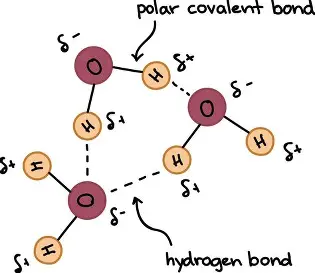
A-Level Biology - biological molecules
1/60
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
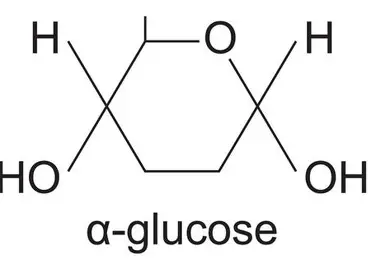
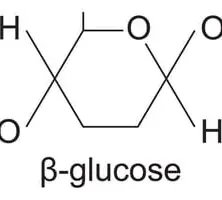
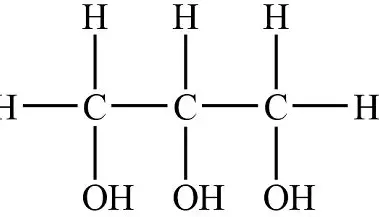
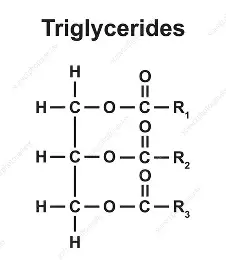
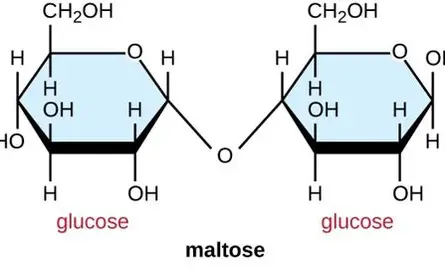
glucose +glucose → maltose + water
glucose + galactose → lactose + water
glucose + fructose → sucrose + water
It is coiled, making it compact
It has branched ends for fast hydrolysis of terminal glucose monomers
It can provide glucose for respiration
It is a large molecule, so cannot cross the cell membrane
What is the procedure for testing non-reducing sugars?
To test for non-reducing sugars, do the reducing sugars test first. If negative, hydrolyse the sample with dilute hydrochloric acid, neutralize with sodium hydrogencarbonate, then retest with Benedict's reagent.
Saturated lipids do not contain carbon-carbon double bonds - all the carbon atoms are saturated with hydrogen
a fatty acid containing two or more carbon-carbon double bonds
Source of energy - when oxidised they release twice the energy as the same mass of carbohydrates. Waterproofing - insoluble in water do used as waxy cuticles.
Protection - fat is found around delicate organs
Insulation - heat retention as lipids are slow conductors, and also electrical (myelin sheath).
Biological membranes - phospholipids contribute to membrane flexibility.
Shake with ethanol then add water. A cloudy emulsion will appear if positive
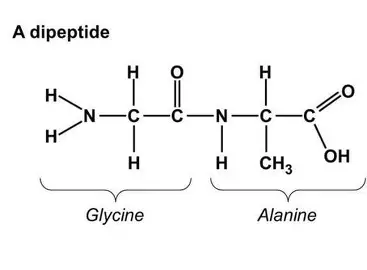
Amino acids contain an amino group (NH2), a carboxylic acid group (COOH)
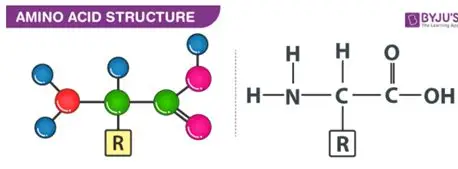
The twisted structure continues to fold to give the complex 3D shape. Interactions between R groups cause bonds to form that hold it in place - ionic bonds, H bonds and disulfide bridges. It gives the protein its 3D shape and functionality, allowing the protein to be recognised and interact in a specific way.