2.1.2 (d) ring structure HEXOSE AND PENTOSE
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What does a 1-4 bond mean
Carbon 1 from one mono joins to carbon 4 Ona second monosaccharide
How many carbon atoms are in a hexose
6
What is an example of a hexose monosaccharide
GLUCOSE
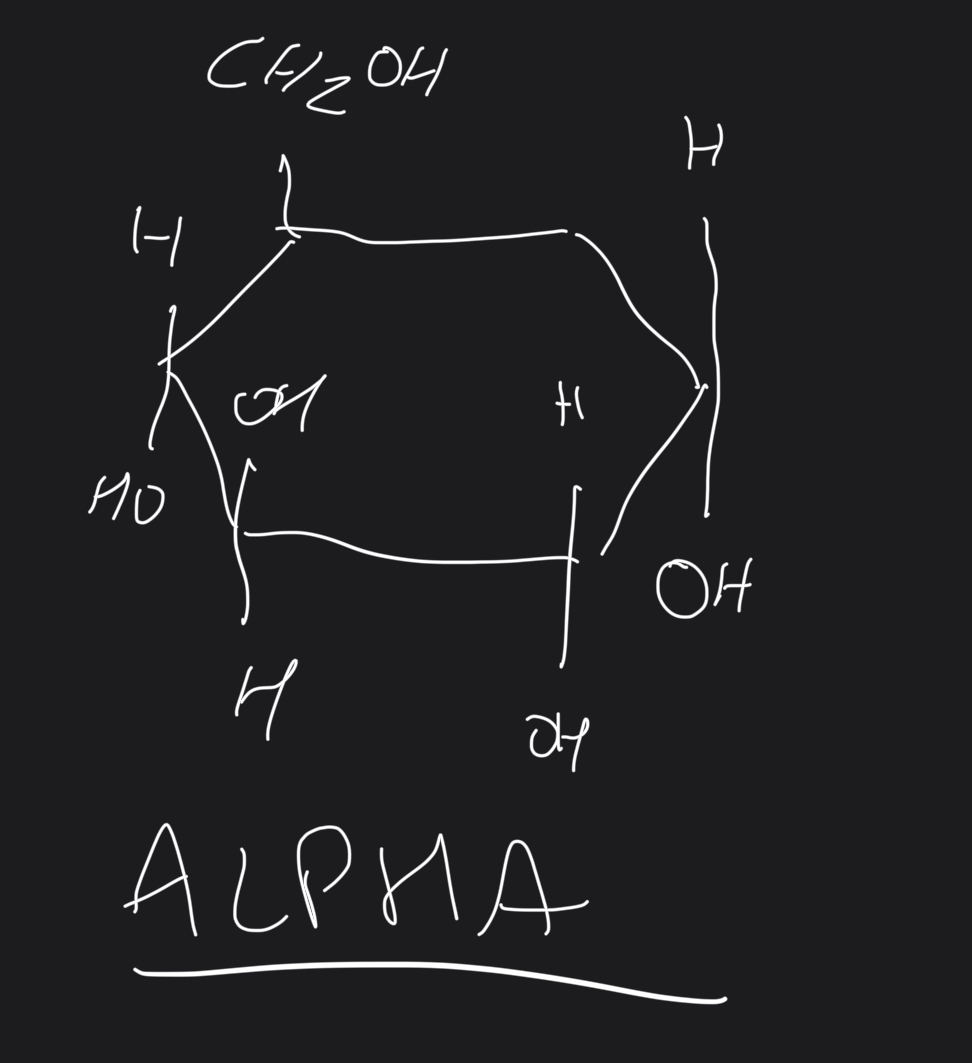
Draw the alpha glucose
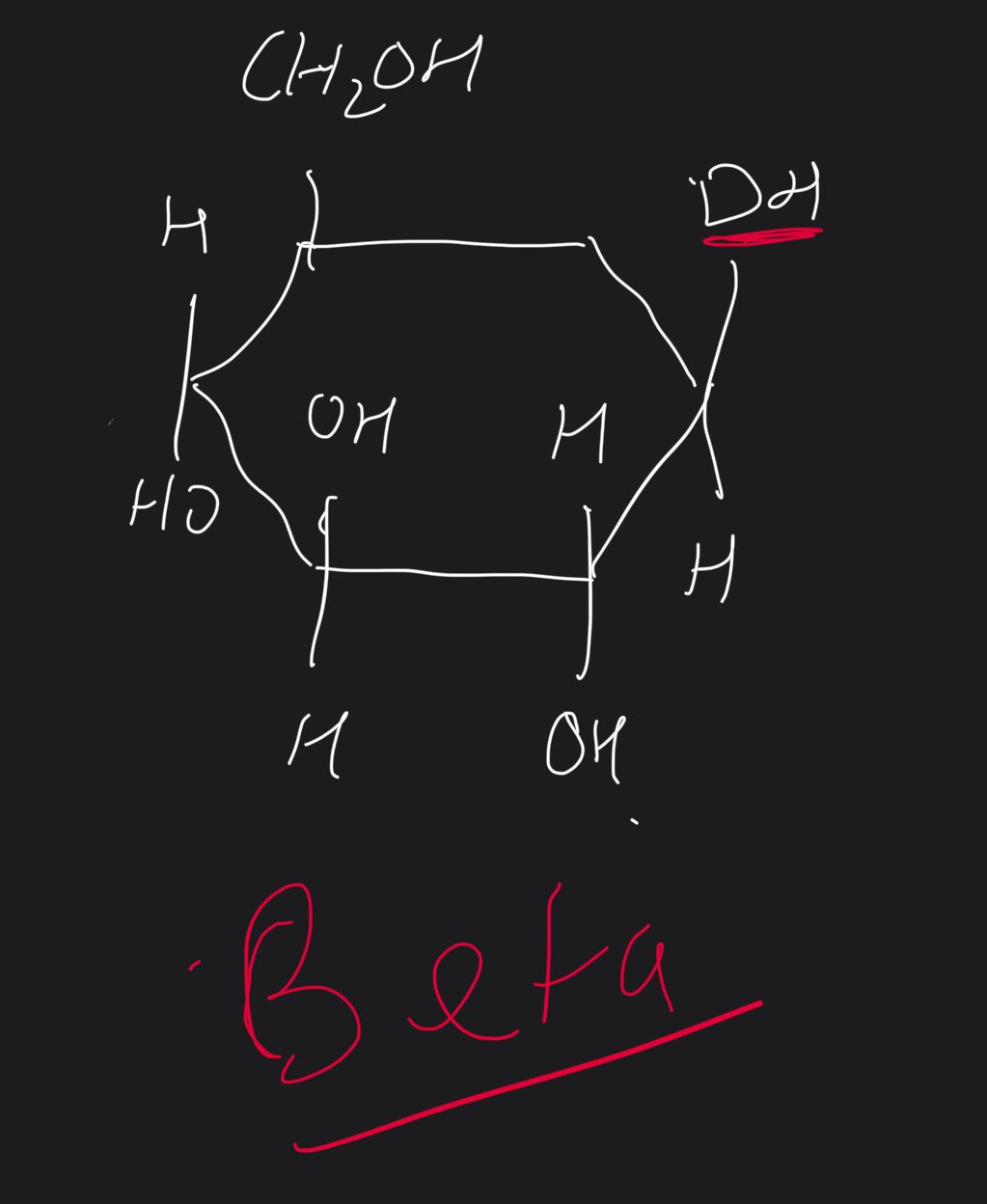
Draw a beta glucose
What is the use of an alpha glucose molecule
It is a substrate in respiration
What is the use f a beta glucose molecule
Polymerises to form cellulose
What is an example of a Penrtose sugar
RIBOSE ( 5 CARBON)
What is the formula for ribose
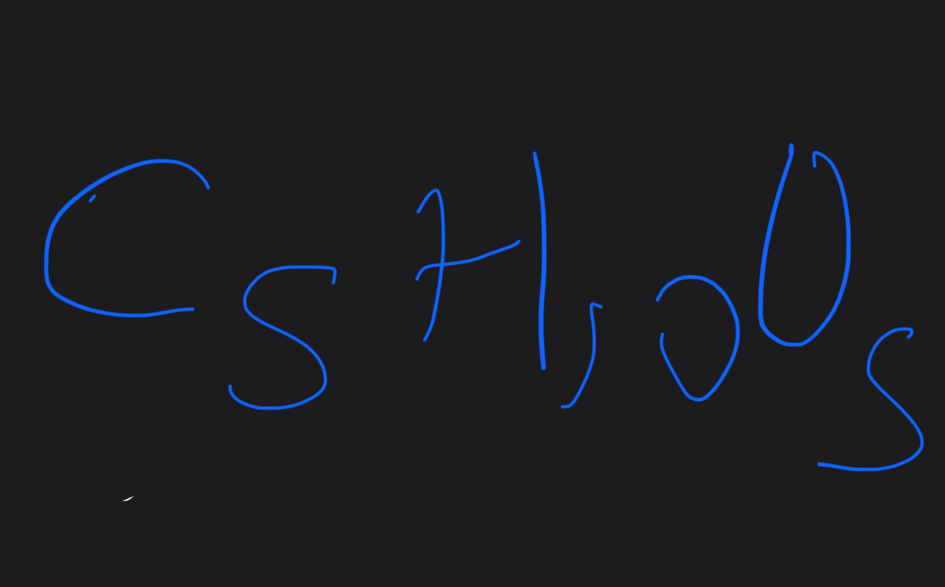
What is the use of ribose
It is a sugar in RNA nucleotides
What are some properties of glucose
Soluble in water
Hydrophilic and can be transported in blood
The hydroxyl group in water make it polar and therefore form hydrogen bonds
REDUCING SUGAR
It contains a free hemiacetal group ( a group which can from an aldehyde) THIS IS A C DOUUBLE 0 BOND
It allows sugars to donate electrons to another molecule;e
What is a glycosidic bond?
Strong covalent bond that links sugar to another group ( it can be a carb group or not)
Formed through condensation reactions where a water molecule is released
The nature of the bond determines its properties ( whether its a or b and how many carbon atoms are included)
Give an example of a glycosidic bond
Form polysaccharides like starch
Form disaccharides like sucrose
What is hydrolysis
When water is addded to a disaccharide to go back to the original 2 monosaccharides
What is a disaccharide
Disaccharides are sugars that are composed of 2 monosaccharide joined together in a condensation reaction forming a glycosidic bond