Week 8 Online Homework
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
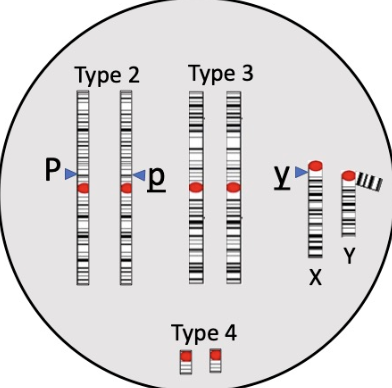
Which of the following shows the full karyotype in the G1-phase of a male individual who is heterozygous for the gene purple (P) located on autosome 2, and who shows yellow body color phenotype associated with a recessive allele of the X-linked gene (Y)?
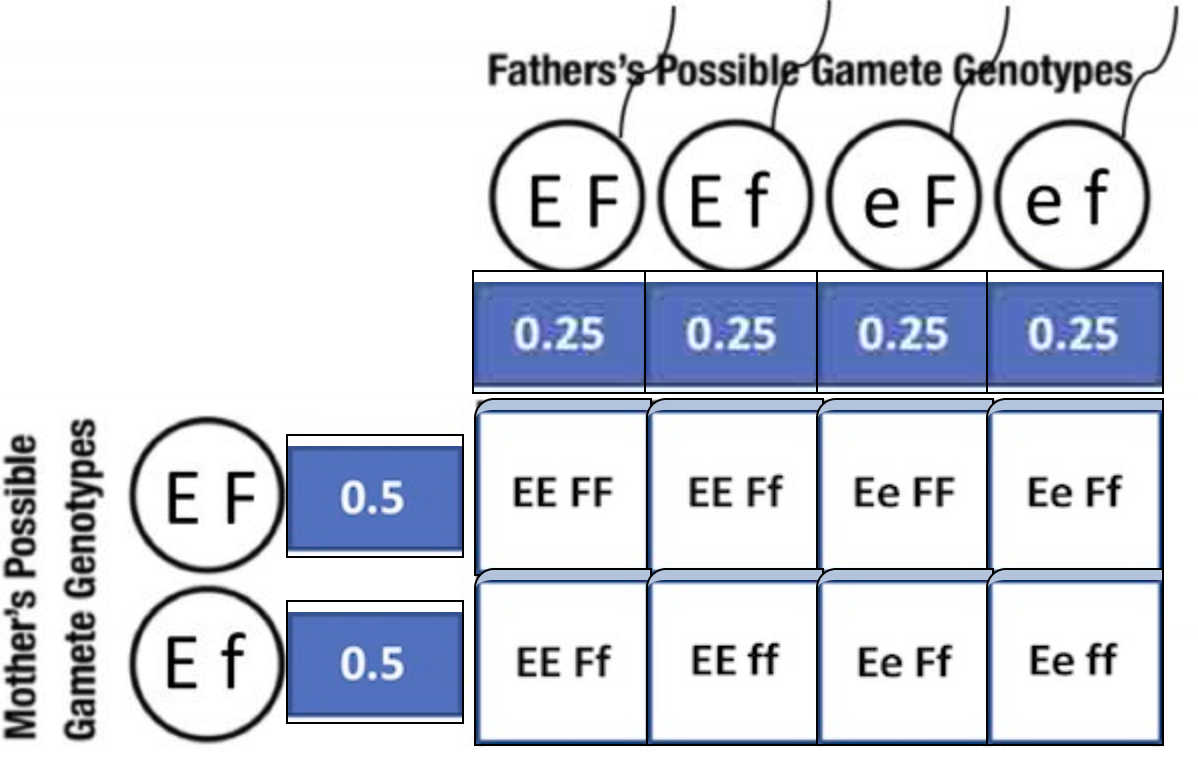
Fill in the gamete genotype probabilities and offspring genotypes to complete Jessica and Tom's Punnett square
Which of the following statements is/are correct statements about a Punnett Square?
It represents all the possible combinations of gamete genotypes between two individuals.
It is a model for the process of fertilization.
It is a combinatorial probability table that allows you to calculate the probabilities of genotypes and phenotypes produced in a genetic cross.
1) Probability first child is colorblind if it is a boy?
2) Probability first child is colorblind if it is a girl?
3) Probability of a colorblind son if the trait is autosomal recessive on chromosome 7?
1/2
1/2
1/4
What is the genotype of your brown long-haired guinea pig parent?
