Physics Fundamentals: SI Units, Measurement, and Vectors
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering SI units, scientific notation, accuracy & precision, vectors, and metric prefixes derived from the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Length
Physical quantity that measures the extent of an object or distance between two points; its SI unit is the meter (m).
Meter (m)
Base SI unit for length; symbol is lowercase m.
SI Unit
Standardized unit in the International System of Units, used worldwide for scientific measurements.
Base Unit
Fundamental SI unit that is independent of other units, e.g., meter, kilogram, second, candela.
Derived Unit
SI unit obtained by combining base units, such as the Newton (kg·m/s²) or kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m³).
Newton (N)
Derived SI unit of force equal to kg·m/s².
Density (kg/m³)
Mass per unit volume; expressed in kilograms per cubic meter, obtained from mass divided by volume.
Candela (cd)
Base SI unit of luminous intensity, used to quantify brightness.
Scientific Notation
Way of writing numbers as a coefficient multiplied by 10 raised to an exponent (e.g., 3.5 × 10⁻⁵).
Exponent (scientific notation)
Superscript power of ten that shows how many places to move the decimal; −5 in 3.5 × 10⁻⁵ indicates a shift left by five places.
Standard Notation
Regular decimal form of a number expressed in scientific notation, e.g., 3.5 × 10⁻⁵ = 0.000035.
Megameter (Mm)
Metric unit equal to one million meters; 1 Mm = 1,000 km.
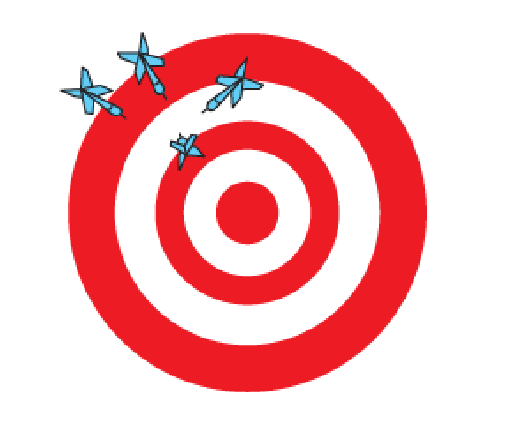
Accuracy
Closeness of a measurement to the true or accepted value.
Precision
Closeness of repeated measurements to one another, indicating small variability.
Systematic Error
Consistent bias in measurement (e.g., miscalibrated scale) that affects accuracy.
Vector Quantity
Physical quantity with both magnitude and direction, represented by an arrow symbol.
Scalar Quantity
Physical quantity described solely by magnitude, without direction.
Drag
Force that opposes the motion of an object through a fluid; a vector quantity.
60° North of East
Direction of a vector that forms a 60° angle above the positive x-axis (east).
Quadrant III
Region of the Cartesian plane where both x and y are negative; contains directions like 25° south of west.
Weight Vector (𝐖⃗)
Symbol for weight written as a bold capital W with an arrow overhead, denoting it as a vector.
Micro Prefix (µ)
Metric prefix meaning 10⁻⁶ (one-millionth) of the base unit.
Centi Prefix (c)
Metric prefix meaning 10⁻² (one-hundredth) of the base unit.
Unit Conversion
Process of translating a measurement from one unit to another, often using scientific notation to compare magnitudes.
brightness of a lamp light in a post
Which of the following situations will
require a base/fundamental SI unit?
-5
3.5 𝑥 10^−5 which is an exponent?
0.000035
What is the standard notation of this scientific notation? 3.5×10^-5
384.4 Mm
The average distance of the Moon from
Earth is 384,400 km. What will be the distance of the
moon from Earth in megameters?
Accurate and Precise
The true length measurement of a
pencil was 10.4 inches. If Ken tried multiple
measurements and came up with the following: 10.3
in, 10.4 in, 10. 1 in, and 10.5 in. What can you say
about the accuracy and precision of the trials?
not accurate but precise
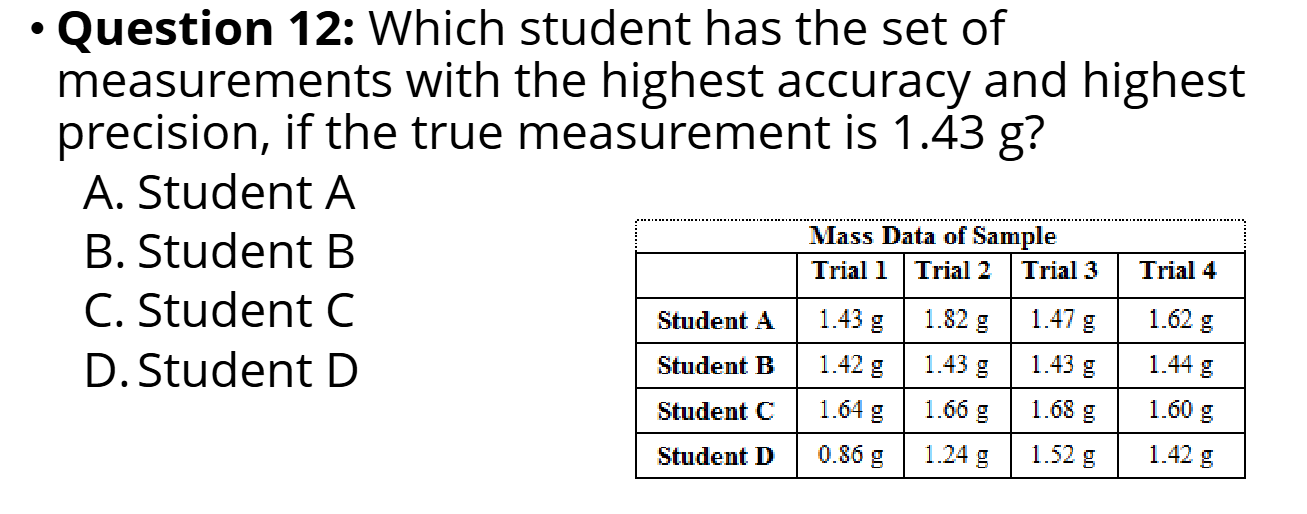
What does the figure represent about
accuracy and precision?

Student B
Drag
Which quantity is a vector quantity
area
drag
energy
power
C

C

C

C
