SAS 1 - Lev Vygotsky's Sociocultural Theory of Development
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Culture (Chiu & Hong, 2007)
a network of knowledge that is both procedural (i.e., learned sequence of responses to particular cues) and declarative (i.e., representations of people, events, and norms) and is produced, distributed, and reproduced among a collection of interconnected people
Material vs. Non-Material Culture
values, beliefs, symbols, and language that define a society
Material vs. Non-Material Culture
includes all society’s physical objects, such as tools and technology, clothing, eating, utensils, and means of transportation
Elements of Culture
Symbols
Symbols
things that stand for something else and that often evoke various reactions and emotions
could be non-verbal communication or actual material objects
Language
structured system of communication that involves words, signs, and other rules that allow humans to express themselves
develops from social interactions, for communication purposes
plays two critical roles in cognitive development
Two Critical Roles of Language in Cognitive Development
the primary means by which adults transmit information to children
a very powerful tool for intellectual adaptation
Three Forms of Language
Social Speech (age: 2)
Private Speech (age: 3)
Private Speech Going Underground (age: 7)
Social Speech
one of the three forms of language
developed at the age of 2
external communication used to talk to others
Private Speech
one the three forms of language
developed at the age of 3
directed to the self and serves an intellectual function
Private Speech Going Underground
one the three forms of language
developed at the age of 7
diminishing in audibility as it takes on a self-regulating function and is transformed into silent inner speech
Technology
the application of scientific knowledge to the making of tools to solve specific problems
Values
judgements of what is good or bad/desirable or undesirable
Norms
standards and expectations for behaving in certain situations
formal
informal
Formal Norms
mores
laws
Informal Norms
folkways
customs
Ethnicity
refer to a common background or social origins, shared culture and traditions that are distinctive, maintained between generations, and result in a sense of identity and group membership, and shared language or religious tradition
Race
refers to a shared genetic heritage, expressed by common external physical characteristics such as physical features, skin color, and hair texture
Othering
a pattern of exclusion and marginalization based on having identities that are different from what is considered normative
Lev Vygotsky
Russian
developed the Sociocultural Theory
Sociocultural Theory
views development as a socially-mediated process in which children acquire their cultural values, beliefs, and problem-solving strategies through collaborative dialogues with more knowledgeable members of the society
Basic Assumptions of Sociocultural Theory
More emphasis on culture affecting development
More emphasis on social factors contributing to development
Important role of language in development
Adults are an important source of development
More Emphasis on Culture Affecting Development
assumes that development varies across cultures and does not refer to universal stages and content of development
More Emphasis on Social Factors Contributing to Development
social interactions and the cultural environment influence how children grow up
Important Role of Language in Development
development results from the internalization of language
Adults are an Important Source of Development
adults transmit their culture’s tools of intellectual adaptation that children internalize
Tools of Intellectual Adaptation
methods of thinking and problem-solving strategies that children internalize through social interactions with the more knowledgeable members of society
Elementary Mental Functions
attention
sensation
perception
memory
Higher Mental Functions
more sophisticated and effective mental processes
Elementary Mental Functions are enhanced to this through Social Interactions
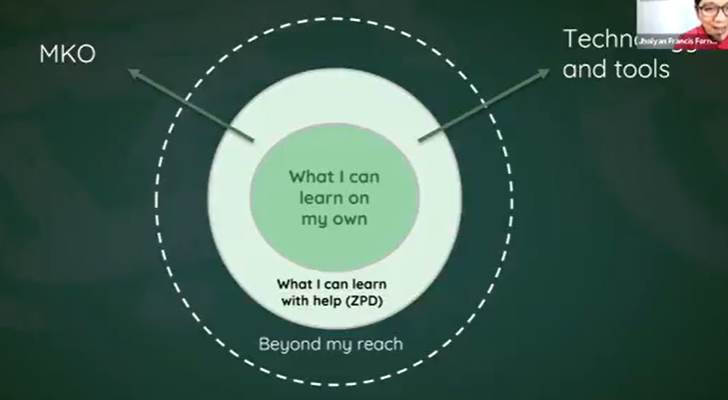
More Knowledgeable Other (MKO)
refers to someone (or something) who has a better understanding or a higher ability level than the learner, with respect to a particular task, process, or concept
Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD)
the difference between what a child or learner can do alone and what he/she/they/it can do with the guidance and encouragement of an MKO
Visual Representation of Vygotsky’s Basic Concepts