ACCTG 331 Exam 3 Review: Revenue Recognition & Balance Sheet
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Revenues
Inflows enhancing assets or settling liabilities.
Revenue Measurement
Critical for accurate financial reporting.
Control Transfer Indicators
Signs control shifts from seller to customer.
Obligation to Pay
Customer must pay seller for goods/services.
Legal Title
Ownership rights to an asset.
Physical Possession
Customer physically holds the asset.
Risks and Rewards
Customer assumes ownership risks and benefits.
Accepted Asset
Customer acknowledges receipt of the asset.
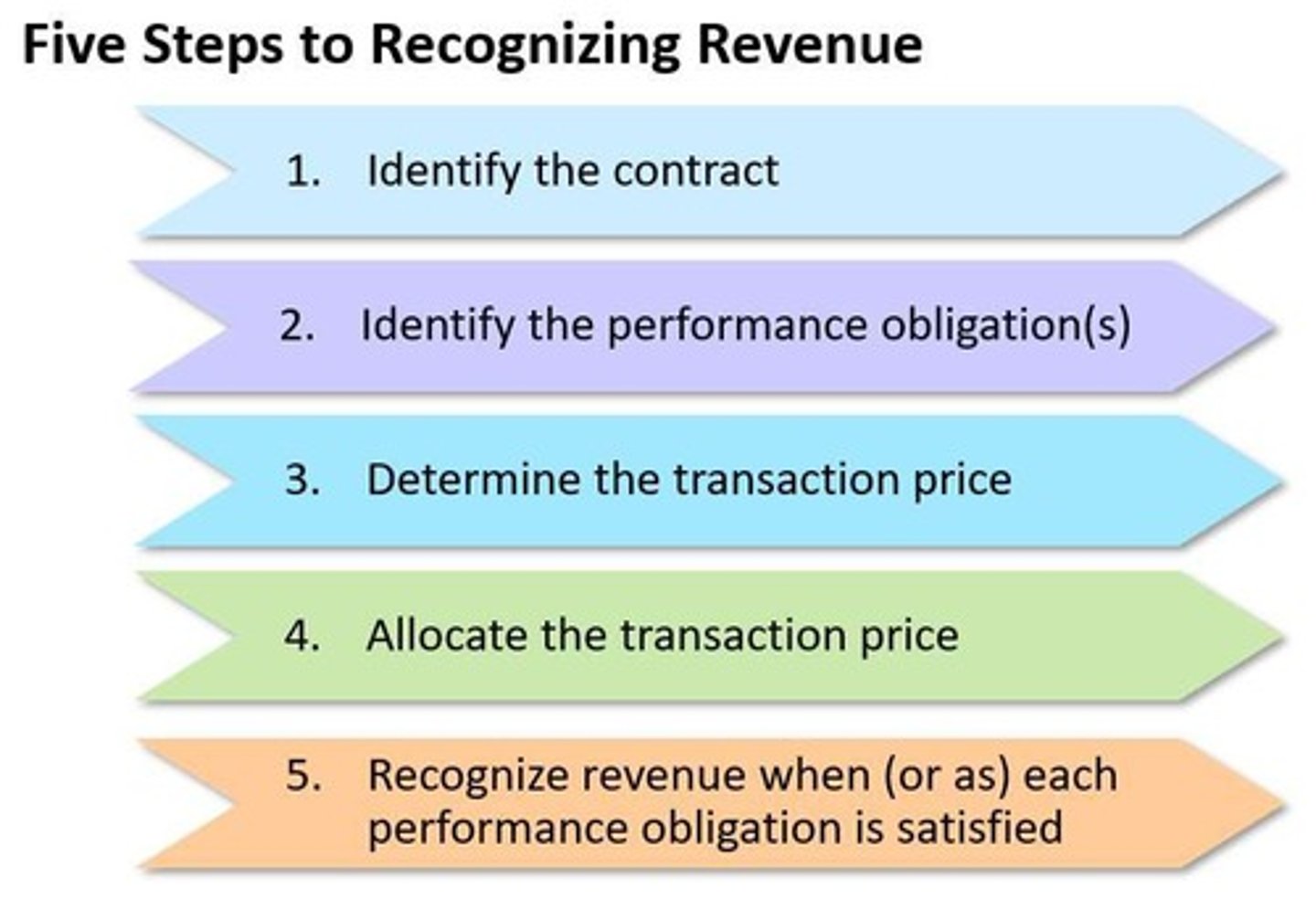
Revenue Recognition Criteria
Conditions for recognizing revenue over time.
