Exam 3 Econ 1014H Mizzou
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Number of Firms in Oligopoly?
A Few Sellers
How do Oligopolies pick best price-output combo?
Game Theory
Are Oligopolies Price takers or makers?
Price Makers
Profit Max of Oligopoly?
MR=MC
Do Oligopolies have no, small, or large barriers to entry?
Large, so few firms
5 barriers to entry
Scale Economies, Switching Costs, Product Differentiation, Absolute Cost Advantage, Government Regulations
Two Types of Oligopoly Models
Cournot and Bertrand
Cournot Competition
-Homogeneous Goods
-Competition based on quantity
-Equilibrium price is lower than the monopoly equilibrium
-Equilibrium quantity is higher than monopoly equilibrium quantity
-Firms that make price/quantity decisions independently
Bertrand Competition
-Based on price
-results in pricing at MC
-heterogenous goods
-equilibrium price likely to be higher than homogenous goods
Bertrand Paradox
Without product differentiation, any competition drives profits to ZERO.
-> Rivals will always want to undercut each other by charging $0.01 less until Price equals Marginal Cost.
Solution: Product differentiation
Cartel
a formal organization of producers that agree to coordinate prices and production
Problems with Colluding?
-Illegal
-Incentives to Cheat
Public Policy?
When there is a proposed acquisition of substantial scale, the government reviews it and decides whether to challenge it
Network Effects?
-increases in the value of a product to each user, including existing users, as the total number of users rises
- can counteract the law of demand
Network Good?
a good whose value to one consumer increases the more that other consumers use the good
Market?
a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or service
Platform?
market where digital tech facilitate interaction
Two-Sided Market?
Network markets comprised of two distinct categories of participant, both of which that are needed to deliver value for the network to work (e.g., video game console owners and developers of video games).
Cross-side network effect?
-positive
- buyers prefer large number of sellers and sellers prefer large number of buyers
same-same network effect
-negative
-large number of sellers means severe competition among sellers
"Subsidy side" of two sided network?
-group of users who when attracted in volume, are highly valued by the "money side" the other user group
positive network externalities
when the value of a product increases with the number of users
Does the internet facilitate price discrimination?
-Yes
-More individualized and interactive
-purchases can be tracked
-easier to personalize price
Search good?
A product with characteristics that enable an individual to evaluate the product's quality in advance of a purchase.
experience goods
refer to those about which the consumer gets relevant information after purchasing them, such as food and entertainment
credence goods?
Like insurance coverage, consumers may rarely learn product attributes
information goods?
Technological products and services
Properties of Information Goods
-Economies of Scale: typically high fixed cost of production but zero or very low cost of reproduction
-Public good traits: non-rival and sometimes non-excludable
-Tech adoption speed is fast
game theory
the study of how people behave in strategic situations
dominant strategy
a strategy that is best for a player in a game regardless of the strategies chosen by the other players
Pareto Effect
no individual can be made better off without making someone else worse off
Pareto efficient
a situation is efficient if no change is possible that will help some people without harming others
Nash Equilibrium
a situation in which economic actors interacting with one another each choose their best strategy given the strategies that all the other actors have chosen
Schelling points
focal point of equilibrium determined by experience
maximin strategy
-in game theory, a strategy chosen to maximize the minimum gain that can be earned
-minimize risk
mixed strategy
-maximize payoff by switching strategy
-no pure Nash equilibrium
-gambling and sports
extensive form game
a representation of games that specifies the order of play
cheap talk
message said without talk to you
costly signal
conveying info in a way only if it costs you something
credible commitment
a long-term strategic decision that is both difficult and costly to reverse
factor of production
an input used in the production of a good or service
Marginal Revenue Product
the change in total revenue associated with one additional unit of input
If wages go down, should you hire less or more workers?
hire more
superstar phenomenon
large scale, perceived as slightly better --> exponential increase in marginal revenue (small dif in quality, huge dif in marginal revenue, huge dif in wage)
Baumol's cost disease
workers have to be paid the market rate even though they a aren't more productive
Leisure
Free time not taken up with work.
Wage Properties
-People work harder up until a point
-Backward bending supply curve
-Income effect
income effect
the change in consumption resulting from a change in real income
What is pay based on?
Marginal revenue of product
subsitution effect
when consumers react to an increase in a good's price by consuming less of that good and more of other goods
Properties of Low Skilled Workers?
