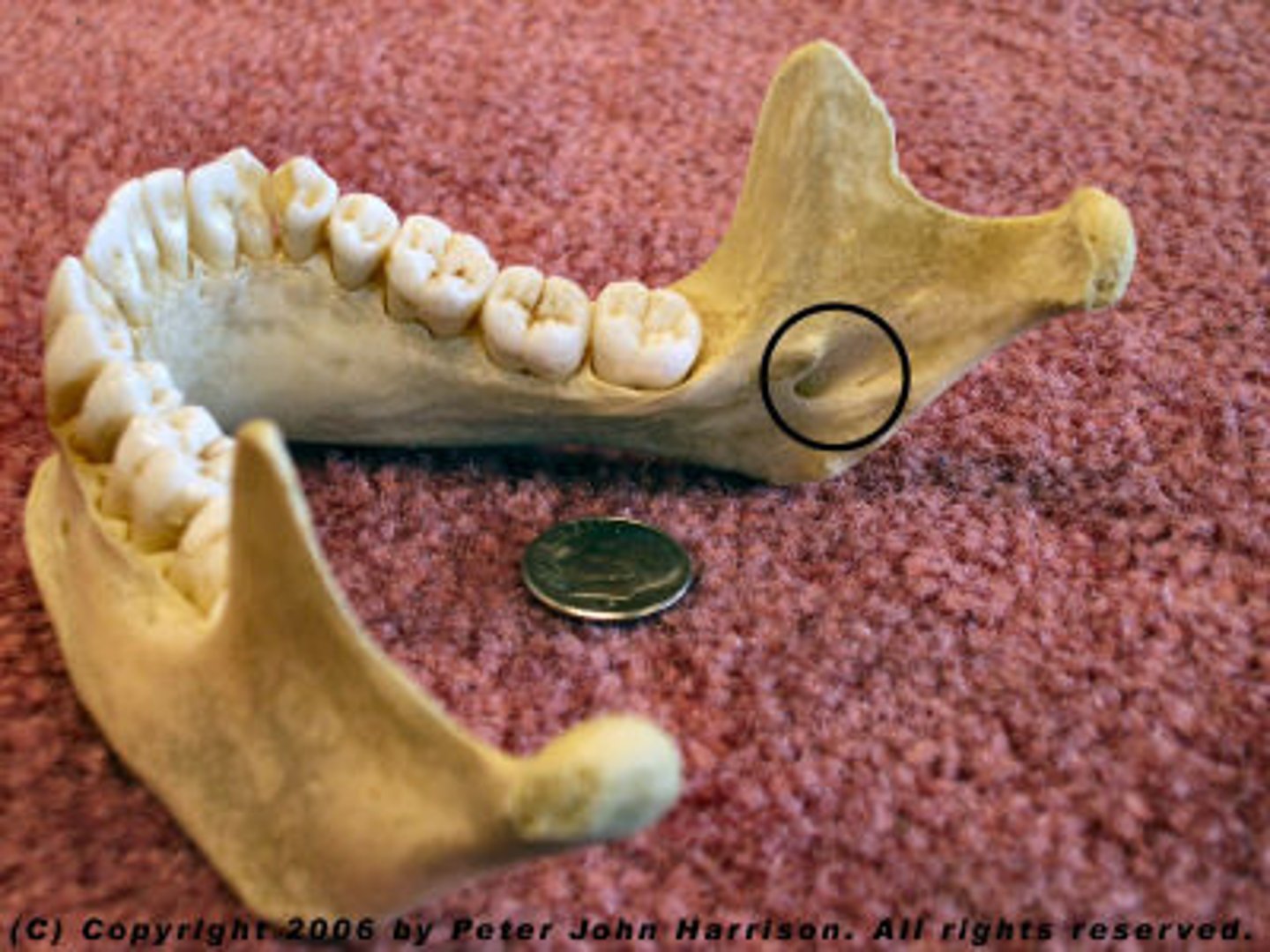
Genial spine
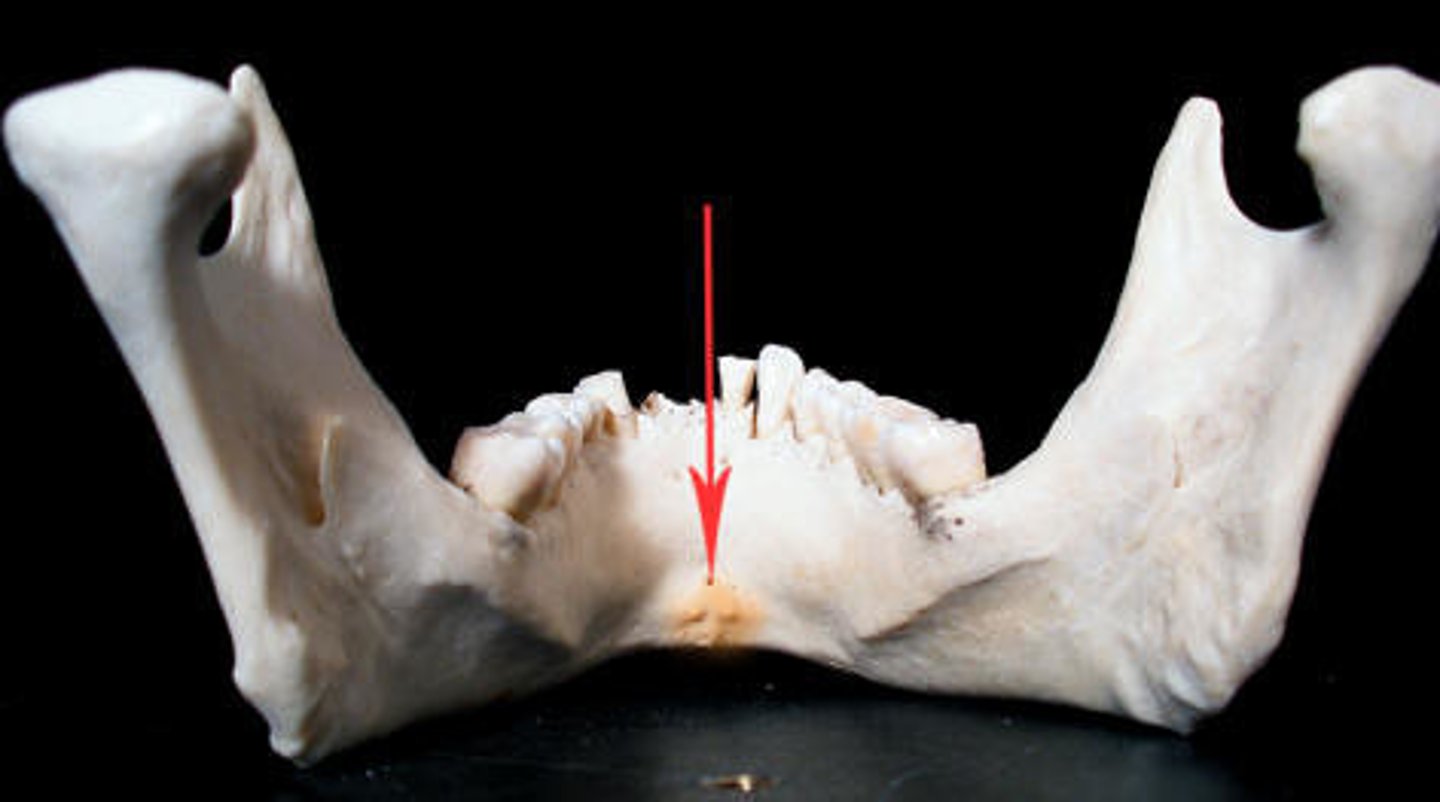
List the different types of tooth
-how many of each are present
Incisor - 4
Canine - 2
Premolar - 4
Molar - 6
