penumbra/ geometric unsharpness quiz
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Which of the following techniques can be used during an imaging procedure to reduce the superimposition of tissues?
Select all that apply.
the use of tube angulation
Obtaining two images, one at 90 degrees angle from the first image
The use of oblique positions
The region of unsharpness found at the edges of the images appearing at the imaging plane is called the:
Penumbra
The structural sharpness recorded in the radiographic image is known as:
spatial resolution
Sharpness of detail
Image sharpness
What is another name for geometric unsharpness?
Select all that apply.
penumbra
Focal spot blur
Refer to the diagram below. The image seen at the area labeled A indicates a type of?

Elongation
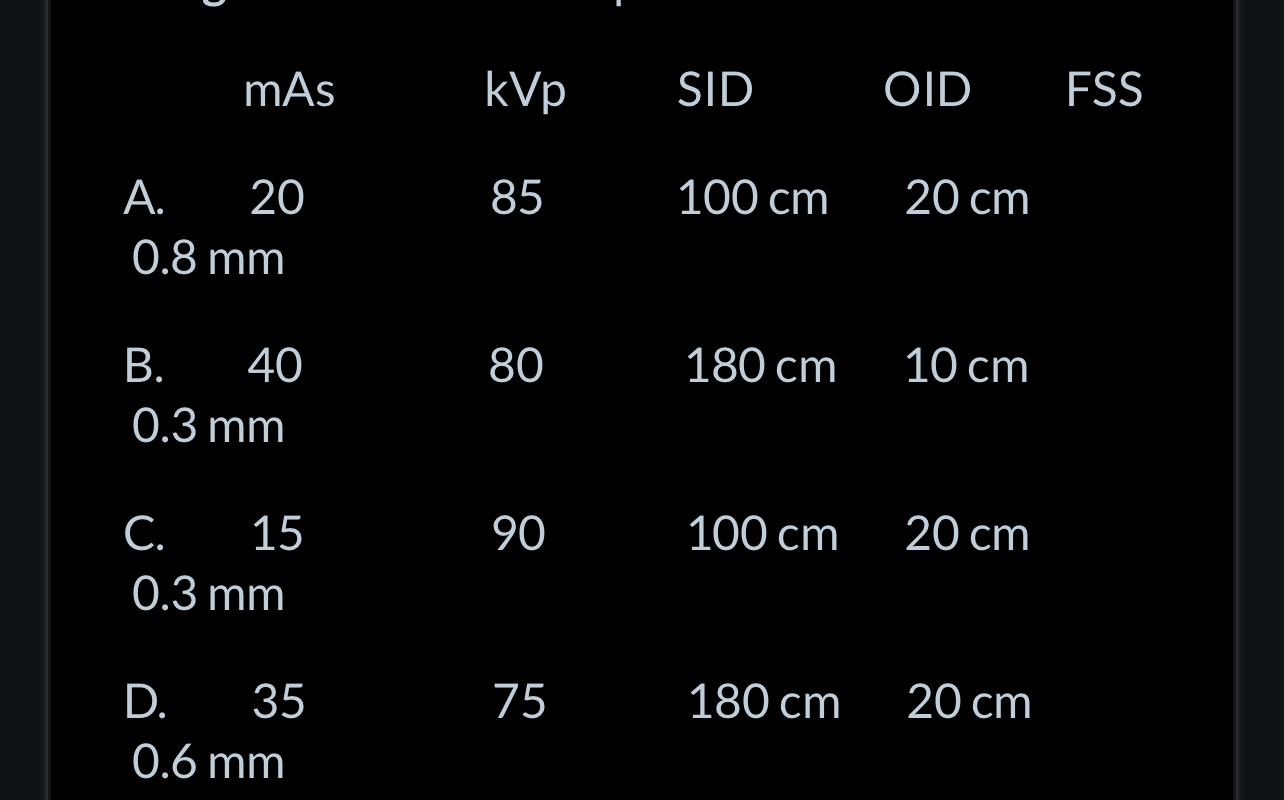
Which of the following sets of factors is associated with a radiographic image possessing the greatest amount of penumbra?
A
The amount of size distortion (magnification) appearing in a digital image can be determined by the formula:
SID/SOD
Elongation and/or foreshortening of a radiographic image will most likely occur from a/an:
Angulation of the central ray
Which of the following changes will be associated with an increase in the size distortion (magnification) that will occur in a radiographic image?
Select all that apply.
a decrease in SID
An increased OID
A decreased SOD
A radiograph is performed using 50 mAs, 80 kVp at 100 cm SID, 40 cm OID and a 2 mm FSS. The magnification factor for this image is:
1.67
Improper tube, object, and IR alignment with no change in the SID will result in:
Shape distortion
The image of a spherical shaped object that is exposed by the central portion of an x-ray beam, will appear to have a:
Circular shape
Grids are not normally employed during a macro-radiographic (magnification) exam because of the reduced amount of scatter that reaches the IR when a ___________________ is used.
