Exercise Science Exam 2
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Athletic Training
Involves prevention, treatment, and rehabilitation of injuries to physically active individuals and athletes (first responders)
Secondary Assessment
Involve collection of injury history, observation of body movement, observation of deformities, assessment of the injured area, assessment of ROM, tests, and decision of course of action.
Sports Medicine
Umbrella term that describes the various issues interrelated among medicine, physical activity, exercise, health promotion, and disease prevention.
Primary Components:
Medical supervision & care of athletes
Use of exercise/sport for those with physical/mental disability
Help people develop/maintain physical fitness & improve sport performance
Use exercise to treat & rehabilitate people
Sports Medicine Physician
Leader of the sports medicine team
Consensus Statements
Guidlines for sports medicine physicians
Isometric Contraction
Muscle contract but do not shorten (no change in length)
Isotonic Contraction
Change in muscle length
Concentric Contraction
Muscle contract and shorten to lift the weight
Eccentric Contraction
Muscle contract but lengthen to control the lowering of weight
Agonist
Cause specific joint movement
Antagonist
Opposing movement to the agonist
Synergist
Muscle that assist the agonist with movement
Stabilizer
Act on one segment so that a specific movement in an adjacent joint can occur; so agonist causes smooth and efficient movement
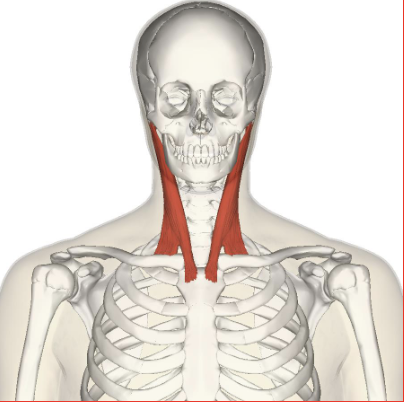
Sternocleidomastoid
Neck flexion, lateral neck flexion, and rotation
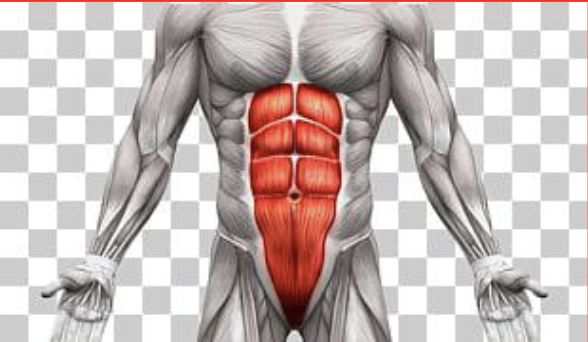
Rectus Abdominis
Trunk flexion; bend at hips forward
Antagonist: Erector Spinae
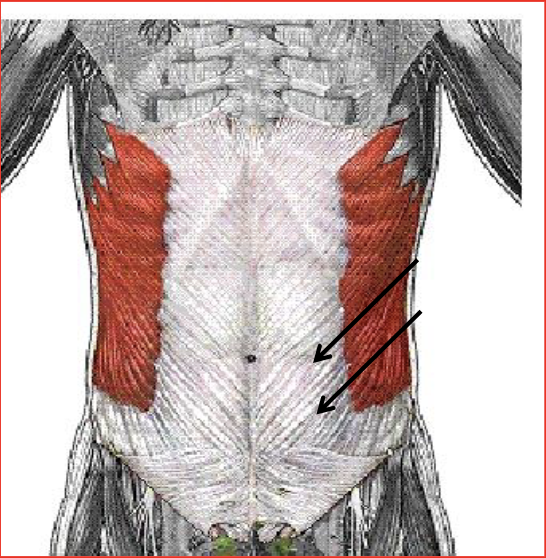
External Obliques
Anterior flexion (flex forward), Lateral flexion (lean to side), and rotates the trunk
Antagonist: Erector Spinae, Opposite Oblique
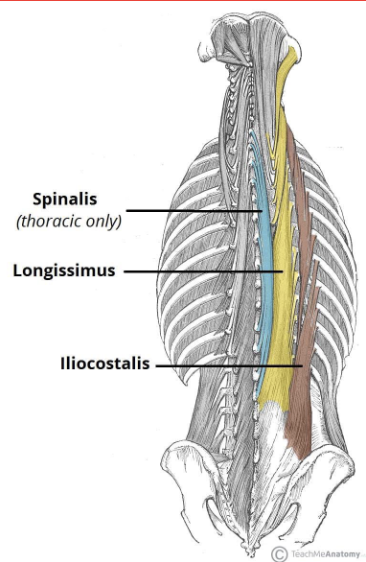
Erector Spinae
Extend the trunk (lean back)
Antagonist: Rectus Abdominis
Pectoralis Major
Flexes shoulder, Horizontal ADduction
Antagonist: Latissimus Dorsi, Posterior Deltoid, and Trapezius
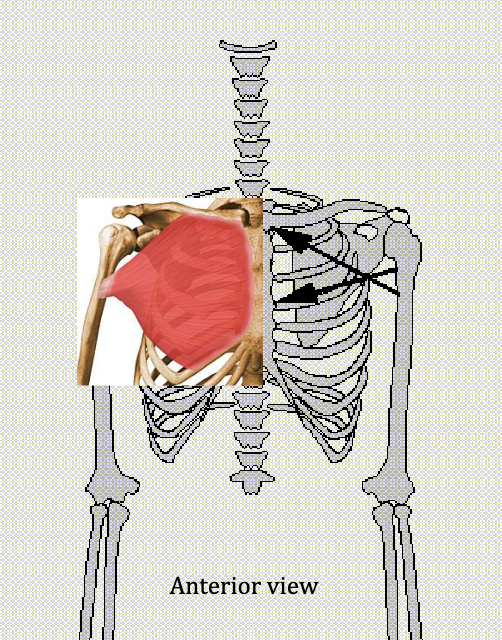
Latissimus Dorsi
Extends and ADducts shoulder
Antagonist: Pectoralis Major, Anterior + Medial Deltoids
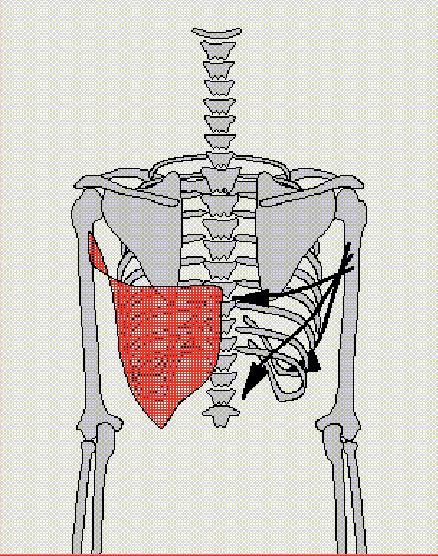
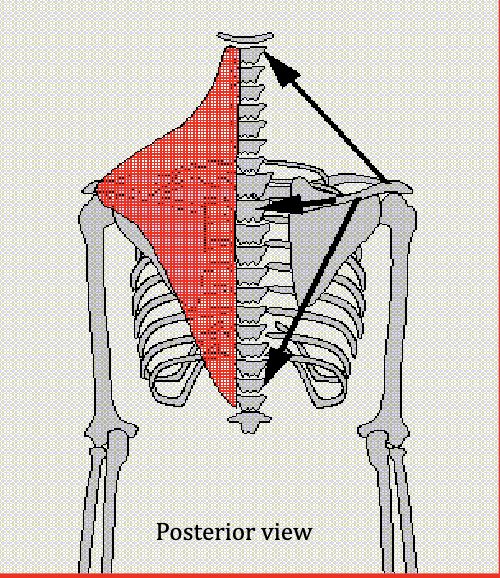
