ap macro unit 1 terms
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Money
Refers to/ recognizes how scarce something is
What is something that has a price?
Scare
Does abundancy eliminate scarcity?
No
TINSTAAFL
There is no such thing as a free lunch
Is scarcity solvable or unsolvable?
Unsolvable
Why are people and governments forced to make trade-offs?
Since scarcity is unsolvable
Are all resources limited?
Yes
Why is scarcity a problem?
Since people and governments have unlimited needs and wants but resources are limited
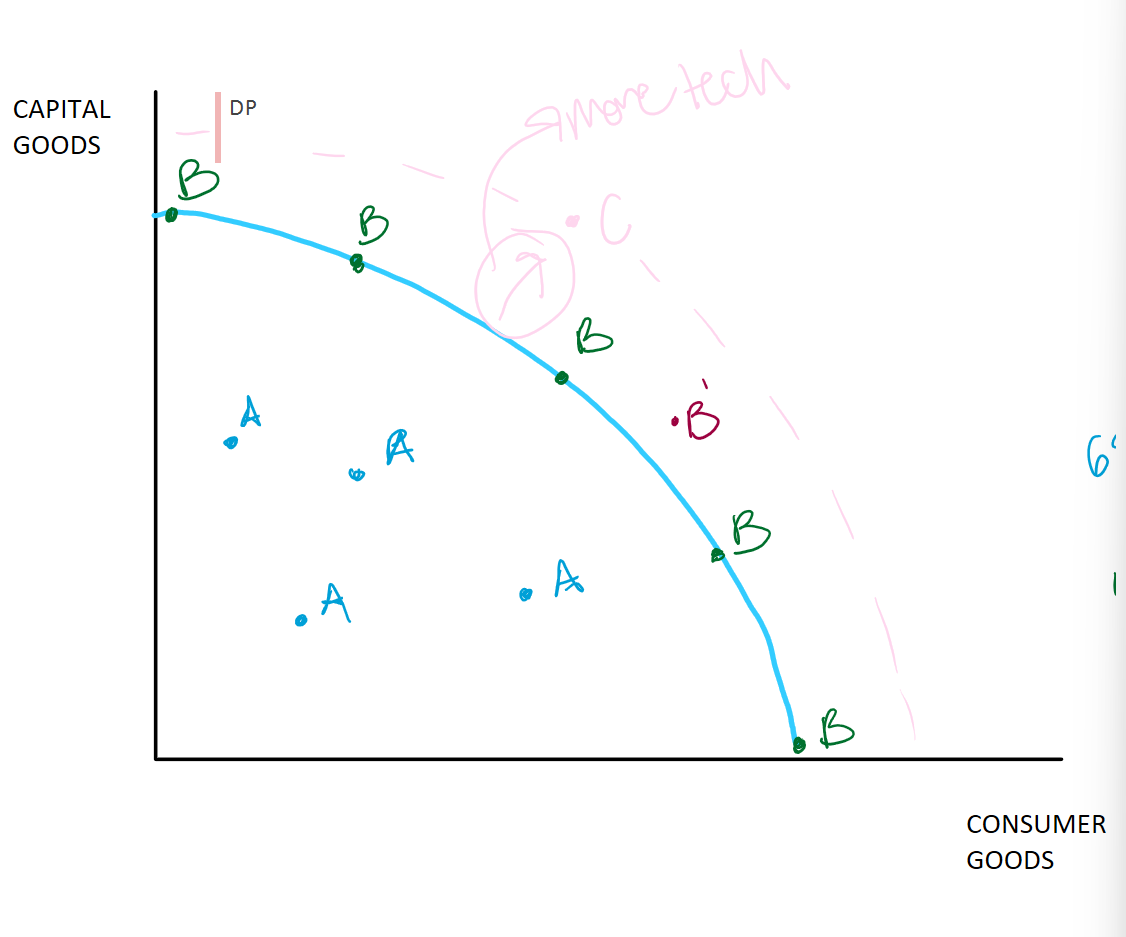
Production Possibilities Frontier Curve
Shows scarcity, opportunity, and trade-offs
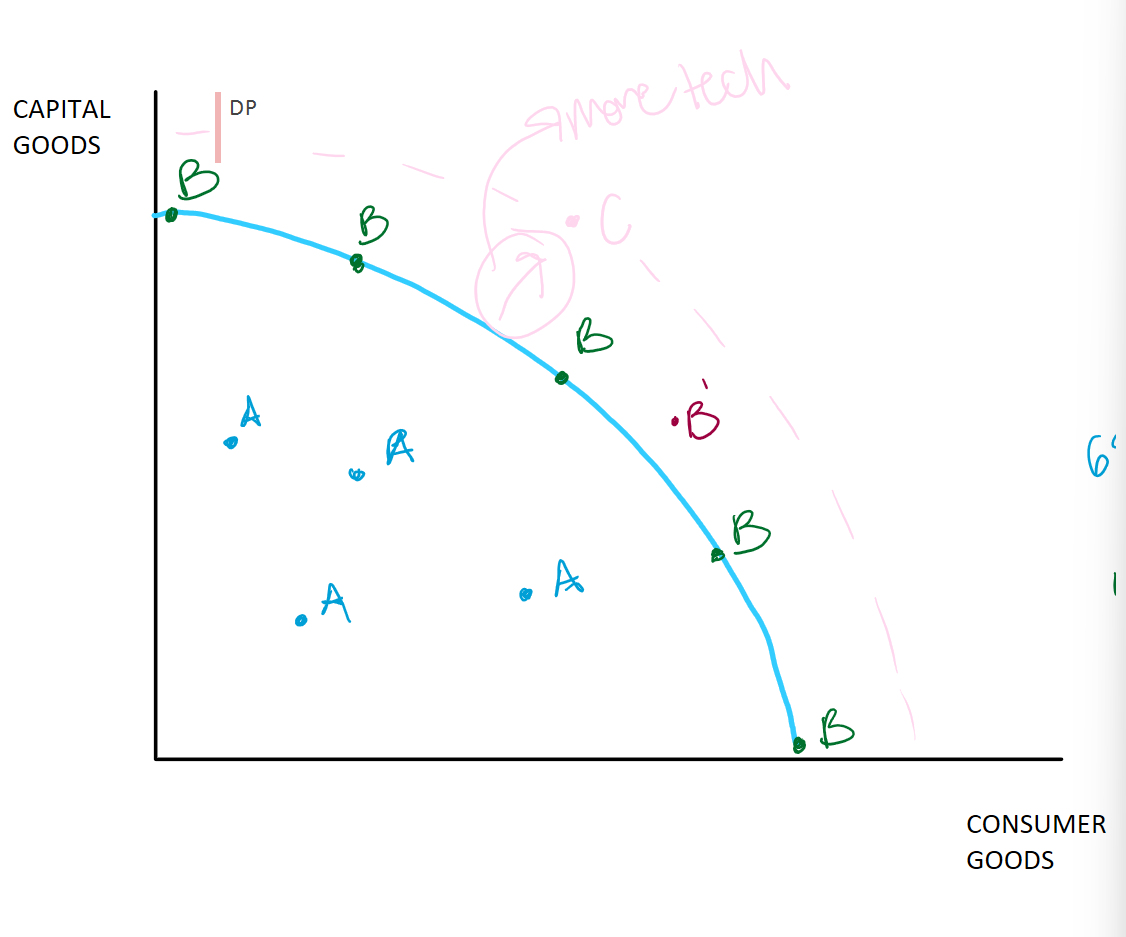
Blue line or frontier/curve
Limit/maximum total production for a given country, economy, society, etc. (due to scarcity)
