Grammar bitch
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:13 PM on 12/18/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
What are the differences between lexical and function words? Provide definitions and relevant examples.
Lexical words carry meaning (you can describe those words to someone (chair, table, folder etc.)), function words carry functional (grammatical) information (hard to define their meaning but they have some grammatical function in the sentence (there, here, before, on, off etc.))
2
New cards
Word Classes:
1. Lexical words
2. Function words
3. Inserts
2. Function words
3. Inserts
3
New cards
Inserts
Inserted remarks (ugh, umm, like etc.)
4
New cards
What is a noun phrase?
A phrase formed by a noun and all its modifiers and determiners
5
New cards
Define and provide examples of head, modifier, compliment
Head - the main word in a phrase (the noun completion is the head of the noun phrase [the completion of the task]
Modifier - modifies the meaning of another element of the sentence (young is a modifier of the NP [a young woman] which modifies the head (woman) of the NP), precedes the noun
Complement - word or word group that completes the predicate in a sentence ('difficult' is a complement in the phrase [Math is difficult])
Modifier - modifies the meaning of another element of the sentence (young is a modifier of the NP [a young woman] which modifies the head (woman) of the NP), precedes the noun
Complement - word or word group that completes the predicate in a sentence ('difficult' is a complement in the phrase [Math is difficult])
6
New cards
What are the main types of nouns?
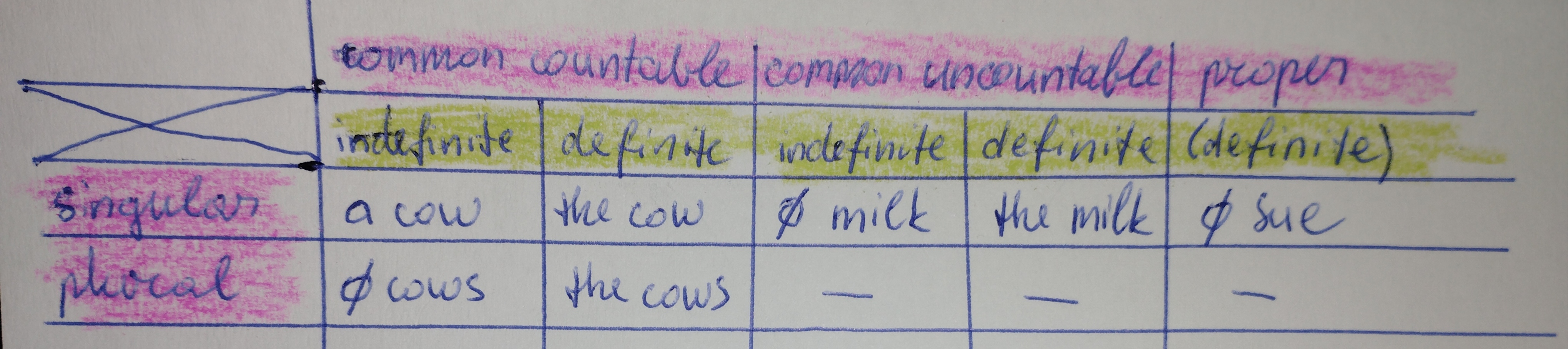
1. Countable - nouns that you can count on your fingers (jars, bags, shirts)
2. Uncountable - nouns thar you cannot count on your fingers (milk, metal, rain)
1. Proper nouns - any kind of names (Anna, Australia, Apple (brand name), Sunday)
2. Common nouns - nouns that describe a type of person, thing, or place or that names a concept (adult, camera, country)
2. Uncountable - nouns thar you cannot count on your fingers (milk, metal, rain)
1. Proper nouns - any kind of names (Anna, Australia, Apple (brand name), Sunday)
2. Common nouns - nouns that describe a type of person, thing, or place or that names a concept (adult, camera, country)
7
New cards
What are the main types of determiners?