FF Bb
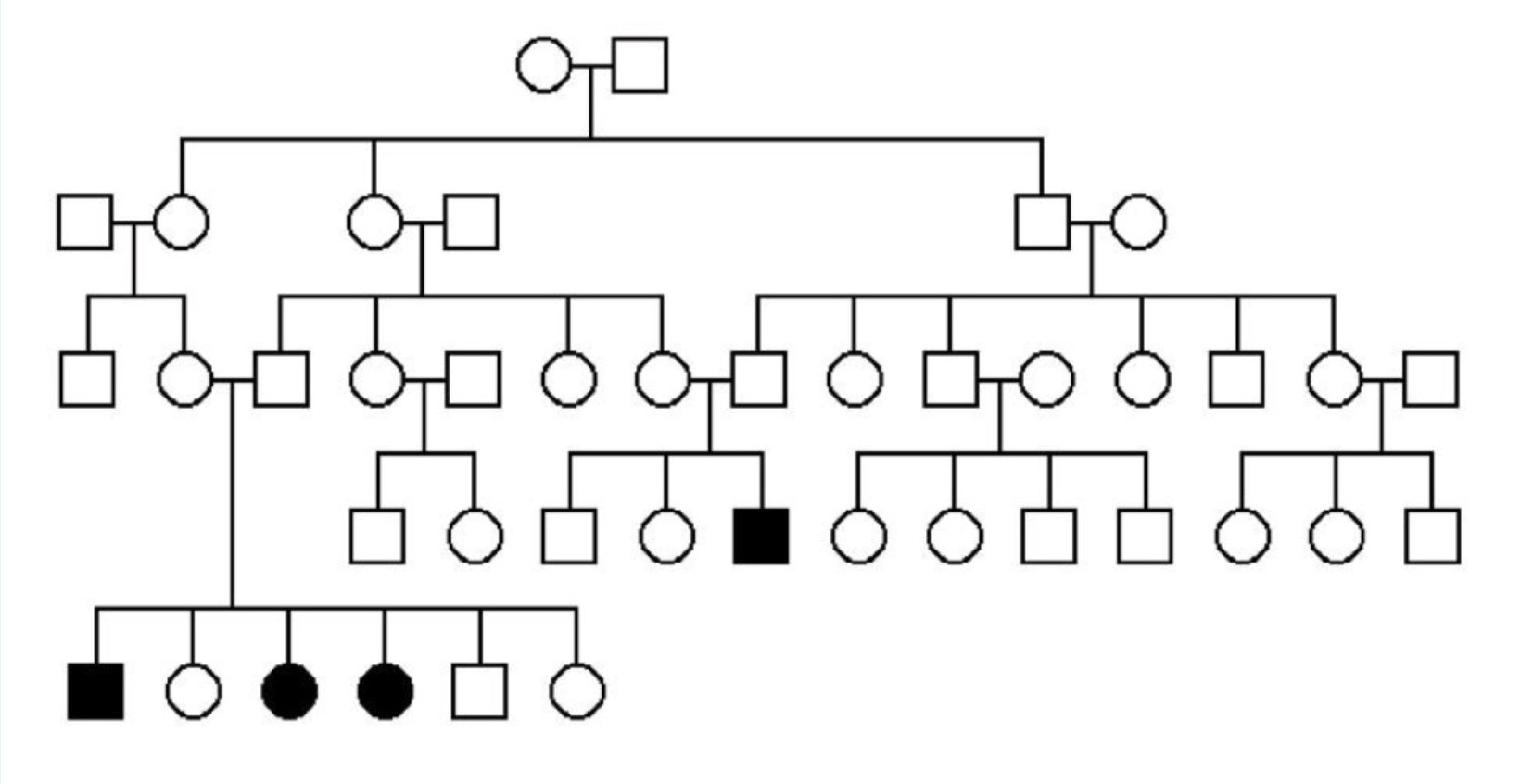
1. Based on the pattern, albinism is what kind of trait?
2. What is the strongest evidence?
autosomal recessive trait
the two females with albinism would not be