respiratory and phonatory systems
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
two parts of respiratory and phonatory systems
upper respiratory tract
lower respiratory tract
upper respiratory tract
a) nasal cavity
b) oropharynx
c) larynx
lower respiratory tract
a) trachea
b) bronchi
c) lungs
three main functions of the nasal cavity
filter
humidify
warm
components of the oropharynx
oral cavity to the level of the BOT
pharynx (naso, oro, hypo)
functions of the oropharynx
swallowing (oral prep & transit)
speech
breathe-respiration
oropharynx- oral cavity is separated from nasal cavity by:
hard palate
soft palate
oropharynx- oral cavity terminates at:
posteriorly
anteriorly
posteriorly- faucial arches (pillars)
anteriorly- lips
oropharynx- pharynx originates at:
posterior portion of the nasal cavity
oropharynx- pharynx extends to:
upper portion of the esophagus- upper digestive tract
oropharynx- pharynx consists of 3 segments:
nasopharynx
oropharynx
hypopharynx
larynx is attached inferiorly to:
trachea
larynx is suspended superiorly from:
hyoid bone
larynx is comprised of 2 paired cartilages:
thyroid cartilage
cricoid cartilage
1 paired cartilage of the larynx
arytenoid cartilage
The arytenoids are responsible for what movements of the vocal folds?
abduction (← →)
adduction (→ ←)
The first entrance to the larynx is the:
laryngeal vestibule (airspace above the VFs)
The 3 major regions of the larynx include:
supraglottis
glottic level
subglottic level
What are the 3 main components of the upper respiratory tract?
nasal cavity
oropharynx
larynx
the lower respiratory tract is housed within the ________ cavity
thoracic
the lower respiratory tract is formed by the:
12 thoracic vertebrae
sternum
ribs
The left and right halves of the thoracic cavity are divided by: (which tract?)
mediastinum
lower respiratory
The mediastinum houses the:
heart
blood vessels
nerves
portion of the esophagus
The trachea is composed of semi-circular:
U-shaped
cartilaginous rings
This trachea extends from the ______ to the _________
larynx (at the cricoid cartilage) to the starting point of the upper thoracic cavity
The inferior end of the trachea divides into 2 branches called the:
______
______
main stem
primary bronchi
the inferior end of the trachea consists of both the:
left bronchus
right bronchus
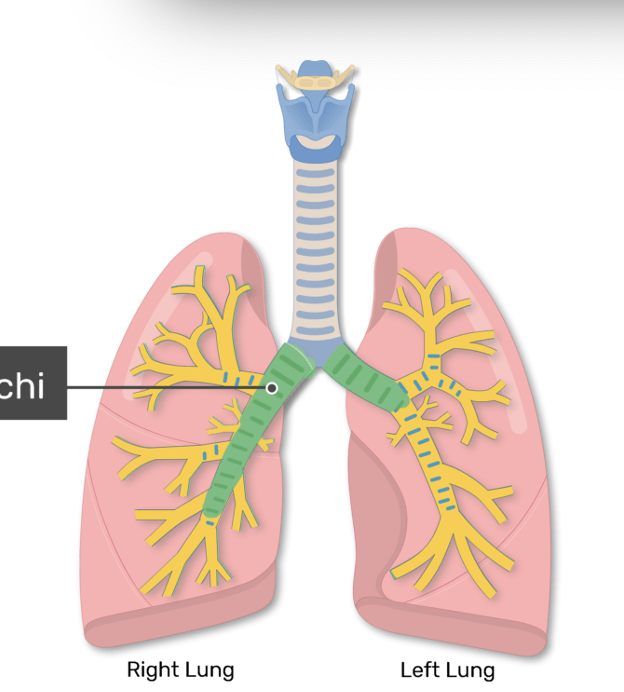
The terminal bronchioles end at the _________
alveolar air sacs
Gas exchange with the bloodstream takes place in the ______
alveoli
The lungs are divided into segments called:
lobes
In total, there are 5 lobes which are split:
__ on the right
__ on the left
3
2 (heart)
What are the 3 main components of the lower respiratory tract?
trachea
bronchi
lungs
Where does gas exchange take place?