Trapezius
Elevates the scapula, Retracts the scapula, and Depresses the scapula
Antagonist: Sternocleidomastoid, Anterior Deltoid, and Pectoralis Major
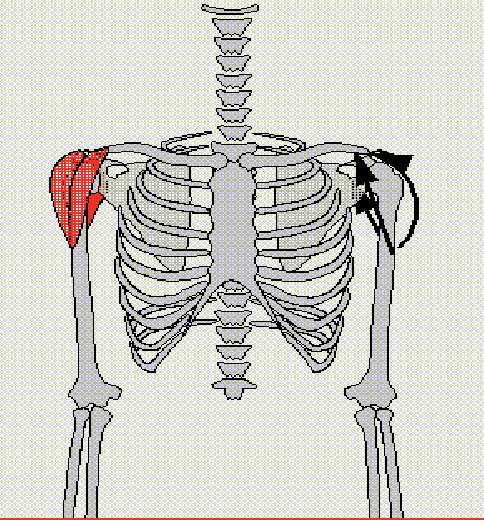
Deltoid
Should flexion, Abduction arm, and Extension arm
Antagonist: Pectoralis Major and Latissimus Dorsi
Infraspinatus and Teres Minor
Shoulder external rotation
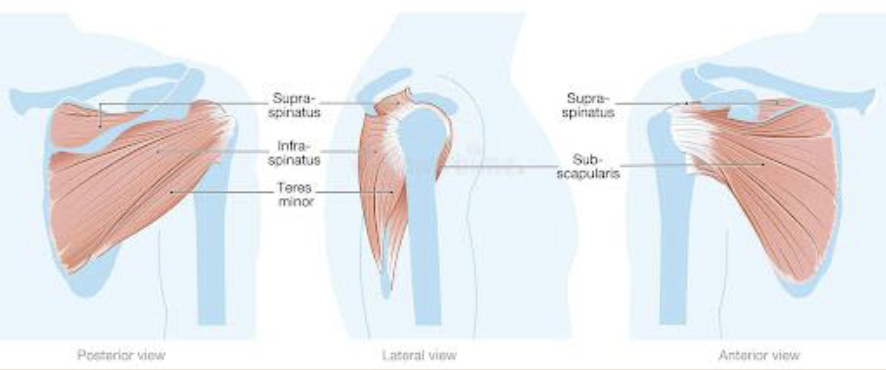
Supraspinatus
Should abduction
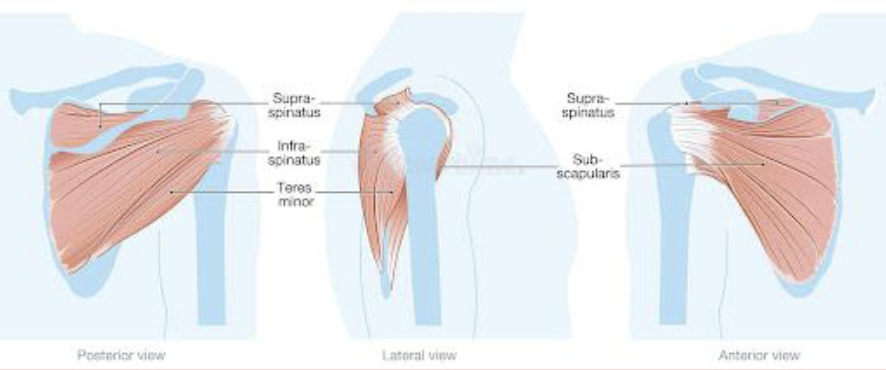
Subscapularis
Shoulder internal rotation
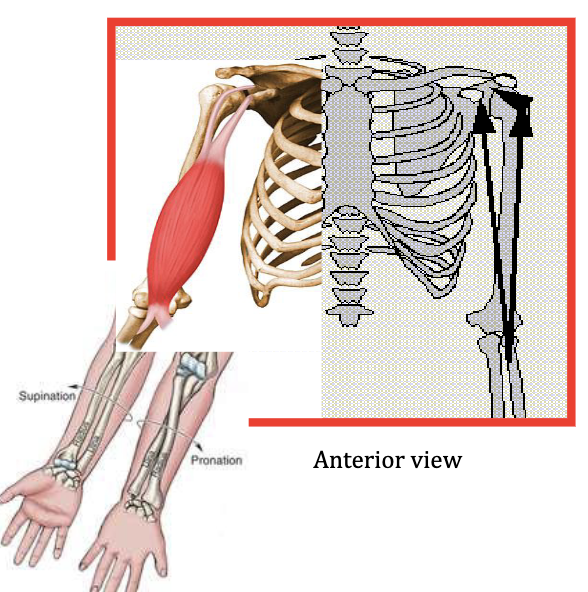
Biceps Brachii
Flexes elbow, Forearm supination - most active in flexion when forearm is supinated
Antagonist: Triceps Brachii
Triceps Brachii
Chief extensor of elbow
Antagonist: Bicep Brachii
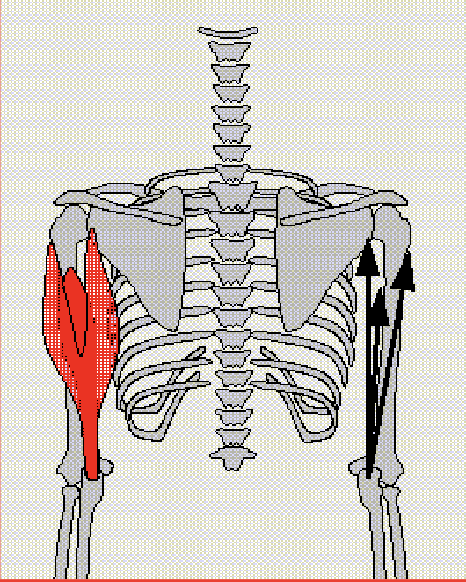
Brachioradialis
Flexes elbow - optimal action with neutral forearm
Antagonist: Triceps Brachii
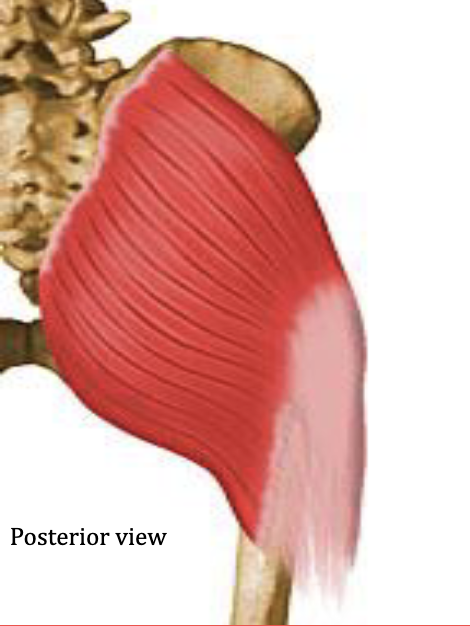
Gluteus Maximus
Extends the hip, ABducts the hip
Antagonist: Iliopsoas (hip flexor)
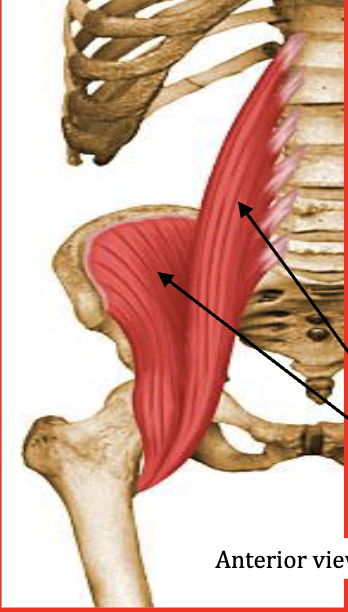
Iliopsoas
Flexes hip and trunk
Antagonist: Gluteus Maximus
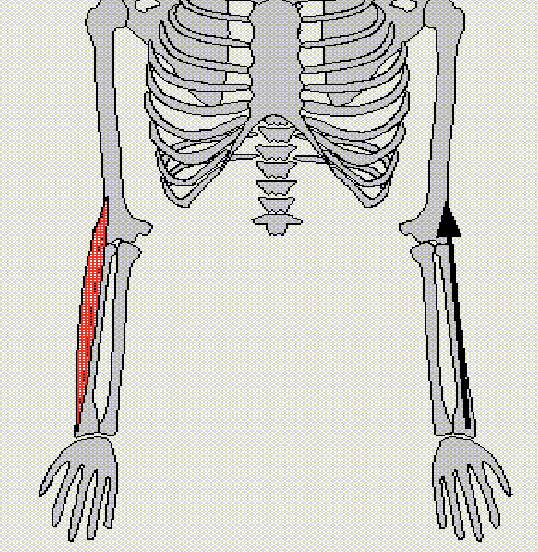
Quadriceps Femoris