1. Zero article
2. Indefinite article - 'a/an'
3. Definite article - 'the'
4. Possessive - 'my/your'
5. Demonstrative - 'this/that, these/those'
6. Quantifier - 'every/each, either/neither, any, no, all, many, some, (a) few, enough, several, both, much, some, (a) little'
7. Numeral - 'one, two/three etc.'
2. Indefinite article - 'a/an'
3. Definite article - 'the'
4. Possessive - 'my/your'
5. Demonstrative - 'this/that, these/those'
6. Quantifier - 'every/each, either/neither, any, no, all, many, some, (a) few, enough, several, both, much, some, (a) little'
7. Numeral - 'one, two/three etc.'
8
New cards
Determiners
Function words used to specify the kind of reference a noun has
9
New cards
What are the different types of nouns according to their morphological composition?
- Simple nouns - don't have prefixes and suffixes (chair, table, room, map)
- Derivative nouns - nouns that have prefixes, suffixes or even both (reader, inability, kindness)
- Compound nouns - nouns built from two or more stems (sunflower, rainfall, snowball, blackbird)
- Derivative nouns - nouns that have prefixes, suffixes or even both (reader, inability, kindness)
- Compound nouns - nouns built from two or more stems (sunflower, rainfall, snowball, blackbird)
10
New cards
What are the main syntactic functions of the noun?
1. The Subject [Lucy went for a walk]
2. Direct object [I love Lucy]
3. Indirect object [Give her a kiss]
4. The Predicative [This is Lucy]
4. The Complement [Lucy is astonishingly beautiful]
5. The Adverbial modifier [Let's meet at Lucy's)
2. Direct object [I love Lucy]
3. Indirect object [Give her a kiss]
4. The Predicative [This is Lucy]
4. The Complement [Lucy is astonishingly beautiful]
5. The Adverbial modifier [Let's meet at Lucy's)
11
New cards
What are the main semantic groups of nouns?
1. Abstract - refer to abstract things that aren't physical entities or substances like events, states of being, times, qualities (party, love, midnight, beauty)
2. Concrete - refer to physical entities or substances (desk, pen, wall, sandwich)
2. Concrete - refer to physical entities or substances (desk, pen, wall, sandwich)
12
New cards
???????????What are the main functions of articles with common nouns?
The Indefinite article with singular nouns
1. The nominating function - when we want to name an object, to state what kind of object is meant; the main function of the indefinite article with countable nouns (I gave her a pen)
2. Oneness
The Indefinite article with uncountable nouns and with nouns which have no reference to the category of countability
1. The aspective function
The definite article with countable nouns (sg and pl)
1. The defining function - definite article serves to single out an object or several object from all the other objects from the same class (As we stood on the steps, we felt the smell of fallen leaves coming from the garden)
2. The generic function
The definite article with uncountable nouns
1. Restricting -
The definite article with nouns which have no reference to the category of countability
1. The defining function
Zero article with plural nouns
1. The nominating function
2. More-than-oneness
Zero article with uncountable nouns
1. The nominating function
