Peds High Yield Info Quiz 1
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
gestational weeks
Measurement of pregnancy duration in weeks.
based on the maternal last menstrual period
first ____ are considered the most critical
13 weeks
when is the highest risk of miscarriage
first 13 weeks
fertilization
union of 2 germ cells > zygotes > blastomere > morula (16 cells) > blastocyst
occurs in fallopian tube
organogenesis occurs during
embryonic period
endoderm
-inner layer
-GI tract, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, thyroid, parathyroid, bladder, urethra
mesoderm
-middle layer
ectoderm
-forms neural tube
neural tube formation
-3-4 weeks
-gives rise to the spinal cord and nervous system
what supplement do we give to prevent neural tube defect
-folic acid
what happens in the respiratory development during week 24-28
-extensive capillary network continues to develop and surfactant production begins
lungs grow for up to
8 years
surfactant
-substance necessary to keep terminal alveolar sacs expanded during expiration
the over rate of survival at 24 weeks barely exceeds 50% due to
pulmonary complications of prematurity
respiratory distress syndrome
-insufficient surfactant > alveolar collapse
bronchopulmonary dysplasia
-prematurity + use of ventilator therapy leads to maldevelopment of bronchopulmonary system
what happens to the heart in weeks 4-7
-undergoes extensive growth and morphological modifications, leading formation of septated chamber heart with primative valves
oxygenation in fetus occurs
in placenta
-oxygenated blood stay in fetal circulation and no in lungs
fetal circulation
-arterioles in low O2 enviroment > hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction > increased resistance of blood flow to arterioles > high pressure in right ventricle and atrium > overall pressure on right side being more
umbilical cord
-connection between placenta and fetus
-2 arteries and 1 vein
-keeps O2 from lungs
ductus venosus
-connection from umbilical vein to IVC
-bypass liver ciruclation
-oxygenated blood from placenta and deoxygenated blood from body gets mixed
foramen ovale
-opening between atria
'-shunts or moves blood from higher pressure righ atrium to lower pressure left atrium
-bypass lungs
ductus arteriosus
-blood vessels connecting pulmonary artery to aorta
-shunts blood from pulmonary atery to aorta
-kept open by prostaglandin
internal iliac artery gives rise to
umbilical artery
full term
-40 weeks
-3500 g or 7.7 lb
term infants
>37 weeks
late pre term
between 34-37w
moderate preterm
32-34 weeks
very preterm
28-32 weeks
extremely preterm
less than 28 weeks
birthweight classification
Extremely low birthweight= <1000g
Vey low birthweight= <1500g
Low birth weight= <2500 g
Normal Birth weight= 3500g
preterm infants lack
