Conservation Laws in Rigid Body Dynamics
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
• Explain work of a force • Solve problems that relate force, velocity and displacements via the principle of work and energy • Derive the conservation of energy form the principle of work and energy • Solve problems that relate force, time, and velocity via the principle of linear/angular impulse and momentum • Calculate the conservation of linear/angular impulse and momentum when particles collide/interact • Apply theory through a series of examples
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is the general formula for work done by a force

How is work expressed in terms of displacement along a force direction?

What is the formula for total work done by a force over a path?
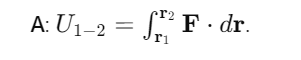
How is work done by weight calculated?
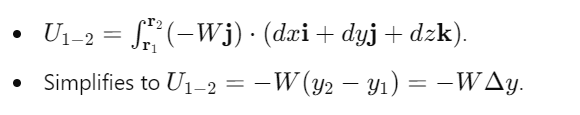
What does the work of weight depend on?

What is the formula for work done by a spring force Fs=−ks
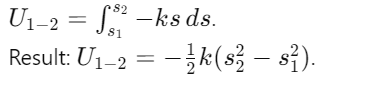
How is work calculated in terms of force and displacement along a curved path?

Why is work path-independent for conservative forces?
Conservative forces like gravity and springs depend only on the start and end points, not the path taken.
What is the equation of motion in the tangential direction?

What is the relationship between acceleration and velocity in terms of displacement?
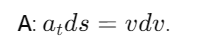
How is velocity related to displacement and time?
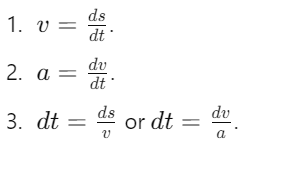
What is the expression for tangential force in terms of mass and velocity?
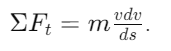
How is the work-energy equation derived from tangential force?
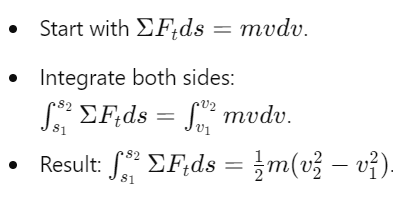
How is the principle of work and energy related to kinetic energy?
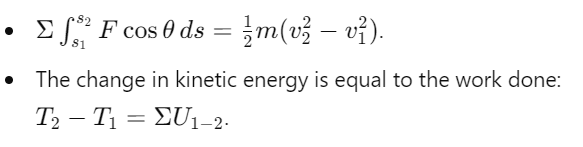
What is the formula for kinetic energy?
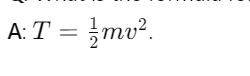
What does the principle of work and energy state?

What is a conservative force?
A force where the work done is independent of the path and depends only on the initial and final positions.
What is the principle of work and energy for a system?
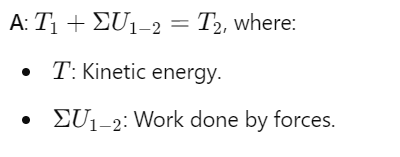
What is the definition of a nonconservative force?
A force where the work depends on the path taken.
Example: Friction force, which dissipates energy as heat.
What does the conservation of energy state?
During motion, the sum of a particle’s kinetic and potential energy remains constant.
How is total mechanical energy expressed?

What is the potential energy formula for weight?
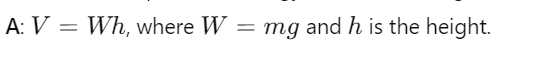
What is the kinetic energy at the top of a height h?

How is velocity related to height under conservation of energy?
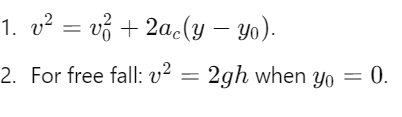
What is the velocity at mid-height h/2?
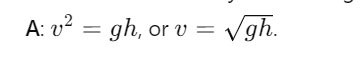
How does energy change during motion from height h to the ground?
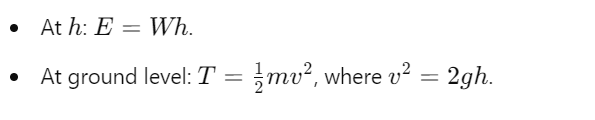
What is the work done by weight during free fall?

How is the principle of linear impulse and momentum derived?
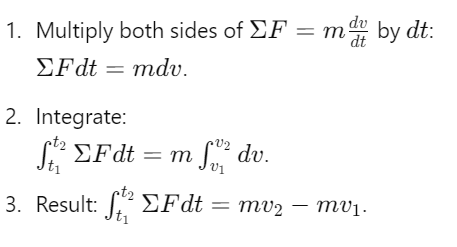
What does the principle of linear impulse and momentum state?
The total impulse equals the change in linear momentum:
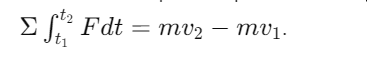
What is linear impulse?

How is linear impulse simplified for a constant force?
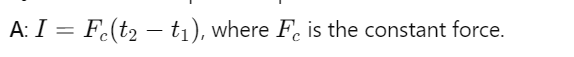
What happens to linear momentum when no external forces act on a system?
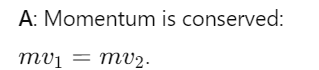
What is the conservation of linear momentum for interacting particles?
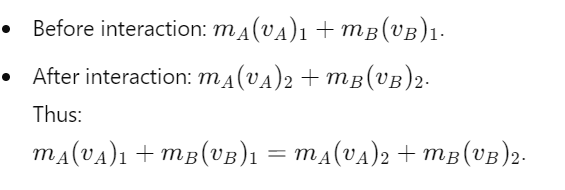
What is the conservation of linear momentum during a perfectly inelastic collision?
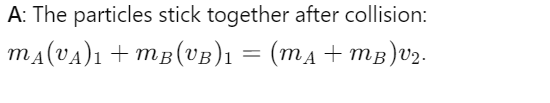
When is momentum conserved in a system?
