ANSC 300 Bones, Joints, & Synovial Fluid
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Skeletal System
is more important for more than just movement
framework and levers
protection
mineral storage
fat storage
production of blood cells
All Skeletons Have Generally ______ Bones.
the same
Axial Skeleton
skull, vertebrae, bones attached to the vertebrae, ribs, ventral connections of the ribs, and the sternum
Appendicular Skeleton
front (thoracic) and hind (pelvic) limbs, pectoral girdle (shoulder), and pelvic girdle (pelvis)
Pectoral Girdle: scapula, clavicle, coracoid
Pelvis Girdle: os coxae (ilium, ischium, pubis)
5 Types of Bone Found in the Body
Short Bones
carpals, tarsals
Flat Bones
skull, pelvis, ribs, sternum
Irregular Bones
vertebrae, some facial
Sesamoid Bones
patella, prox. and distal sesamoids
Long Bones
limbs mostly
Skull
made up of multiple bones
Neurocranium (brain): upper and posterior
Viscerocranium (facial structures): lower and anterior part
Vertebrae
includes spinous and transverse processes, and vertebral foramen
thoracic vertebrae, lumbar vertebrae, sacral vertebrae, & caudal vertebrae
Intervertebral Disc
is a cushion of cartilage between vertebrae that permits limited movement
Nucleus Puplosus: soft interior of the disc
Anulus Fibrosus: collar that supports the periphery of the disc
What Happens with a Herniated Disc?
when the nucleus pulposus ruptures through the annulus fibrosus
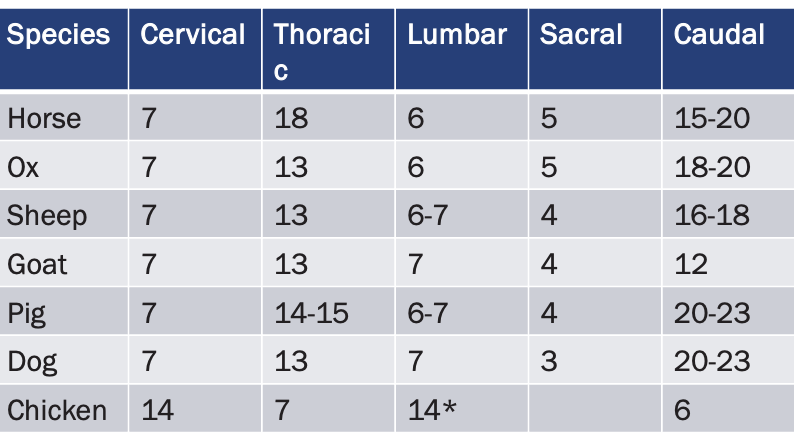
Vertebral Formulas for Different Species
CERVICAL:
Horse, Ox, Sheep, Goat, Pig, Dog: 7
Chicken: 14
THORACIC:
Horse: 18
Ox, Sheep, Goat, Dog: 13
Pig: 14-15
Chicken: 7
LUMBAR:
Horse, Ox: 6
Sheep, Pig: 6-7
Goat, Dog: 7
Chicken: 14
SACRAL
Horse, Ox: 5
Sheep, Goat, Pig: 4
Dog: 3
CAUDAL:
Horse: 15-20
Ox: 18-20
Sheep: 16-18
Goat: 12
Pig, Dog: 20-23
Chicken: 6
Pelvis
ilium, ischium, and pubis
Pelvis: os coxae
