bio unit 2 (digestive system and enzymes)
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
chemical reaction
changes one set of molecules into a new set of substances.
A chemical reaction occurs when chemical bonds between atoms are broken or formed, resulting in the production of one or more new substances.
reactants
products
the elements or compounds that enter into a chemical reaction.
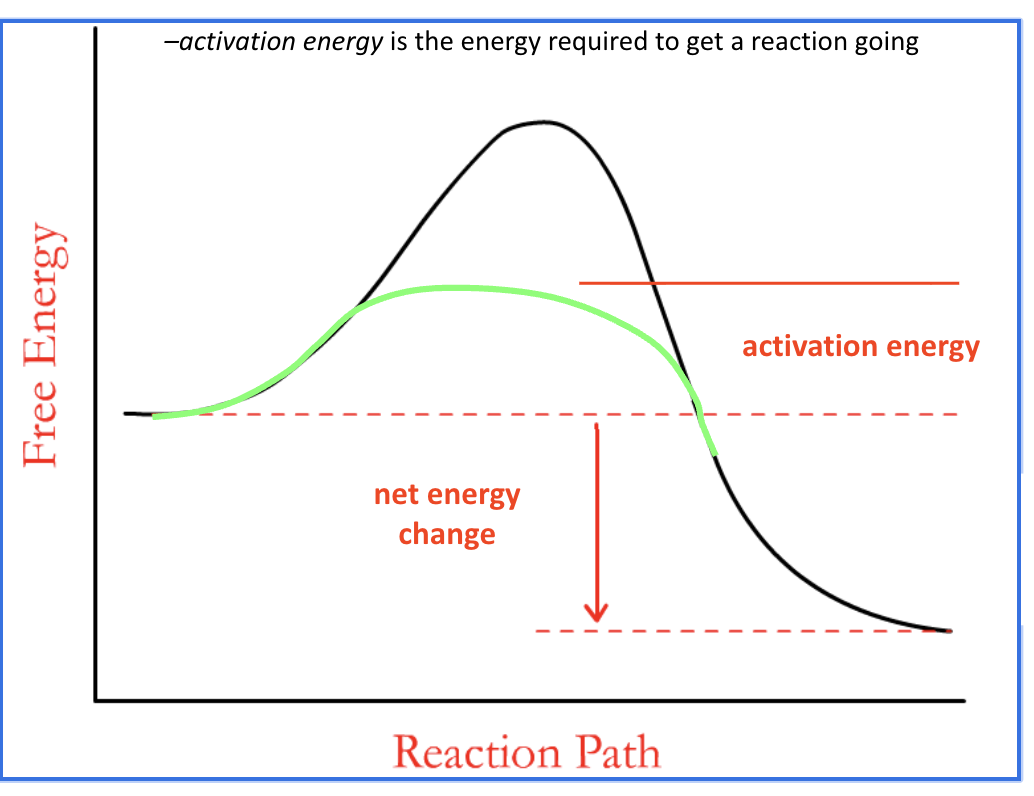
activation energy
The elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction.
The energy needed by the reactants in order to start a reaction.
It is the energy required to break bonds in the reactant molecules.
catalyst
a substance that will make a chemical reaction take place more rapidly and at a lower temperature.
enzyme
organic molecules that act as catalysts
Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalyst.
Enzymes are essential for the functioning of any cell.
Enzymes speed up the chemical reaction that take place inside cells.
Lower the activation energy for a chemical reaction.
Enzymes are so specific for their substrate that they can only catalyze one chemical reation.
Enzymes are proteins.
Enzymes are specific for just one reaction.
Each enzyme has an optimum temperature at which it functions best.
Enzymes require water to function.
Enzymes are not consumed or used up during the reaction.
what does lowering activation energy do
Lowering the activation energy makes the reaction take place much faster and at a lower temperature.
substrate
The reactants of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
The enzyme will speed up the conversion of the substrate to new and different products.