alveolli sacs
3 types of breathing
quiet
forced
speech
types of breathing chart for active and passive

Volume of air inhaled and exhaled during normal quiet breathing
Tidal Volume (TV)
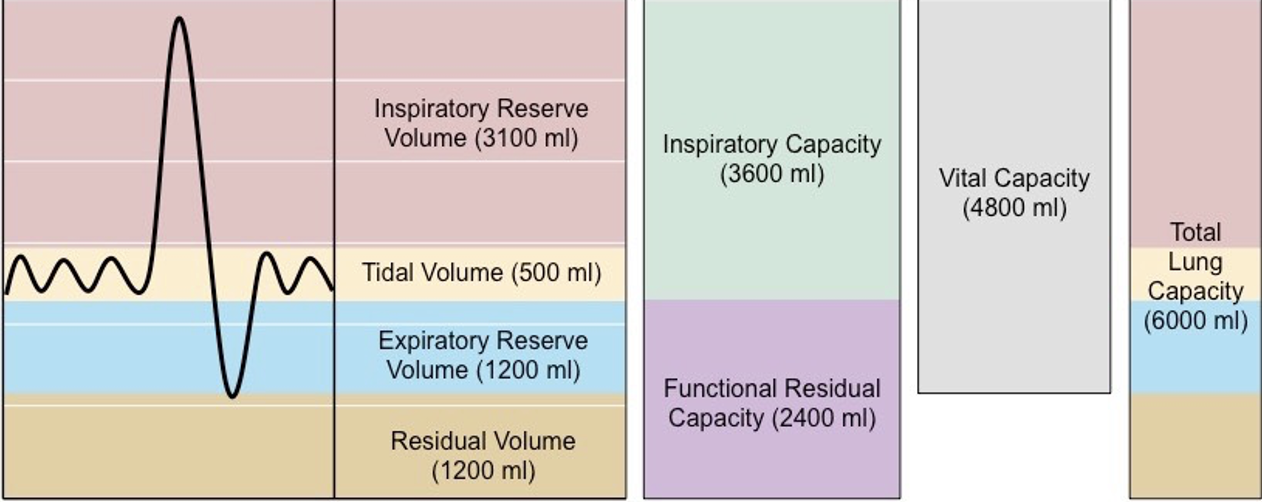
Volume of air that can be inhaled beyond a normal tidal inspiration
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
Volume of air that can be exhaled beyond a normal tidal expiration
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)