What does the mandibular condyle articulate with?
Temporal bone
What muscle is responsible for winking?
Orbicularis occuli
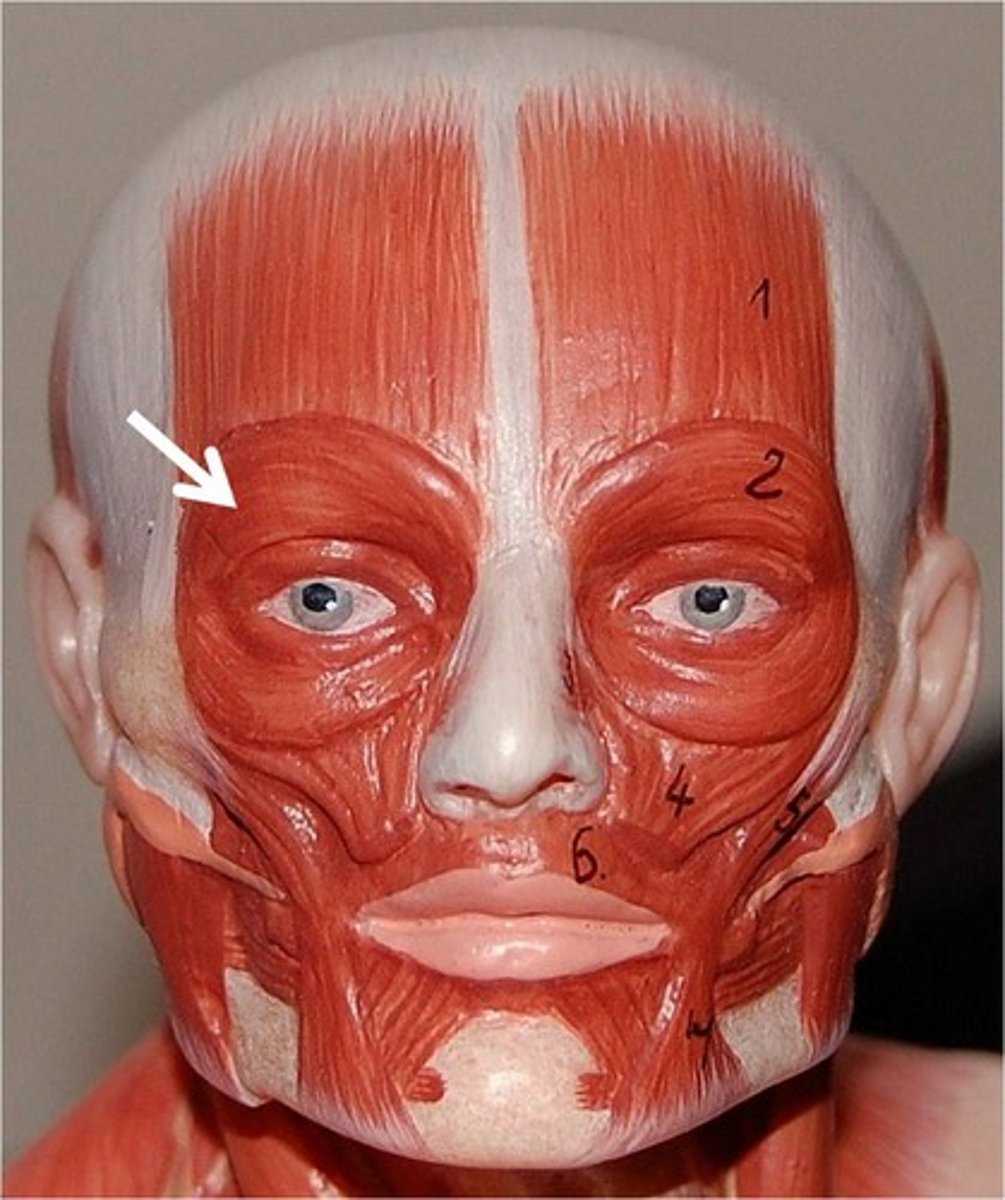
What muscle is responsible for puffing out your cheeks?