-corrdinate sucking, swallowing, breathing
-lack of body fat store
-pulmonary immaturity
-predisposes intraventricular hemorrhage
-compromises nutritional management
what supplement is recommended for all preterm infants
-iron
apnea
-respiratory cause lasting >20 sec
-apnea of prematurity is most common cause
hyaline membrane disease
-most common cause of respiratory distress in preterm infant
- >50% infants born at 26-28 weeks
-caused by surfactant production deficiency > poor lung compliance > trying hard to breathe > respiratory failure
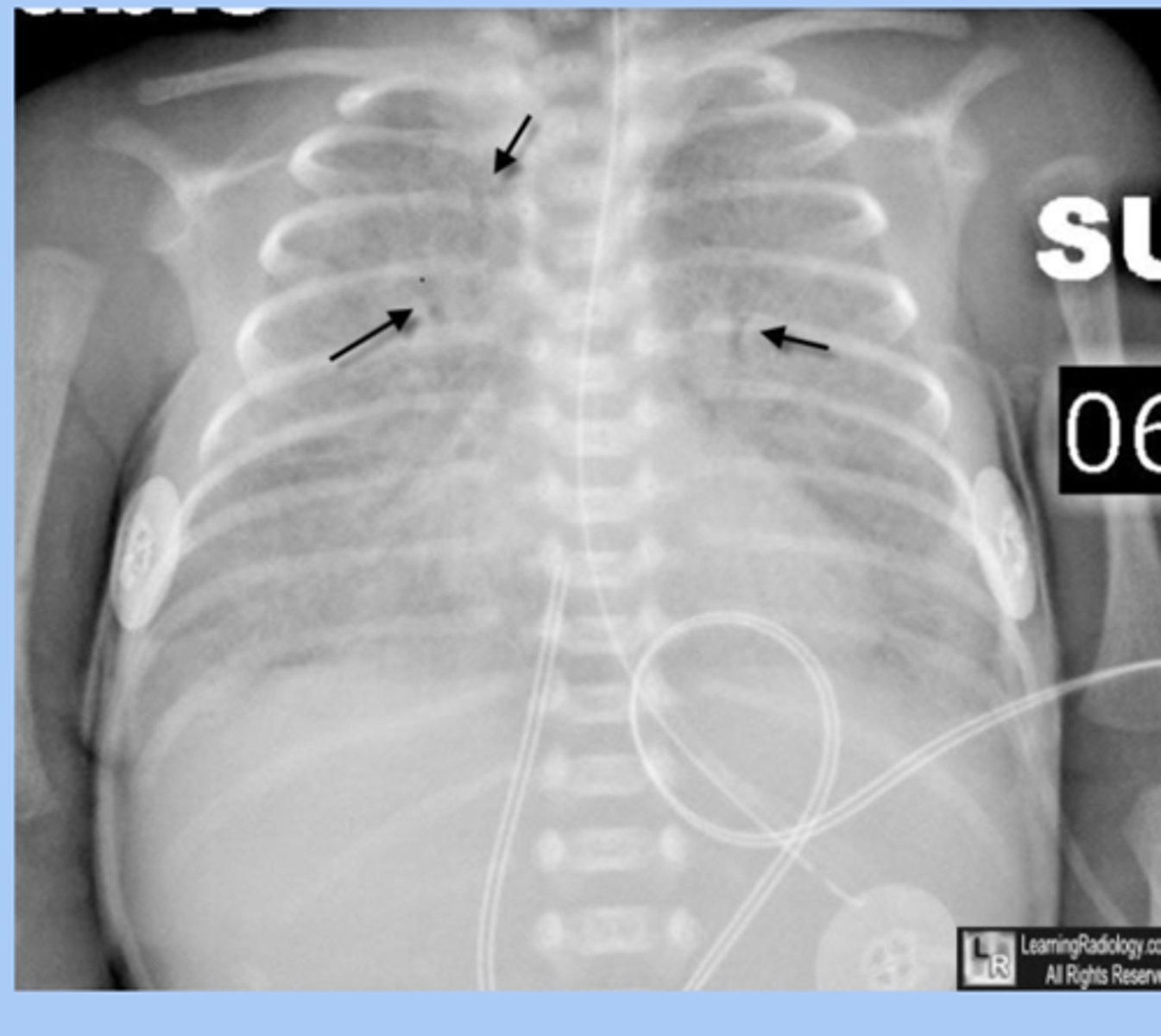
CXR of hyaline membrane disease shows
-bilateral atelectasis with ground glass appearance
hyaline membrane disease prevention
-antenatal administration of corticosteroids to mother
-surfactant administration
Nectrotizing Enterocolitis
-most common acquired GI emergency
-cellular damage, cellular death, necrosis of colon and intestine
-sx: abdominal distension, heme + stool
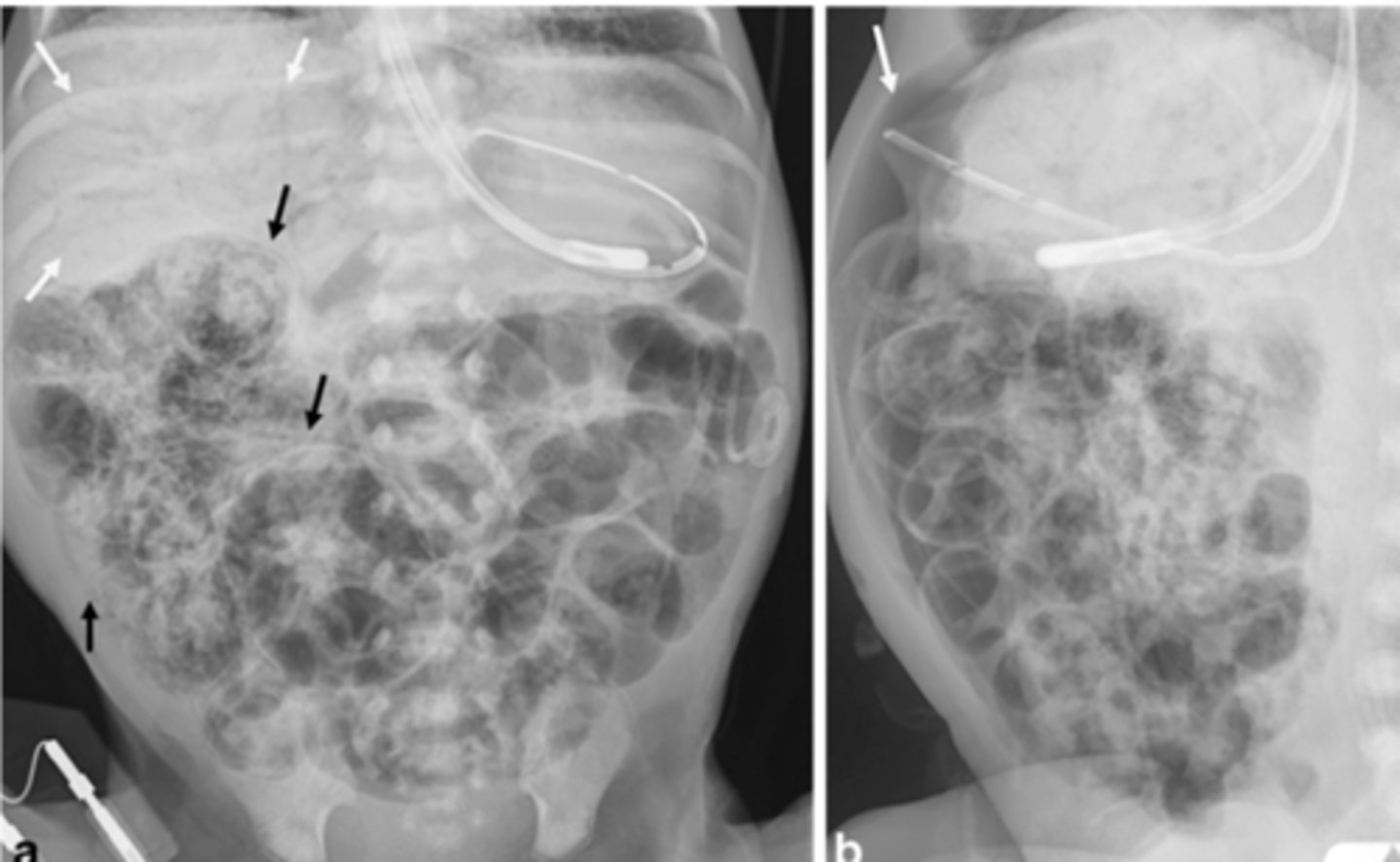
necrotizing enterocolitis dx
-abdominal plain film series
-pneuatosis intestinalis
-tx: removal of necrotic bowel and ostomy vs end to end anastomosis
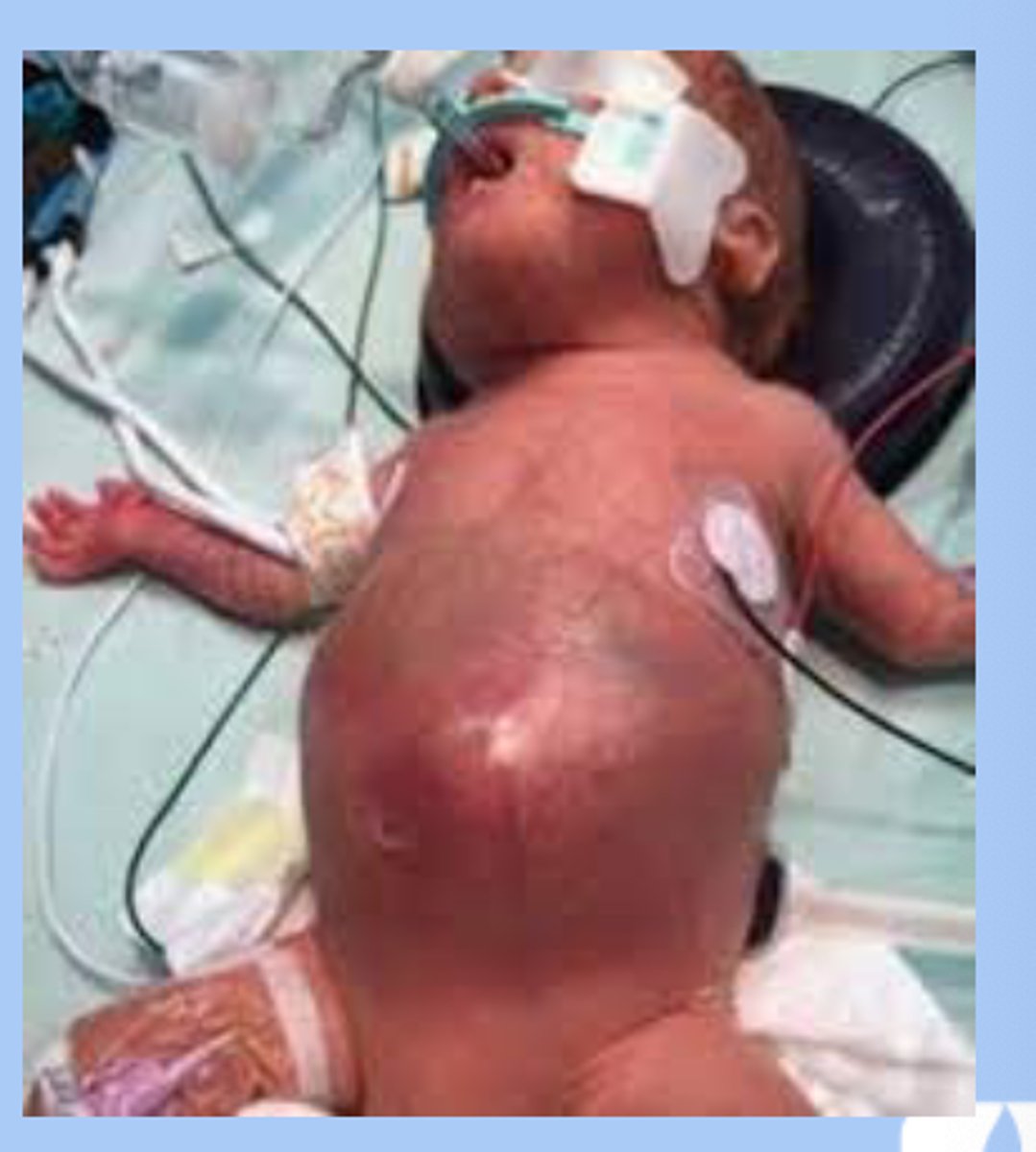
Intraventricular hemorrhage
- 50% occur before 24 hr of age and virtually all occur by fourth day
-confimed with ultrasoun
-routine scanning done at 10-14 days in all infants born before 29w
retinopathy of prematurity