Volume of air that remains in the lungs beyond a maximum forced expiration
Residual Volume (RV)
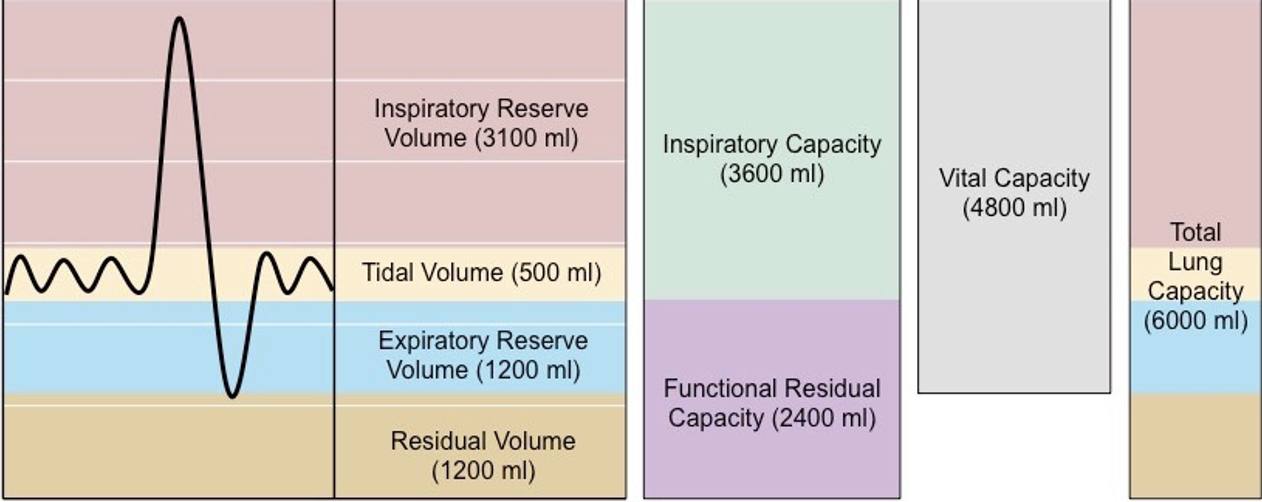
Volume of air that remains in the lungs beyond a normal tidal expiration
Functional Residual Capacity (FRC)
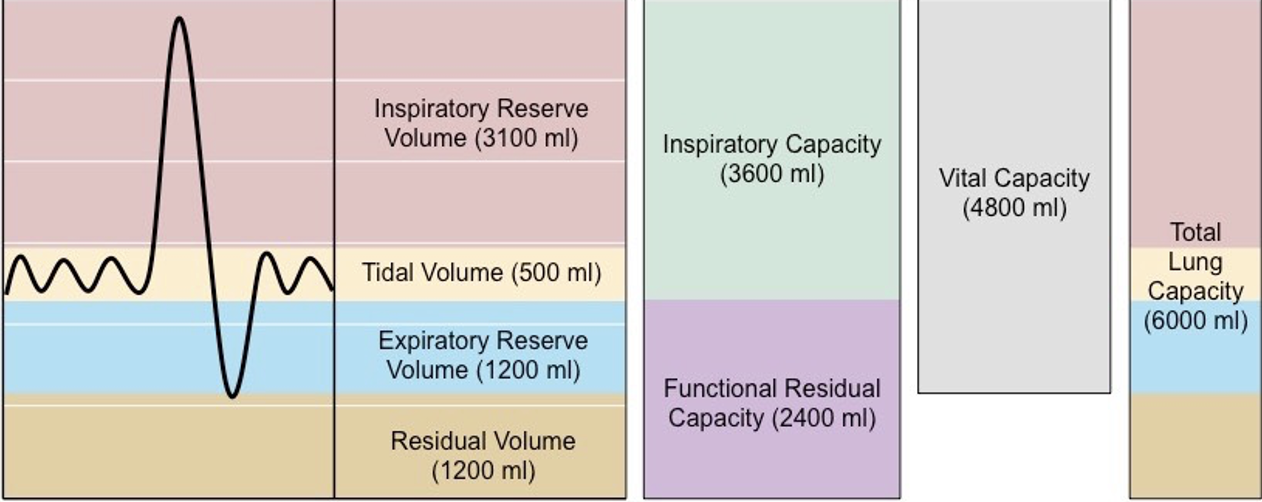
Volume of air maximally exhaled after a maximum inspiration.
Vital Capacity (VC)
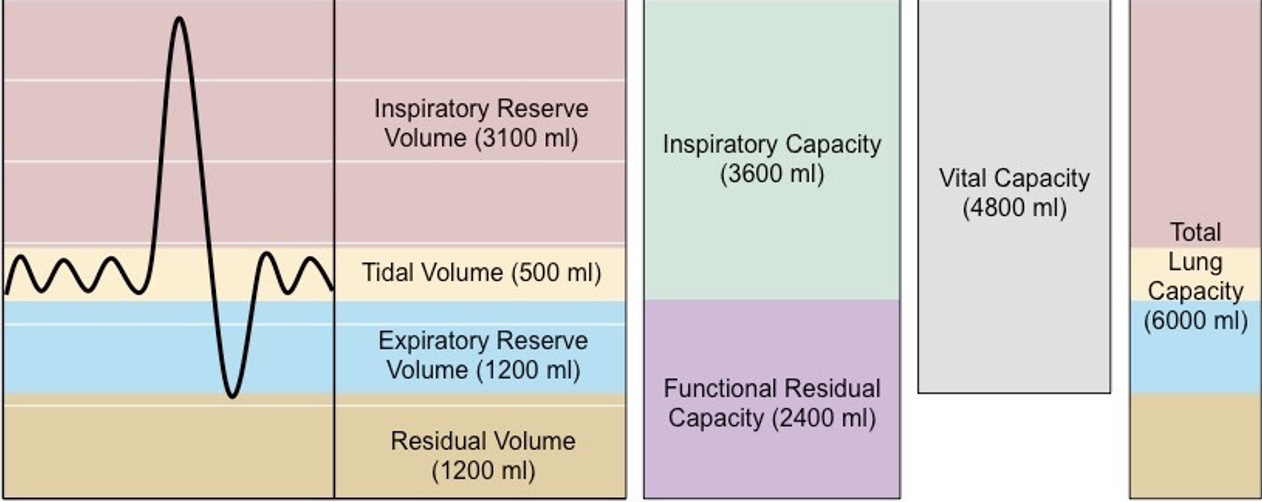
Reflects inspiratory/expiratory muscle strength.
