Chapter 56 Campbell Biology
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/45
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
1
New cards
Conservation Biology
Using knowledge of ecology, physiology, molecular biology, genetics, evolution, etc to conserve biodiversity
2
New cards
biodiversity

3
New cards
3 Levels of Biodiversity
Genetic, Species and Ecosystem Diversity

4
New cards
Genetic Variation
comprises variation WITHIN a population and BETWEEN populations
adaptations to local conditions.
adaptations to local conditions.
5
New cards
Species Diversity
the number of species in an ecosystem or across the biosphere
variety of species in an ecosystem or throughout the biosphere
endangered and threatened species
variety of species in an ecosystem or throughout the biosphere
endangered and threatened species
6
New cards
endangered species
A species whose numbers are so small that the species is at risk of extinction
7
New cards
threatened species
A species that could become endangered in the near future
12% birds, 21% mammals
12% birds, 21% mammals
8
New cards
Ecosystem Diversity
The variety of ecosystems on Earth is a third level of biological diversity.
Human activity is reducing ecosystem diversity, the variety of ecosystems in the biosphere
Human activity is reducing ecosystem diversity, the variety of ecosystems in the biosphere
9
New cards
Endangered Species
Species in danger of extinction through all or most of its range
may go extinct/ endagered in one area an not another
may go extinct/ endagered in one area an not another
10
New cards
global extinction
a species can no longer be found anywhere
11
New cards
Threatened Species
Species likely to be endangered in the near future
12
New cards
Ecosystem Services
encompass all the processes through which natural ecosystems help sustain human life.
Processes that ecosystems carry out like air and water purification, pollination, soil preservation, etc that help sustain human life
Processes that ecosystems carry out like air and water purification, pollination, soil preservation, etc that help sustain human life
13
New cards
4 main threats to biodiversity
1. Habitat Loss
2. Introduced Species
3. Overharvesting
4. Global Change
2. Introduced Species
3. Overharvesting
4. Global Change
14
New cards
Introduced Species
Non-native species humans move intentionally or unintentionally to a new area via ships and airplanes, etc (Ex. Zebra mussels)
Free from the predators, parasites, and pathogens that limit their populations in their native habitats, such transplanted species may spread rapidly through a new region.
disrupt their new community, often by preying on native organisms or outcompeting native organisms
Free from the predators, parasites, and pathogens that limit their populations in their native habitats, such transplanted species may spread rapidly through a new region.
disrupt their new community, often by preying on native organisms or outcompeting native organisms
15
New cards
Habitat Loss
human alteration of habitat is the greatest threat to biodiversity throughout the biosphere
agriculture, urban development, forestry, mining, and pollution.
cause for 73% of the species that have become extinct, endangered, vulnerable
98% of the tropical dry forests of Central America and Mexico have been cut down.
agriculture, urban development, forestry, mining, and pollution.
cause for 73% of the species that have become extinct, endangered, vulnerable
98% of the tropical dry forests of Central America and Mexico have been cut down.
16
New cards
habitat fragmentation
Breakup of a habitat into smaller pieces, usually as a result of human activities.
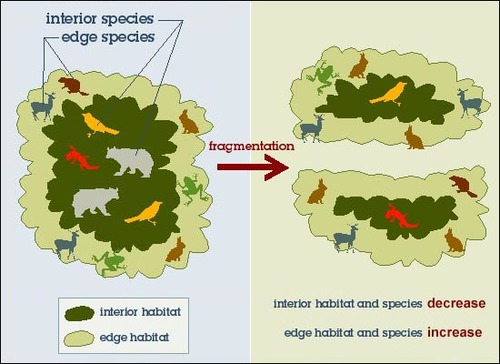
17
New cards
Overharvesting
human harvesting of wild plants or animals a rates exceeding the ability of population of the species to rebound
low reproductive rates, such as elephants, whales, and rhinoceroses.
low reproductive rates, such as elephants, whales, and rhinoceroses.
18
New cards
global change
includes alterations in climate, atmospheric chemistry, and broad ecological systems that reduce the capacity of Earth to sustain life.
acid precipitation
acid precipitation
19
New cards
acid precipiation
ain, snow, sleet, or fog with a pH less than 5.2.
The burning of wood and fossil fuels releases oxides of sulfur and nitrogen that react with water in air, forming sulfuric and nitric acids. The acids eventually fall to Earth's surface, where they cause chemical reactions that decrease nutrient supplies and increase concentrations of toxic metals.
The burning of wood and fossil fuels releases oxides of sulfur and nitrogen that react with water in air, forming sulfuric and nitric acids. The acids eventually fall to Earth's surface, where they cause chemical reactions that decrease nutrient supplies and increase concentrations of toxic metals.