possible if the trait were X-linked
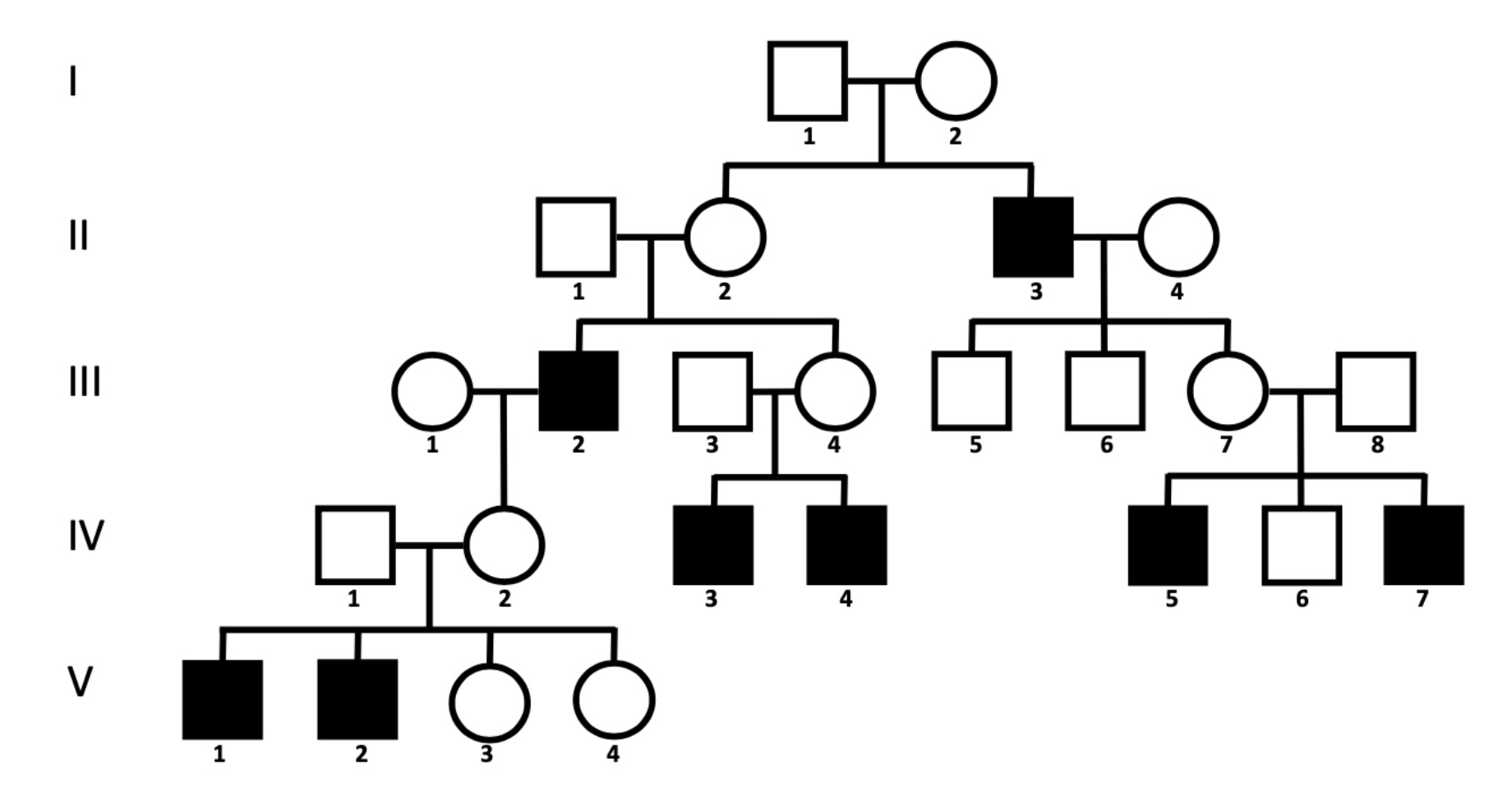
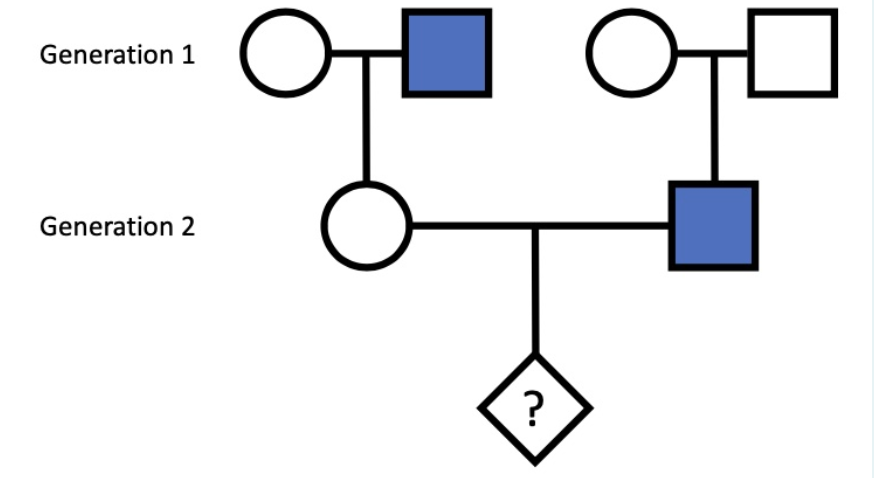
Based on this pedigree, what is the most likely mode of inheritance for this condition?
