biology- ecosystems term 2
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
4 levels of environmental organisation
The 4 levels of environmental organization are individual, population, community, and ecosystem, representing a hierarchy of biological interaction and complexity.
what is a species
A species is a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring, sharing common characteristics and genetic heritage.
what are producers
Producers are organisms, typically plants and algae, that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, forming the base of the food chain.
what are consumers
Consumers are organisms that obtain energy by feeding on other organisms, including plants and animals, and are classified into primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers based on their position in the food chain.
what are the trophic levels for a food web
The trophic levels for a food web are hierarchies that describe the feeding positions of organisms within an ecosystem, typically categorized as producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers.
what is competition
Competition is the interaction between organisms or species in which they vie for the same resources, such as food, space, or mates, negatively impacting each other's growth and survival.
example: male deer fighting for resources
what is predation
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, hunts and feeds on another organism, the prey, influencing population dynamics and ecosystem balance.
example: cow and grass
what is a symbiotic relationship
A symbiotic relationship is a close, long-term interaction between two different species, which may benefit one or both organisms. Examples include mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism.
what is mutualism
Mutualism is a type of symbiotic relationship where both species involved benefit from the interaction, enhancing their survival and reproduction.
example: flowering plants and pollinators
what is commensalism
Commensalism is a type of symbiotic relationship where one species benefits while the other is neither helped nor harmed.
example: barnacles and whales
what is parasitism
Parasitism is a type of symbiotic relationship where one organism, the parasite, benefits at the expense of the other, the host, often harming it in the process.
examples: ticks on mammals, tapeworms in intestines
what is biological classification
first: genus second: species
what are the 8 levels of taxon
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species.
what is artificial selection
Artificial selection is the process by which humans breed specific organisms for desired traits, selecting individuals with favorable characteristics to reproduce.
analogous structure
Structures in different species that have similar functions but evolved independently, not from a common ancestor.
natural classification
A system of organizing living organisms based on shared characteristics and evolutionary relationships, reflecting their phylogeny.
what is homologous
structures Structures in different species that are similar due to a shared ancestry, but may serve different functions.
what is reproductive isolation
Reproductive isolation refers to mechanisms that prevent different species from interbreeding and producing fertile offspring, thus maintaining species integrity.
pre zygotic
isolation mechanisms that occur before fertilization, preventing mating or fertilization between species.
post zygotic
isolation mechanisms that occur after fertilization, reducing the viability or fertility of hybrid offspring.
what are abiotic factors
Non-living components of an ecosystem that influence living organisms, such as temperature, water, sunlight, soil, and climate.
what are biotic factors
Living components of an ecosystem that affect other organisms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms.
what is zonation
The spatial arrangement of different habitats and communities within an ecosystem, often influenced by environmental gradients.
side to side
what is stratification
The layering of different habitat types in an ecosystem, typically based on factors like light penetration, temperature, or vegetation types, which can affect species distribution.
up and down
what is an adaption
A trait or characteristic that enhances an organism's ability to survive and reproduce in its environment.
structural adaption
A physical feature of an organism that enhances its survival and reproductive success in a specific environment.
example: the long neck of a giraffe, which allows it to reach leaves high in trees.
physiological adaption
A functional change in an organism's biological processes that enhances its survival and reproductive success in its environment.
example: secretion of toxins by plants to deter predators
behavioural adaption
A change in an organism's behavior that improves its chances of survival and reproduction in its environment. Example: migration of birds to find food or suitable climates.
what is natural selection
Natural selection is the process whereby organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring. It is a key mechanism of evolution.
what is the water cycle
The continuous process by which water circulates through the Earth's ecosystems, including evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and infiltration.
what is the carbon cycle
The process by which carbon is exchanged between the Earth's biosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere, involving processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and combustion.
what is an ecological niche
An ecological niche refers to the role and position a species has within its environment, including how it interacts with other organisms, uses resources, and responds to environmental conditions. It encompasses factors such as food sources, habitat, behavior, and competition.
what is a keystone species
a species that would greatly affect an ecosystem if removed, trophic cascade (changes in food web and predators)
what is an organism
single and individual living organism
what is a population
a number of organisms in the same species that live in an area
what is a community
a group of various species in a common location
what is an ecosystem
where living organisms interact with each other and surroundings (abiotic and biotic factors)
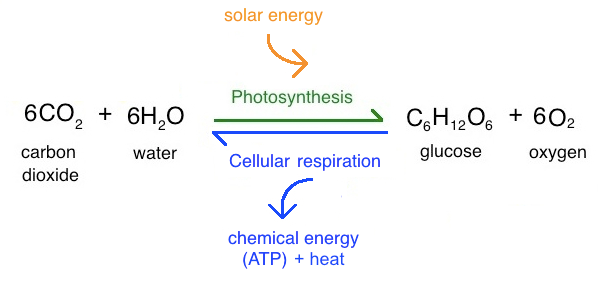
Photosynthesis formular
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2.
Carbon dioxide+water=glucose+oxygen
ecosystems changing over time
daily change
light intensity
temperature
humidity
seasonal change
seasons
reproduction of plants and animals to create offspring
long term changes
colonization of new species to an area
natural disasters
human activity
ecological sucession
primary succession
starts with lifeless area on bare rocks and begins when spores of autotrophic organisms are blown by wind to settle on rocks
organisms grow and die overtime and create rich and diverse ecosystem
secondary succession
may occur in already mature ecosystem if it experiences disaster or human activity
populations will return over time
why is ecological niches important
resource allocation
ecosystem stability
energy flow
stops possible extinction
what is the chemical process for cellular respiration