20
New cards
Extinction vortex
small pop vunerable to interbreed inter breeding and gentic drift, loss of genetic variaation that enables evolutionary response and leads to smaller and smaller popualtions until none are left
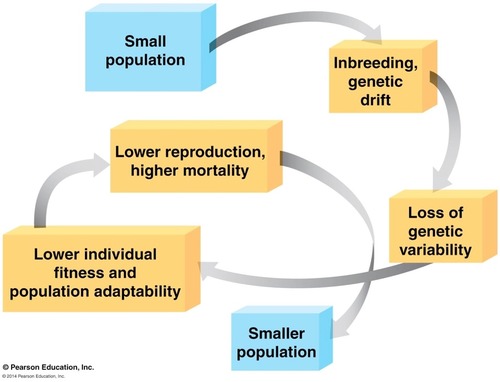
21
New cards
mimimum viable population
MVP
. The minimal population size at which a species is able to sustain its numbers
. The minimal population size at which a species is able to sustain its numbers
22
New cards
effective population size
the number of individuals in a population who contribute offspring to the next generation
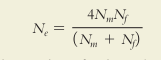
23
New cards
declining population approach
focuses on threatened and endangered populations that show a downward trend, even if the population is far above its minimum viable population
emphasizes the environmental factors that caused a population decline in the first place.
emphasizes the environmental factors that caused a population decline in the first place.
24
New cards
Movement Cooridor
In fragmented habitats,
Narrow strip or series of small habitat clumps that connect isolated patches in order to bridge fragmented habitats
Movement corridors can also promote dispersal and reduce inbreeding in declining populations
Narrow strip or series of small habitat clumps that connect isolated patches in order to bridge fragmented habitats
Movement corridors can also promote dispersal and reduce inbreeding in declining populations
25
New cards
importantce of cooridor
increase the exchange of individuals among populations of many organisms, including butterflies, voles, and aquatic plants.
CONNNECT ISOLATED PATHCES
especially important to species that migrate between different habitats seasonally.
CONNNECT ISOLATED PATHCES
especially important to species that migrate between different habitats seasonally.
26
New cards
4 types of environmental change caused by humans
1. Nutrient Enrichment
2. Toxins in the Environment
3. Greenhouse Gasses + Global Warming
4. Depletion of Atmospheric Ozone
2. Toxins in the Environment
3. Greenhouse Gasses + Global Warming
4. Depletion of Atmospheric Ozone
27
New cards
Biodiversity Hot Spot
Small area with many species found nowhere else in the world (aka endemic species) and lots of endangered species
less than 1.5% of Earth's land but are home to more than a third of all species of plants, amphibians, reptiles (including birds), and mammals. Aquatic ecosystems also have hot spots, such as coral reefs and certain river systems.
less than 1.5% of Earth's land but are home to more than a third of all species of plants, amphibians, reptiles (including birds), and mammals. Aquatic ecosystems also have hot spots, such as coral reefs and certain river systems.
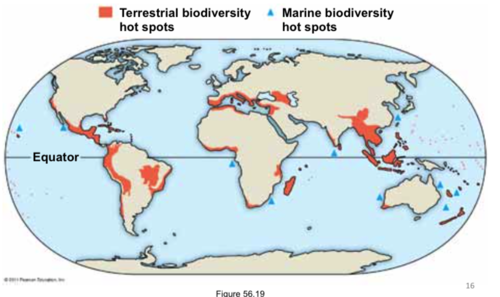
28
New cards
nature reserve
protected "islands" of biodiversity in a sea of habitat altered or degraded by human activity.
29
New cards
Zoned Reserve
Extensive region that includes areas undisturbed by humans surrounded by areas changed by human activity and used for economic gain
support human activities, but regulations prevent the types of extensive alterations likely to harm the protected area.
ex costa rica
support human activities, but regulations prevent the types of extensive alterations likely to harm the protected area.
ex costa rica
30
New cards
urban ecology
examines organisms and their environment in urban settings.
quality and flow of their water and the organisms living in them.
quality and flow of their water and the organisms living in them.
31
New cards
Global Warming
The warming of the earth due to increases carbon dioxide levels
32
New cards
Assisted Migration
Translocation of species to a good habitat outside its native range to protect it
33
New cards
Ozone Layer
O3; it is depleted due to chlorine emissions which break it down into oxygen
34
New cards
Critical Load
The amount of an added nutrient that can be absorbed without damaging the ecosystem
usually nitrogen or phosphorus
usually nitrogen or phosphorus
35
New cards
nutrient enrichment
removes nutrients from one part of the biosphere and adds them to another.
nutrients in farm soil may run off into streams and lakes, depleting nutrients in one area, increasing them in another, and altering chemical cycles in both.