Vital Capacity (VC)
Amount of air that is inspired and expired per minute.
minute volume
4 lung volumes
tidal volume
inspiratory reserve
expiratory reserve
residual volume
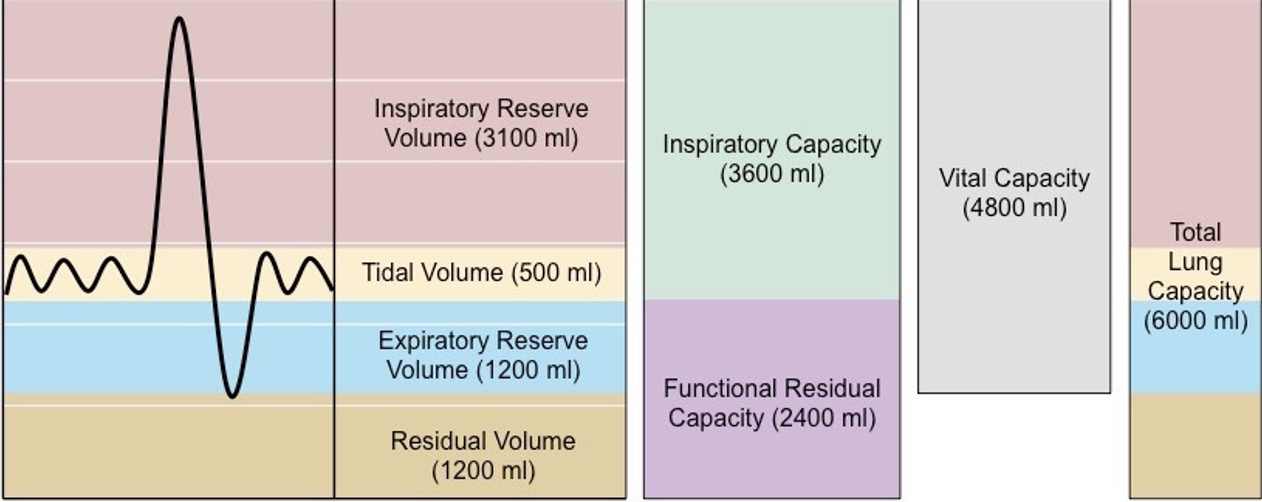
3 lung capacities
total lung capacity
vital capacity
function residual capacity
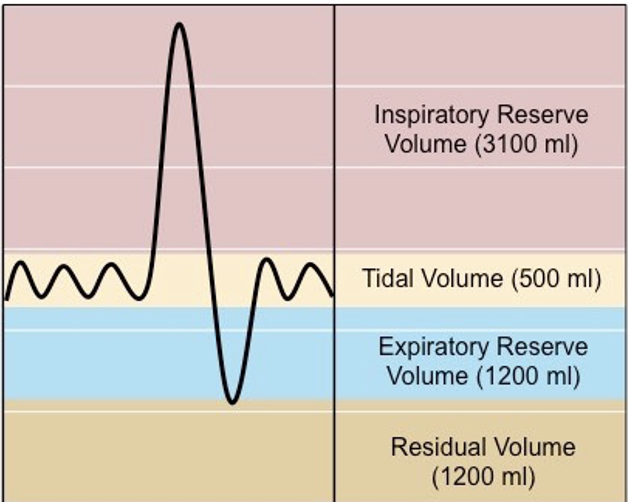
which lung volume? quiet breathing
tidal volume
which lung volume? bigger breath beyond tidal
inspiratory reserve
which lung volume? bigger exhale beyond tidal
expiratory reserve
which lung capacity? sum of all volumes
total lung capacity
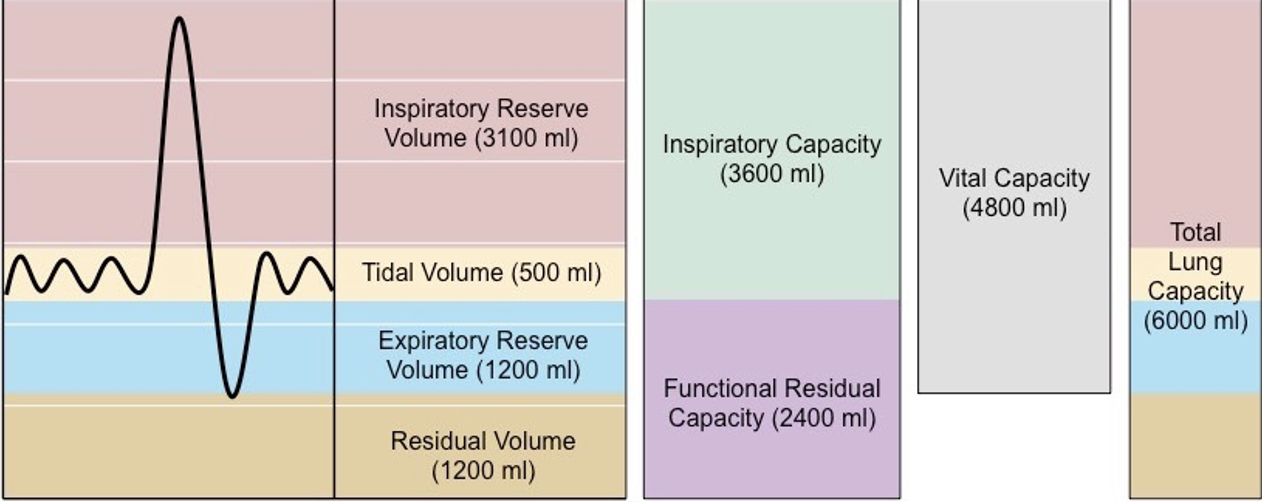
which lung capacity? tidal + inspiratory reserve + expiratory reserve
vital capacity
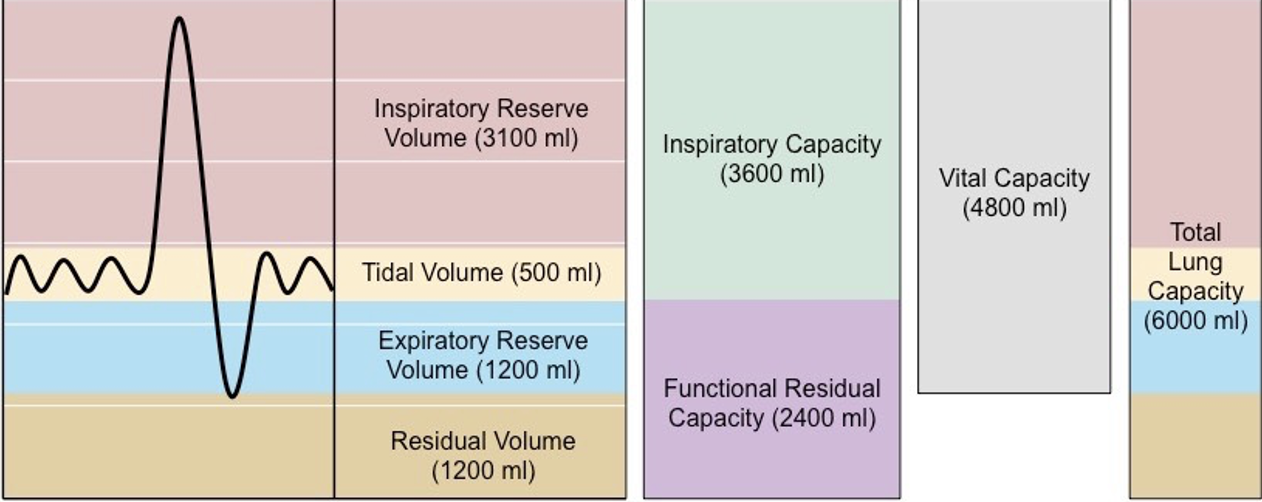