how do enzymes work (picture)
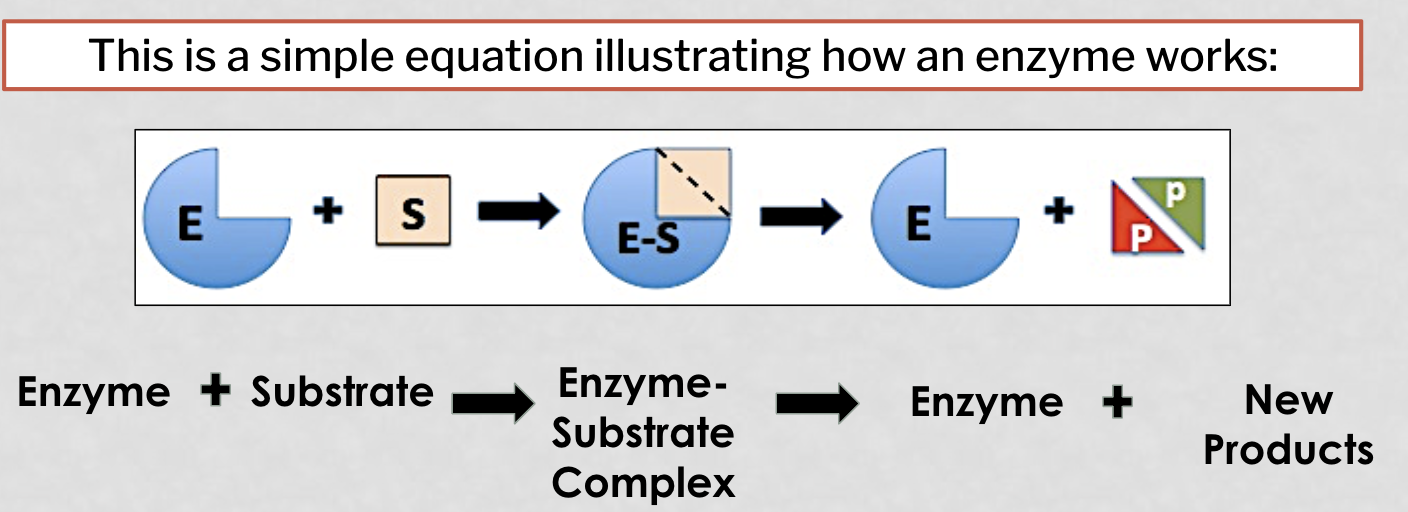
active site
the pocket or grove in which sbustrates must fit
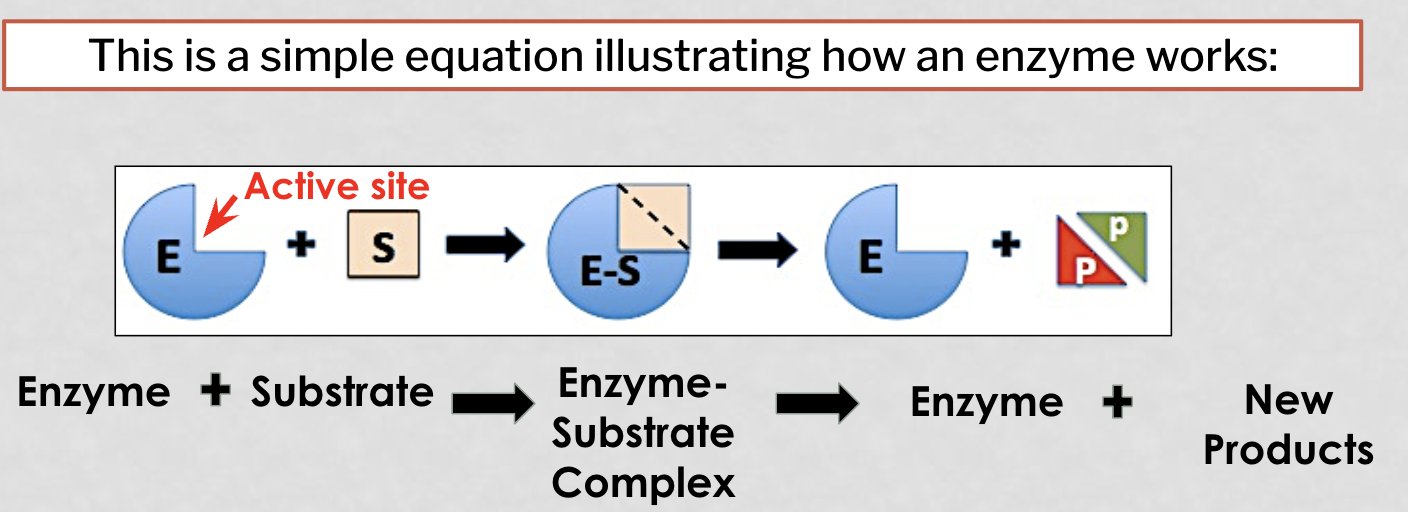
How does an enzyme speed up a chemical reaction
lowers activation energy for a chemical reaction
denatured
If the temperature exceeds the optimum, the enzyme may become denatured.
The bonds that determine the shape of the enzyme are altered, changing:
the shape of the enzyme.
primary protein bonds
peptide bonds - sequence of amino acids
1 peptide chain involved
secondary structure
hydrogen bonds- formed between oxygen of the carboxyl groups and the hydrogen of the amine groups in carbons backbone
a-helix= helix shape
beta (b)- pleated sheet = folded
tertiary
hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulfide bridges, hydrophobic interaction - r group side chain of different amino acids interact to further fold protein
one polypeptide chain
quaternary
hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulfide bridges, hydrophobic interactions -bonds formed between individual ploy peptide chains
2 or more polypeptide chains
Quaternary structure occurs when multiple proteins come together to form a protein complex.
These proteins are all folded at the tertiary level.
Not all proteins are involved in quaternary structures.
Held together by interactions between the variable side chains and hydrogen bonding between the peptide backbones of the different proteins.
hydrogen bonds
Hydrogen bonds between side chains; bond between H atom of one amino acid and the oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine atom of another amino acid.
