covalent bonding UPDATED
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
covalent bond
a strong electrostatic attraction between the negatively charged shared electrons and the positive nuclei
how do you know what bonds with what in order to make dot and cross diagrams
- look at the charge on each ion
- this tells you about how many bonds it can form (each shared electron is a covalent bond)
- then you can work it out from there)
in ammonia (NH3) what bonds to what
each hydrogen bonds to the nitrogen
in water what bonds to what
each hydrogen bonds to the oxygen
in carbon dioxide what bonds to what
each oxygen bonds to the carbon
in methane what bonds to what
each hydrogen bonds to the carbon
in ethane what bonds to what
all hydrogens bond to a carbon and carbons bond to each other
in chloromethane what bonds to what
all hydrogens bond to carbon and chlorine bonds to carbon
in ethene what bonds to what
carbons bond to each other and all hydrogens bond to a carbon
what structures are there for covalent bonding
- simple molecular structures
- giant covalent structures
why do simple molecular structures have low bpt and mpt
- atoms within molecule held together by very strong covalent bonds
- however intermolecular forces between molecules are very weak
- little energy needed to overcome weak intermolecular forces
- therefore low bpt and mpt
why do the mpt and bpt of substances with simple molecular structures increase as relative molecular mass (Mr) increases
- intermolecular forces are stronger between molecules with higher Mr
- this is bc there are more points along larger molecules for intermolecular forces to act
- so more energy needed to break the forces
- mpt and bpt increase
what physical state are most simple molecular substances
usually gases, liquids or easily melted solids at room temp
which do giant covalent structure have very high bpt and mpts
- all the atoms are bonded to each other by strong covalent bonds
- there are lots of these bonds
- this means lots of energy is needed to break them
- therefore very high mpt and bpts
can giant covalent structures conduct electricity
no charged particles so generally cannot conduct electricity
are giant covalent structures soluble or insoluble in water
usually insoluble in water
can simple molecular structures conduct electricity
- no overall charge or charged particles
- cannot conduct electricity
2 examples of giant covalent structures
- diamond
- graphite
why does diamond have a high mpt/bpt
- made up of carbon atoms that each form 4 covalent bonds
- these covalent bonds are strong and take lots of energy to overcome
- high mpt/bpt
why is diamond hard
- strong covalent bonds hold the atoms in a very rigid lattice structure
- so it is really hard
electrical conductivity of diamond
- does not conduct electricity
- no charged particles that are free to move
examples of charged particles
electrons or ions
why is graphite soft and slippery
- each carbon atom only forms 3 covalent bonds
- this creates layers of carbon atoms