Benefit Consumption
Customer uses seller's work as performed.
Asset Control
Customer controls asset during its creation.
No Alternative Use
Seller's asset has no other use.
Progress Payment Rights
Seller entitled to payment for work done.
Performance Obligation Satisfaction
Revenue recognized when obligation is fulfilled.
Output-Based Estimate
Measured by goods/services transferred to date.
Input-Based Estimate
Measured by effort relative to total expected.
Multiple Performance Obligations
Contracts with more than one obligation.
Identify Performance Obligation
Recognizing distinct goods/services in contracts.
Distinct Goods/Services
Capable of being separate and identifiable.
Prepayments
Part of transaction price, not obligations.
Quality-Assurance Warranties
Part of performance obligation for acceptable quality.
Right of Return
Potential failure to satisfy performance obligation.
Extended Warranties
Considered performance obligations in contracts.
Extended Warranty
Warranty purchased separately or beyond quality assurance.
Material Right
Customer receives something not otherwise available.
Transaction Price
Total amount seller expects to receive.
Variable Consideration
Price depends on future event outcomes.
Right of Return
Sales allowing customers to return products.
Principal vs Agent
Determines seller's role in transaction.
Time Value of Money
Value of money changes over time.
Seller Payments to Customer
Incentives or discounts provided to customers.
Adjusted Market Assessment Approach
Price based on market sale conditions.
Expected Cost Plus Margin Approach
Cost estimation plus profit margin added.
Residual Approach
Total price minus known selling prices.
Performance Obligation