1. The nominating function - when we want to name an object, to state what kind of object is meant; the main function of the indefinite article with countable nouns (I gave her a pen)
2. Oneness
The Indefinite article with uncountable nouns and with nouns which have no reference to the category of countability
1. The aspective function
The definite article with countable nouns (sg and pl)
1. The defining function - definite article serves to single out an object or several object from all the other objects from the same class (As we stood on the steps, we felt the smell of fallen leaves coming from the garden)
2. The generic function
The definite article with uncountable nouns
1. Restricting -
The definite article with nouns which have no reference to the category of countability
1. The defining function
Zero article with plural nouns
1. The nominating function
2. More-than-oneness
Zero article with uncountable nouns
1. The nominating function
13
New cards
Limiting attribute
Quality or characteristic of an object which makes it distinct from all the other objects of the class (That he should help a promising young man was perhaps 'the most important consideration' of all)
14
New cards
Descriptive attribute
Is used to describe an object or give additional information about it. It doesn't single out an object but only narrows the class to which it belongs (Give me 'a book' ----> Give me 'an English book' ----> Give me 'an interesting English book')
15
New cards
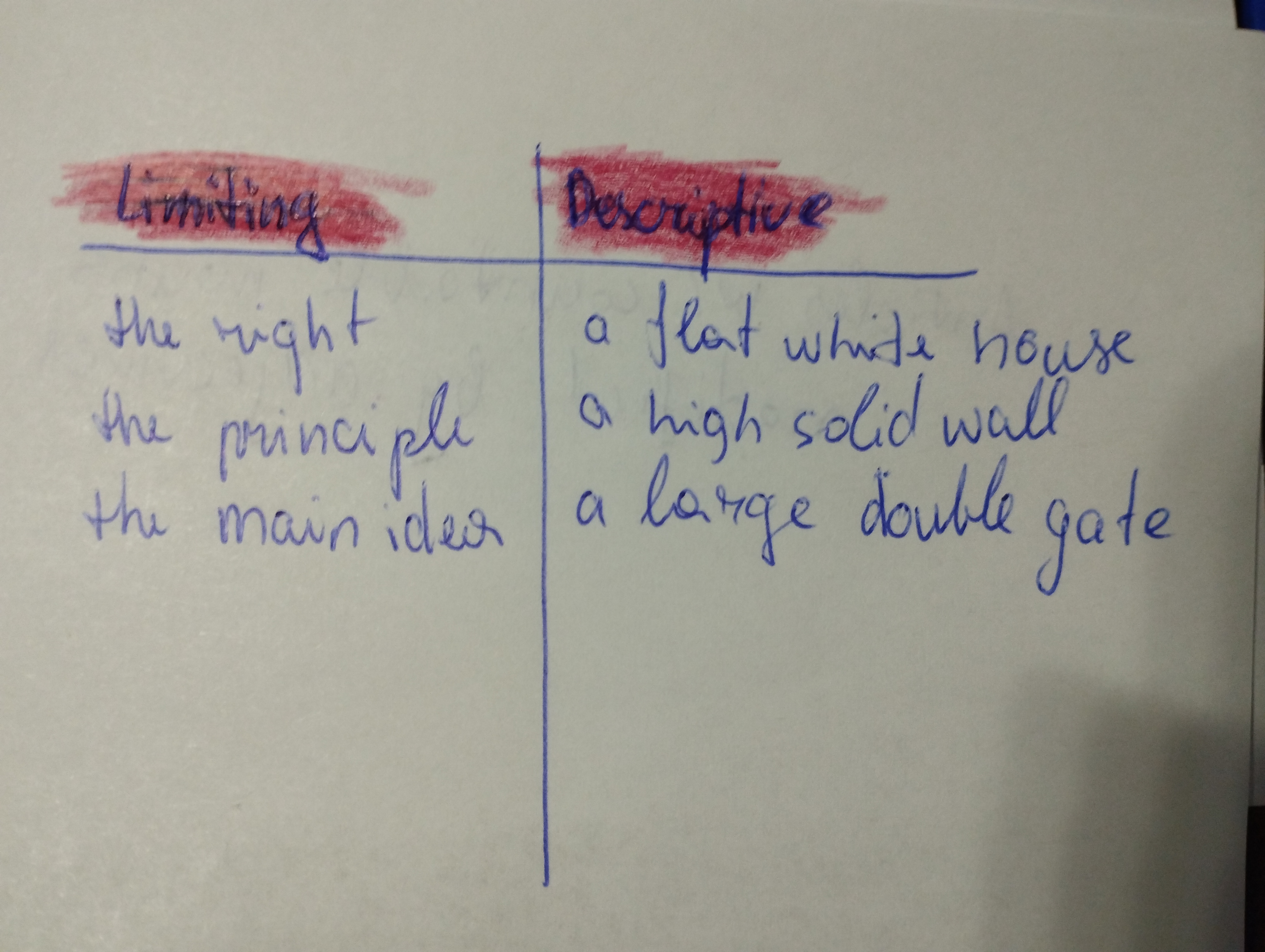
Describe the use of articles with countable nouns modified by adjectives
Limiting (the right, the principle, the main idea)
Descriptive (a flat white house, a high solid wall, a beautiful blonde girl)
Descriptive (a flat white house, a high solid wall, a beautiful blonde girl)
16
New cards
Describe the use of articles with countable nouns modified by numerals
Cardinal numerals are descriptive. (He had refused (zero article) three invitations to the party
Ordinal numerals are usually limiting. (the second bell rang, a third cup of tea)
0 article 'in chapter 5' because 5 belongs to chapter
Ordinal numerals are usually limiting. (the second bell rang, a third cup of tea)
0 article 'in chapter 5' because 5 belongs to chapter

17
New cards
Describe the use of articles with countable nouns modified by participles
Depends on the context. Participles: Pre-position (a newly painted house); Post-position (the fence surrounding the garden)

18
New cards
Describe the use of articles with countable nouns modified by -ing forms
+ of/at/for
Tend to be limiting (the thought of leaving him...) (It is a question of instructing and training the new members)
Tend to be limiting (the thought of leaving him...) (It is a question of instructing and training the new members)

19
New cards
Describe the use of articles with countable nouns modified by an infinitive
Descriptive; situation is important (an hour to spare; a meeting to be held in March)

20
New cards
Describe the use of articles with countable nouns modified by attributive clause
g

21
New cards
??????Describe the use of articles with countable nouns modified by appositive clauses
f
22
New cards
Describe the use of articles with countable nouns modified by nouns in the common case

23
New cards