Extend knee - segment flexes hip
Antagonist: Hamstring
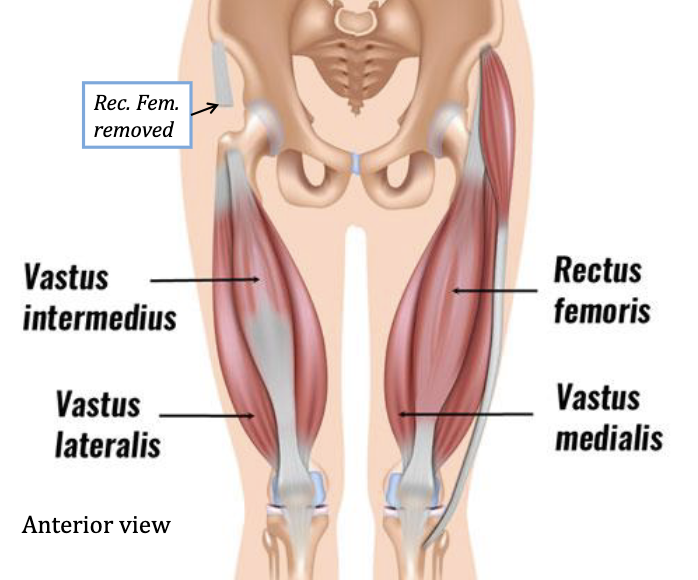
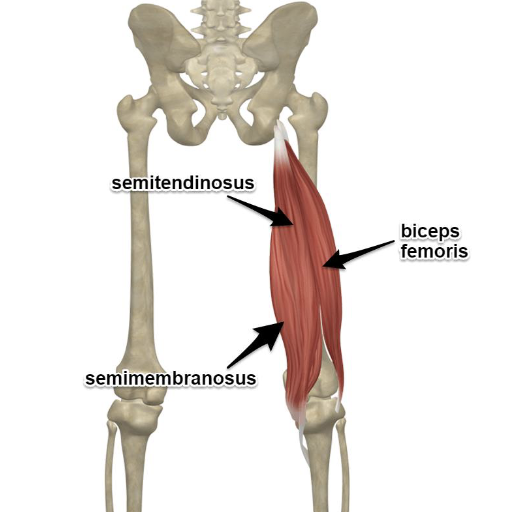
Hamstrings
Flexes knee and extends hip
Antagonist: Quadriceps
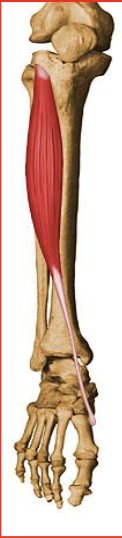
Gastrocnemius
Plantar flexes the ankle and assists in knee flexion
Antagonist: Tibialis Anterior

Tibialis Anterior
Major dorsiflexion the ankle
Antagonist: Gastrocnemius
Compression
Pressing or squeezing force directed through a body
Tension
Pulling or stretching force directed through a body
Shear
Force directed parallel to a surface
Fractures
Causes: trauma/large load application, osteoporosis, and overuse/abrupt increase in intensity
Osteoporosis
Condition where bones become brittle and weak due to decrease in bone mineral density and mass
Friction Blisters
Caused by shear forces between layers of the skin
Sprains
Tearing/damage to a ligament
Ligament
connective tissue connecting bone to bone
ACL Tear
Major ligament inside the knee joint
Typically caused by shear forces
lnar Collateral Ligament Tear
Medial side of elbow; connects humerus to ulna
Typically caused by shear forces
Strains
Tearing/damage to muscles or tendons
Tendons
Connective tissues connecting muscles to bones
Hyaline Cartilage
More gel-like interior
Most common type in the body
Most join surfaces, trachea, ribs, and nose
Fibrocartilage
Cushion areas of high compressive forces
Disc of the back, knees, shoulder, and hip
Meniscal Tear
Caused by loaded twisting
High compression and shear forces
Commonly cause during cutting maneuvers in sports
Labral Tear
Cartilage injury
Caused by trauma, overuse, and compression/shear forces
Dislocation
When bones of a joint are moved out of alignment
Herniation
When all or part of the soft, jelly-like center of spinal disk pushes through a weakened part of the disk’s outer ring
Concussion
A traumatic brain injury that affects brain function
For nutrients to effect exercise they must be…
Ingest
Digest
Absorbed
Transported in cells
Carbohydrates
Blood glucose and muscle glycogen provide energy for exercise
Important during moderate to high intensity exercise
Carbohydrate Normal Daily Intake
3-10g/kg/day
Glycemic Index
How fast a food affects blood sugar
Glycemic Load
How much a food affects blood sugar
Protein
Consumption of adequate amounts and types is important for ensuring the optimal performance.