Promise to transfer goods or services.
Revenue Recognition Timing
When revenue is recognized for obligations.
Franchise Arrangement
Franchisor grants rights to franchisee for products.
Intellectual Property License
Rights to use franchisor's intellectual property.
Long-Term Contracts
Contracts spanning multiple accounting periods.
Single Performance Obligation
Single promise in long-term contracts.
Revenue Over Time
Recognizing revenue as progress is made.
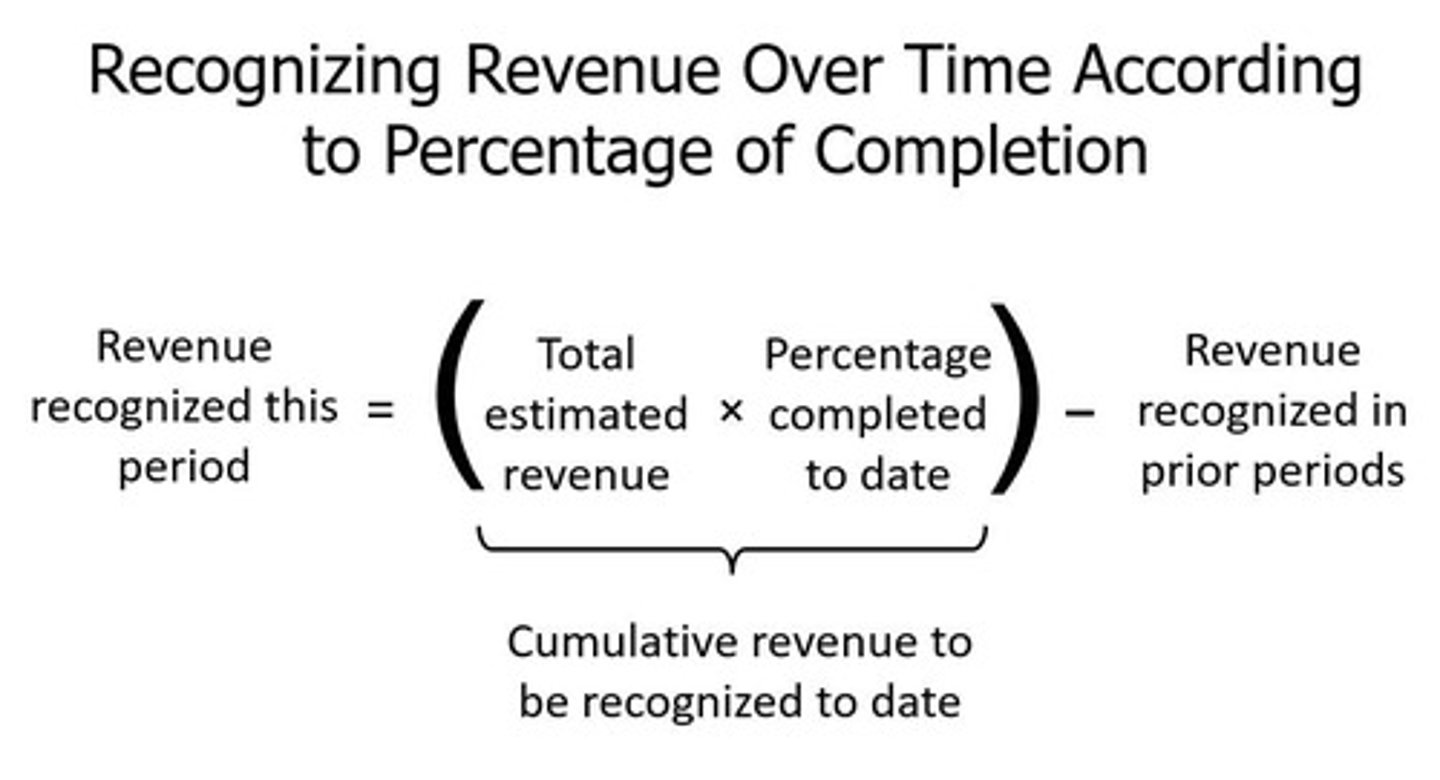
Contract Completion Revenue
Revenue recognized upon finishing the contract.
Construction Billings
Total billed amount for construction services.
Accounts Receivable
Money owed to a company for services.
Cash Collected
Total cash received from customers.
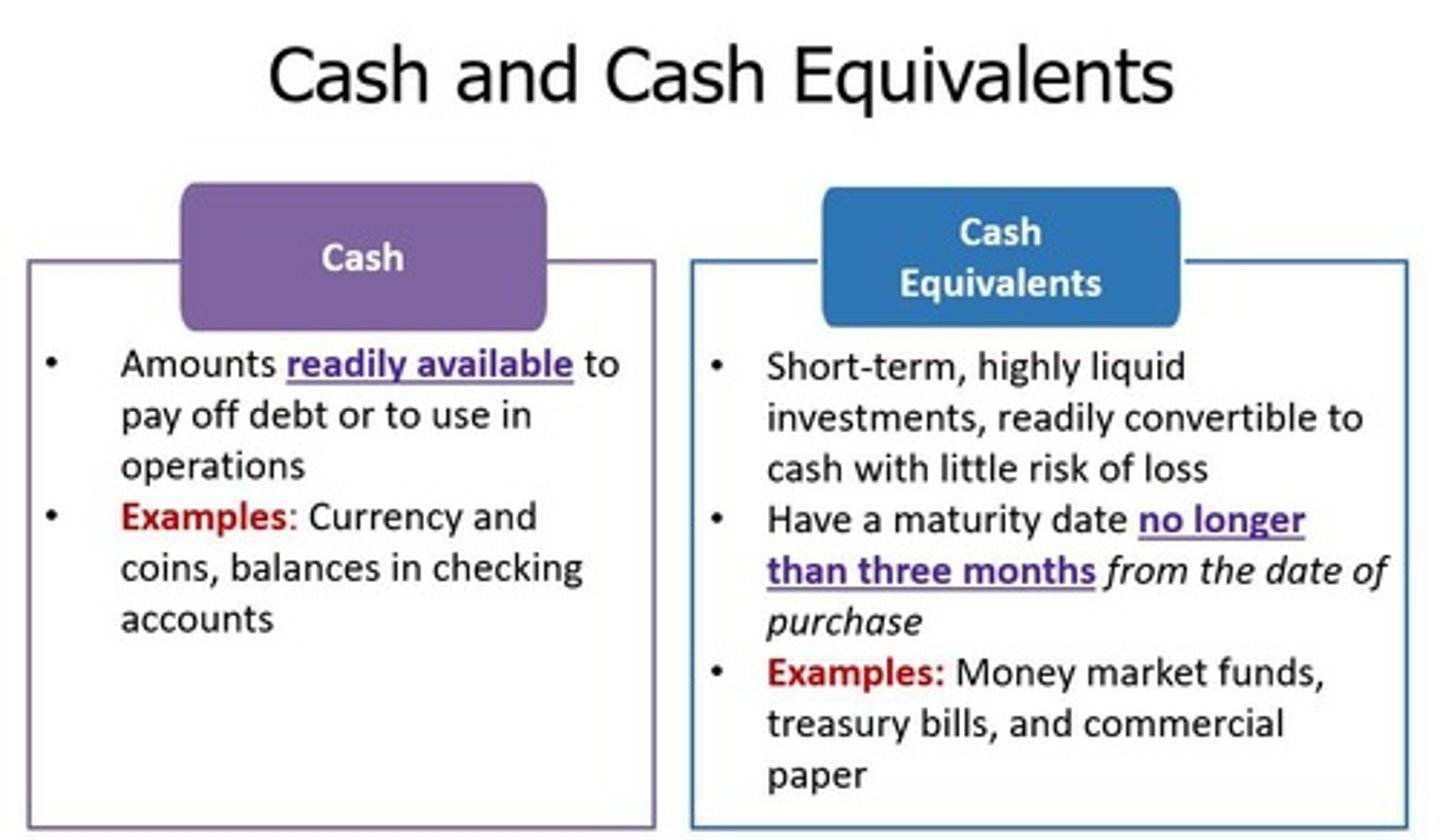
Restricted Cash
Cash not available for current use.
Debt Instruments
Require borrower to set aside funds.
Compensating Balance
Amount maintaining a minimum balance for loans.
Cash Equivalents
Highly liquid investments easily convertible to cash.
Accounts Receivable
Revenue recognized from credit sales.
Performance Obligation
Condition satisfied when delivery occurs.
Initial Valuation
Revenue equals amount entitled upon performance satisfaction.
Transaction Price Allocation
Distributing price among performance obligations in contracts.
Gross Method
Records sales at full price, adjusts for discounts.
Net Method
Records sales net of discounts, adjusts for forfeits.
Sales Returns
Merchandise returned for refund or credit.
Sales Allowance
Price reduction incentive to avoid returns.
Accrual of Returns
Recognize returns at sale to avoid income distortion.
Credit Losses
Inherent costs of granting credit, often termed bad debts.