Obicularis oris
What muscle is responsible for raising your eye brows?
Frontalis
What muscle is responsible for smiling?
Zygomacticus major
What three muscles in the head close the mouth?
Masseter, lateral pterygoid, medial pterygoid
What is the most important muscle for opening the mouth?
Lateral Pterygoid
What are the two main functions of the tensor veil palatini and levator veil palatini?
Closes off nasopharynx
Opens auditory tube
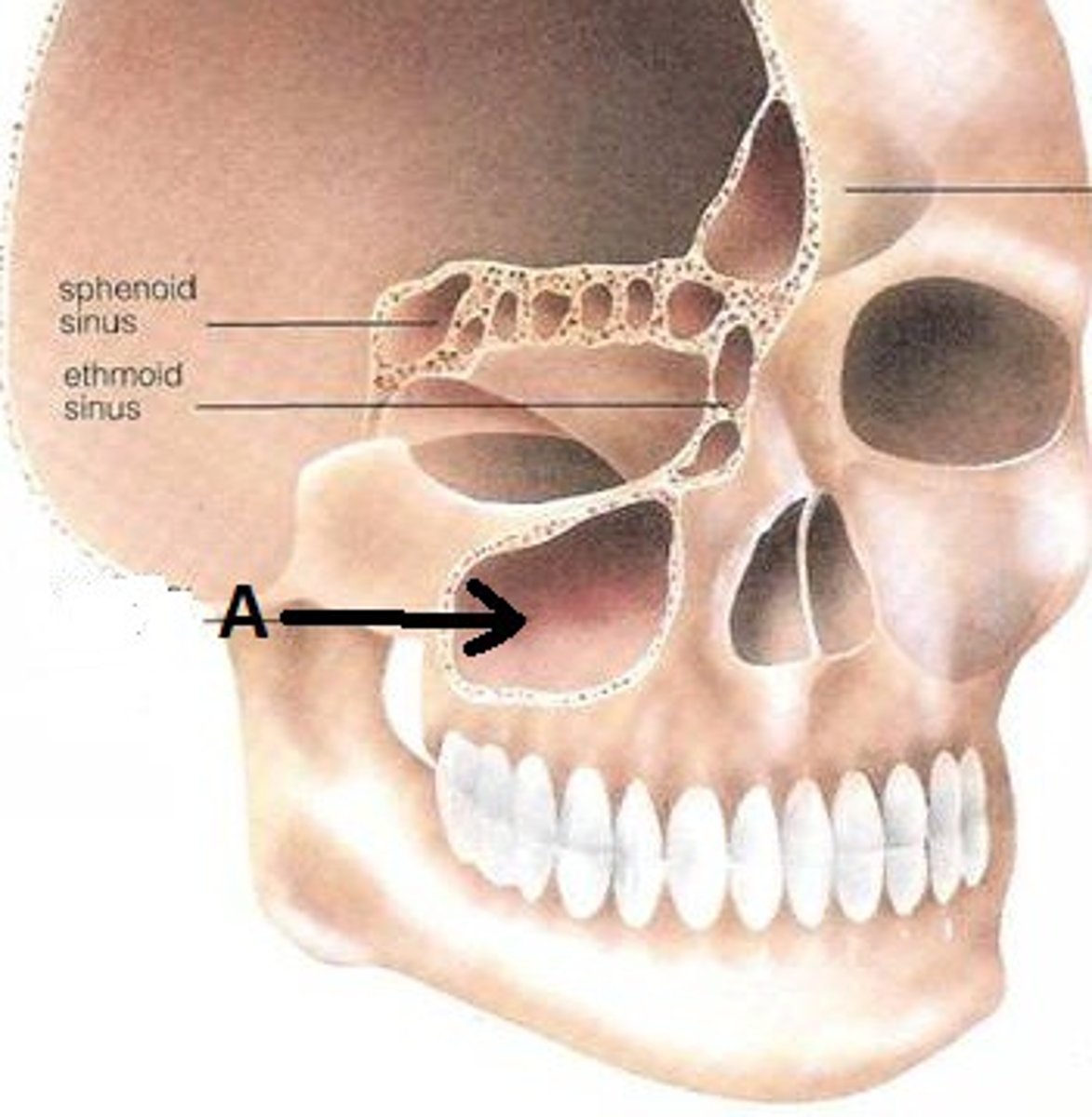