-leadign cause of blindness
-all infants for <30 w or <1500 g should be screened with dilated fundoscopic exam
follow up
-outpatient follow up within 2-3days
new born period
first 28 days of life
newborn medical hx
1.maternal and parental medical and genetic hx
2.maternal past obstetric hx
3.current antepartum and intrapartum obstetric hx
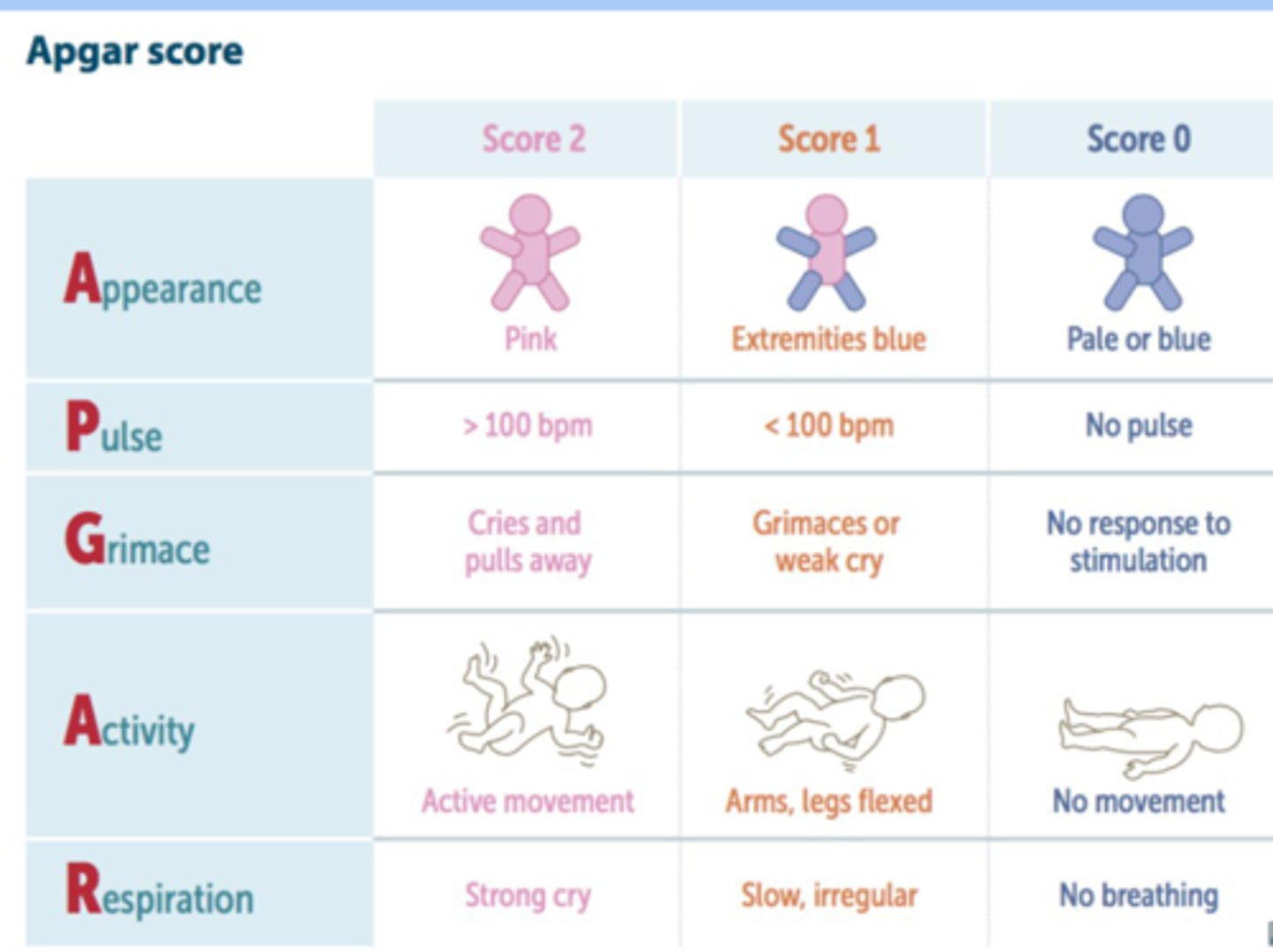
APGAR score
-standardized assessment of a newborns health immediately after birth
-at 1 and 5 min of age
-normal 7-10
-requires immediate resuscitation 0-3
skin exam
-color: visible jaundice <24 hr never normal
-facial redness= polycythemia
head and face
suture lines: palpate all should be freeky mobile
mouth
-observe and palpate for any cleft palate deformities
neck and chest
asses clavicals for any evidence of fracture: crepitus, deformity, bruising
cardio
auscultate heart sounds for extra sounds, murmurs
MSK/spine
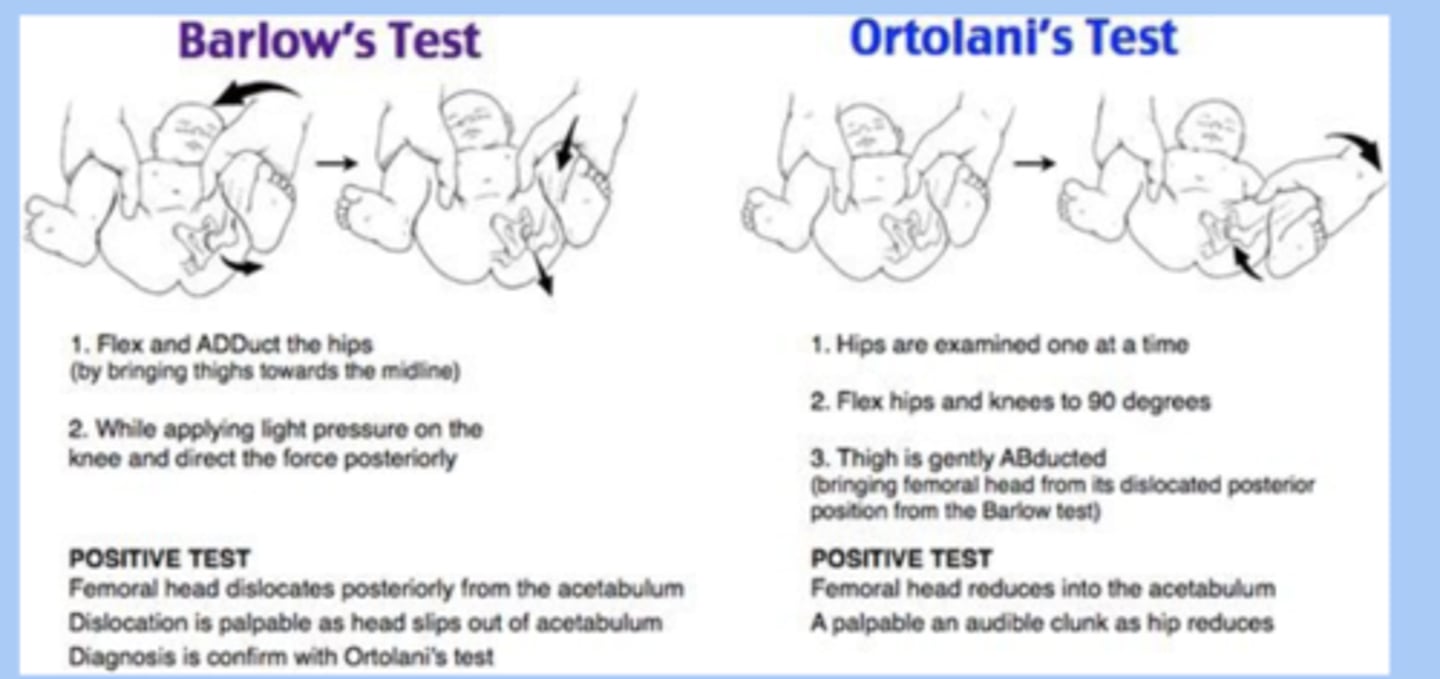
ortolani and barlow maneuvers
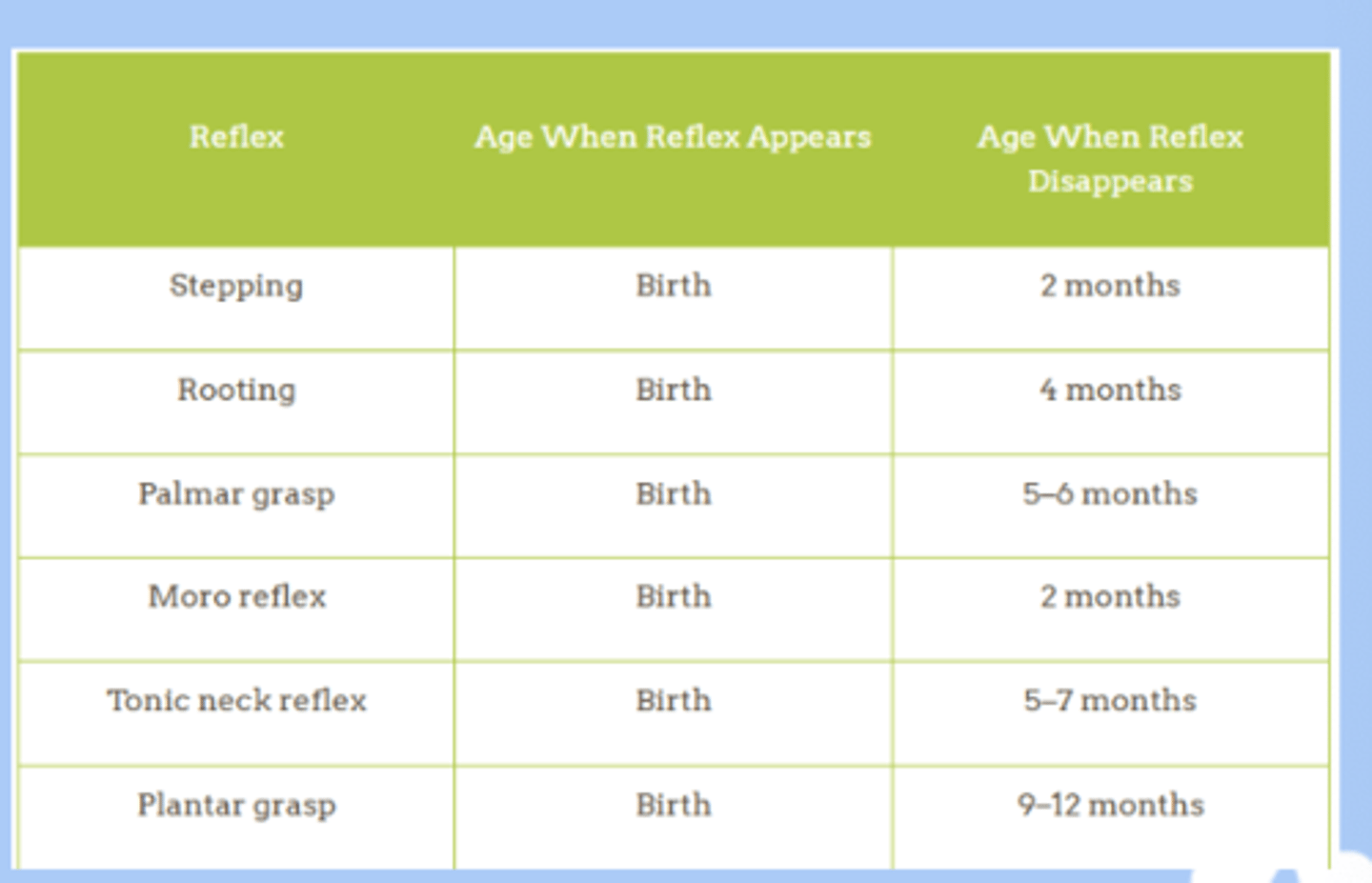
neurologic developmental reflex
-stepping
-startle
-sucking
-palmar grasp
-tonic neck
-plantar grasp
-babinski reflex
routine preventative measures in nursery
-prophylactic erythromycin to the eyes
-1mg vit K IM or SQ for hemorrhage
-hep B
-heel stick blood collection
-hearing screening
feeding
-healthy full term should feed every 2-3 hr on demand
-increased from 0.5-1 to 1.5-2 on day 3
