Gestalt & Typography
1/69
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
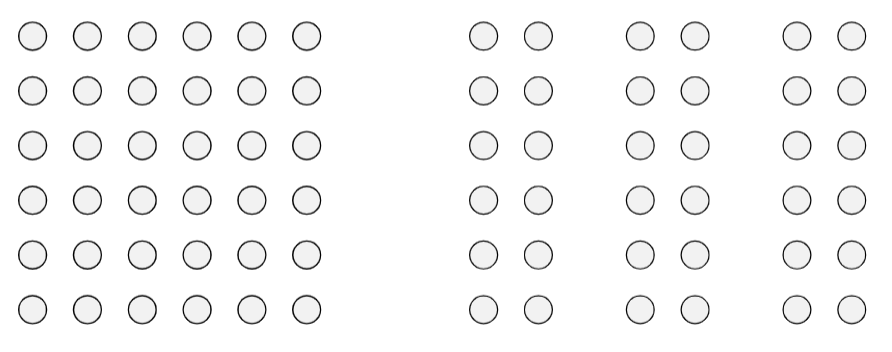
Proximity
Objects that are close to each other are perceived as a group.
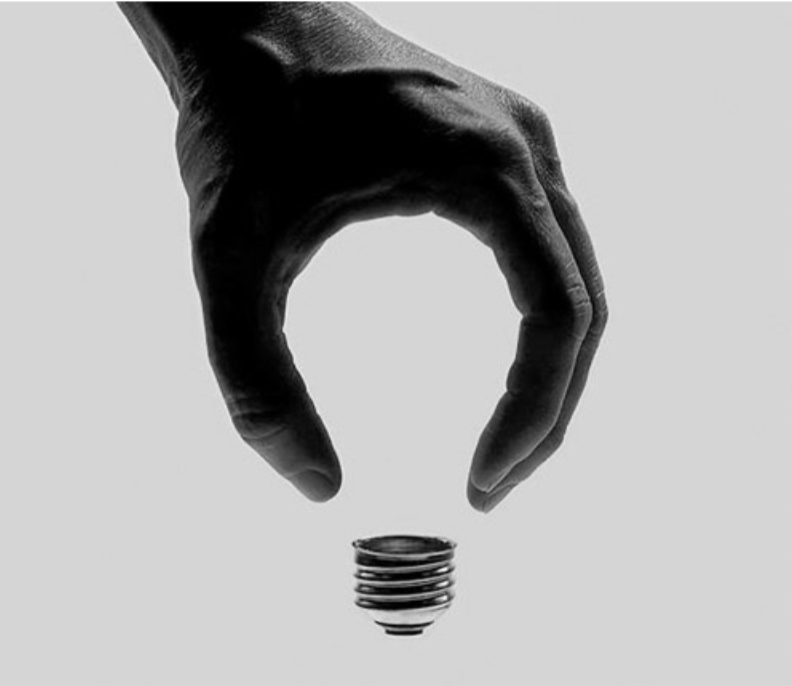
Figure/Ground
Relationship between an object (figure) and its background (ground).

Closure
To perceive incomplete shapes as complete figures.

Enclosure
Elements are grouped together by a surrounding border or shape.
Direction
The visual path that leads the viewer's eye through a design.