Maxillary sinus
Where mucous formulates then drains into the nasal cavity in times of sick
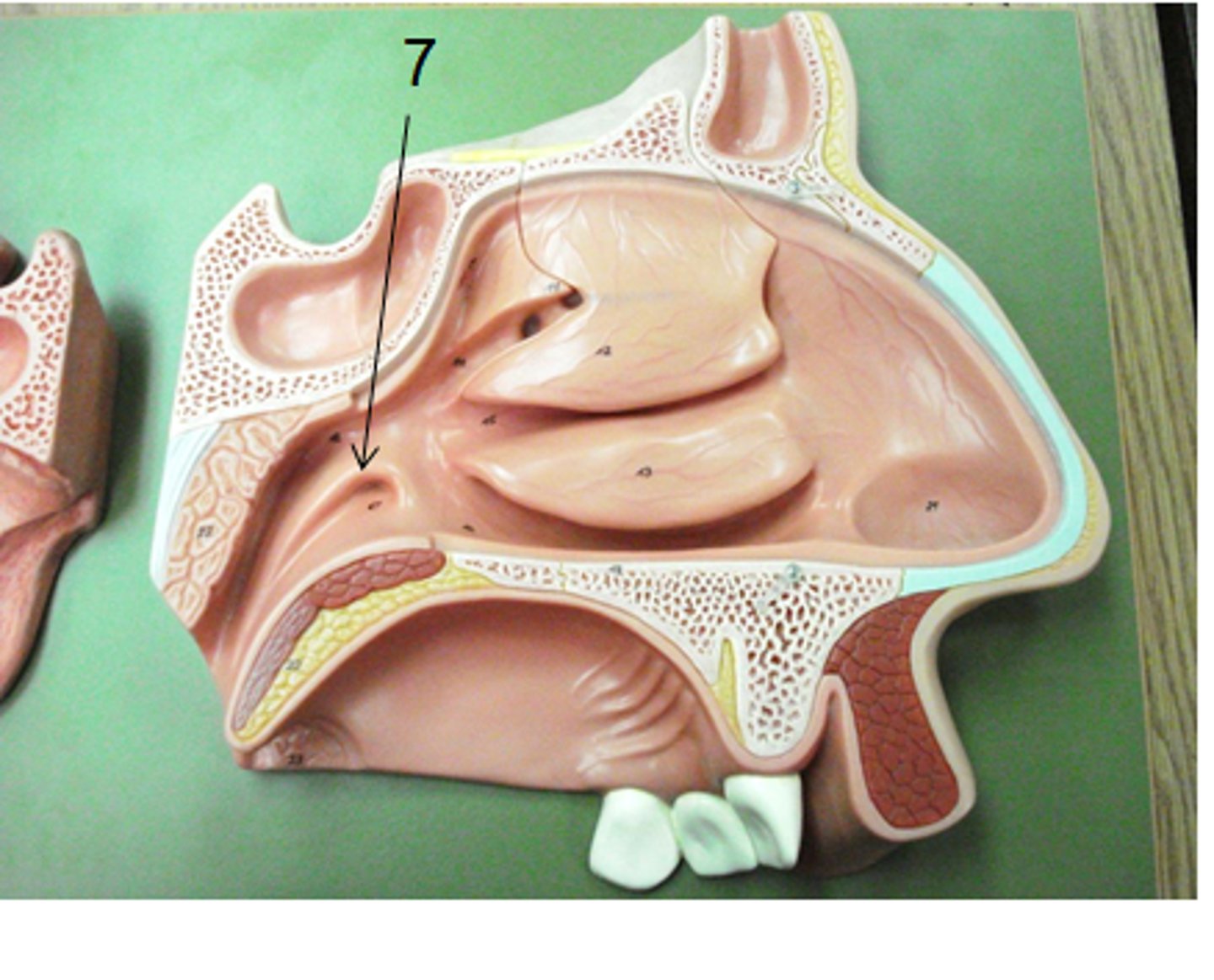
Nasal Conchae
Folds of bone inside the nasal cavity
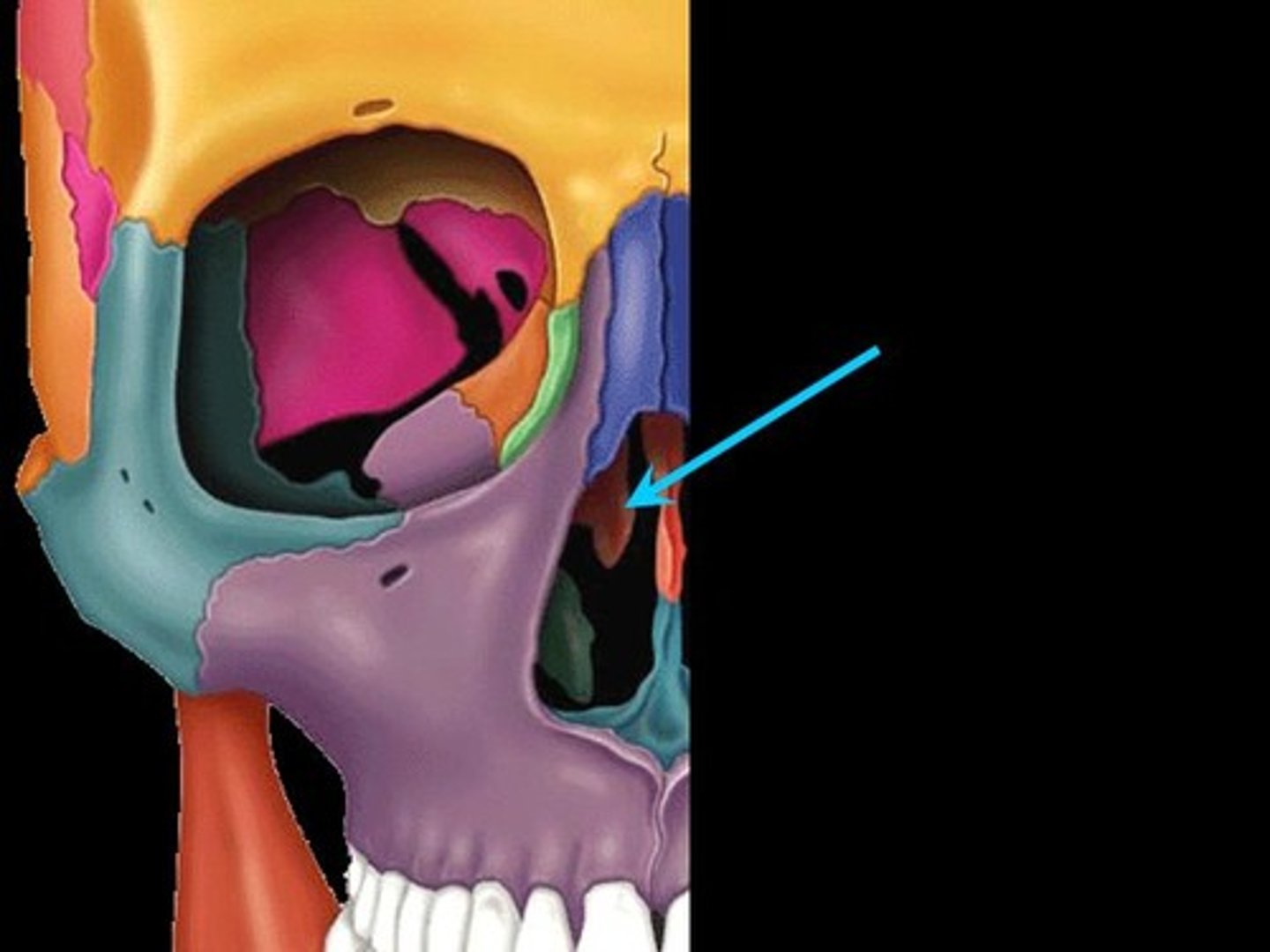
Auditory hiatus