which lung capacity? expiratory reserve + residual volume
functional residual capacity
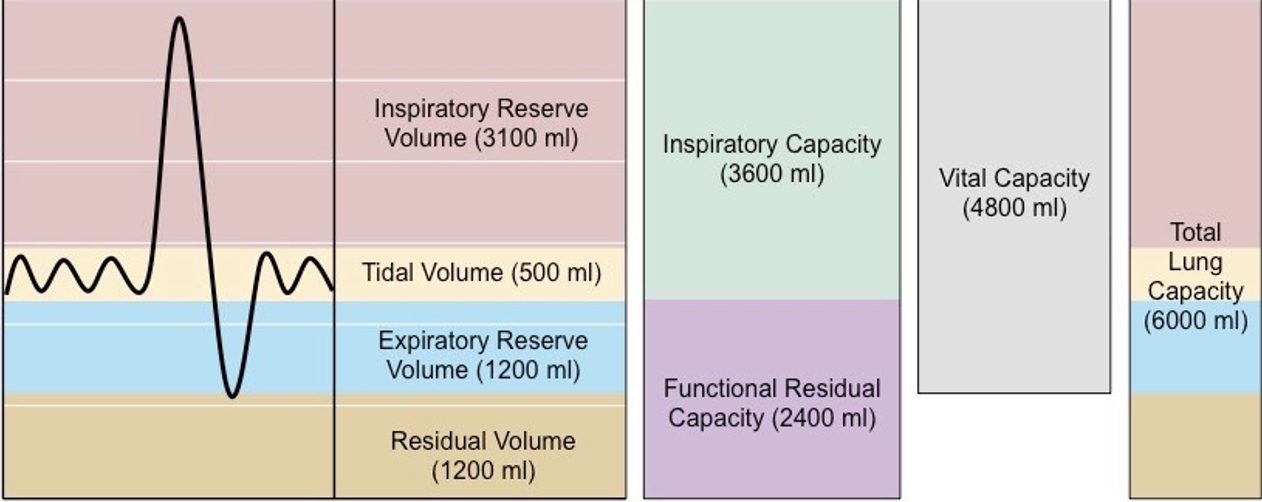
lung volumes and capacity measures are obtained during: ____ or ____ and tested via ___ or _____.
pulmonary function testing or PFT; spirometry or peak flow meter
What are the 3 main types of breathing patterns?
quiet (rest)
forced
speech
Which is the only type of breathing pattern that includes passive respiration?
quiet (expiration)
Which measure of lung capacity gives you information about inspiratory and expiratory muscle strength?
vital capacity
main muscle of inspiration for breathing
diaphragm
dome shaped muscle at the base of the rib cage
central pattern generator is located in the _______ (_______ & ______)
brainstem (pons & medulla)