X-Linked Recessive
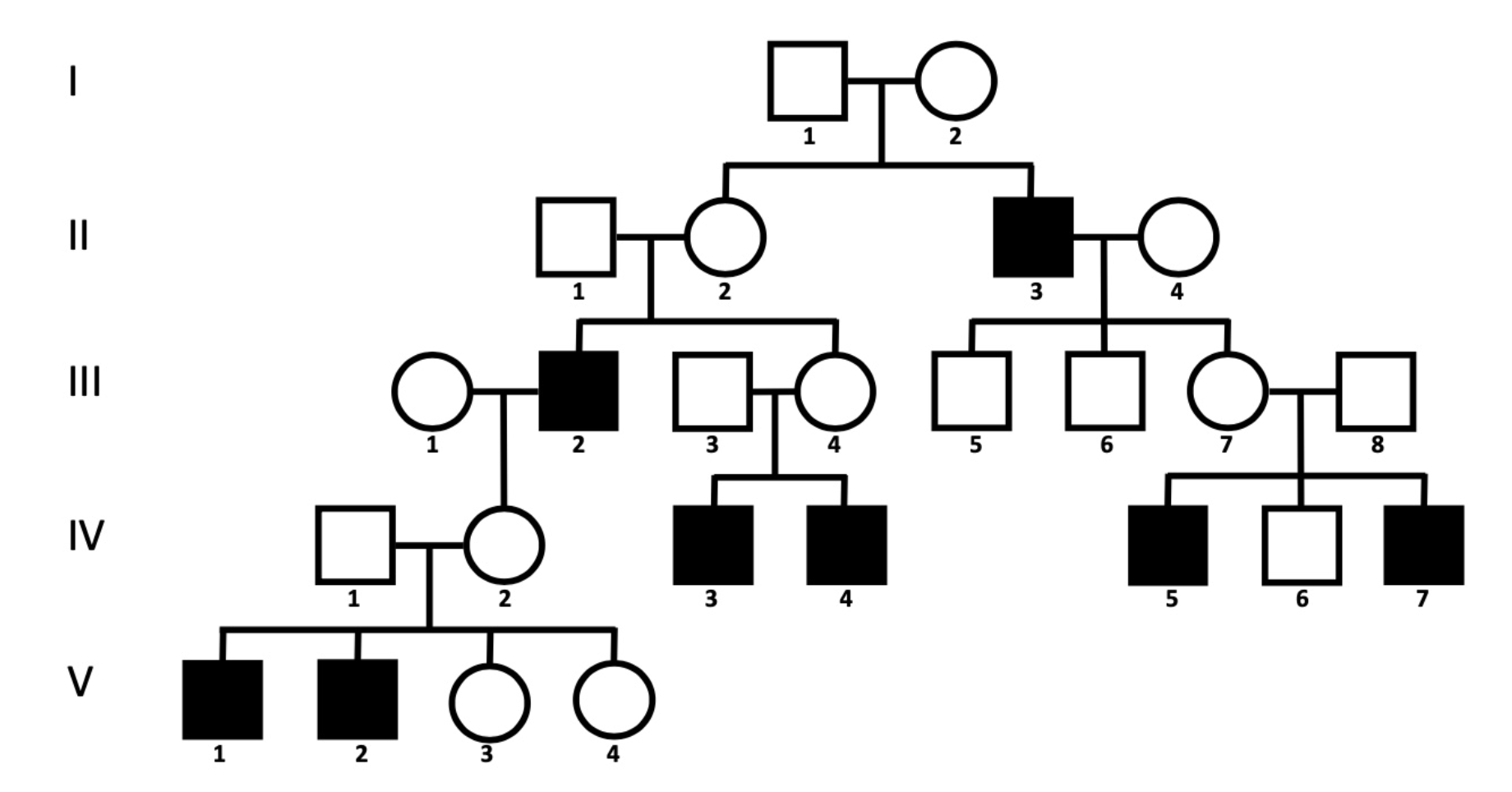
Identify the genotype of individuals in generations I and II:
Individual I-1: X(A) Y
Individual I-2: X(A) X(a)
Individual II-1: X(A) Y
Individual II-2: X(A) X(a)
Individual II-3: X(a) Y
Individual II-4: X(A) X_
What is the most likely genotype of the individual you could not fully determine in question 2 (II-4)?
