Test Review Nervous Sysand the brain
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Structure between cell body and axon
Axon hillock
Branches conducting impulses toward the cell body
Dendrites
What is myelin?
A white, fatty substance found in the myelin sheath around some nerve fibers.
Branches between axon and synaptic knobs
Axon collaterals
Are there Centrioles in Nerve cells
No, nerve cells do not contain centrioles
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Includes brain and spinal cord, works as the “control center”, process and interprets information
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Works outside the CNS, includes the nerves that extend from the brain and spinal cord “communication lines”, uses million of sensory receptions to monitor changes inside and outside the body
Motor
Transmits impulse from CNS to organs, muscles and glands
Sensory
Convey impulses to CNS from sensory receptors, includes information from the skin, skeletal muscles (voluntary), joints and organs to CNS
Mixed neurons
a nerve containing both sensory (afferent) and motor (efferent) fibers
Gray matter
Outer “bark” (nerve cell fibers that are unmuerinated)
White matter
Inner area of cerebellum and cerebrum (myelinated nerve fibers)
What are astrocytes
Are star-shaped and are responsible for anchoring neurons to capillaries for blood and nutrient supply
What are microglia
Acts as a macrophage to rid of microbes and dead nervous tissues
Multipolar neuron
a type of neuron that possesses a single axon and many dendrites (and dendritic branches)
Bipolar neuron
a type of neuron characterized by having both an axon and a dendrite extending from the soma (cell body) in opposite directions
Unipolar neuron
a neuron in which only one process, called a neurite, extends from the cell body
Be able to label a Motor Neuron
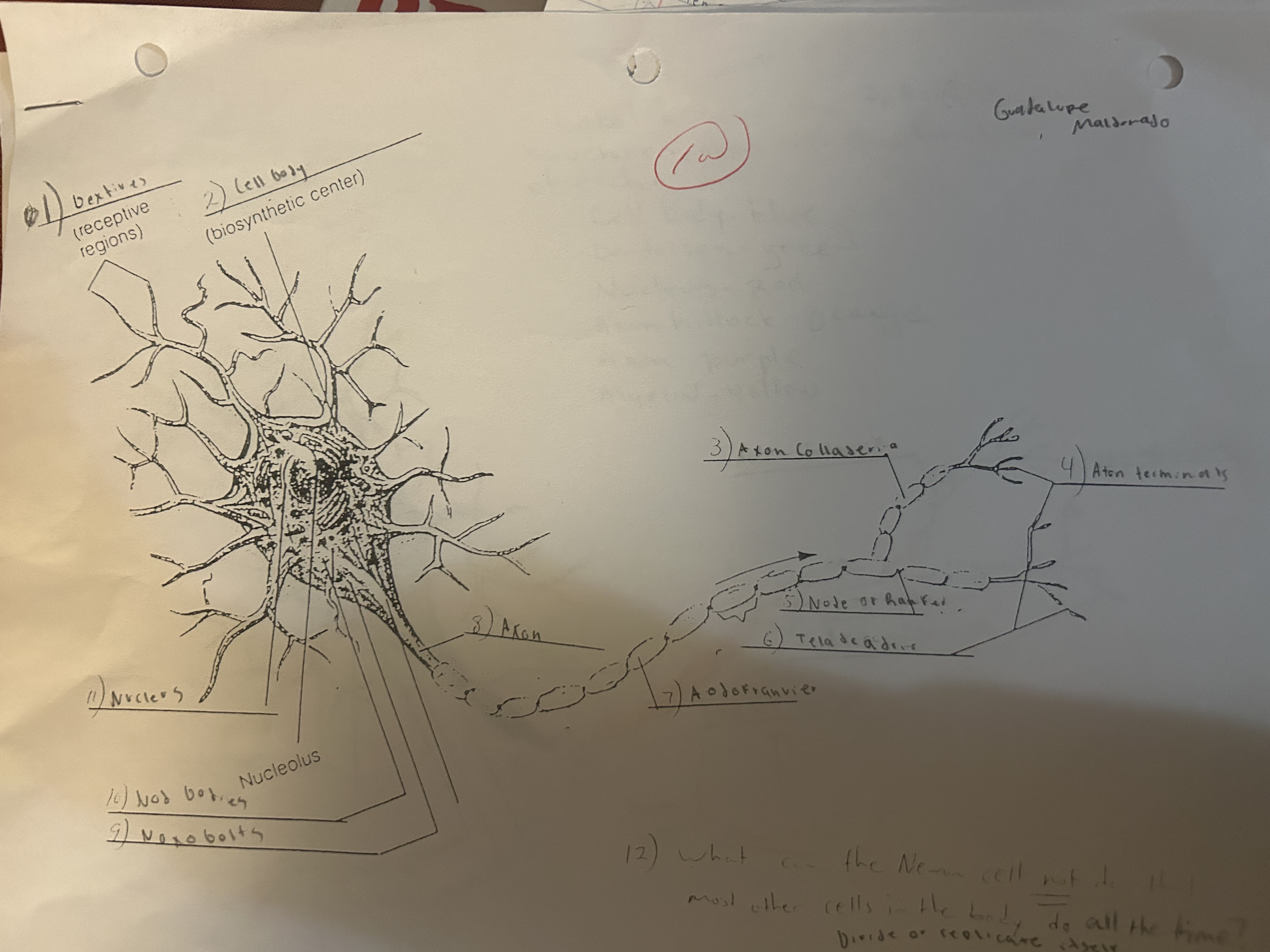
The anterior lobe of the brain associated with conscience, intelligence and personality.
Frontal lobe
The posterior lobe of the brain associated with vision.
Occipital lobe
The inferior lateral lobe of the brain found below myelin
Temporal lobe
Divided into left and right hemispheres this region of the brain controls all voluntary actions.
Cerebrum
This region of the brain is centrally located and consists of thalamus, hypothalamus and epithalamus.
Diencephalon
This region leads to the central brain from the spinal cord made up of midbrain, pons, and medulla.
Brain stem
This region is used with learned behaviors like balance, posture and coordination
Cerebellum
An outward fold on brain surface.
Gyri
Shallow groove on brain surface.
Sulcus
Deep groove on brain surface.
Fissure
Mylenated nerve fibers that allow for communication.
Cerebral white matter
Nerves which crossover in Medulla.
Projection fibers
Connect gyri in same hemisphere.
Association fibers
Connects left and right hemisphere of cerebrum.
Commissure
Controls Autonomic nervous system.
Hypothalamus
Contains the pineal gland which controls sleep cycle.
Epithalamus
Tissue which produces Cerebral Spinal Fluid.
Epithalamus
Relay station for senses except smell.
Thalamus
Area of brain stem controlling heart beat, breathing, swallowing and vomiting.
Medulla
The process of crossing over of the nerve tracts.
Decussation
The bulge of the brain stem, serves as passage for cranial nerves V, VI, VII.
Pons
Contains two peduncles and the substantia nigra who's destruction leads to Parkinson's disease.
Substantial nigra
Branching white fibers in the cerebellum(tree of life)
Arbor vitae
Inner most meninges, tightly covers brain.
Pia mater
Middle layer of meninges with projections that extend into the other two layers. (spider webb)
Arachnoid mater
Tough outer layer of meninges.
Dura mater
Results from a blow to the head, there are varying degrees most are harmless, but repeated events could cause permanent damage.
Concussion
Circulation blockage in brain.(Brain Attack)
Stroke
Plaque deposits build up causing degeneration of cortex leading to mental deterioration.
Alzheimer’s
Bacterial or viral infection of meninges.
Meningitis