Collection of specialized ___________________ that communicate information regarding the levels of ______ in the blood to the respiratory control center
nerve (sensory) cells, O2; chemoreceptors (stimulate)
Other types of cells which respond to events of the ____________________. They also contribute to cycles of ________________ by responding to the expansion and deflation of lungs and bronchi.
respiratory cycle, ventilation; stretch receptors (inhibit)
So then once inspiration is triggered, how does respiration take place?
Recall that:
Gas exchange occurs within the bloodstream
This takes place in the alveoli
A small vessel which transports three things to the organs and body systems (what is it and what 3 things?)
capillaries
blood
nutrients
oxygen
arteries role = Carry blood ______ the heart
away from
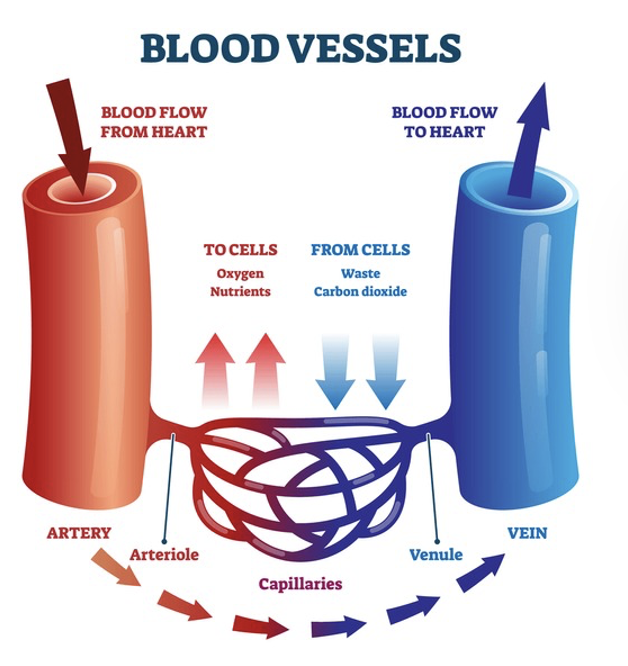
veins role = Carry blood ______ the heart
to
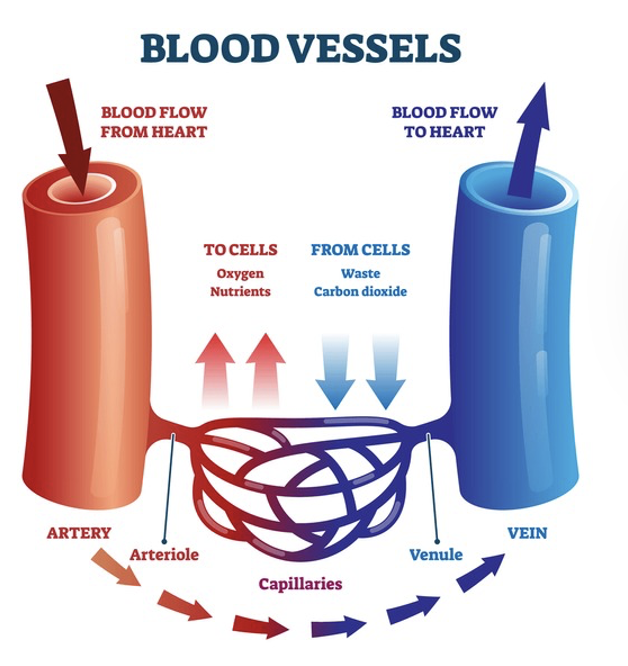
The primary function of the capillaries is to…
exchange materials between the blood and tissue cells
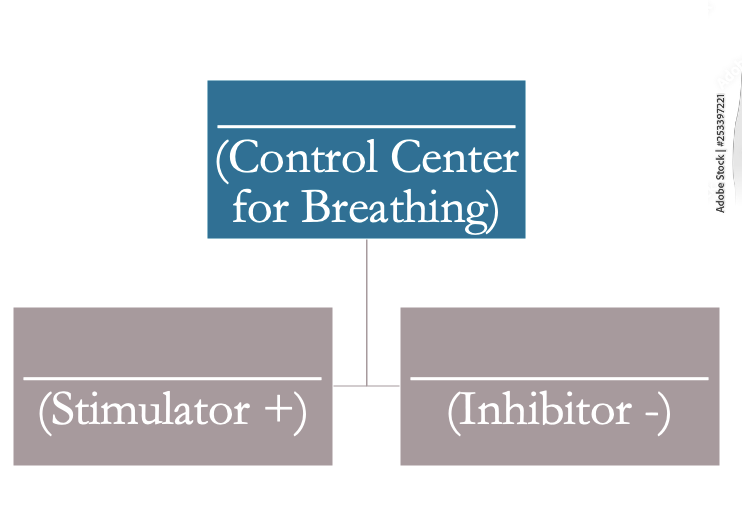
central pattern generator→control center for breathing
chemoreceptors→ stimulator +
stretch receptors→ inhibitors -
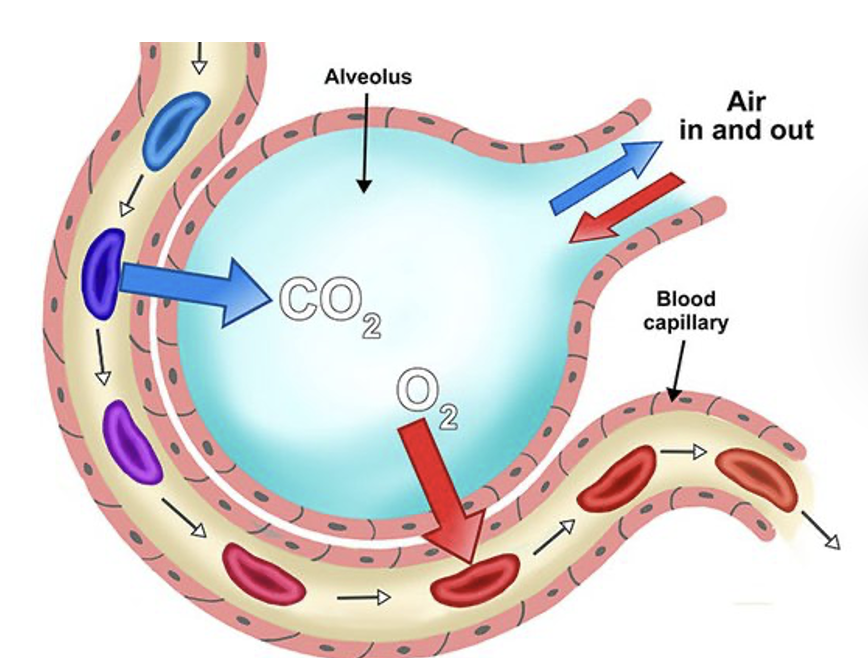
define respiration
exchange of gas (oxygen or carbon dioxide)
once oxygen comes in:
where does it go?
via what vessel?
heart→ artery → body
CO2 goes out:
where does this come from?
veins
So, what is the difference between respiration and ventilation??