In the lateral wall of the nasopharynx and opens up into the auditory tube
-connects middle eat to nasopharynx
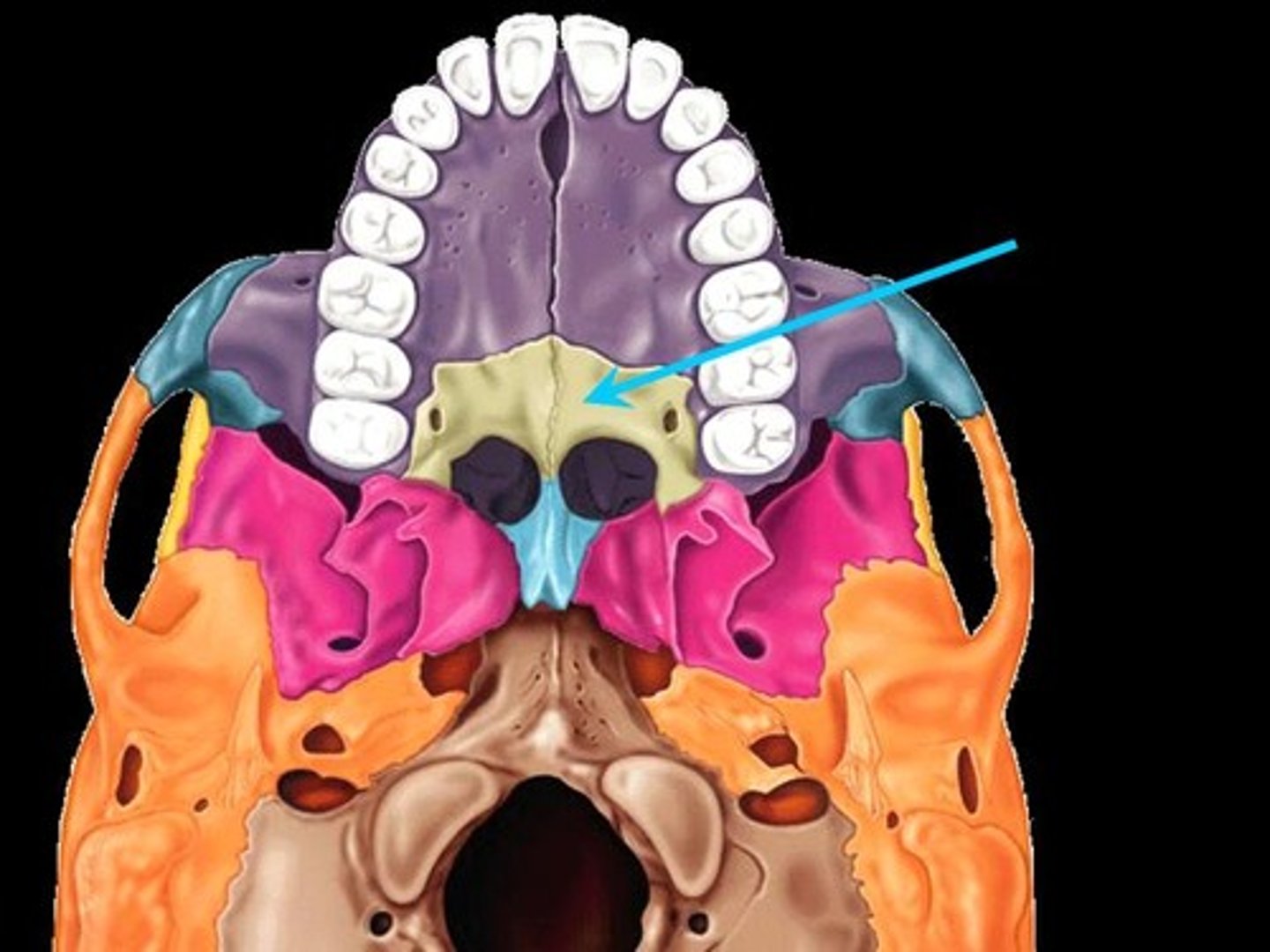
Hard palate
the roof of the oral cavity, made up of maxillae and Palatine
Soft palate