what vitamin is recommended for all exclusively breastfed infants
vit D
healthy newborn should gain
1oz a day
neonatal jaundice
-65% of newborn develop visible jaundice with TSB higher than 6
-extremely high levels rare but can cause bilirubin encephalopathy and kernicterus, deafness, neuro defects
routine bilibrun screening for
ALL newborns at 24-48 hrs after birth
total bilibrun
direct (conjugated) + indirect (unconjugated)
-unconjugated most common from in neonatal period
combs test if
corn for pathologic cause of neonatal jaundice
physiologic jaundice
-unconjugated bilirubin
-after birth there is increased turnover in fetal RBC > production of more bilirubin and less clearance
-visible jaundice AFTER 24 hr
breastfeeding jaundice
-unconjugated bilirubin
-AFTER 24 hrs
pathologic neonatal jaundice
-FIRST 24 hr of life
-caused by hemolysis > unconjugated billirubinemia from RBC lysis
-serum bilirubin= elevated
-fractioned bilirubin= unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia
-coombs test= +
-RI= normal
neonatal jaundice tx
-supportive care
-phototherapy
-anemia patients need transfusions
transient tachypnea
-mild short term self limiting condition
-delayed clearance of fetal lung fluid via the circulation and pulmonary lymphatic
-resolution usually occurs within 12-24hr
meconium aspiration
-earliest stool of newborn
-MSAF newborns pass meconium during labor
maternal opiods use
