3.1 Business growth and 3.2 business objectives
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Reasons why firms grow
Owners/shareholders desire for higher levels of profit
Desire to reduce average costs by benefiting from economies of scale
Growth provides opportunities for product diversification
Desire for stronger market power (monopoly) so as to increase profits
Reasons why small firms exist
They offer a more personalised service and focus on building relationships with their customers
Many small firms operate in mass markets with low barriers to entry
They provide a product that is in a niche market - smaller market size but can be very profitable
Owners goal is not profit maximisation but rather an acceptable quality of life (satisficing)
Economies of scale
Occurs when an increase in the sale of output results in a lower cost per unit
Product diversification
Occurs when a firm is able to increase the number of products that it offers and reduces risk
if one product fails others may well still be successful
barriers to entry
Conditions that make it difficult to enter a market to compete with the existing suppliers
diseconomies of scale
Occurs when an increase in the sale f output results in a higher cost per unit
Public sectors
owned and controlled by the Government
Their goal is not profit maximisation but to provide a service
There are a wide variety of government owned organisations in the UK
private sector
organisations are owned and controlled by private individuals
Types of ownership vary from sole trader to partners to company shareholders
The goal of most private sector organisations is profit maximisation
This often means the private sector is more efficient than the public sector, with higher levels of productivity
not-for-profit orgnaisations
They exist to provide a service or meet a need
Many sell goods/services and use the profits they generate to further their objectives, e.g. The British Heart Foundation
The government exempts them from paying direct taxes
How businesses grow
organic growth
forwards and backwards vertical integration
horizontal integration
conglomerate integration
Organic growth (internal)
usually generated by
gaining greater market share
product diversification
opening a new store
international expansion
Investing in new technology/production machinery
Inorganic growth
Vertical integration (forward or backwards)
Horizontal integration
Conglomerate integration
forward vertical integration
nvolves a merger or takeover with a firm further forward in the supply chain
E.g. A dairy farmer merges with an ice-cream manufacturer
merger
Occurs when 2 firms combine to create a new firm
takeover
The purchase of a controlling interest in one firm by another
Backward vertical integration
Involves a merger/takeover with a firm further backward in the supply chain
E.G An ice-cream retailer takes over an ice-cream manufacturer
Vertical integration
Refers to a merger/takeover of another firm in the supply chain/different stage of the production process