Continuity/Continuation
Eye is drawn along paths, lines, and curves. (repetition)
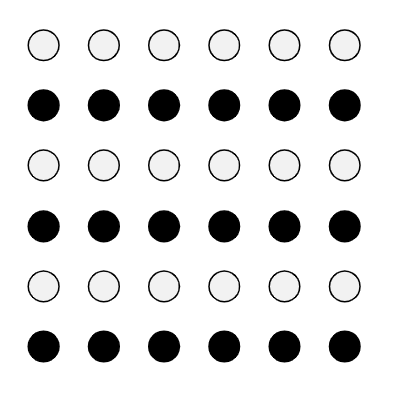
Symmetry
A balanced arrangement of elements that creates harmony in a design. (Ex: Mandala)
Gestalt
The whole is greater than the sum of its parts.
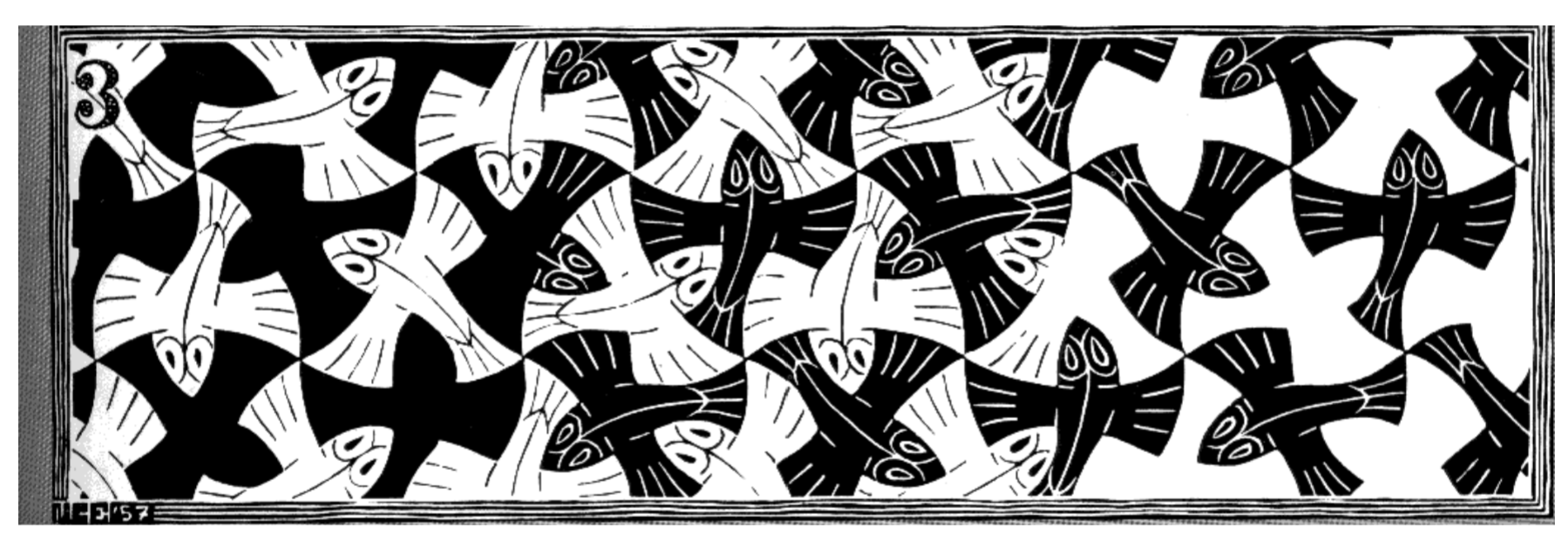
Similarity
Elements that are similar are perceived to be more related than elements that are dissimilar.
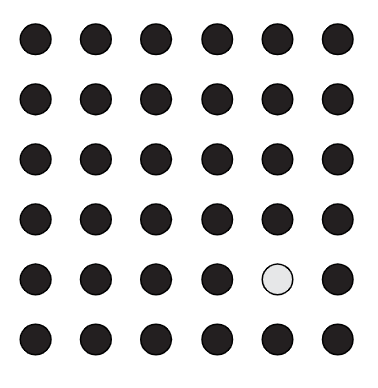
Anomaly
An element that deviates from the expected pattern, drawing attention to itself.
Semiotics
The study of visual signs and the way in which they communicate meaning.

Pictograph
A pictorial sign for a word or phrase that looks like what it represents.

Ideograph
A graphic image representing an object or concept (without indicating the sounds used to say it) selected by agreement or custom (or more broadly accepted) to become fixed pictorial symbols —- (road signs)
Alphabet
A set of letters or symbols in a fixed order used to represent the basic sounds of a language.
Photograph
An image created by capturing light
Illustration
A visual representation created to explain or decorate a text.
Rebus
A puzzle that uses pictures to represent words or parts of words.
Signs
Symbols that convey information or represent something.
Icon
A graphic representation that symbolizes an object or concept.

Symbol
A mark or character used to represent something else.
Index
A sign that has a direct correlation to the object it represents.

Meta-symbol
A symbol that represents another symbol or concept. (ex: symbol of peace)
Digital Icon (GUI)
A pictograph or ideogram used within a graphical user interface (GUI).
Emoji
A small digital image or icon used to express an idea or emotion.