-withdrawl: problem sleeping and feeding, fever, seizure
-begin 1-3 days
-4-5x risk of SIDS
maternal alcohol use
-fetal alcohol syndrome
-determined by degree and timing of ethanol exposure
-IUGR or small, feeding issue, sleep issue, delayed speech, low IQ
maternal use of tobacco
-nicotine concentration are 15% higher than in maternal blood
-infants exposed to nictoine are increased risk for preterm labor and SIDS
well child check
review basic developement: milesone, sleep, nutrition, screeing
milestone are
progressive
-childreen should not lose milestones previously accomplished
-regression can be indicative of developemnt disorder
2 mon milestone
-holds fingers closed but begins to open hands
4 mon milestone
-holds head without support, swings arm, hold toy, brings hand to mouth, pushes up on elbow
vital signs
-height
-weight
-BMI at age 2
-head circumference
-temp
-BP at age 3
-RR
-HR
growth parameters
-height and weight at every visit
-children under 2 plot weight-for-length
-children over 2 plot BMI
-head circumference
-18 mon most children tend to follow the curve
1-2w visit
-infant should be at or above birth weight
-umbilical cord should be off
chronologic age is a
poor indicator of physiologic and psychosocial development
puberty
-activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary gonadal axis in late childhood
-nutrition and general health can affect this