H-bonds are sensitive to changes in pH and temperature and will be broken if the protein is outside of the normal pH or temperature range
Help hold different parts of the protein together but relatively weak compared to disulfide bonds but are essential in maintaining the stability of the protein's shape.
disufilde bridges
Disulfide bridges are covalent bonds between the sulfur atoms present in the side chains of two cysteine amino acids.
Disulfide bridges are very strong and are not sensitive to changes in pH or temperature.
Create loops or bridges within the protein structure, stabilizing its three-dimensional shape.
stronger structure
Cysteine AA’s do not have to be near each other in the sequence to form the bond.
Usually found in proteins exposed to harsh conditions
High temperature
Extreme pH like in digestive system!
ionic bonds
Ionic bonds occur when positively charged amino acids (e.g., lysine or arginine) interact with negatively charged amino acids (e.g., aspartate or glutamate).
These interactions can create attraction or repulsion between different regions of the protein, affecting its folding and stability.
hydrophobic interactions
Hydrophobic interactions are not true chemical bonds but rather the tendency of nonpolar amino acids to cluster together within the protein's interior, away from the surrounding water.
This clustering helps proteins fold into their native, functional conformation.
alimentry canal
a continuing tube in the body that starts at mouth and goes through the anus
accessory organs
salvivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
mouth
food is warmed to body temp
teeth break food
tongue moves food into bolus
salivia moistens food and beginas to break down carbs (amylase)
pharynx and esophagus and epiglottis
pharynx- connects mouth to esophagus
esophagus - tube that moves food down to stomach (peristalsis)
epiglottis - flap near opening of larynx that closes of trachea
stomach
what type of acid?
what is digested food called?
what is the enzyme called?
what is digested good called?
hydrochloric acid
glands produce mucus to protect itself
pepsin
chyme
sphincter muscles
control flow of food entering and leaving stomach
heartburn
sphincter is weakened, regurgitation of acids from stomach into esophagus
small intestine
what are the three parts?
abosorbs nutrients using villi
first - deoudenum
middle - jejunum
final connects to first - ileum
segmentation vs peristalsis found in SI
peristalsis - contracts food
segmentation - moves food back and forth
pancreas
makes enzymes and insulin (regulate blood sugar)
break down food in small intestine
liver AND BILE AND GALLBLADDER
produces bile which breaks down fat into smaller components (EMULSIFICATION)
bile stored in gallbladder
liver also store vitamins, breaks down toxins, breaks down old cells, produces proteins, store glycogen for energy
COLON AKA LARGE INTESTINE and cecum
food that cannot be further digested
reabsorbs water
feces travel from colon to small intestine to rectum
cecum - small pouch that connect ileum to SI
(parts in order - cecum, ascending colon traverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid)
human body temp in celsius
36.5-37.5
enzymes for carbs
salvary glands - amylase
pancreas - pancreatic amylase
small intestine - maltase
enzymes for proteins
stomach - pepsin
pancreas - trypsin
small intestine - peptidase
enzymes for fats
pancreas - lipase
lipase
Central role in the digestion and breakdown of fats, specifically triglycerides into simpler components, such as fatty acids and glycerol.
It is produced by various organs in the body, with the pancreas being a primary source.
Lipase is primarily active in the small intestine, where it complements the action of bile produced by the liver. Bile emulsifies fats, breaking them into smaller droplets, and lipase then acts on these smaller droplets to further digest the fats.
salivary amylase
Produced by the salivary glands
Role in the initial digestion of carbohydrates such as starches and glycogen, into simpler sugars, mainly maltose.This process is the first step in the digestion of carbohydrates and takes place in the mouth as food is being chewed.
Salivary amylase functions optimally in a slightly acidic to neutral pH range.
Its activity is stopped in the stomach due to the acidic environment, but it resumes in the small intestine, where the pancreas secretes another amylase enzyme called pancreatic amylase to continue carbohydrate digestion.
protease example
PEPSIN
Secreted in the stomach.
The main enzyme involved in protein digestion.
It breaks down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids that can be easily absorbed in the small intestine.
The digestive power of pepsin is greatest at the acidity of normal gastric juice (pH 1.5–2.5). In the intestine the gastric acids are neutralized (pH 7), and pepsin is no longer effective.
TRIPSIN
Produced in the pancreas and is released into the small intestine.
Key role in the digestion of proteins by breaking down large protein molecules into smaller peptides.
Trypsin works in the alkaline environment of the small intestine, which is necessary to neutralize the acidic chyme coming from the stomach.
duodenum
The duodenum receives chyme produced by the stomach through a ring of smooth muscle called the pyloric sphincter
Glands called produce alkaline mucus to neutralize the acidic chyme and activate many enzymes
The duodenum receives bile from the liver and gallbladder, pancreatic juice from the pancreas, and its own enzymes, which work collectively to chemically digest food into micronutrients to be absorbed.
Here, most water and electrolytes from digested food are absorbed into the bloodstream through the walls of the small intestine
induced fit
enzymes changing their shape to fit a substrate