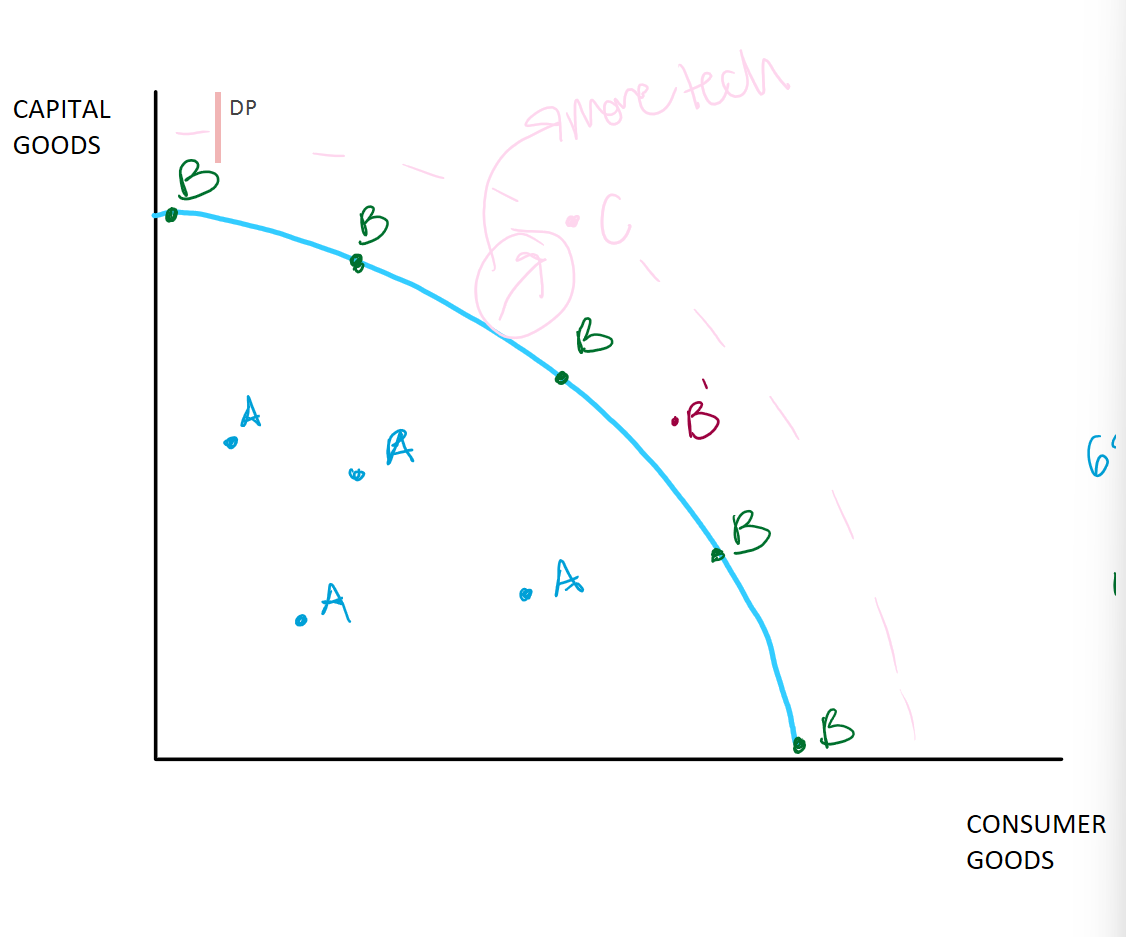
Consumer goods
Items people will use for themselves (coffee, blueberries, etc)
Capital goods
Items used to make other things (deep fryer at Sonic)
A or Inefficient level of production (increasing unemployment)
Not maximizing all possible resources
Could be producing more
Where is A on the PPF curve?