- the layers are only held together weak forces
- this means they can slide over each other
- this makes graphite soft and slippery
why does graphite have a high bpt/mpt
- the covalent bonds in the layers are strong
- they require lots of energy to break
why can graphite conduct electricity
- carbon only makes 3 bonds instead of 4
- this means that only 3 of carbons outer electrons are used in bonds
- so each carbon atom has one delocalised electron
- this is charged and is free to move
example of simple molecular structure
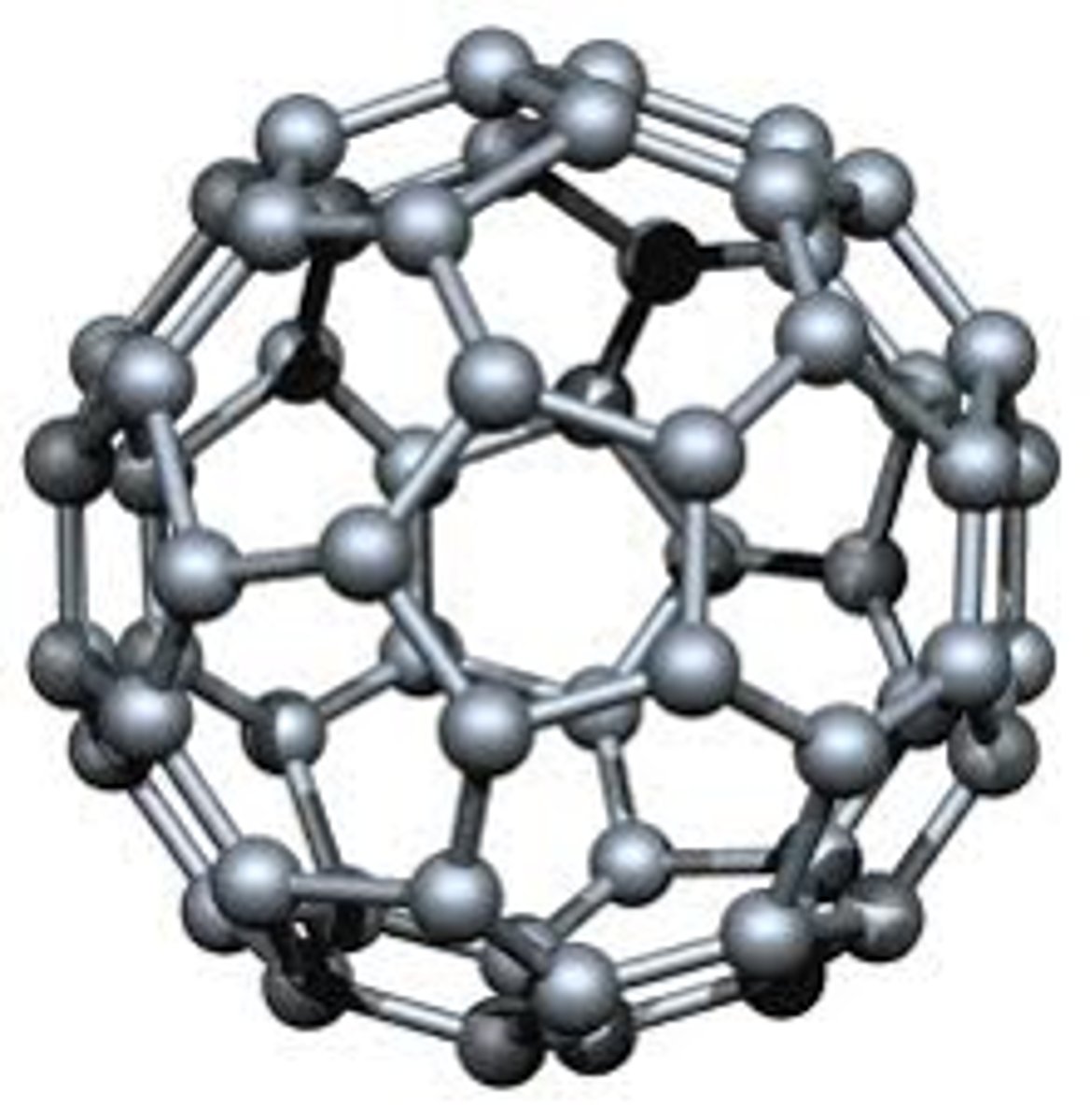
C60 fullerene
what are C60 fullerene molecules
hollow spheres made up of 60 carbon atoms
why is C60 fullerene soft
- molecules only held together by weak intermolecular forces
- so they can slide over each other
- this means the material is soft
why is C60 fullerene a poor electrical conductor
- it does have charged particles (each carbon forms only 3 bonds, so each carbon has 1 delocalised electron)
- but the electrons can't move between molecules
- so C60 fullerene is a poor electrical conductor
what is the name for C60 fullerene
buckminsterfullerene
what is the bpt/mpt of C60 fullerene like and why
- low mpt/bpt
- bc weak intermolecular forces between the C60 molecules
- and little energy needed to overcome these
what does diamond look like
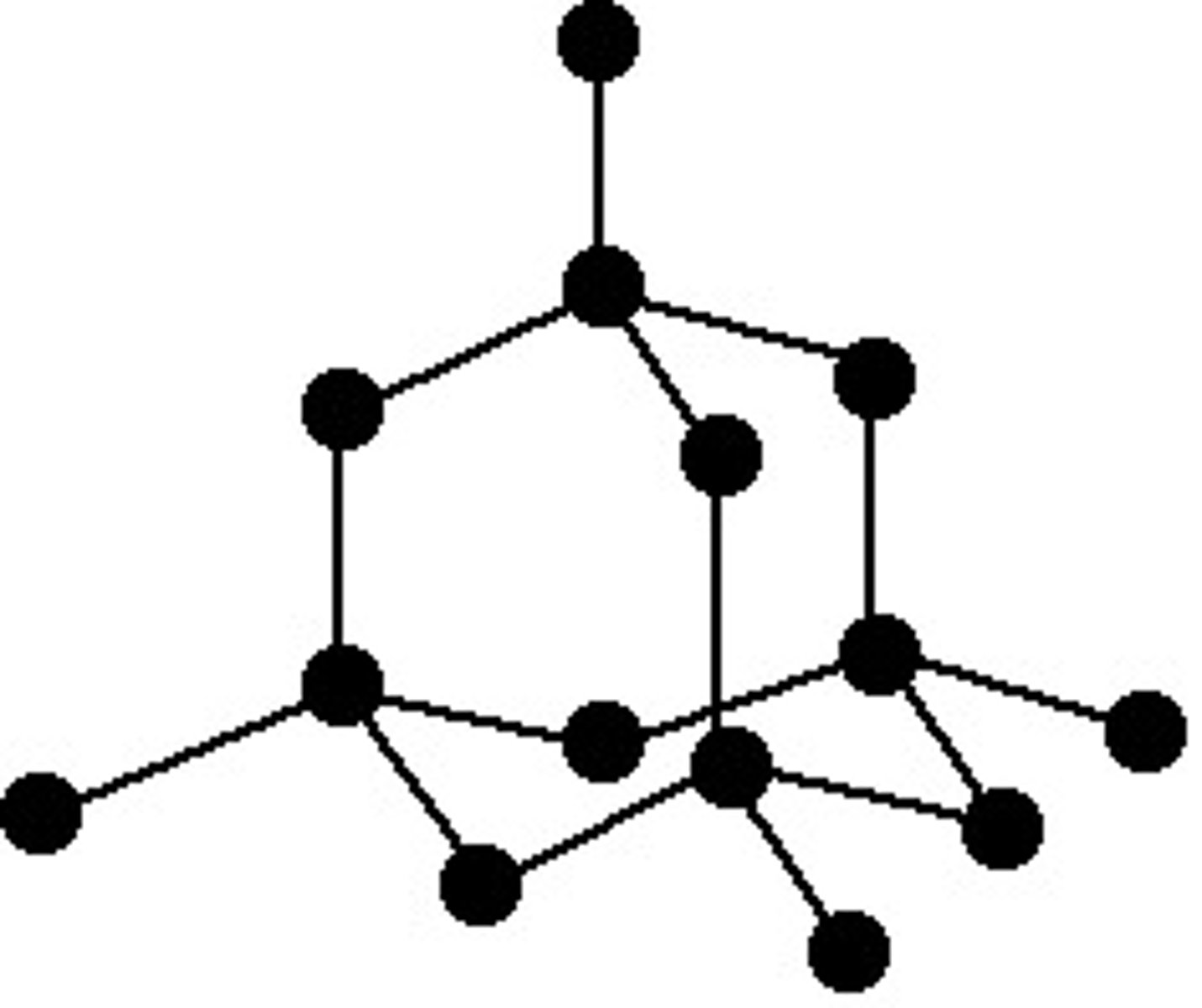
what does graphite look like
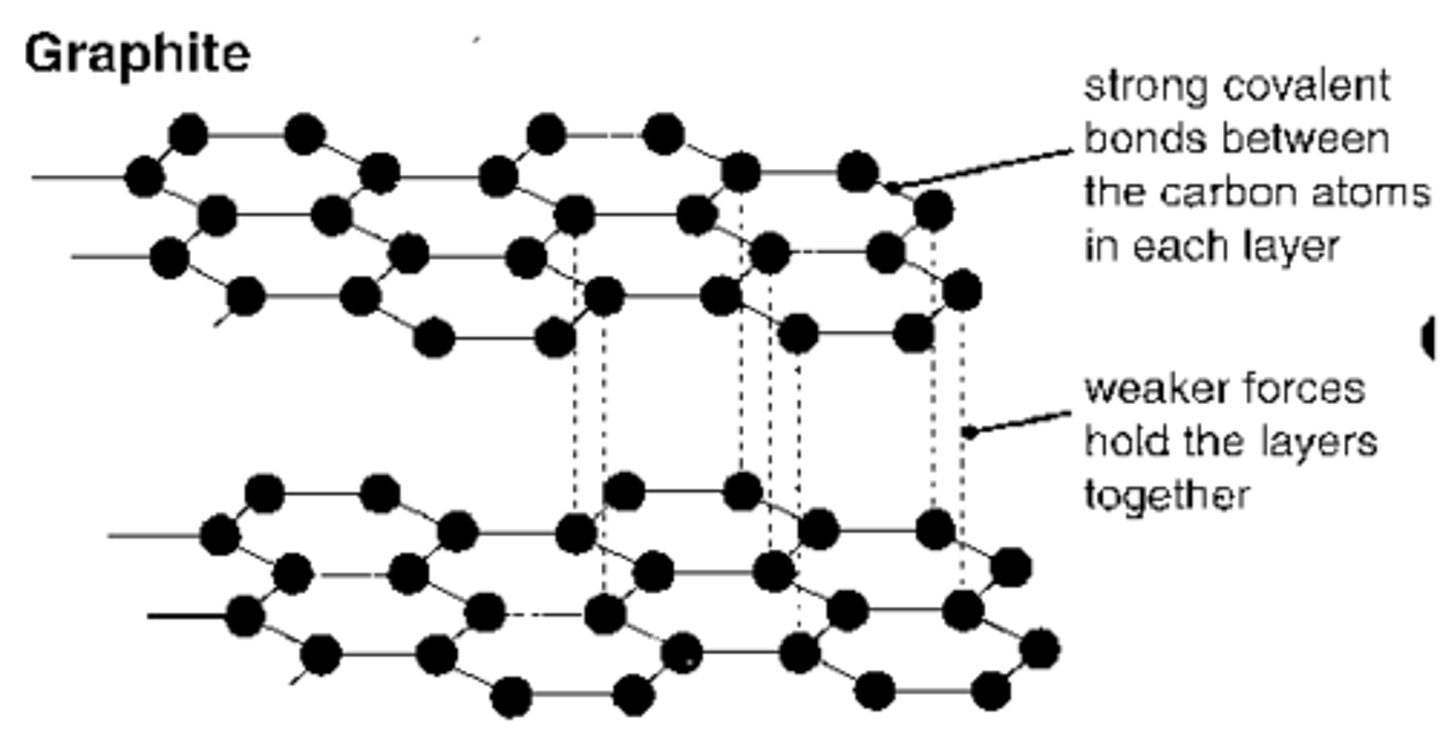
what does C60 fullerene look like
do covalent compounds usually conduct electricity
no