-Used to be a higher demand
-With free trade, most of the work by them is done overseas
-Relative demand dropped for this labor
Properties of High-skilled workers?
-Bachelors degree
-large wage differential
Human Capital?
the skills and knowledge gained by a worker through education and experience
signaling theory
employers value educated people not bc of the knowledge they learned but bc getting a degree sorted people into high-skilled and low-skilled workers
sheepskin effect
The phenomenon that the return to a year of education is higher when that year includes the awarding of a degree or education credential
efficiency wages
above-equilibrium wages paid by firms to increase worker productivity
Gini Coefficient
A measure of income inequality within a population, ranging from zero for complete equality, to one if one person has all the income.
Basic Themes of Inequality?
-inequality produces incentive to produce wealth
Endowment effect
we place greater value on objects we own over objects we do not own
Standard Economics
people take a broad, long-term view in which their utility is based on the discounted value of future wealth
Behavior Economics
people are motivated by gains and losses, which are temporary events
framing effect
one of two equivalent outcomes is consistently preferred merely because it is positively presented or framed
Prospect theory
describes how people choose between alternatives that involve risk, including both gains and losses
Disposition Effect
the tendency of investors to sell shares whose price has increased, while keeping assets that have dropped in value
choice architecture
a framework setting out different ways in which choices can be presented to consumers, and the impact of that presentation on consumer decision making
Libertarian Paternalism