Separates oropharynx from nasopharynx
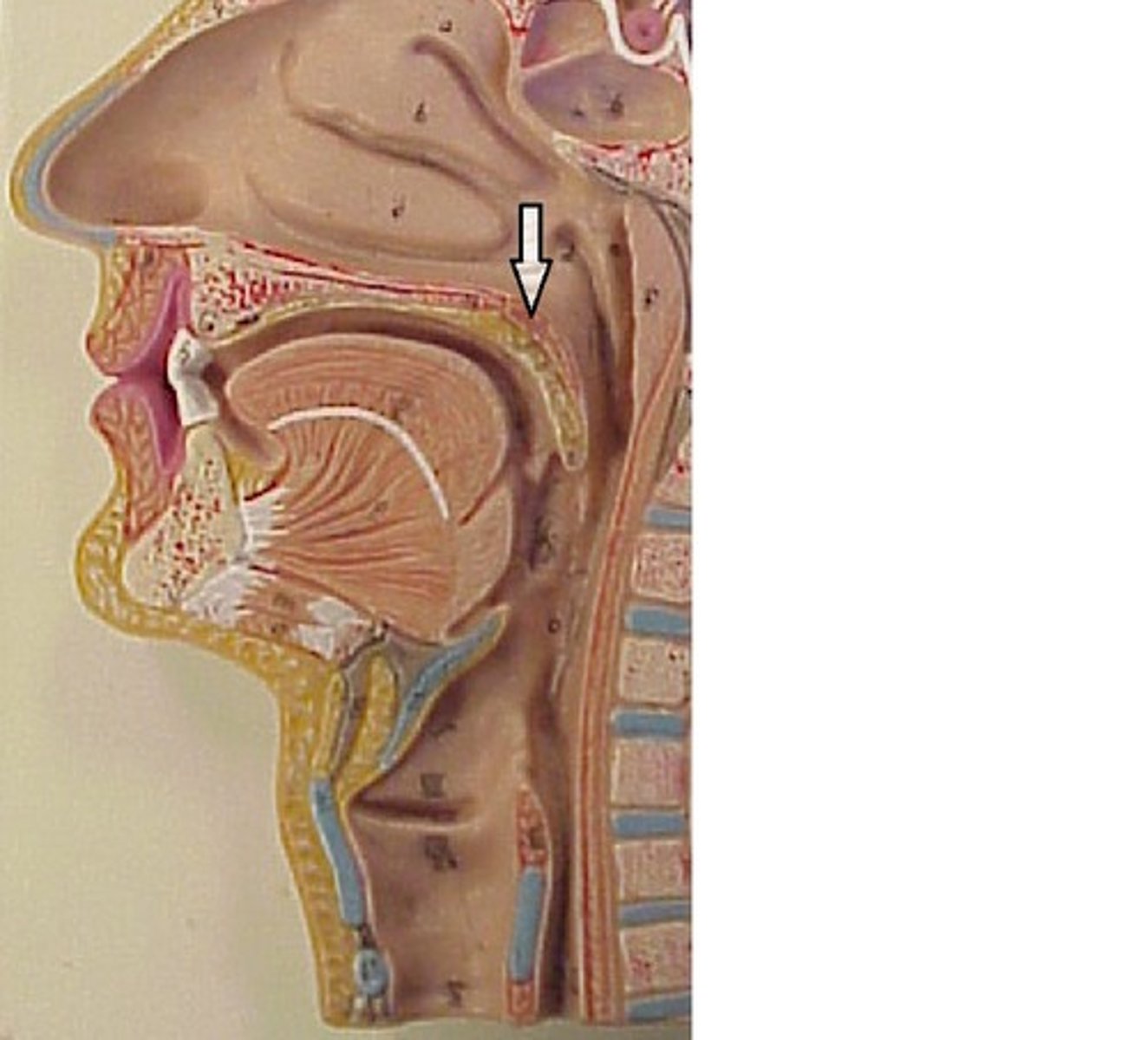
Palatoglossal fold
on either side/infront of soft palate
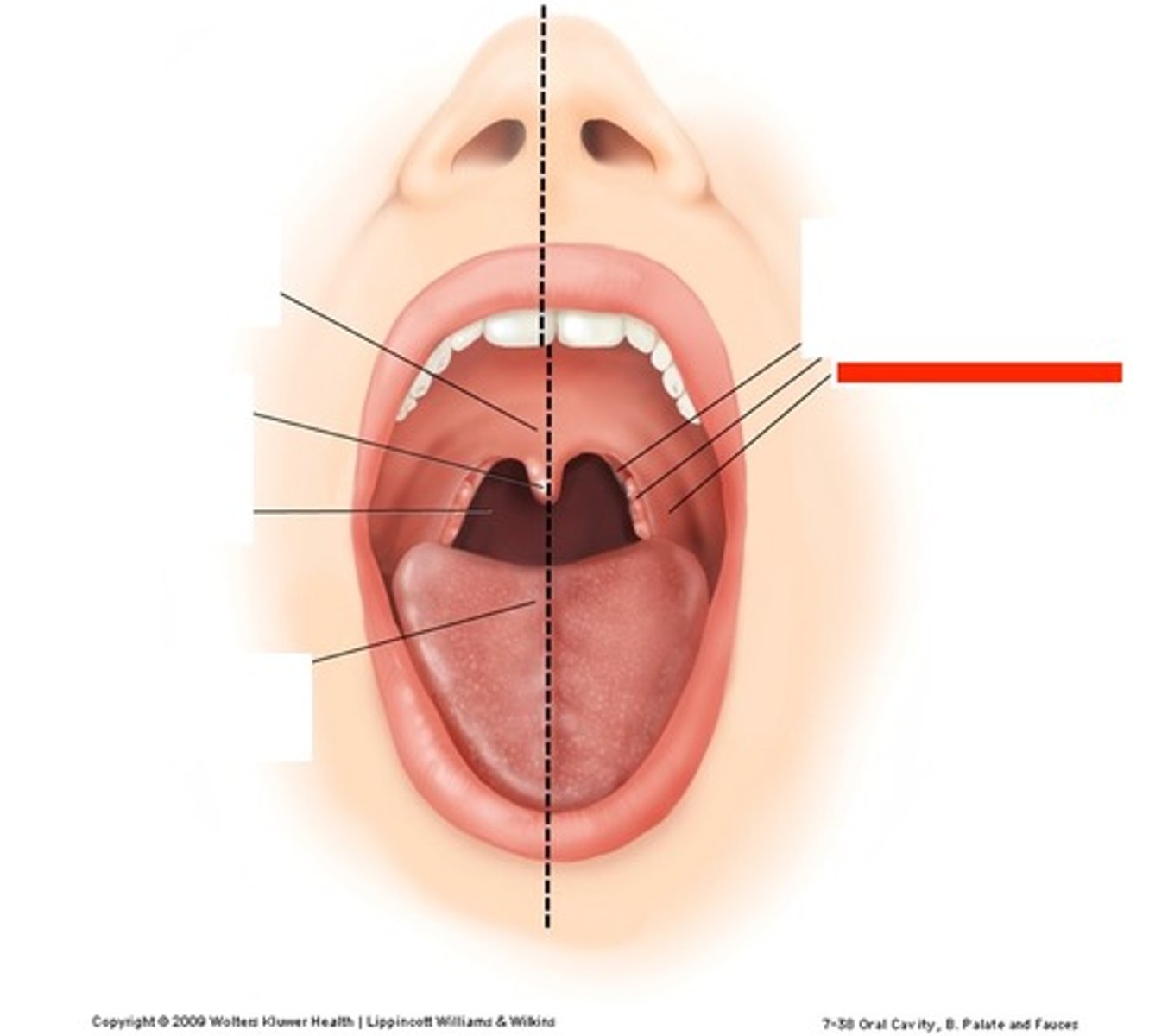
Palatine tonsil
bumpy shit inside the soft palate(D)