Pictorial Icon
An icon that visually represents a specific object or concept.
Emblem
A symbolic representation that conveys a specific meaning or identity.
Lettermark or Monogram
A logo consisting of letters, usually the initials of a brand or organization.
Wordmark or Logotype
A logo that consists of the brand name in a stylized typeface.
Combination Mark
A logo that combines both text and a symbol.
Mascot
A character or figure that represents a brand or organization.
Typeface/Family
A set of characters that share a common design.
Fonts
Specific styles and sizes of typefaces.
Serif
A typeface with small lines or decorative strokes at the ends of its characters.
San Serif
A typeface without the small lines or decorative strokes at the ends of its characters.
Weight
The thickness of the characters in a typeface.
Width
The horizontal measurement of characters in a typeface.
Thick/Thin Contrast (modulation)
The variation in thickness of strokes in a typeface.
x-height
The height of the lowercase letters in a typeface, specifically the height of the letter 'x'.
Ascenders
The parts of lowercase letters that extend above the x-height.
Descenders
The parts of lowercase letters that extend below the baseline.
Stress/Axis
The direction of the thickest part of a letterform.
Typeface Categories
Different classifications of typefaces based on their characteristics.

Blackletter
A style of typeface characterized by its ornate and gothic appearance.
Script
A typeface that mimics handwritten text.
Italic
A style of typeface that slants to the right.
Old Style/Humanist
A typeface category that features a classic and traditional appearance.
Transitional
A typeface category that bridges the gap between Old Style and Modern typefaces.
Modern
A typeface category characterized by its clean lines and minimal ornamentation.
Slab Serif
A typeface with thick, block-like serifs.
Sans Serif
A typeface without serifs, known for its clean and modern look.
Decorative
A typeface designed primarily for decorative purposes rather than readability.
Monospace
A typeface where each character occupies the same amount of horizontal space.
Wood Type
A type of typeface made from wood, typically used for large display printing.
Roman/Regular
A standard style of typeface that is upright and not italicized.
Bold
A typeface style that is thicker and darker than the regular style.
Italic
A style of typeface that is slanted and often used for emphasis.
Light
A typeface style that is thinner than the regular style.
Condensed
A typeface style that is narrower than the regular style.
Extended
A typeface style that is wider than the regular style.
All Caps
Text that is set entirely in uppercase letters.
Small Caps
A style where lowercase letters are replaced with smaller uppercase letters.
Raster vs. Vector
Raster graphics are made of pixels, while vector graphics are made of paths defined by mathematical expressions.
Screen vs. Print
Screen graphics are optimized for display on screens, while print graphics are designed for physical reproduction.
True Type
A font technology developed by Apple and Microsoft that allows for scalable fonts.
.ttf
A file extension for TrueType font files.
.ttc
A file extension for TrueType Collection font files.
Open Type
A font format that supports advanced typographic features.
.otf
A file extension for OpenType font files.
Web Fonts
Fonts that are specifically designed for use on websites.
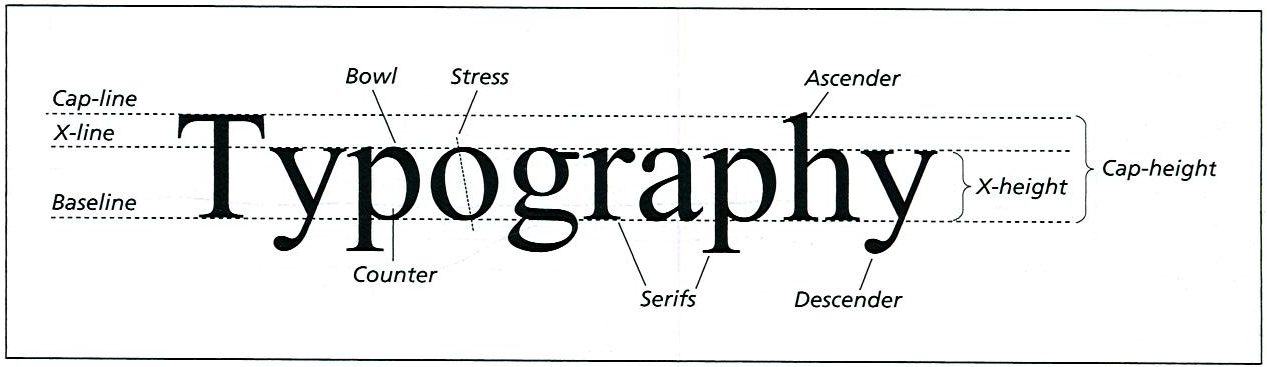
Typeface Characteristics
Serif vs. Sans Serif
Weight & Width
Contrast (Thick & Thin Strokes)
x-height
Ascenders/Descenders
Stress (Vertical/Horizontal)