UNDER THE CURVE
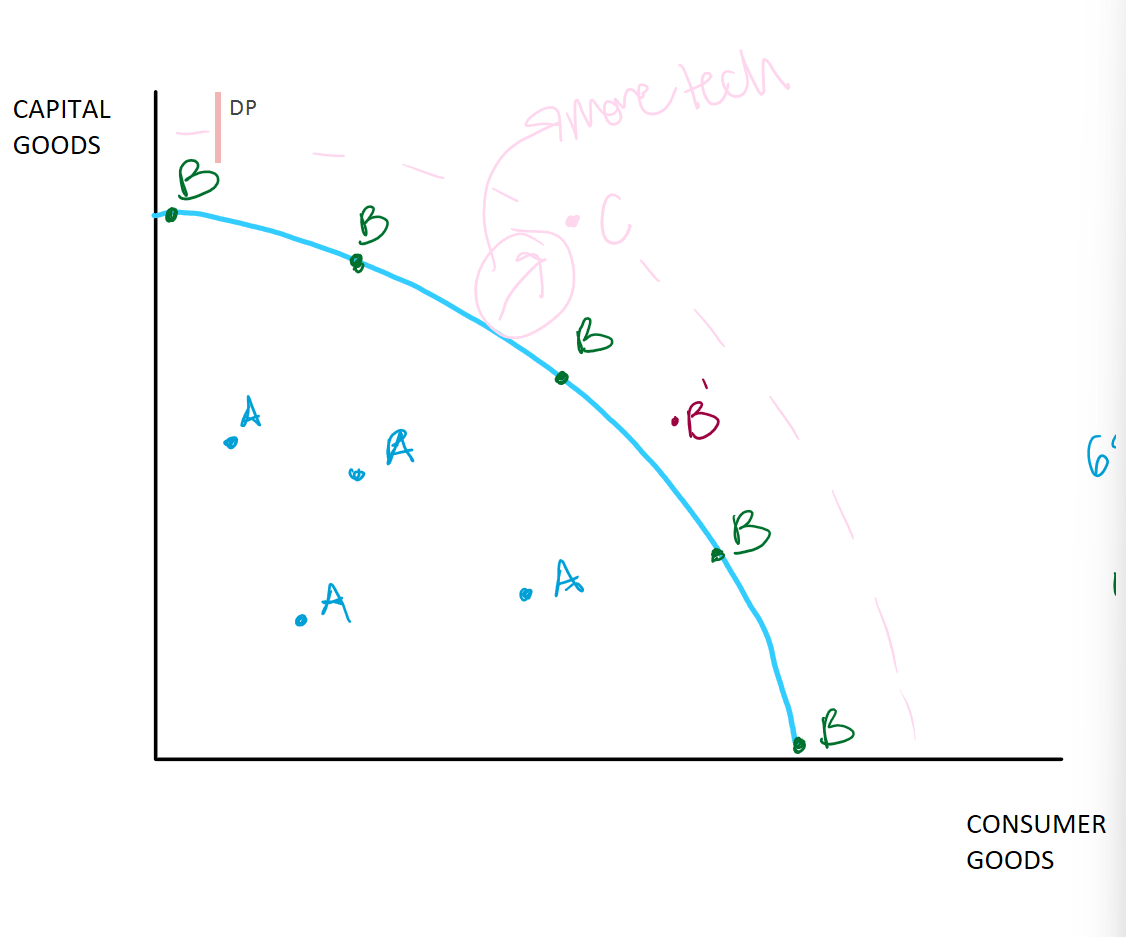
B or efficient, goal, desired, ideal
Maximizing our scarce resources
Dealing with scarcity in the best way possible; not wasting as much as point A
raw materials, tech, labor
Where is b or efficiency on the curve?
ON THE CURVE
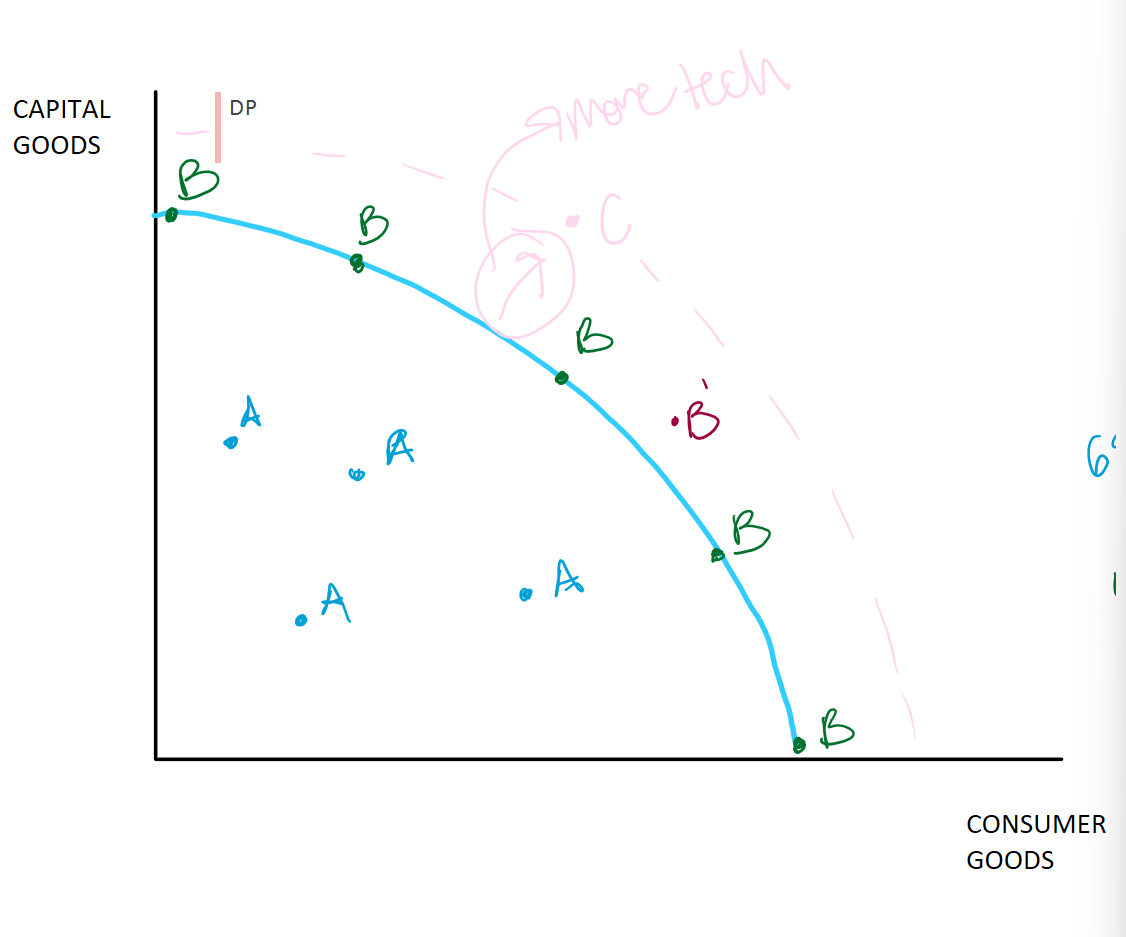
Does maximizing scarce resources or being at B on the curve lead to a better life?
Since lower prices and mass production which produce more things
B’ or Over extended
Pushing production/use of resources beyond a sustainable level
ex: wwii production
Where is B’ or over extended on the curve?
JUST OUTSIDE THE CURVE
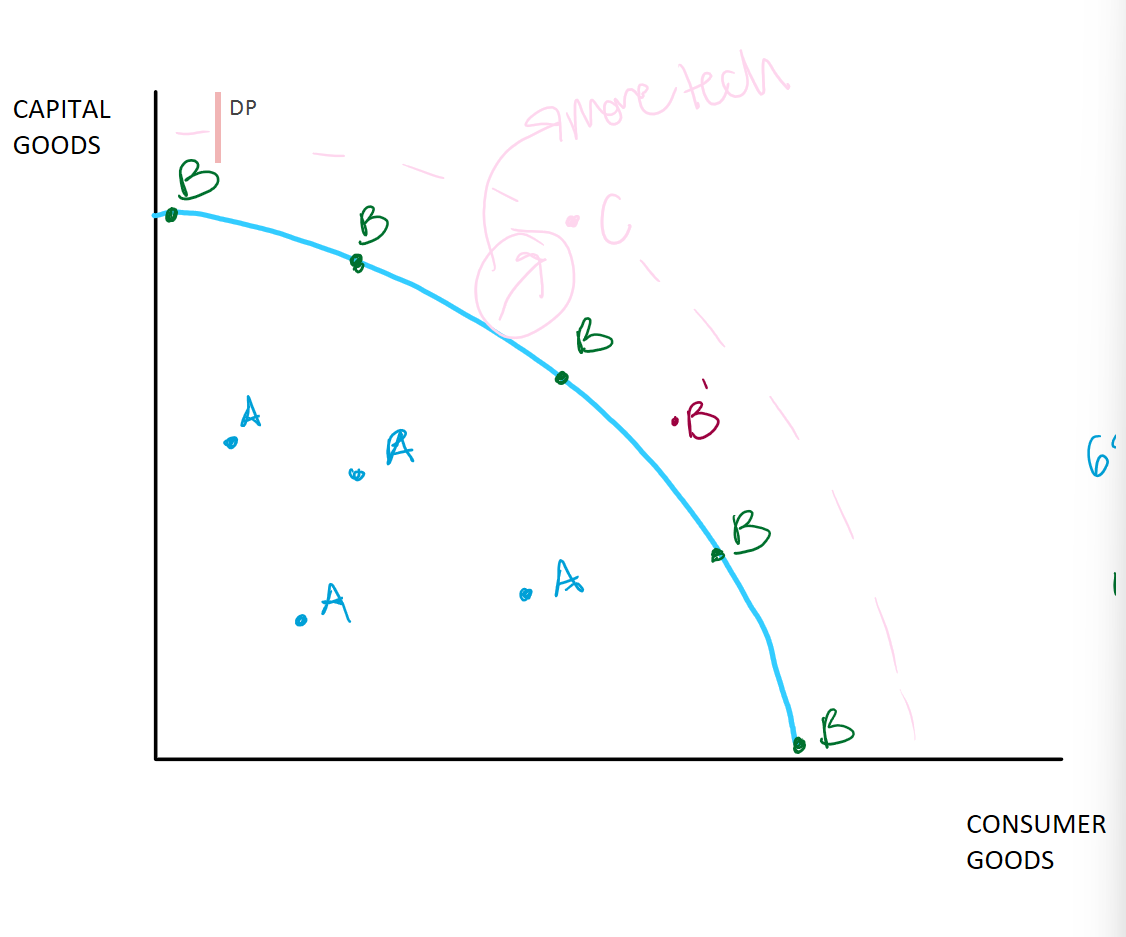
C or Not yet attainable, not yet possible (more tech needed)
More tech needed
Might be possible in the future
Technology or more resources(increase of) allows person to do things they could not do before
Where is C on the curve?
OUTSIDE OF THE CURVE
What is the definition of Factors of Production?
4 items needed to produce any good or service
4 Factors of Production
Land
Labor
Capital
Entrepreneurs
Land
Physical land, natural resources like oil, coal, natural gas, metal ores, minerals
Labor
Workers
What is the most expensive factor of production?
Workers
Capital
Tools, machinery, equipment (money to buy these items)
Entrepreneurs