Long OID
Tube angulations in many radiographic examinations are useful for the visualization of:
Tissues that are superimposed
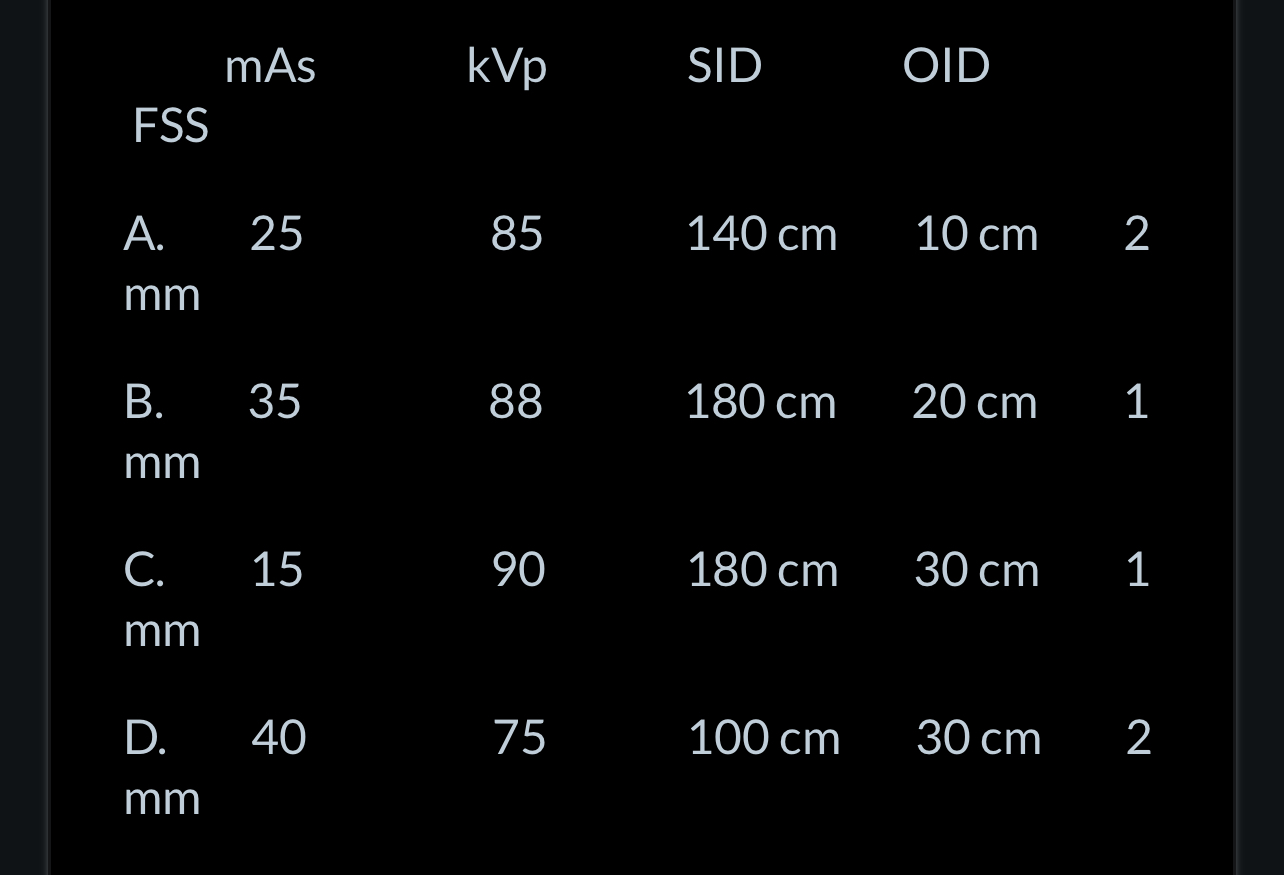
Which of the following sets of technical factors will produce a radiograph showing the greatest magnification?
D
As the distance from a radiation source increases, the object receives less radiation. This occurs principally because x-ray photons:
Are distributed over a larger area
Magnification radiography is being performed using a 140 cm SID, 40 cm OID and a 0.3 mm FSS. The magnification factor for this set of factors is?
1.4
The formation of penumbra around a radiographic image is affected by changes in:
Select all that apply.
OID
SID
If a heart measures 12.5 cm from side to side at its widest point, and its image on a digital chest radiograph measures 15.0 cm, the magnification factor for this image is:
1.2
Which of the following can be used to maintain the same relative size of a radiographic image, if an increase in the OID is required?
Increase the SID
The image of a disk-shaped object that is exposed on the central axis of the beam will appear as a/an_____________shaped image.
Circular
Which of the following changes will increase the amount of shape distortion appearing on a digital image?
Employing tube angulations
An object measuring 18 cm in length is imaged at a 100 cm SID and a 10 cm OID distance. How long will the resulting radiographic image be?
20 cm
Which of the following radiographic images of the skull is likely to have the greatest amount of shape distortion?
PA with a 30 degree caudal angulation
If an x-ray beam was produced from a single point source, the resultant image would consist of:
Umbra only
A 10 cm object is radiographed using a 90 cm SID and a 60 cm OID. The image of the object should measure:
30 cm
The sharpness of detail of a radiographic image will be improved by employing a:
Select all that apply.
longer SID
shorter OID
Smaller FSS
The true image shadow of a radiographic image is termed the:
Umbra