3.6 Human Evolution
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Biological evoluation
The changes in genetic informaton through the transfer of DNA from one generation to the next.
Occuts slowly compared to cultural
Scapula
A and H both have scapula on the back and side of the rib cage
H scapula is further back with different angles becuase hanging not required
Allows better throwing power and accuracy, reduces upper body mass, keeps COG over base support
Hunting advantage, more effiect, surival, repro
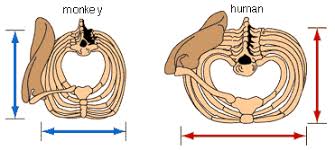
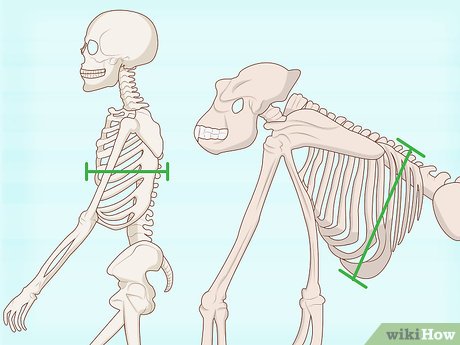
Rib cage
A barrel shaped extended outward (deeper)
H flatter and broader
Allows skull and upper body mass carried directly above hip joints, COG over base support, balance (bipedalism)
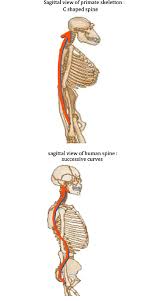
Spine
A c shape
H s shape
Allows skull and upper body mass carried directly above hip joints, COG over base support, balance (bipedalism) and efficicency walking on two legs
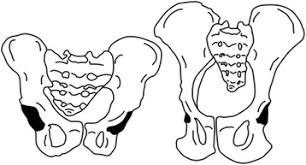
Pelvis
A longer narrower
H shorter wider (bowl shape)
Allows better support of mass over COG, balance (bipedalism), support upright structure and leg movement
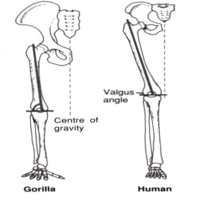
Femur / legs
Valgus angle
A short femurs, little to no valgus angle
H long femur, increased valgus angle
Increased stride length, brings knee under pelvis, COG support directly above knee, balance (bipedalism)
Arms
A longer arms
H shorter arms
The shift to bipedalism, no longer need long arms for climbing
Tool use
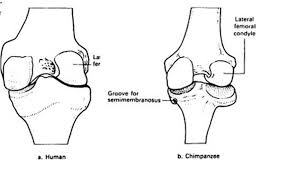
Knee joint
A smaller knee joint, less lateral buttressing
H larger knee joint, more laternal buttressing
Prevents lateral movement of joints when load increases during bipedalism
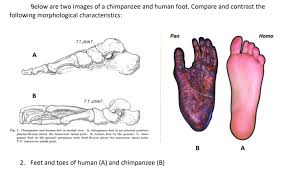
Feet
Arch
Big toe
A feet on outer side of pelvis, no arch, opposed big toe
H feet directly under pelvis, arch, foward facing big toe
Feet under spine for COG support and balance of weight transfer when walking
Arch acts as shock absorber for weight transfer
Big toe in line improves weight transfer, heel to toe, thrust off big toe
(bipedalism)
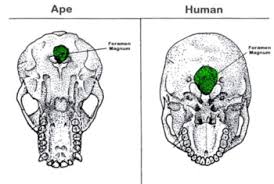
Foramen magnum
A towards back of skull
H center of skull
Allows Hs heaveir skull to balance ontop of spine, less muscle and energy required to keep up and face eyes foward
(bipedalism)
Bipedalism
“This resulted in improved efficiency (bipedalism) of walking on two legs, and so able to save energy which can be used for other things such as getting resources, brain growth, reproduction. Therefore, increasing survival chances and reprouctive sucess, allowing the ability to pass on faveourable alleles more often sucessfully and this increasing the sucess of the species”
Bipedalism advantages
LTGHT
Efficent locomotion - homins can walk further in search for food/water
Thermoregulate - less exposure of body to sunlight, boday stays cooler in hot African Savannah
See over gress - upright position spot prey/predators
Free hands - carry resources/tools/weponds (save energy spent making)
Tools/weponds - upright stance weilding stick and throwing stones (hunter gatherers)
More likey to survive, life process carried out, reprodue, passing on bipedal alleles to next generation, increases in frequency in population over time
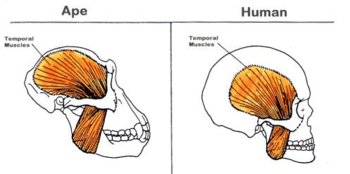
Jaw muscles
A larger
H reduced
A change from tough plant based diet to a softer protien diet with more energy and nutrients meant large jaw muscles were not selected for since forces of chewing now necessary
Energy can be used on other things such as growth, reproduction, gathering resources
Teeth
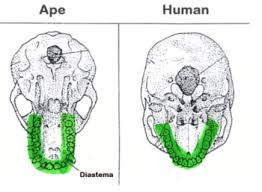
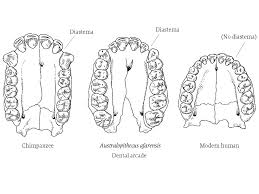
A larger canines and molars, u-shaped dental arcade, and a diastema (gap)
H smaller teeth, v-shaped dental arcade, no diastema (gap)
A change in diet…… smaller jaw size, selected for smaller teeth and v-shaped dental arcade because helped with processing cooked food.