Describe the category of number in English
Nouns, pronouns, determiners and verbs can be singular or plural in English
24
New cards
How are the plural forms of nouns formed? What are the spelling rules of regular plurals?
By adding -s to the singular (cow - cows, hero - heroes, baby - babies, wife - wives)
Nouns ending in -s, -sh, -ch, -x form the plural by adding -es to the singular (class - classes, match - matches, dish - dishes)
A few nouns form their plural by making some changes to inside vowels (foot - feet, woman - women, mouse - mice)
Nouns ending in -s, -sh, -ch, -x form the plural by adding -es to the singular (class - classes, match - matches, dish - dishes)
A few nouns form their plural by making some changes to inside vowels (foot - feet, woman - women, mouse - mice)
25
New cards
How is the plural of compound nouns formed?
By pluralizing the semantic head (the word that conveys the primary meaning): doctor of philosophy - doctors of philosophy; passerby - passersby;
26
New cards
What are irregular plurals?
Plurals that are note formed by adding -s or -es at the end (woman - women, foot - feet, man - men)
27
New cards
Describe the category of case in English
Case shows a noun's or a pronoun's relationship with other words in a sentence
Main cases:
- the Genitive case
- The common case
Main cases:
- the Genitive case
- The common case
28
New cards
What are the rules of the genitive case formation?
With singular nouns and with plural nouns not ending in s it is usually formed by adding 's to the word (dog's dinner; men's room)
With plural noun we add s' (dogs' dinner (dinner of multiple dogs))
With singular noun ending in s we can add either 's or s' (Chris' hat; Chris's hat)
We can also form genitive case by preceding the noun with ''of'' (the edge of the table)
With plural noun we add s' (dogs' dinner (dinner of multiple dogs))
With singular noun ending in s we can add either 's or s' (Chris' hat; Chris's hat)
We can also form genitive case by preceding the noun with ''of'' (the edge of the table)
29
New cards
What is the difference between the specifying and classifying genitive?
Specifying - it can be replaced by the of-phrase (glory's edge - the edge of glory), it is used with proper names or it could also be used with collective nouns (the government's decision)
Classifying (descriptive) - denotes a quality and refers to a whole class of similar objects (a girls' school --> a school for girls). It is also used with nouns denoting time and distance (an hour's trip, a week's time)
Classifying (descriptive) - denotes a quality and refers to a whole class of similar objects (a girls' school --> a school for girls). It is also used with nouns denoting time and distance (an hour's trip, a week's time)
30
New cards
What is the group genitive?
’s may be added not only to a single noun, but to a whole group of words (Jack and Anne's house (the house belongs to Jack and Anne), the Prime Minister of England's residence)
31
New cards
What is the double genitive?
A phrase in which possession is indicated by 'of' and followed by the possessive from of a noun (a friend of Anne's)
32
New cards
??????????What are the main uses of the articles with countable nouns modified by nouns in the genitive case?