Tuber coxae & Tuber ischiadicum: hooks and pins
Acetabulum: femur articulation cavity
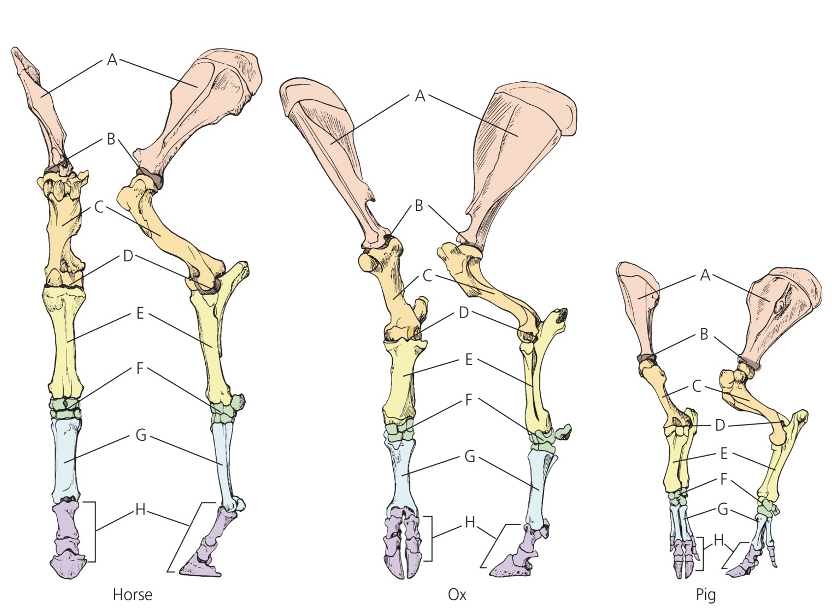
Thoracic Limb
A. Scapula
B. Shoulder
C. Humerus
D. Elbow
E. Radius
F. Carpus
G. Metacarpus
H. Phalanges (or phalanx)
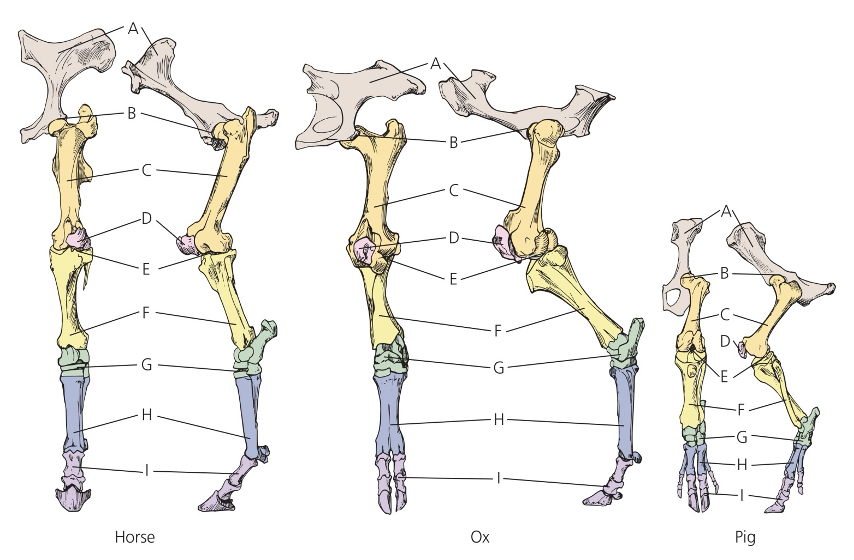
Pelvic Limb
A. Ilium
B. Pubis
C. Femur
D. Patella
E. Stifle?
F. Tibia
G. Tarsus (hook)
H. Metatarsus
I. Pastern Joint
The Radius is _____ to the Metacarpus
proximal
The Skull is ______ to the Os Coxae
cranial
The Phalanges are _____ to the Femur
distal
The Lumbar Vertebrae is ______ to the Cervical Vertebrae
cotal
Long Bone
Layers (top to bottom):
Epiphysis
Metaphysis
Diaphysis
Metaphysis
Epiphysis
Compact Region: appears to be solid
Spongy Region (aka cancellous bone): appears to be spongy, contains trabeculae (spicules) of mineralized tissue (regions between the trabeculae are filled with bone marrow)
Periosteum: composed of outer fibrous layer and inner cell-rich layer containing osteoblasts, covers bone exterior
Endosteum: lines the inner surface of bones, specifically the medullary cavity and covers the trabeculae of spongy bone
Epiphysis
extremity of the long bone
Metaphysis
expanded or flared part of the bones at the ends of the diaphysis
Diaphysis
cylindrical shaft between the epiphyses
Physis
epiphyseal plate
Bone Composition
composed of water, minerals, and organic matter
calcium and phosphorus are important
Wet Weight: 25% / 45% / 30%
Dry Weight: 0% / 70% / 30%
Types of Cells Found in Bone
Osteoprogenitor Cells: stem cell
Osteoblast: forms bone matrix
Osteocyte: maintains bone tissue
Osteoclast: derived from blood-producing stem cells (monocytes)
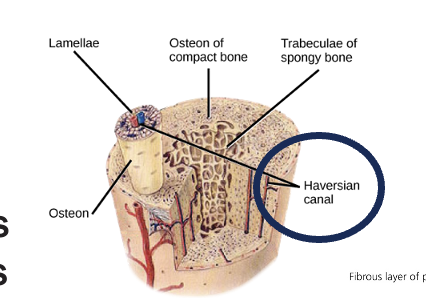
Haversian Systems
contain a canal surrounded by layers of bone
bone vessels are contained in:
haversian canals
volkmann canals
osteocytes communicate via canaliculi
How Do They Communicate?