Respiration:
Gas exchange for oxygenation
The actual movement of gas across a membrane
A ventilator cannot do this for you
Ventilation:
The act of breathing and/or moving air (physical process)
A ventilator pushes air into the lungs to quite literally ventilate them
Respiration is gas exchange for _______________
oxygenation
Ventilation is the act of ____________ and/or ______________
breathing and/or moving air
the route of ventilation
Mouth and nasal passages → pharynx → vocal folds → trachea → carina → bronchi → bronchioles → alveoli
ventilation is only functional IF what structures are functional?
brainstem, cranial and peripheral nerves, diaphragm, intercostal musculature, and lungs
carried out by the lungs
ventilation vs respiration
ventilation
occurs in alveoli and the walls of blood capillaries
ventilation vs respiration
respiration
ventilation vs respiration
voluntary or involuntary
ventilation: voluntary
respiration: involuntary
Diseases & Conditions Impacting the Respiratory System
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Restrictive lung disorders
Neuromuscular diseases and conditions
Cardiopulmonary conditions
Sepsis
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
dyspnea
shortness of breath
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Represents a group of diseases due to irreversible destruction of lung tissue
two causes of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
a) chronic bronchitis
b) emphysema
chronic bronchitis
caused by excessive mucus and narrowing of small airways due to edema
emphysema
caused by deterioration of the alveolar walls
restrictive lung disorders are caused by any of the following:
respiratory muscle weakness
paralysis
reduced elasticity of the lungs and chest wall
_____________________ = elasticity of lungs and chest wall
compliance
2 main contributors to restrictive lung disorders
connective tissue disorders
pneumonia
connective tissue disorders
affect lung compliance by both loss of lung tissue and fibrotic changes in the lungs (ex: scleroderma, lupus)
pneumonia
acute infection and inflammation in alveoli and capillaries
neuromuscular conditions
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Muscular Dystrophy (MD)
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)
Stroke
Poliomyelitis
Spinal Cord Injury
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Degenerative disease that causes motor neurons of brain and spinal cord to deteriorate. Respiratory system progressively declines.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Demyelinating disease of the white matter of the central nervous system. Respiratory complications arise due to plaque development in the cervical spinal cord.
Muscular Dystrophy (MD)
Progressive, hereditary disease which impacts striated muscle (such as diaphragm and heart) resulting in respiratory muscle weakness.
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)
Acute, demyelinating disease that causes rapid deterioration of extremity muscle function. Often impairs respiratory function- requiring rapid intubation/mechanical ventilation.
Brainstem stroke affects the stroke affects the
Cortical stroke…
central control system for respiration
have a peripheral effect on respiration (impacts abdominal and thoracic muscle tone and body posture, and consequently lung expansion)
Poliomyelitis
Viral disease that causes severe muscle weakness with associated respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation
Spinal Cord Injury
Injury above 4th vertebrae results in nonfunctional respiratory system from nerve damage to the diaphragm (the primary muscle of inspiration, innervated by phrenic nerve)
Cardiopulmonary Disorders:
the purpose of the lungs is to accomplish what?
successful gas exchange depends on adequate what?
what are interdependent on each other for stable O2 and CO2 levels?
gas exchange
circulation of the blood to the alveoli
heart and lungs
congestive heart failure (CHF)
Heart cannot pump out a sufficient amount of blood
Heart contracts less over time, this limits its ability to fill with blood
Heart cannot keep up with the body’s demand for oxygen rich blood
sepsis
A systemic inflammatory response to an infectious source
Inflammation affects the organ systems and may cause them to go into organ failure. This includes the respiratory system.
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
Occurs secondary to various acute medical conditions
Damage to area of oxygen transfer (alveolar-capillary membrane) resulting in severe impairment in gas exchange in the lungs
Fluid leaks into alveoli
Loss of surfactant (coating of alveoli which keeps them inflated)
Collapse of alveoli (atelectasis)
= loss of oxygen in arterial blood
hypoxemia