a policy that tries to influence people to choose in a way that will make them better off (as judged by themselves) but in a way that also preserves freedom of choice
Consumer Theory?
characterizes consumers choices in a systematic way
indifference curve
-a curve that shows consumption bundles that give the consumer the same level of satisfaction
-slopes downward
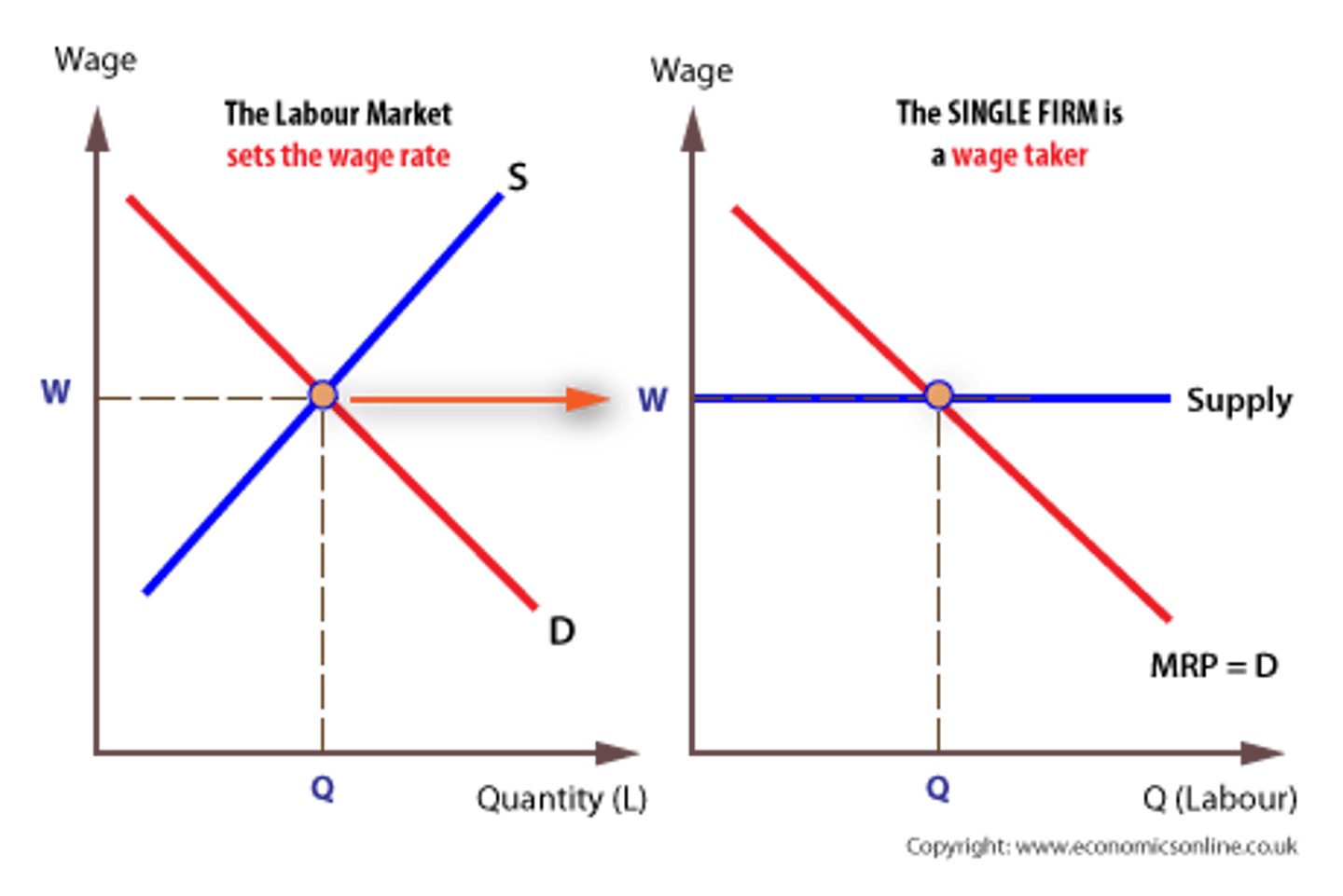
Labor Market Graph
Strategic form game
players make their choices simultaneously
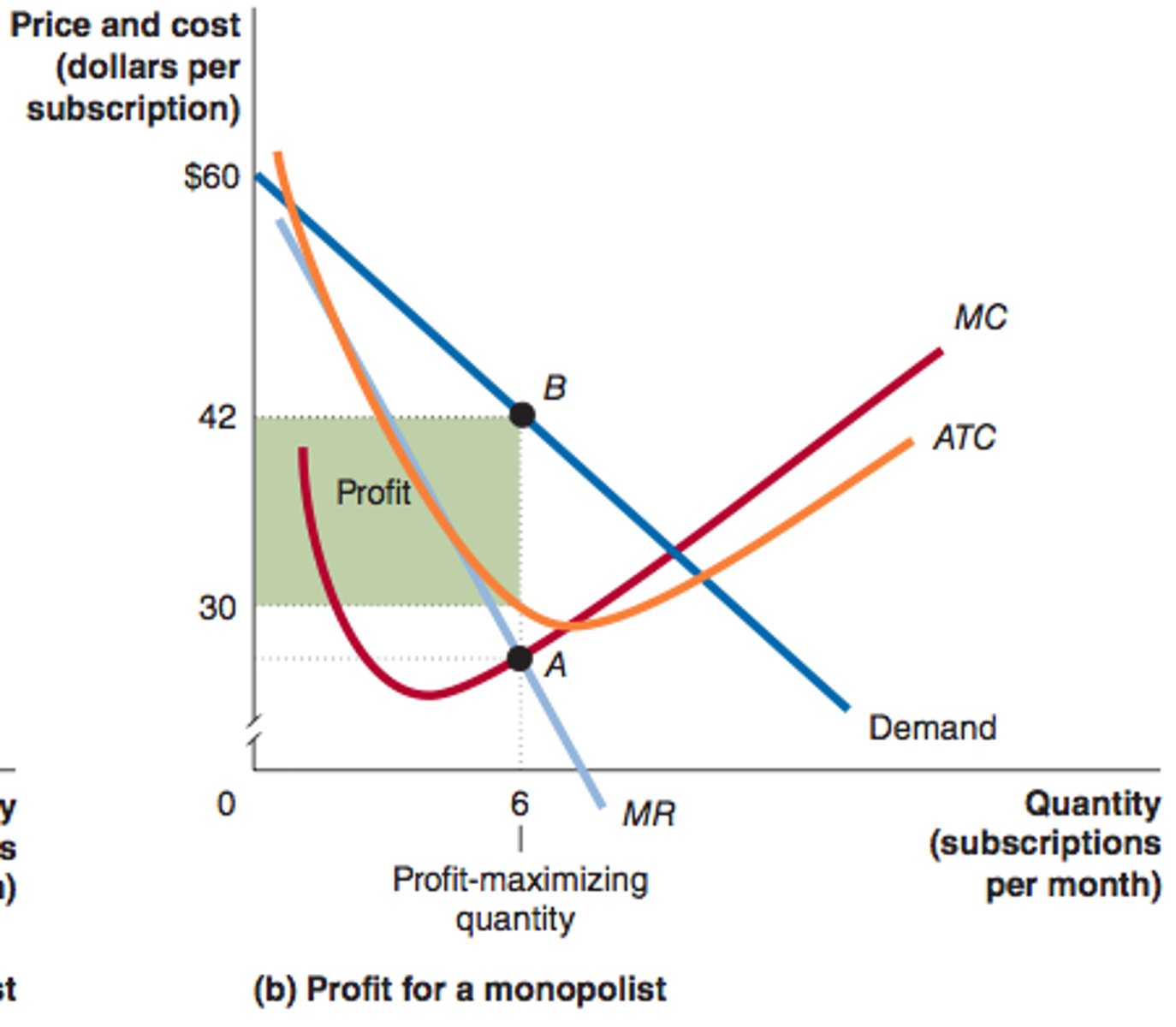
monopoly graph
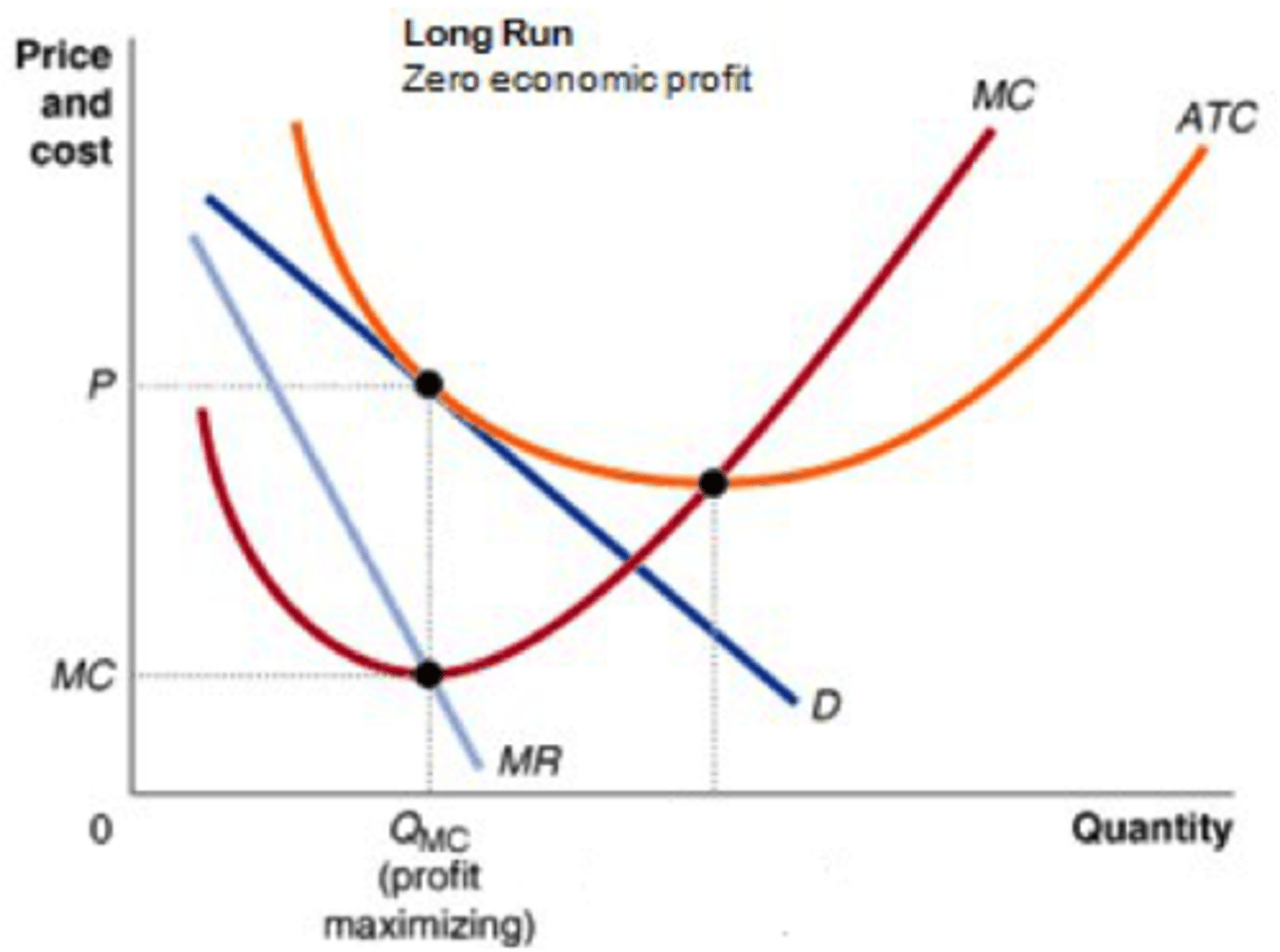
monopolistic competition graph
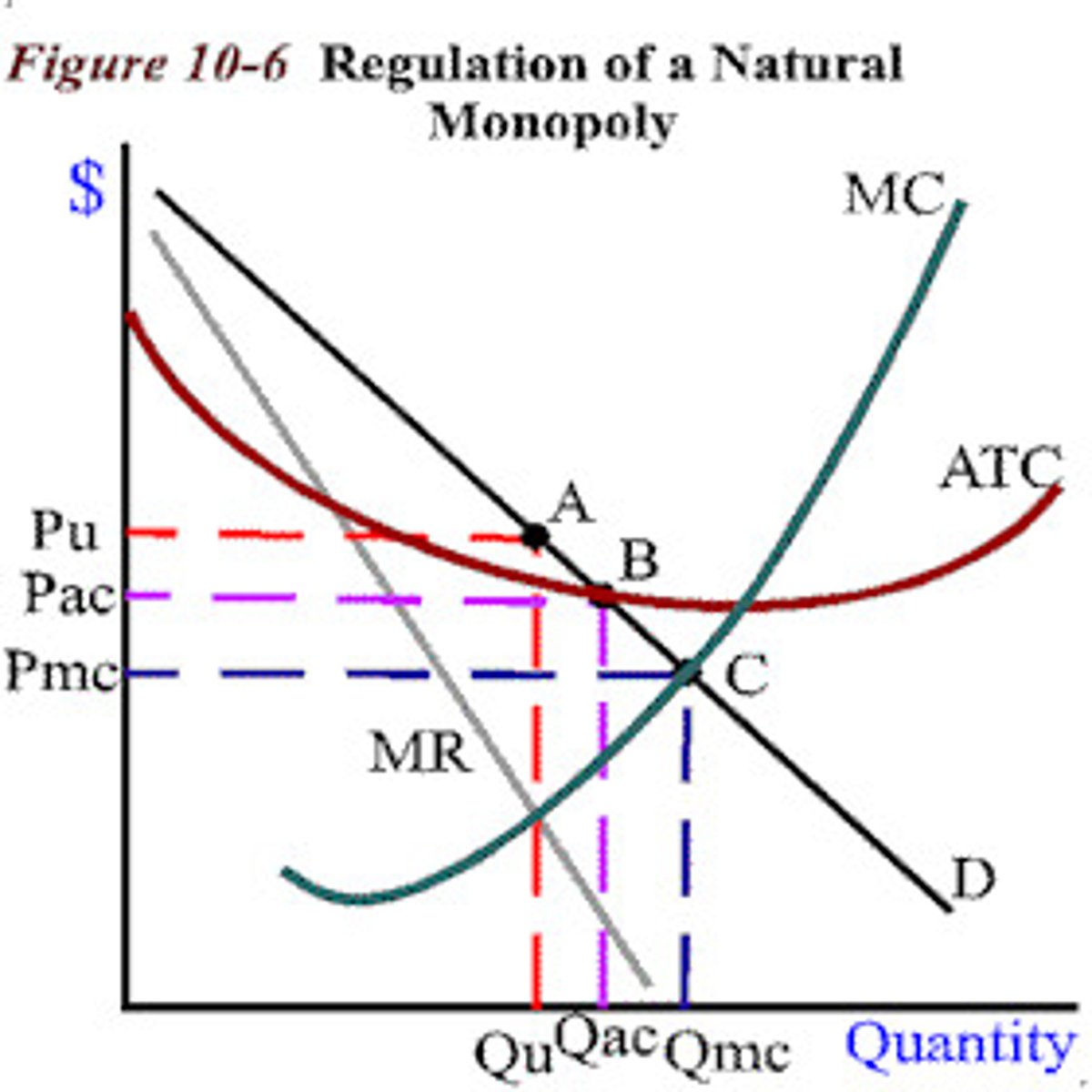
natural monopoly graph