Subsequent Valuation
Assessing collectability of accounts receivable post-sale.
Noncurrent Restricted Cash
Restricted cash linked to noncurrent debt obligations.
Current Restricted Cash
Restricted cash linked to current debt obligations.
Effective Interest Rate
Actual interest cost higher than stated rate.
Low Interest Account
Account with minimal or no interest for balances.
Sales Discounts
Reductions in sales price for early payment.

Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Estimate of uncollectible accounts receivable.
Direct Write-Off Method
Writes off bad debts when deemed uncollectible.
Allowance Method
Estimates bad debts and reduces receivables accordingly.
GAAP
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles for financial reporting.
Contra-Asset Account
Account reducing the carrying value of assets.
Bad Debt Expense
Recognized when estimating uncollectible accounts, not when written off.
Uncollectible Accounts
Accounts deemed unlikely to be collected.
Income Tax Purposes
Direct Write-Off Method is required for tax reporting.
Accounts Receivable
Money owed to a company by customers.
Balance Sheet
Financial statement showing assets, liabilities, and equity.
Carrying Value
Net amount at which an asset is recognized.
Discount on Note Receivable
Future interest revenue deducted from face value.
Short-Term Notes
Notes due within one year, often noninterest-bearing.
Face Amount
The nominal value of a note or bond.
Material Bad Debts
Significant amounts requiring estimation under GAAP.
Recognition of Bad Debt
Acknowledgment of potential losses before actual write-off.
Write-Off
Removal of an uncollectible account from records.