X(A) X(A)
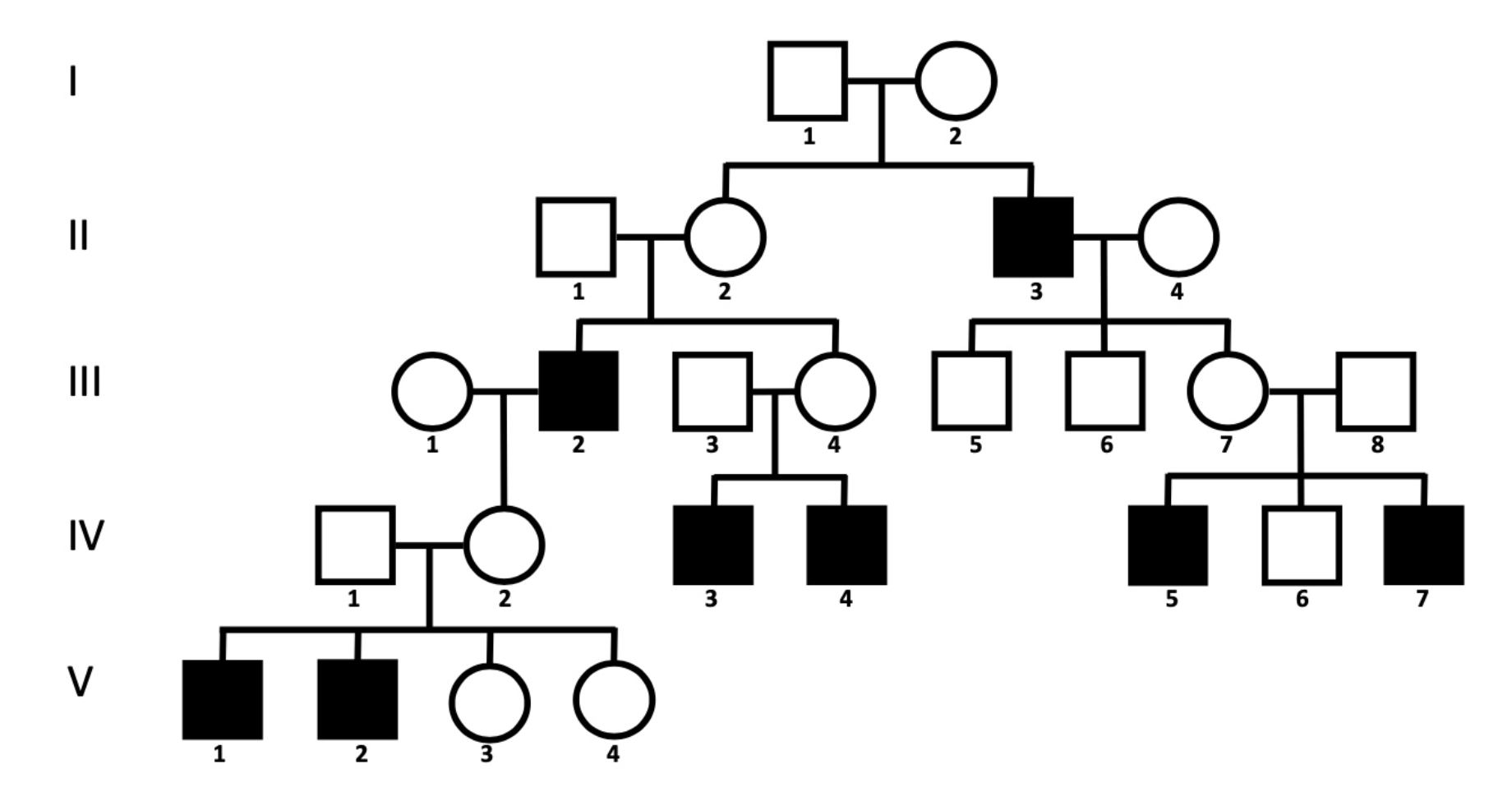
4.
a) If couple III-7 and III-8 have another child, what is the probability that a child of any sex will have missing teeth?
b) What is the probability of missing teeth if the child is female?
0.25
0
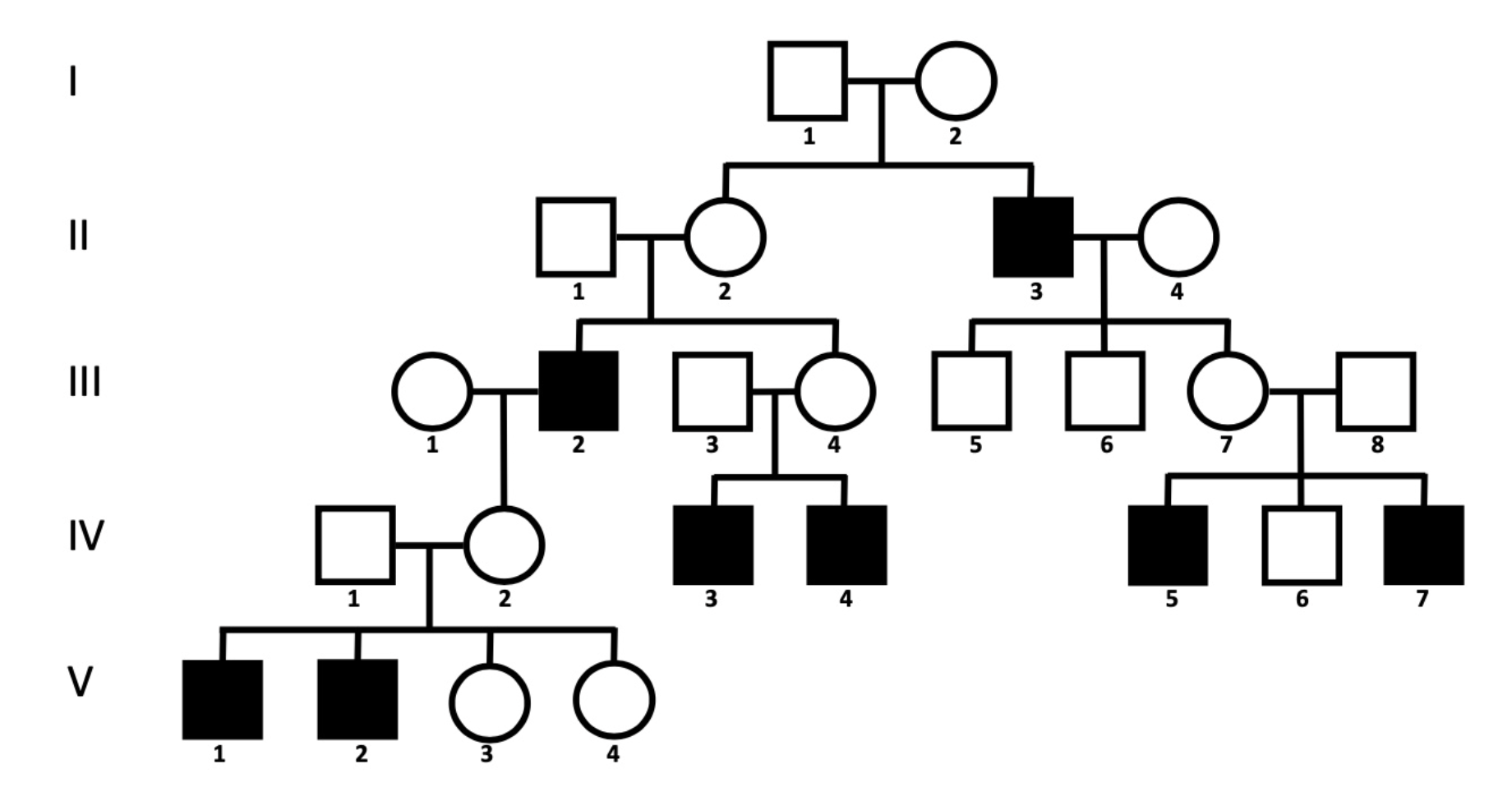
Is the probability of having missing teeth higher for male than female children