Risk takers who start a business, people with ideas
New product, better way of doing something
Absolute advantage (Best)
Who can make/produce the most of a good or service. Total production capabilities
Comparative Advantage
If you have a lower opportunity cost in producing a good/ service compared to another producer/ business/ country
Opportunity Cost
What you give up to get what you want. What you lose
Is it possible for one producer to have absolute advantage in one good, both goods, or neither good?
Yes
Is it possible to have a comparative advantage in production of both goods?
No
Demand
Desire, ability, and willingness to buy a good or service
Who controls demand?
Households or consumers/ buyers
Quantity Demand
Amount people chose to buy at a certain price
If a price is low, will buyers want to buy more or less?
More
If a price is high, will buyers want to buy more or less?
Less
What does change in price affect?
Change in quantity demand / amount we buy
Does not change how we feel about the item
CAUSES MVOEMENT ALONG DEMAND CURVE
Law of Demand
Price and QD are inversely related
Does law of demand cause movement along the curve?
Yes
Would price falls result in higher or lower quantity demand?
Higher
Would a price rise result in a higher or lower quantity demand?
Lower
Demand
Changes based on certain determinants:
Income
Price of related goods
Complements and substitutes
Tastes
Expectation
Number of buyers
Demand move to right?
Increase/ more demand
Demand move to left?
Decrease/ less demand
Supply
Amount of a good or service made available for purchase
Who controls supply?
Producers/ sellers/ firms
Quantity Supplied
Amount businesses chose to make
Would a business chose to make more or less if price that buyers pay is high?
More
Would a business chose to make more or less if price that buyers pay is low?
Less
Change in price
Change in quantity/supplied/ what they chose to make
Does not change what a business can do
Movement along the supply curve
Law of Supply
Price and quantity supply are directly or positively related
If price falls, is quantity supplied higher or lower?
Lower
If price rises, is quantity supplied higher or lower?
Higher
Supply
Can change based upon these determinants:
Input prices
Number of sellers
Technology
Government policies and expectations
Supply move to right
Increase/ more supply
Supply move to the left
Decrease/ less supply
Intersection point of a Supply and Demand Graph
Equilibrium
Equilibrium Meaning
Place where supply and demand curves cross/intersect
Place where quantity supplied = quantity demanded
Market clearing price (which is the goal)
At that price, the numbers of buyers = number of sellers