Future Interest Revenue
Interest expected to be earned over time.
Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts
Contra-asset account estimating future bad debts.
Balance Sheet Approach
Method for estimating allowance based on aging accounts.
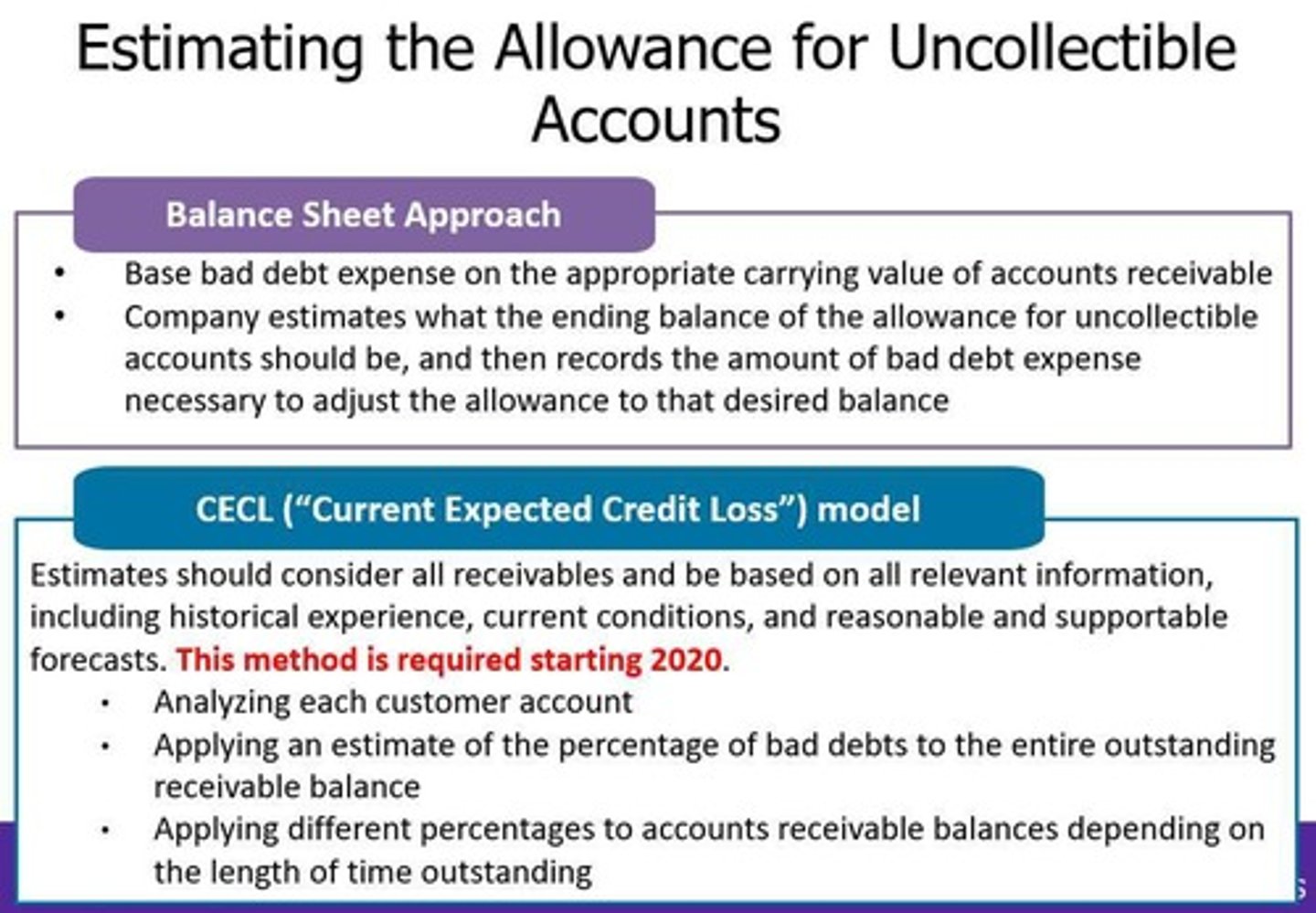
Aging Information
Analysis of accounts receivable by the length of time outstanding.