Large canines not required for threat displays and sexual dimorphism
Smaller jaw = no diastema
Energy can be used on other things such as growth, reproduction, gathering resources
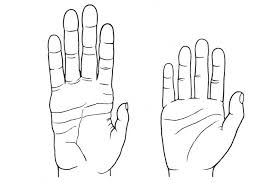
Hand - fingers and tumbs
Occured after bipedalism when hands were free to evolve
A long curved fingers, shorter thumb = POWER GRIP
H shorter straighter fingers, long opposable thumbs = PERCISSION
Power grip
the abiliy to have a clap-like formation around an object
the fingers and palm are particularly fixed
pressure is applied by the thumb
grip allows more force to grasp bra
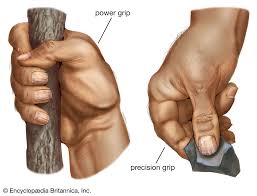
ches
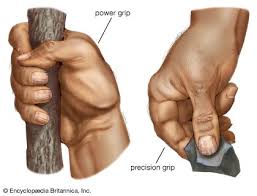
Percision grip
the ability to preform fine manipulative movements
opposable thumbs and fingers allowed accuracy
more specilised tools
greater access to protien rich diet providing energy and nutrients
brain development (e.g. increased cerebelum for fine motor control)
(e.g. later homins able to develop and use tools becuase has more active strike)
Change in enviroment on bipedalism and hand evoluation
africa 6mya climate became warmer and dryer
forests receding to scattered wooded savanah
more open habbitats, food resources become dispersed
reduced need for branchiation, selected for locomotion (bipedalism)
hands no longer needed to support weight, free to make/use tools/weponds
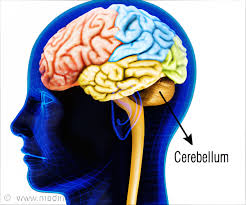
Cerebellum
A small
H highly developed
Change in diet…. energy for brain development, and upright (bipedalism) increased cerebellum size
Fine motor skills, balance, and manipulative momements
Tool development and easier access to food = more brain growth = increased survival
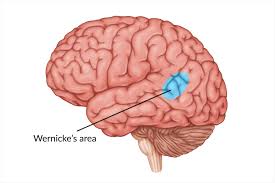
Wernickes area
Developed in H brains
Change in die = energy = brain development AND increased group living selecting for communicaiton
The understanding and comprehension of spoken language
Improved comms, teaching and learning, cooperation, tool development, improved hunter gatherer
survival, repro sucess, passing on fave alleles, species sucess
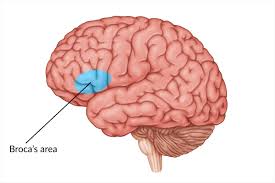
Brocas area
Developed in H habilis brains
Change in die = energy = brain development AND increased group living selecting for communicaiton
Language processing, speech production, comprehension
Improved comms, teaching and learning, cooperation, tool development, improved hunter gatherer
survival, repro sucess, passing on fave alleles, species sucess
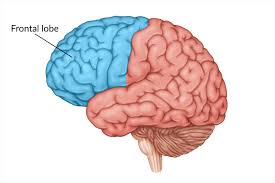
Frontal lobe
Abstract thought, foward planning, imagination, inovation, social control
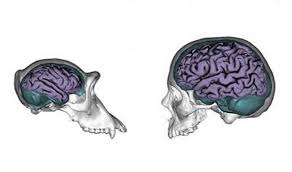
Cranical capacity / expansion
A 400-500 CC
H 1350 CC
A change in diet = energy for brain development and growth
Free manipulative ability, free hands, social groups, co-op selected for bigger brain with more folding (especially in frontal lobe)
Englarged brain = increased abstract thought, thinking, planning = better resource gathering / tools / hunting = better survival
Multi regional theory
Suggests that H.erectus migrated out of Africa 1.5mya and evolved into H.sapiens simaltaneously in Africa, Europe, Asaia through constant gene flow of neighbouring populations
Multi regional evdience
Fossil
Transitional fossils found outside of Africa represent intermediates between H.erectus, Neanderthals, H.sapien
Suggests the physical diffs between them are due to diff selectiom pressures in diff regional differences
Suggests H.sapien evolved from H.erectus outside of Africa (gene flow occured)
Multi regional evdience
mtDNA
Neanderthals mtDNA is substainaly different from modern H.sapien
Suggests N was a diff subspecies but belonged to the smae species as anatomicaly modern Hominins
Multi regional evdience
Nulear DNA
Some similarities in DNA sequences of Neanderthals, H.sapien, H.donesivans
Suggests interbreeding did occus, supports gene flow occurance between regions
Out Of Africa (OOA)
Suggests that H.sapiens left Africa 65,000ya (having evolved from H.erectus) and replaced early hominins such as H.erectus, Neanderthals, Denoisvans present in other parts of the world.
