Tissue Lecture Exam
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/55
Last updated 4:00 AM on 10/3/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
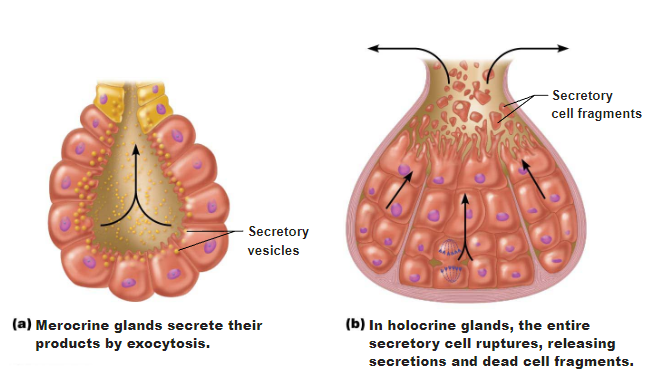
Merocrine
Secrete products by exocytosis
2
New cards
Holocrine
Accumulates products then ruputures
3
New cards
Apocrine
Accumulates products but only ruptures at the apex
4
New cards
Goblet cells
Found in simple columnar epithelium and pseudostratified columnar epithelium
5
New cards
Intercalated discs
found in Cardiac Muscle tissue
6
New cards
Where would you find macrophages? (loose connective tissue)
Areolar and reticular CT
7
New cards
White fat
Used for nutrient storage, shock absorption, insulations, and energy storage
8
New cards
Brown fat
Used to heat bloodstream and body
9
New cards
Hyaline cartilage
Found in the ends of long bones
10
New cards
Elastic Cartilage
Found in ears and epiglottis
11
New cards
Fibrocartilage
Strong and able to absorb impact found in intervertebral discs and knee
12
New cards
Tissues with extremely well regenerative capacity
Epithelial tissue, bone, areolar, dense irregular, and blood forming tissue
13
New cards
Tissues with moderate regenerative capacity
Smooth muscle and dense regular
14
New cards
Tissues with no regenerative capacity
Cardiac muscle and nervous tissue
15
New cards
Examples of connective tissue
Areolar, adipose, reticular, dense regular, dense irregular, elastic CT, hyaline, fibrocartilage, elastic cartilage, bone, and blood
16
New cards
What would you find in a bone?
Osteoblasts, Hematopoietic stem cells, collagen, inorganic calcium slats, osteocytes (MAINTAIN MATRIX IN THE BONE), lacunae, and osteons
17
New cards
Fibroblasts
Found in CT proper
18
New cards
Chondroblasts
Found in cartilage
19
New cards
Osteoblasts
found in bone
20
New cards
Microvilli
help increase surface area in epithelial cells (places of absorption)
21
New cards
Cilia
help move things across a cell (like mucous)
22
New cards
What connective tissue elements makes up the extracellular matrix?
Ground substance and fibers
23
New cards
Simple squamous epithelium (location and function)
Found in air sacs of lungs and are involved in absorption, secretion, and filtration processes
24
New cards
Simple cuboidal epithelium (location and function)
Found in Kidney tubules and are involved in secretion and absorption
25
New cards
Simple columnar epithelium (location and function)
Found in digestive tract, gallbladder, ducts of some glands, bronchi, and uterine tubes. Are involved in absorption and secretion of mucus, enzymes, and other substances
26
New cards
What type of cells will you see in Areolar CT?
Fibroblasts, macrophages, fat cells, and some white blood cells
27
New cards
Main function of epithelial tissue
Protections, absorption, filtration, excretions, secretion, sensory reception
28
New cards
Collagen Fibers
Strongest and most abundant fiber, provides high tensile strength
29
New cards
Elastic Fibers
Network of long thin elastic fibers that stretch and recoil
30
New cards
Reticular Fibers
Short, fine, and highly branched collagenous fibers
31
New cards
Steps in preparing tissue to be viewed under a microscope
1. fixed and preserved with a solvent
2. cut into thin slices to transmit light or electrons
3. stained to enhance contrast
2. cut into thin slices to transmit light or electrons
3. stained to enhance contrast
32
New cards
Tissue
A group of cells similar in stricture that perform common or related functions
33
New cards
Histology
The study of tissues
34
New cards
Endocrine glands
Secrete internally (EX hormones), ductless, and travel through bloodstream
35
New cards
Exocrine glands
Secrete on body surface and cavities through ducts
36
New cards
Steps in tissue repair
1. Inflammation (blood vessels dilate, blood clotting occurs)
2. Organization (blood clot is replaced with granulation tissue, debris is phagocytized, fibroblasts produce collagen fibers to bridge gap, and the epithelium begins to regenerate)
3. Regeneration (the scab detaches, fibrous tissue matures, epithelium thickens to resemble nearby tissue, ends in regenerated epithelium with underlying scar tissue)
2. Organization (blood clot is replaced with granulation tissue, debris is phagocytized, fibroblasts produce collagen fibers to bridge gap, and the epithelium begins to regenerate)
3. Regeneration (the scab detaches, fibrous tissue matures, epithelium thickens to resemble nearby tissue, ends in regenerated epithelium with underlying scar tissue)
37
New cards
Main components of CT
Interstitial fluid, cell adhesion proteins, proteoglycans, water
38
New cards
Main job of Connective Tissue
Support, protections, binding of tissues
39
New cards
Cardiac muscle
Involuntary and found in the heart
40
New cards
Skeletal muscle
Voluntary and found attached to bones
41
New cards
Smooth muscle
Involuntary and found in hollow organs
42
New cards
Cutaneous membrane
SKIN, a dry membrane
43
New cards
Mucous membrane
also called mucosae, lines body cavities that are open to the exterior (EX respiratory, urogenital, and digestive), moist membrane, epithelial sheet lies over layer of loose connective tissue called LAMINA PROPRIA, may secrete mucus
44
New cards
Serous membrane
Also called serosae and found in ventral cavities. Made from simple squamous epithelium (mesothelium) resting on areolar CT. PARIETAL serosae lines internal body cavity walls while VISCERAL covers internal organs. moist membranes.
Pleurae - lungs
Pericardium - heart
Peritoneum - abdomen
Pleurae - lungs
Pericardium - heart
Peritoneum - abdomen
45
New cards
Mesenchyme
All connective tissues arise from this as their origin
46
New cards
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Found in skin, nonkeratinized are found in moist linings
47
New cards
Primary tissues
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nervous
48
New cards
What makes up myofilaments?
Actin and Myosin, they help contract muscles
49
New cards
Membrane linings and coverings are composed of what 2 tissues?
Epithelial and CT Proper tissues
50
New cards
Apical surface
Top surface, used to define stratified epitheliums
51
New cards
Basal surface
Bottom layer
52
New cards
Histology tree
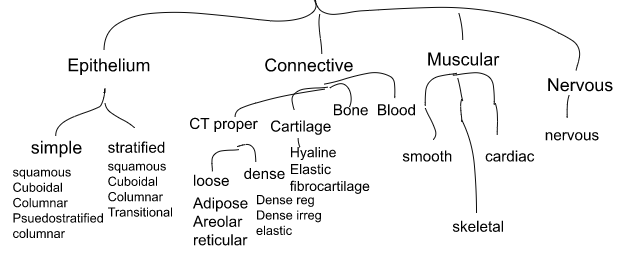
53
New cards
Mesothelium
serous membranes in the ventral body cavities
54
New cards
Endothelium
lining of lymphatic vessels, blood vessels, and heart
55
New cards
How do you define a stratified epithelium?
By the apical surface
56
New cards
Categorize structure of glands