Horizontal integration
A merger/takeover of a firm at the same stage of the production process
Conglomerate integration
Merger/takeover of firms in an entirely different industry
Advantages of organic growth
The pace of growth is manageable
Less risky as growth is financed by profits and there is expertise in the industry
Avoids diseconomies of scale
The management know and understand every part of the business
Disadvantages of organic growth
The pace of growth can be slow and frustrating
Not necessarily able to benefit from economies of scale
Access to finance may be limited
advantages of vertical integration
Reduces the cost of production as middle party profits are eliminated
Lower costs make the firm more competitive
Greater control over the supply chain reduces risk as access to raw materials is more certain
Quality of raw materials can be controlled
Forward integration adds additional profit as the profits from the next stage of production are assimilated
Forward integration can increase brand visibility
Disadvantages of vertical integration
Reduces the cost of production as middle party profits are eliminated
Lower costs make the firm more competitive
Greater control over the supply chain reduces risk as access to raw materials is more certain
Quality of raw materials can be controlled
Forward integration adds additional profit as the profits from the next stage of production are assimilated
Forward integration can increase brand visibility
advanatages of horizontal integration
Rapid increase of market share
Reductions in the cost per unit due to economies of scale
Reduces competition
Existing knowledge of the industry means the merger is more likely to be successful
A firm may gain new knowledge or expertise
Disadvantages of horizontal integration
Diseconomies of scale may occur as costs increase, e.g. unnecessary duplication of management roles
There can be a culture clash between the two firms that have merged
constraints on business growth
The size of the market: the more niche the market, the smaller the number of potential customers. Even large firms face this constraint as they move closer to capturing the domestic market - to increase market size, they will have to expand internationally
Access to finance: small firms find it harder to access loans as they are considered to be more risky than larger firms. Due to the perceived risk, interest rates for any loans acquired tend to be higher
Owner objectives: Many owners desire to grow a business to a point that provides a desired lifestyle or standard of living - and not beyond
Regulation: Large firms are often constrained by competition regulation that aims to limit monopoly power. Firms that sell demerit goods also find growth can be limited by government policies such as age restrictions, minimum prices and indirect taxes
reasons for demergers
Reducing diseconomies of scale 0- Decreasing the size of the firm can reduce the diseconomies and lower the cost/unit which increases the profitability