growth spurt
-girls: 11-12
-boys: 13-14
-last about 2-4 years and longer in men
sexual maturation in females
-first sign is growth spurt
-development of breast buds at 8-11
-menarche is usually 2 years after breast budding
-9-15
sexual maturation in males
-increase in testicular volume with reddening
-thickening of scrotal skin
-10-12
confidentiality
-adolescents are more likely to disclose sensitive information if they are assured confidentiality
-can be broken for life-threatening concerns of self or others
-offer private time w pt starting at 10
HEADSS assessment
-Home
-Education/employment
-Activities
-Drugs/diet
-Sexuality
-Suicide/depression
(for appropriate psychosocial hx)
depression screening
-starting at age 12 yearly universal screening
-PHQ-S Questionnaire
abuse and violence
-ask if there is presence and security of firearms in the home
-leading cause of death in american children and teens
pharmacological screening
-reserved for situations in which the patients behavioral dysfunction or medical condition are of sufficient concern to outweigh practical and ethical drawbacks of testing
adolescence physical exam
-vital signs, BMI, CDC, BP
-skin
-spine: scoliosis
adolescence GU exam
-important for determining puberty stage
-sextual maturity rating: Tanner Score
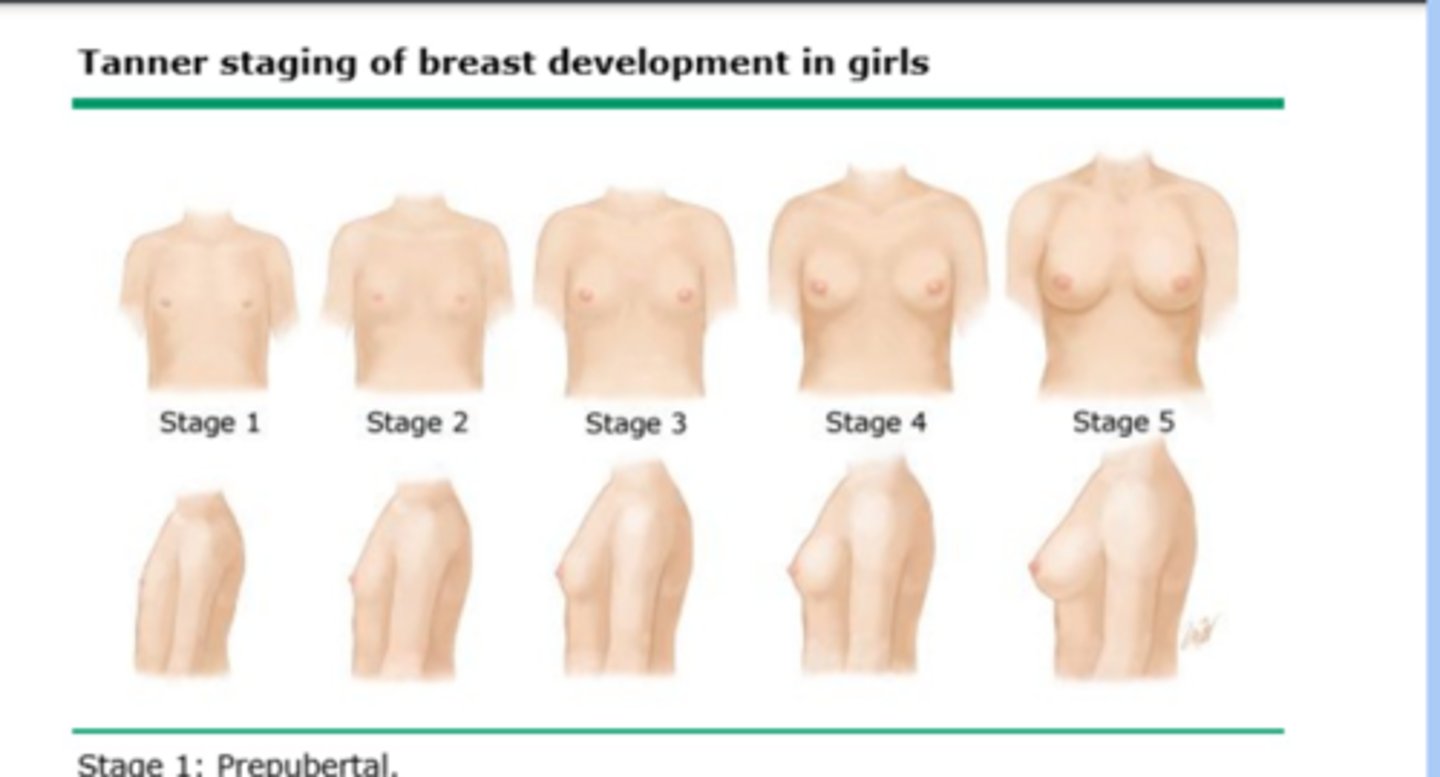
tanner stages female breast and genitalia
-stage 1: no development
-stage 2: breast bud