the interstitial fluid diffuses through the canalicular network from the blood vessels in the canals for maintenance of the osteocytes; facilitation of fluid transport may be caused by periodic contraction of the osteocytes
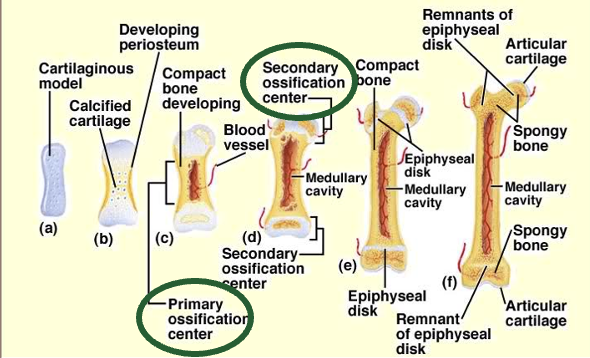
Long Bone Growth
is mainly in length
part of growth and development
Ossification: bone formation
endochondral
intramembranous
Epiphyseal Plate is the key for long bones
Diametrical Growth
is important throughout life
What Bone Cells are Key for this Process?
osteoblasts and osteoclasts
Why is this Important through Life (and Not Just Growth)?
it helps maintain bone strength, adaptability, and health
Four Zones of a Epiphyseal Plate
Epiphyseal Bone
Reserve Cartilage → youngest
Proliferation
Hypertropy
Calcified Matrix → oldest
Trabeculae
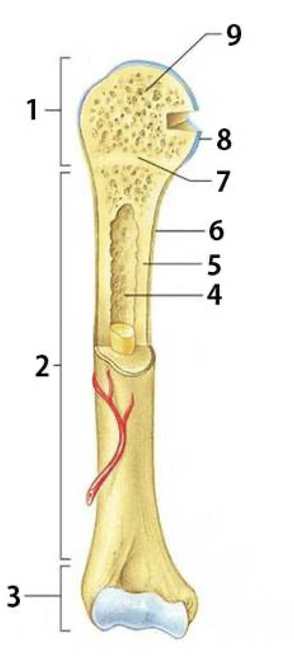
Long Bone Structure
Epiphysis
Diaphysis
Epiphysis
Medullary Cavity
Endosteum
Periosteum
Epiphyseal Plate
Articular Cartilage
Spongy Bone
Joints
are the movable union between two bones
are named for the bones that are articulating
the “yes” and “no” joints are two key joints of the vertebral column
simple vs. compound
Classification: 2 Ways
Structure:
fibrous
cartilaginous
synovial
Function:
immovable
slightly moveable
freely moveable
Synovial Joints
allow one surface to glide over another
contain a capsule filled with fluid
joint capsule is a 2-layered structure
ligaments are key to joint formation
synovial fluid lubricates and nourishes articular cartilage
What is Hyaluronic Acid?
found in the skin, eyes, and joints that maintains hydration and tissue structure
Key Joints
Knee: radiocarpal, middle carpal, carpometacarpal
Fetlock: metacarpophalangeal (MP)
*Pastern: proximal interphalangeal (PP)
*Coffin: distal interphalangeal (DIP)
Hock: tibiofibular, intertarsal (proximal + distal), tarsalmetatarsal
Fetlock: metatarsophalangeal (MP)
*Pastern: proximal interphalangeal (PIP)
*Coffin: distal interphalangeal (DIP)
The “Yes” and “No” Joints are Two Key Joints of the Vertebral Column
“Yes” Joint: Alanto-Occipital Joint
“No” Joint: Alanto-Axial Joint