Cultural differences- Sometimes these differences are irreconcilable and not worth the expense to change
remove loss making divisions - It can be more profitable to remove loss-making divisions and replace them with outsourcing
Increased business focus- If efforts and resources are scattered across a large number of firms/ industries it can be hard to maintain focus and profitability. Narrowing the focus can improve profitability
Impact of demerges on the firm
Opportunity for a more narrow focus on the core business
Removing loss-making portions of the business
Increased efficiency and lower costs/unit
Increasing the annual profits for the year that the demerger occurred
Removing some difficult cultural differences
impact of demergers on employees
Some workers may lose their jobs
Reduced friction from cultural differences can help build better team dynamics
A smaller workforce provides more opportunity for promotion
Less complications in daily tasks due to more narrow focus
impacts of demergers on consumers
If successful, better quality products and customer service
If successful, lower prices due to the firms new efficiencies
If unsuccessful, a narrower product range and perhaps worse quality/customer service
Business objectives
profit maximisation
revenue maximisation
sales maximisation
satisficing
profit maximisation
When MC < MR additional profit can still be extracted by producing an additional unit of output
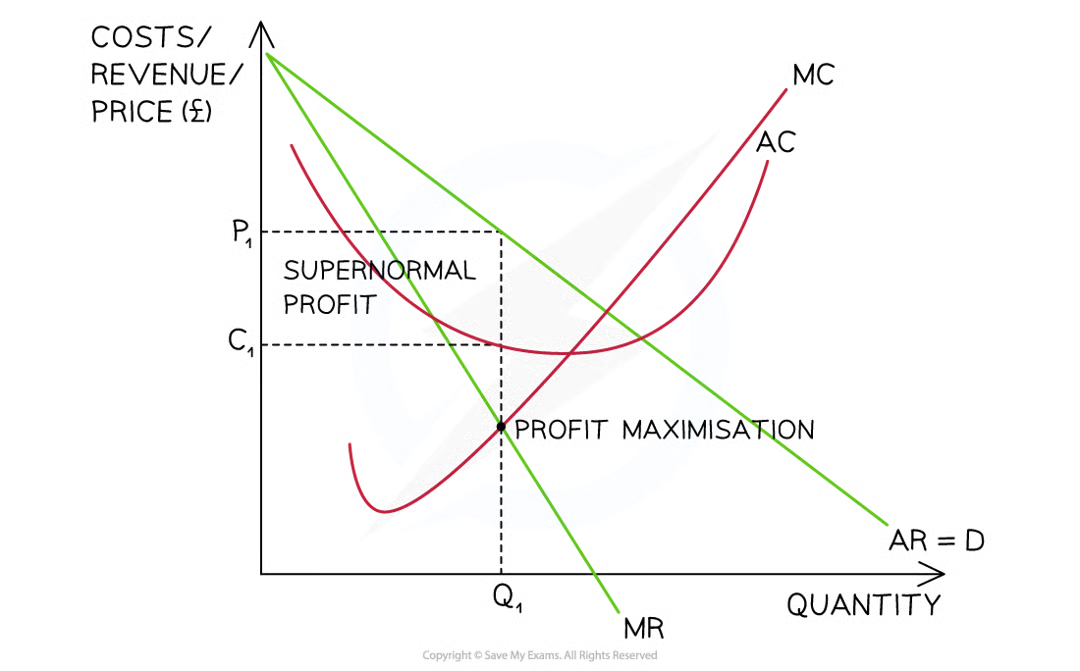
Profit maximisation rule = A firm should continue producing additional units until MC= MR
At the profit maximisation level of output (MC = MR)
The selling price is P1
The average cost is C1
The supernormal profit =(p1-c1) x Q1
Revenue maximisation
Firms will also maximise revenue in order to increase output & benefit from economies of scale
In the short-term firms may use this strategy to eliminate the competition as the price is lower than when focusing on profit maximisation
level of output where MR = 0

Sales Maximisation and satisficing
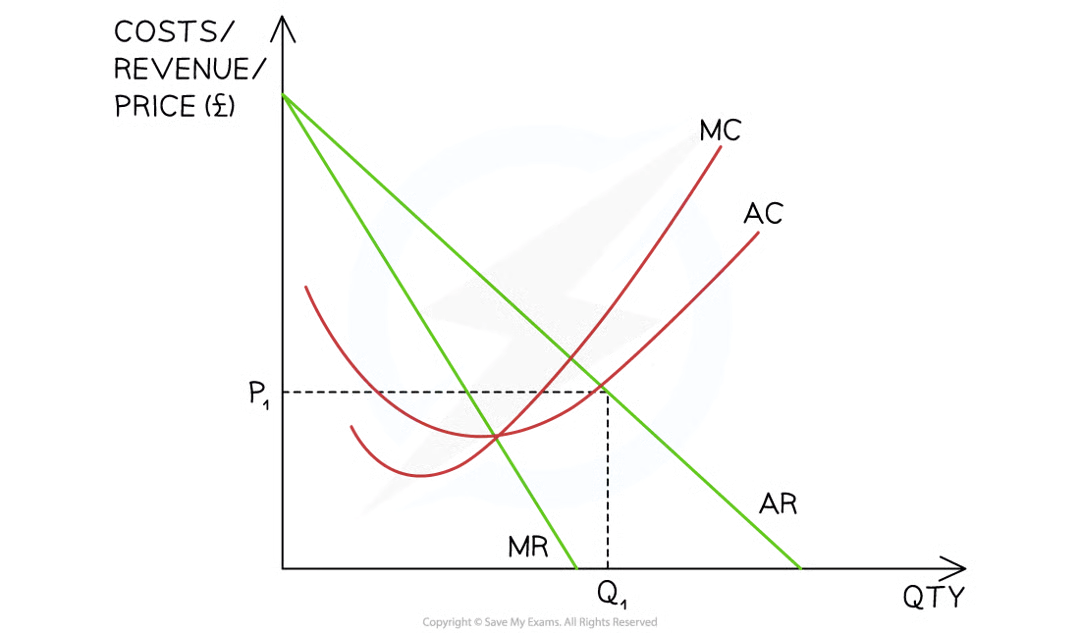
This occurs at the level of output where AC = AR (normal profit/breakeven)
In the short-term firms may use this strategy to clear stock during a sale
They sell remaining stock without making a loss per unit
At the sales maximisation level of output (AC = AR)
The selling price is P1
The average cost is also at P1
The firm is breaking even (normal profit)
Satisficing
Opting for a satisfactory level of profit rather than profit maximisation
occurs as a result of the principle agent problem
principle agent problem
Occurs when one group (the agent) makes decisions on behalf of another group (the principle) often placing their priorities above the principles
Rationally, managers know shareholders want to profit maximise
Rationally, managers want to maximise sales or revenue so as to increase their wages
Managers (who control the business) settle for a level of output somewhere between profit and sales maximisation
This increases their wages and reduces potential conflict with shareholders