-stage 3: further enlargement
-stage 4: projection of areola and papilla
-stage 5: mature stage
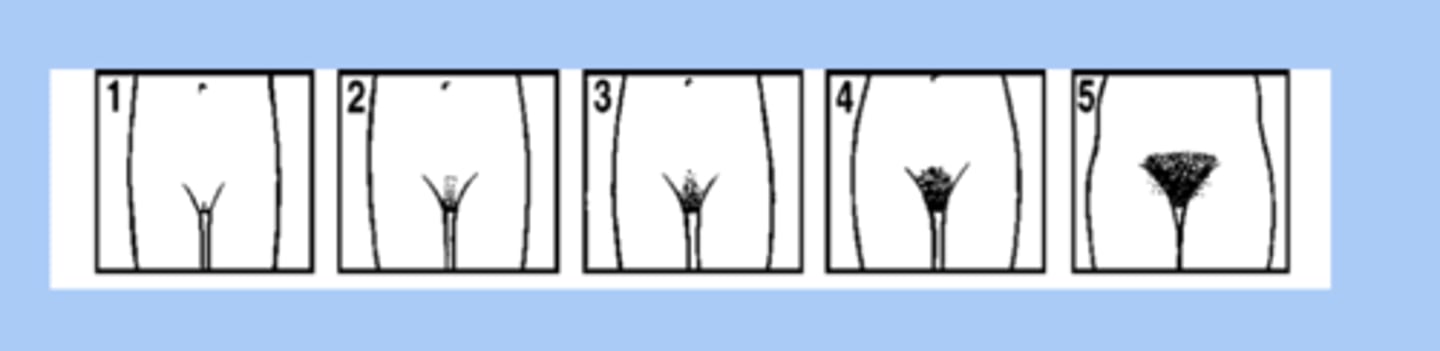
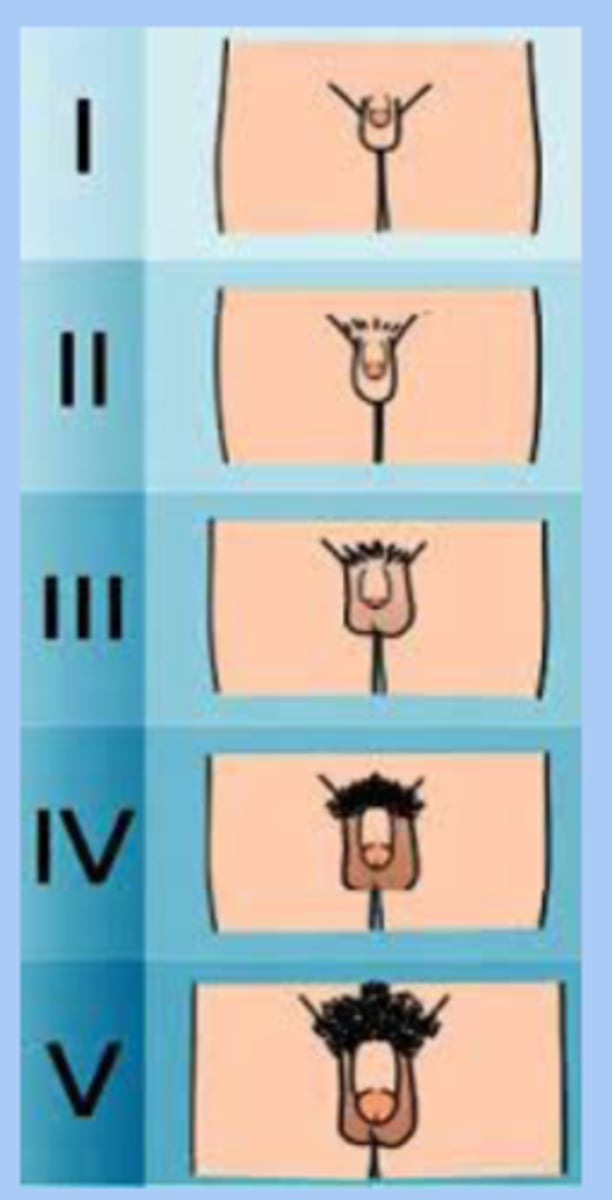
tanner stage genitalia
-stage 1: vellus is over area
-stage 2: sparse growth of long, slightly pigmented
-stage 3: hair is darker and coarse
-stage 4: hair is know adult are is covered
-stage 5: hair is adult in quanility and type
male GU exam
-tanner score
-chest
-genitalia: testicle and penile
tanner stage genitalia male
-stage 1: testes and scrotum and penis same size
-stage 2: testes get larger, thickening and reddening of skin, light hair
-stage 3: growth of penis in length and width, more hair darker
-stage 4: further largening of penis and scrotum and dark hair
-stage 5: genitalia in adult size, adult hair
BP screening starts at
3 years old
BP percentiles
-prehypertension: 90-95
-stage 1: 95 to >99
-stage 2: 99 +5 mmHg
obesity screening
-screen all children ages 3-18 for obesity
-calculate BMI and plot
-BMI >95th percentile = obese
anemia screening
-all children at 12 mon of age with CBC or H/H
increased risk of IDA from
-excess or early cows milk intake >16-20ox per day
lead screening
-all children at age 1 and 2 with serum lead level
-repeat testing ages 3-6
hearing screening
-newborns
- 4,5,6,8,10 years
vision screening
-ages 3-5 refer is worse than 20/40
-ages 6+ refer if worse than 20/30