if the individuals III-2 and III-7 were to have offspring?
No
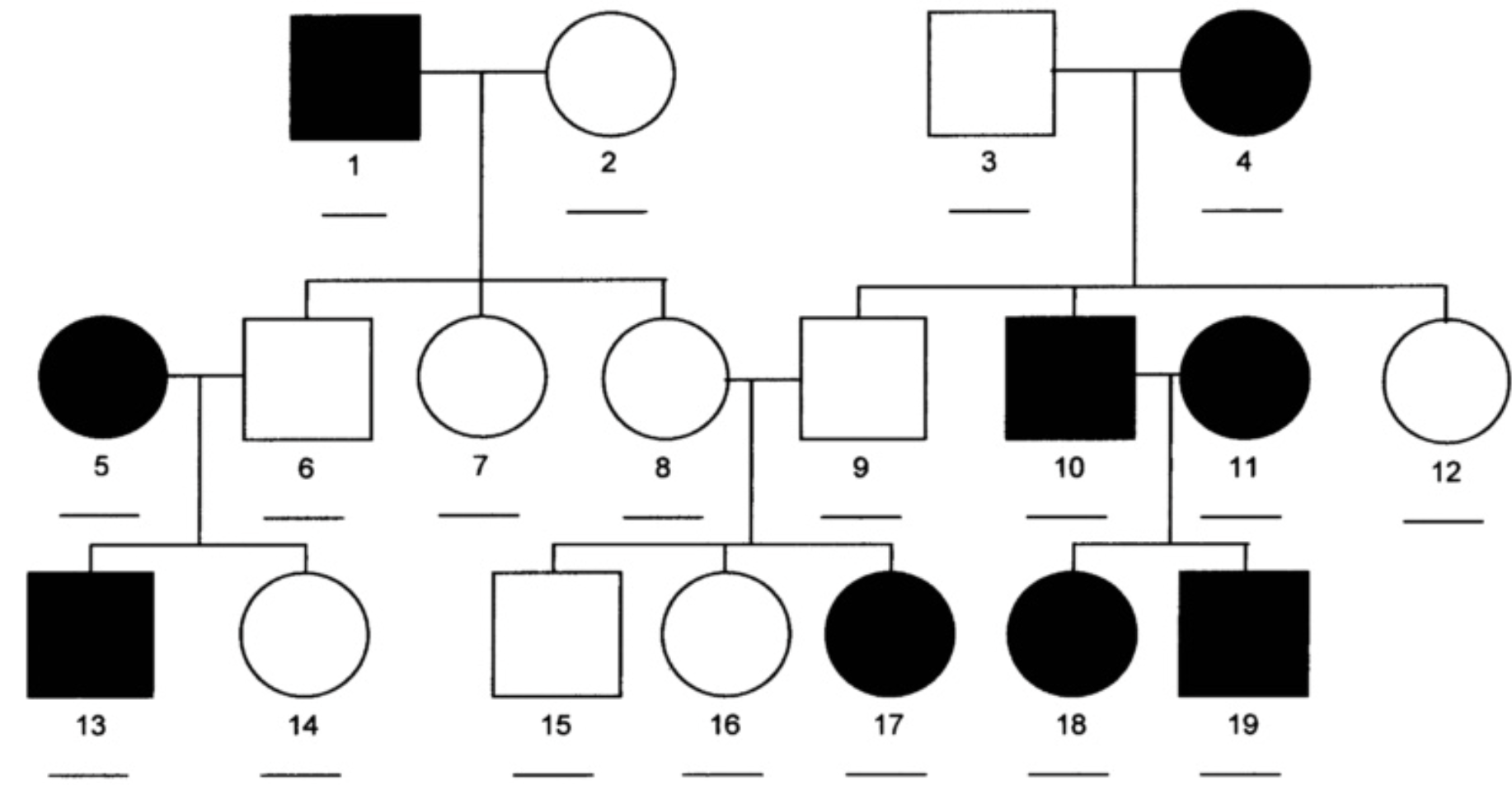
Based on the second pedigree, the gene associated with hypodontia in this second family likely _____ the same gene as in the family shown in the first pedigree, because the trait in the second family is _____, indicating that hypodontia is a/an _____ phenotypic trait.