No gene flow between Afrian, Asain, European populations
OOA evdience
Fossil
The oldest H.sapien fossil in Africa 200,000 - 300,000ya
Found at the same time as H.erectus and Neanderthals
Therefore they existed at different pops
Suggests that evoluation occured in Africa
OOA evdience
mtDNA
mtDNA is inherrited maternally
used as molecular clock
doesnt undergo recombination
only changed by random mutations that occur at a known constat rate
able to work out time of divergance
Suggests the oldest living modern human 200,000ya in Africa based on the number of accumunlated mutations that occur at a constant rate in mtDNA
Suggests H.erectus evolved in Africa first
African populations are older than non-African pops
OOA evdience
Nulcear DNA
Nuclear DNA identifies specific genes, simalrites, determine shared traits, lineage connections
The further away non-African pops are from Africa = less GV
African pops = more recent origin = more GV
Older Africa pops = larger GV as more time for mutations
Suggests H.erectus evolved to H.sapein in Africa
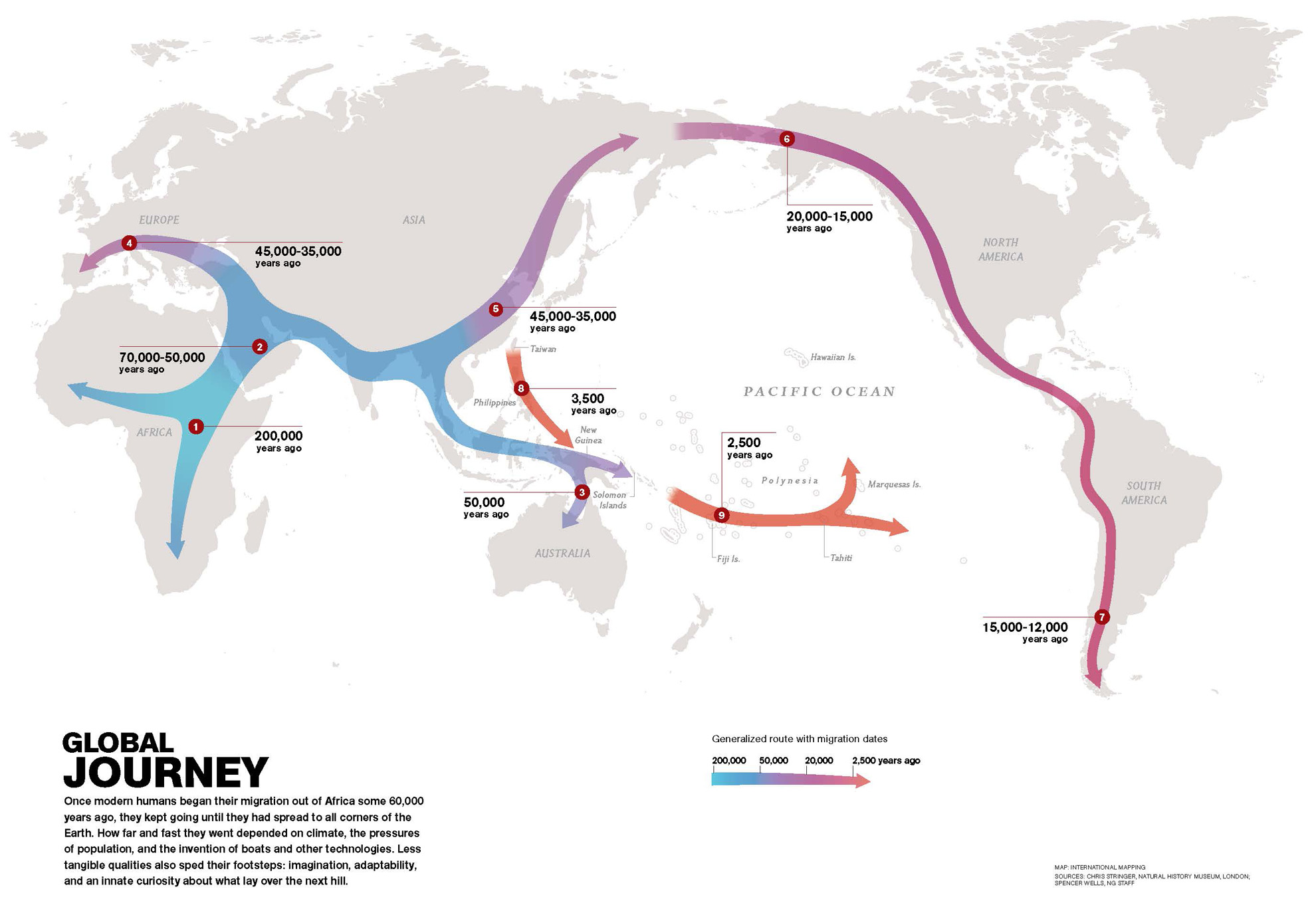
Dispersal routes
EAST - WEST migration, along coast and around equator
route was faster and favoured
warmer conditions which hominins were adapted to
well resourced (seafood, freshwater rivers)
south - north, through central Asia
not favoured, slower due to terrain, colder, limmited food supply
later migration into North America occured following ICE AGES where sea levels lower (glacial), land bridges form (bering straight from Europe to North America)
Cultural evoluation
Involves the transmission of knowledge from within one genetration or across generations
by teaching, learning, or passing on information that is not genetically derived
relatively fast compared to biological, can occur within one generation
Oldawan
~2mya
Africa
H.habilis
Pebbles / stones
Hard hammer percussions, 6 blows
Large round rock, roughly flaked
choppers, scrapers, flakes
cutting, skinning, butchering, crack bones for marrow
Supported H.habilis as scavenger
Better process carcasses and access energy dense bone marrow
Increase energy = fuel brain development

Acheulean
~1mya
Africa and Middle East
H.erectus
Stones
Hard and soft hammer percussions, 50 blows
Bifacial, teardroped shaped, hand axes
Butchering, chopping, scraping
Cleavers, picks, hand axes
Supported H.erectus shift to HUNTER GATHERER
Incresed meat intake = brain development

Mousterian
200,000 - 40,000ya
Africa, Middle East, Europe
Neanderthals
Flint and stone