33
New cards
What are the main uses of the articles with countable nouns modified by prepositional phrases?
Attributes may be expressed by nouns with various prepositions. Depending on the context or the situation, they may be either descriptive (a marriage with a boy in a jazz band) or limiting (the boats in the harbor).
34
New cards
What are the tendencies for using the genitive (ʼs) or the of structure?

35
New cards
What is the difference between anaphoric and cataphoric use of the definite article?
Anaphoric - the phrase with the refers back to a previously
mentioned item (A boy just walked into a busy street. The boy looked confused as to why it was so busy.)
Cataphoric - definite reference is established by something following later in the text ('It's' nice, 'the table')
mentioned item (A boy just walked into a busy street. The boy looked confused as to why it was so busy.)
Cataphoric - definite reference is established by something following later in the text ('It's' nice, 'the table')
36
New cards
Describe and illustrate the generic function of the definite article
Reference is generic when a noun
phrase refers to the whole class, rather
than just one or more instances of the
class and all three articles can be used
('A doctor' is not better than his patient; 'Doctors' are not better than their patient; 'The doctor' is not better than his patient)
phrase refers to the whole class, rather
than just one or more instances of the
class and all three articles can be used
('A doctor' is not better than his patient; 'Doctors' are not better than their patient; 'The doctor' is not better than his patient)
37
New cards
What are the main tendencies in the use of articles with countable nouns in predication, apposition and other syntactic patterns?

38
New cards
Explain the difference in use of object pronouns (*me, you, him…*), possessive determiners (*my, your, his…*) and possessive pronouns (*mine, yours, his…*)
39
New cards
What is the difference between central and peripheral adjectives?
Central adjective has to fulfill this criteria:
1. Can be inflicted
2. Can be both predicative and attributive
3. They are descriptive
4. They are gradable
(e.g. surprising - peripheral because can’t be inflicted although is both predicative (the gift is surprising) and attributive (surprising gift), descriptive (describes a noun e.g. surprising gift) and gradable (a bit surprising, very surprising, the most surprising)
\
Peripheral adjectives don’t fulfill one or more of the criteria
\
Therefore, the difference between central and peripheral adjectives is that peripheral adjectives don’t have one or more of the central adjective characteristics.
1. Can be inflicted
2. Can be both predicative and attributive
3. They are descriptive
4. They are gradable
(e.g. surprising - peripheral because can’t be inflicted although is both predicative (the gift is surprising) and attributive (surprising gift), descriptive (describes a noun e.g. surprising gift) and gradable (a bit surprising, very surprising, the most surprising)
\
Peripheral adjectives don’t fulfill one or more of the criteria
\
Therefore, the difference between central and peripheral adjectives is that peripheral adjectives don’t have one or more of the central adjective characteristics.
40
New cards
Give some examples of adjectives used attributively and predicatively. ????????Adjectives with *a-* prefix are usually… attributive or predicative?
Attributive (a nice man, an evil witch, a malicious virus)
\
Predicative (a man who is nice, a witch who is evil, a virus that is malicious)
\
\
\
Predicative (a man who is nice, a witch who is evil, a virus that is malicious)
\
\
41
New cards
Explain and illustrate the three ways of forming new adjectives: participial forms, derivational suffixes, compounding.
1. Participle forms - adjectives are derived from verbs and usually end in -ed or -ing (reading glasses, baked beans, broken table)
2. Derivational suffixes - adjectives are derived from nouns by adding a suffix like -ish, -al, -ly, -like, -ous, -ary, -ic, -less, and ful (normally, tasteless, gastric etc.)
3. Compounding - adjectives are made by putting two words together (fast-paced, well-known, quick-witted)
42
New cards
What are the main rules for the adjective order in groups of adjectives? In paired adjectives?
43
New cards
List the syntactic roles that adjectives can take. Give some examples and explain the syntactic structures involved.
44
New cards
What are the main morphological categories of adverbs? Give some examples.
45
New cards
What are the main syntactic functions of adverbs? Give some examples of adverbials of time, frequency, place, direction, and manner.