is not, autosomal recessive, polygenic
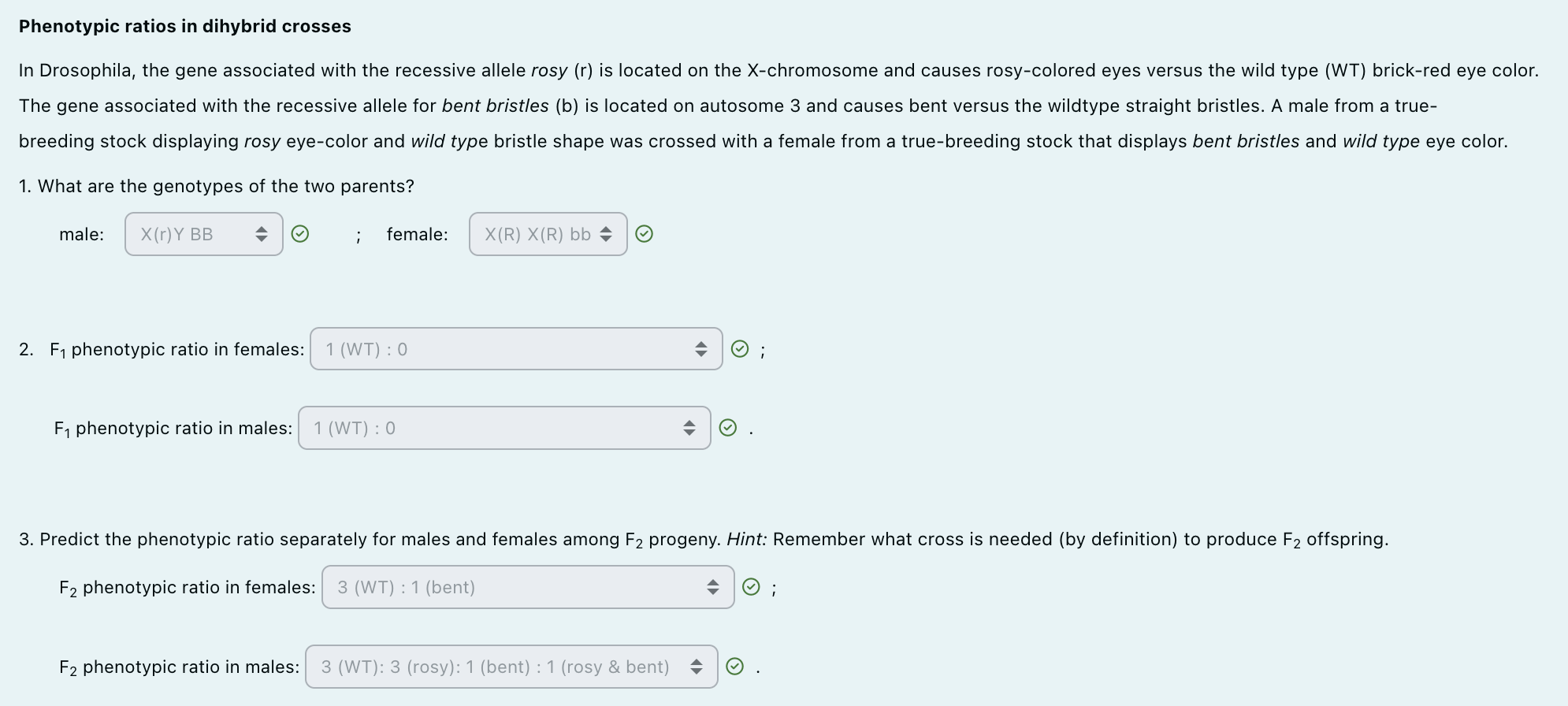
In Drosophila, the gene associated with the recessive allele rosy (r) is located on the X-chromosome (X-linked) and causes rosy eyes. The gene associated with the recessive allele for bent bristles (b) is located on autosome 3 (autosomal). A true-breeding male with rosy eyes and wild-type (WT) bristles is crossed with a true-breeding female with bent bristles and WT eyes.