LEVALLOIS METHOD (preparing core, striking off large oval flake) 150 blows
Tourtise-shell apperance
SPEAR POINTS, hand axes, scrappers (dressing animal hides for clothing and tempory shelters)
Supported N hunting capacity via tool making
Allowed them to survive colder climates (Europe) to avoid
competition, increase survival

Upper paleolithic
~50,000ya
Everywhere
Neandertals and early H.sapien
Stone, wood, bone
Soft hammer percussion, punch blade method, pressure flaking, 250 blows
Spear throwers (kill prey from afar)
Bone needles (stitch clothing)
Fish hooks (costal exploration)
More varied hunting tools
Access to costal areas
Diet variety
Tailored clothes for cold enviroments
Increase survival

Neolithic
~12,000ya
Everywhere
H.sapien
Stone, bone, antler, flint, wood
Pressure flaking, pollished stone
Sickles, curved blades, secreeted edges, mounded handles
Tools for agriculture (plant cultivation and animal donestication)
Quern and rubbing stone = processing seeds grains
Sickles and scythes = harvesting crops, cutting vegitation
Hunter gatherer to AGRICULTURE FARMING
Increased productivity, constant food supply, trade, specilised pollished tools

Fire advantages
Remain active at night:
extended hours, continue activity in dark / caves, tool making, communication, teaching of skills = productivity
Warmth:
allowed expannsion into cooler areas during ice age, migration OOA, less energy used for thermoregulation, energy redirected for brain development, teaching, consuming food etc
Protection + prey:
scare / burn / harm predators, defense increasing survival, heard prey
Cooking:
made meat easier to mechanically chew and digest, more nutrients high protien energy diet via improved hunting, energy for brain development, further improves tool making, communitcation
perserve meat via smoking decreasing rick of starvation
kill parasites and toxins (pathogens) reducing disease
Social interaction:
bringing food back to communal fire increased social interaction, further development of tool cultures, social organisation, hunting preparation, shake knowledge, plan, possible language development (in later homins)
Fire disadvantages
Burning (injury)
Ecological destruction
Attract compeditors
Increased work required
Spirituality
Art
aligned dead bodies east - west
legs curled sleeping posture
head resting on stone
decorated with red orche and black maganise dioxide flowers
suggests concept of afterlife rituals spiritually
development of frontal lobe = abstract thought
jewlery, cave art