Lies between palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal folds
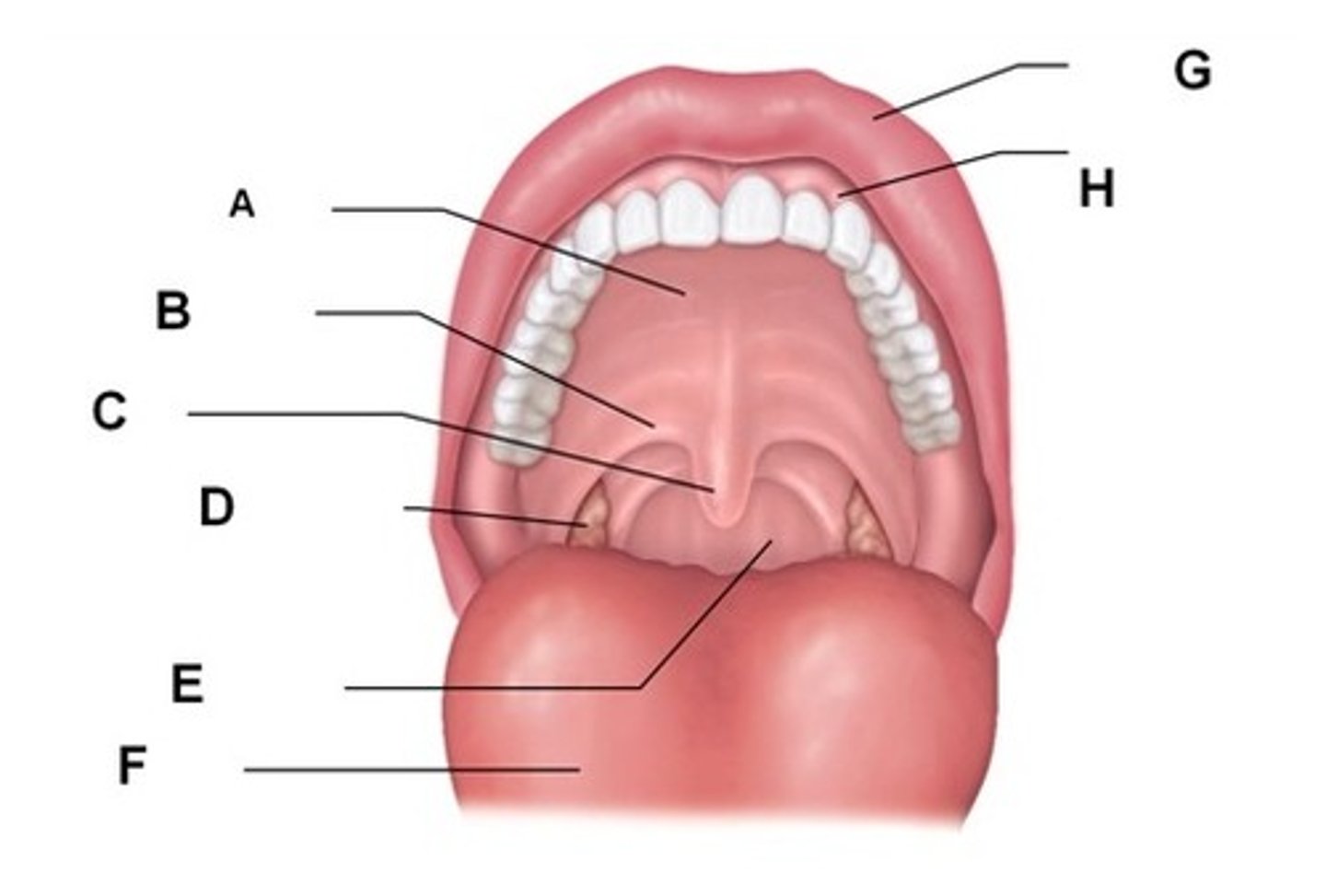
Palatopharyngeal fold
Inferio-superior to palatine tonsils
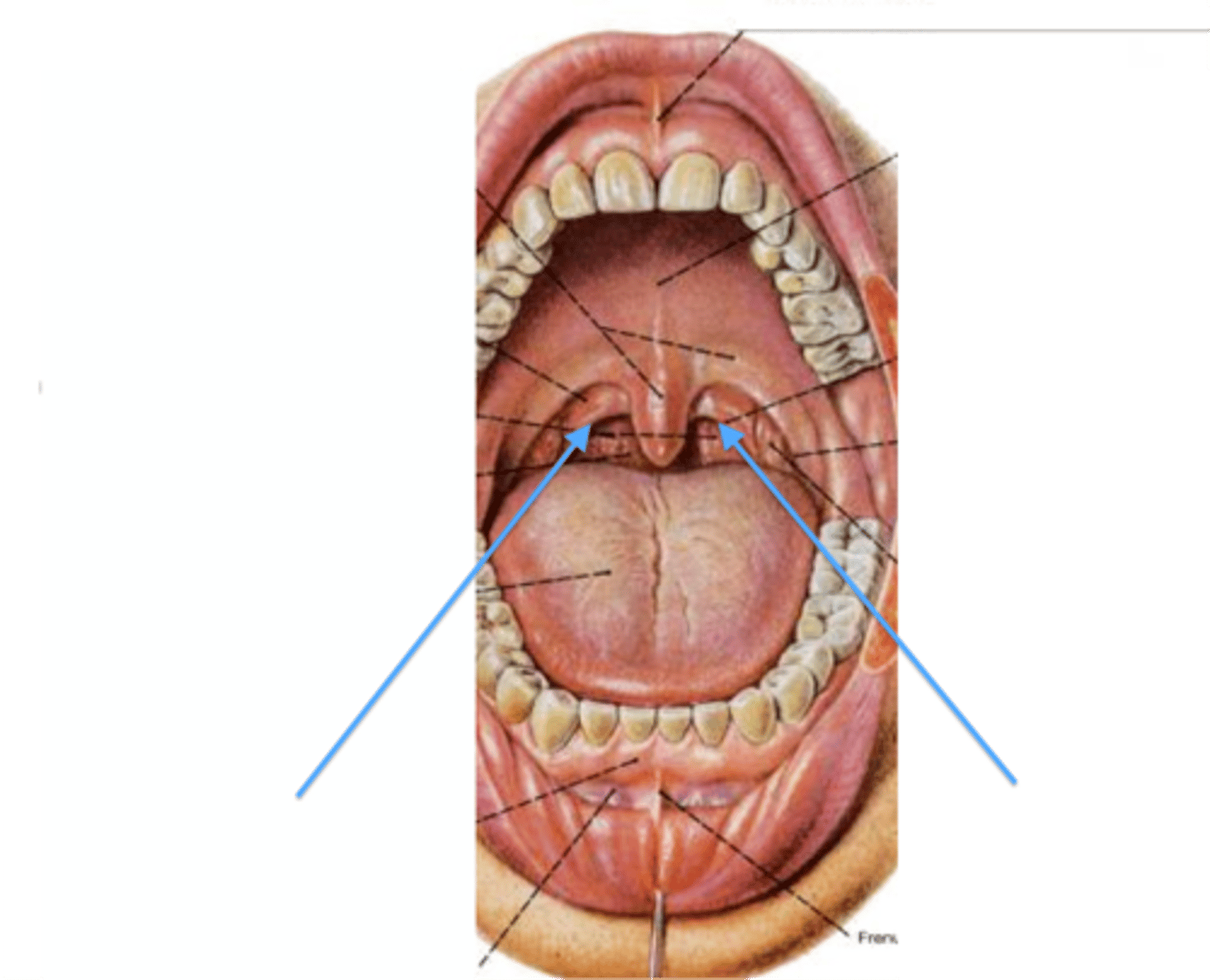
Nasal septum
Formed by ethmoid and vomer