The rare mutant allele associated with the rod-like eye phenotype is:
dominant
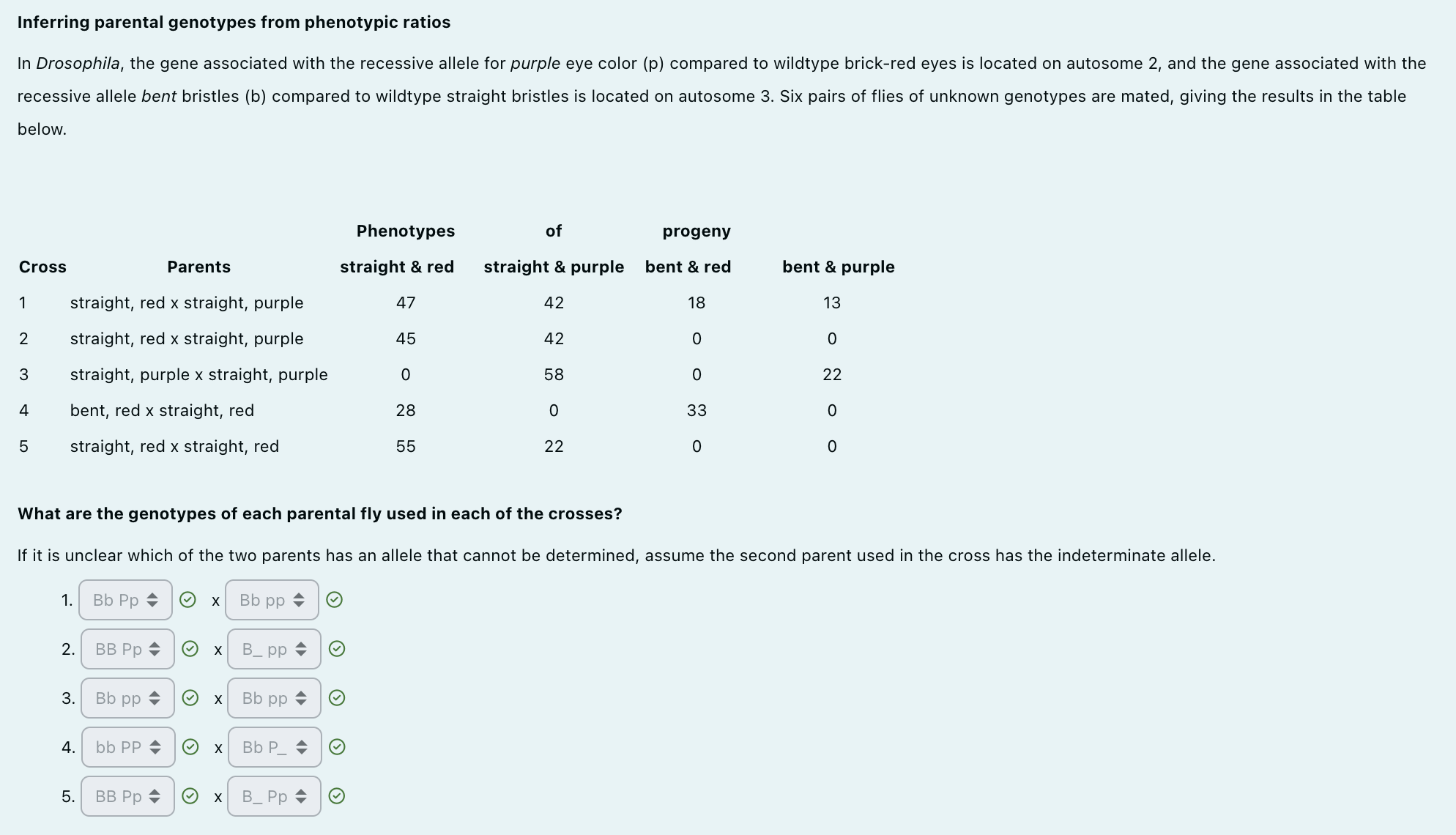
In Drosophila, purple eye color (p) is an autosomal recessive trait on chromosome 2, and bent bristles (b) is an autosomal recessive trait on chromosome 3. The dominant alleles are wildtype red eyes (P) and straight bristles (B).
What are the genotypes of the cross you set up?
male: Ee ff
female: Ee Ff
What is the phenotypic ratio expected among dozens of offspring from the cross in Question 11?
3:3:1:1