Help make amino acids readily available to the body tissues for continued protein synthesis.
Protein Daily Intake
Normal range: 1.2-2.0 g/kg/day
Fats
Important for weight event athletes.
Possible advantage for endurance athletes.
Needed for absorption of fat soluble vitamins and concentrated energy for the body
Hyperlipidemia
High levels of fat in the blood
Hypercholesterolemia
High cholesterol
Fats Daily Intake
Normal daily intake is no less than 20% of total daily calories
Euhydrated
Normal hydration
Hypohydrated
Under hydrated (dehydration)
Hyperhydrated
Overhydration
CHO Loading
Method of maximizing CHO stores prior to an event through exercise and dietary manipulation
CHO intake during prolonged activity
30-60g/hr or 0.6 g/kg/hr
Post-Workout Protein Intake
0.3 g/kg of body mass or 20-30 grams after resistance exercise for muscle growth
CHO and Protein - Post Workout
3:1 or 4:1 CHO to Protein grams
CHO = 1.0-1.2 g/kg
Protein = 0.3 g/kg
Creatine Monohydrate
Enhanced peak power production during intense exercise
Risks: non-responders, cramping, and GI issues
Caffeine
Elevated mood, decreased fatigue and pain, lowered perception of effort, and increased fat metabolism.
Risks: Nervousness, tremors, GI problems, and addictive
Bicarbonate
Increased blood pH and buffering H+, delayed onset of anaerobic fatigue.
Risks: GI discomfort
Beta-Alanine
Improved high intensity performance, increase in muscular endurance, decrease fatigue, and decrease RPE.
Risks: Paresthesia
Salt
Maintain higher plasma volume, decrease HR, decrease urine output, decrease RPE, and increase performance.
Sport and Exercise Psychology
Study of behavior, thoughts, and feelings of healthy, disabled, and diseased individuals engaging in physical activity, exercise, sport, and athletic competition.
Sport Psychology
The field within exercise science that examine how psychological influence athletic performance.
Psychological Principles
Maintain stress
Dealing with anxiety
Improving motivation
Improving focus during competition
Personality
Entire qualities and traits, including character and behavior that are specific to someone
Plays an important role in behaviors that individuals exhibit
Not easily modifiable
Trait Framework
Everything we do is a result of personality
Interaction Framework
Traits and the environment interact to determine how we act
Motivation 3 Parts
Direction: Where people invest their energy
Intensity: How much energy is invested
Persistence: How long energy is invested at a given intensity
Task Orientation
Self-refrences definition of success
Focus on improvement, gaining a new skill
Ego Orientation
Success is defined by being better than others
Focus on winning, being the best
Extrinsic
When individuals engage in a certain behavior to gain some external reward
Intrinsic
When individuals engage in behavior because the individual enjoys the process and gains pleasure and satisfaction from participation
Autonomy
Endorse and be origin of own behavior
Do what we want to do
Competence
Interact effectively in environment
Need challenging activities and positive feedback can help if sincere
Connectedness
Feel connected with, cared for, and close to others/community
Arousal in Sports Psychology
Degree of mental and physical activation/intensity
Performance Arousal Curve
Optimal level of arousal for performance
Imagery
Creating a mental image of a situation using all of you senses
Flow State
A psychological state that is intrinsically rewarding, where everything seems to click into place, even during extreme challenges
Choking
Progressive and uncontrollable deterioration of performance when in high pressure situations
The Yips
Psycho-neuromuscular impediment affecting the execution of fine motor skills during sporting performance
Environmental Exercise Physiology
Study acute and chronic effects of exercising in various environmental conditions
Radiation (R)
Energy transferred via infrared waves
Conduction (K)
Energy transfer via direct contact
Convection (C)
Energy transfer via mass motion of molecules
Evaporation (E)
Phase change of liquid to a gas through the transfer of heat energy