Fertilizer: human activities have more than doubled Earth's supply of fixed nitrogen available to primary producers.
nutrients in farm soil may run off into streams and lakes, depleting nutrients in one area, increasing them in another, and altering chemical cycles in both.
Fertilizer: human activities have more than doubled Earth's supply of fixed nitrogen available to primary producers.
36
New cards
eutrophication of lakes
Nutrient runoff can also lead to the eutrophication of lake
Such conditions threaten the survival of many organisms.
Such conditions threaten the survival of many organisms.
37
New cards
toxis in enviroment
elease an immense variety of toxic chemicals, including thousands of synthetic compounds previously unknown in nature, with little regard for the ecological consequences.
BIO Magnification
BIO Magnification
38
New cards
Biological Magnification
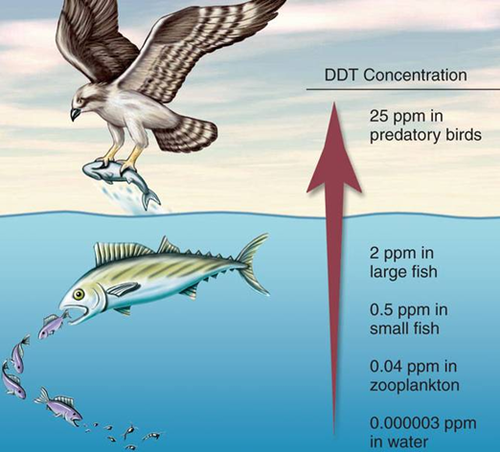
Toxins accumulate so their concentration increases as you go up the food chain
biomass at any given trophic level is produced from a much larger biomass ingested from the level below
top-level carnivores tend to be most severely affected by toxic compounds in the environment.
ex DDT, chemical used to control insects such as mosquitoes and agricultural pests lead to decline in the populations of pelicans, ospreys, and eagles
biomass at any given trophic level is produced from a much larger biomass ingested from the level below
top-level carnivores tend to be most severely affected by toxic compounds in the environment.
ex DDT, chemical used to control insects such as mosquitoes and agricultural pests lead to decline in the populations of pelicans, ospreys, and eagles
39
New cards
climate change
directional change to the global climate that lasts for three decades or more (as opposed to short-term changes in the weather).
40
New cards
Solutions to Address Climate Change
using energy more efficiently and by replacing fossil fuels with renewable solar and wind power. nuclear
reduce deforestation
reduce deforestation
41
New cards
destruction of ozone
42
New cards
sustainability
as a tool to establish long-term conservation priorities.
43
New cards
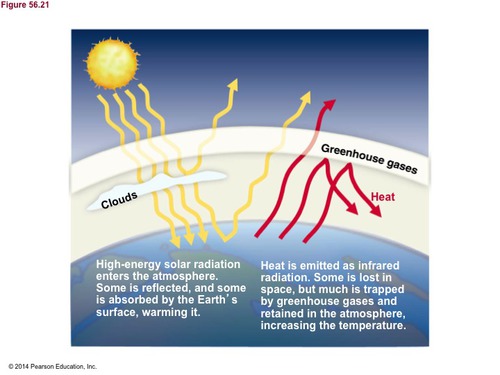
Greenhouse Effect
CO2 and water vapor absorb infrared radiation and reflect it back towards earth
Carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat emitted from Earth's surface and then radiate much of that heat back to Earth.
Carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat emitted from Earth's surface and then radiate much of that heat back to Earth.
44
New cards
Biological Effects of Climate Change
species may not be able to survive the rapid climate change projected to result from global warming.
habitats today are more fragmented
already altered the geographic ranges of hundreds of species leading to declining population sizes and shrinking geographic ranges
far north, most aaffected
habitats today are more fragmented
already altered the geographic ranges of hundreds of species leading to declining population sizes and shrinking geographic ranges
far north, most aaffected
45
New cards
ozone
Life on Earth is protected from the damaging effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation by a layer of ozone located in the stratosphere 17-25 km above Earth's surface.
The destruction of atmospheric ozone results primarily from the accumulation of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), chemicals once widely used in refrigeration and manufacturing.
In the stratosphere, chlorine atoms released from CFCs react with ozone, reducing it to molecular O2- liberate the chlorine, allowing it to react with other ozone molecules in a catalytic chain reaction.
The destruction of atmospheric ozone results primarily from the accumulation of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), chemicals once widely used in refrigeration and manufacturing.
In the stratosphere, chlorine atoms released from CFCs react with ozone, reducing it to molecular O2- liberate the chlorine, allowing it to react with other ozone molecules in a catalytic chain reaction.
46
New cards
Sustainable Development
Economic development that meets the needs of people today without limiting the ability of future generations to meet their needs
develop, manage, and conserve Earth's resources as responsibly as possible.
develop, manage, and conserve Earth's resources as responsibly as possible.