Physio Ch. 13
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Yall better say thank you to Chance for his quizlet! I changed some stuff a bit
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
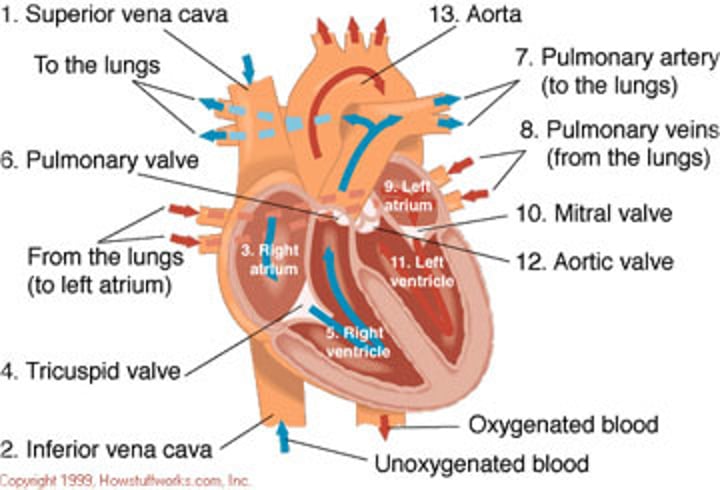
order of flow in the heart
right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary artery, lungs, pulmonary vein, left atrium, mitral valve, left ventricle, aortic valve, aorta
location of SA and AV nodes
right atrium
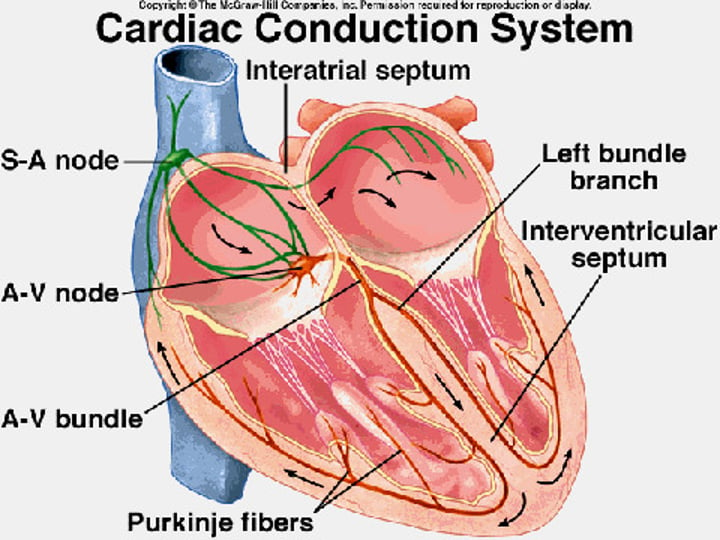
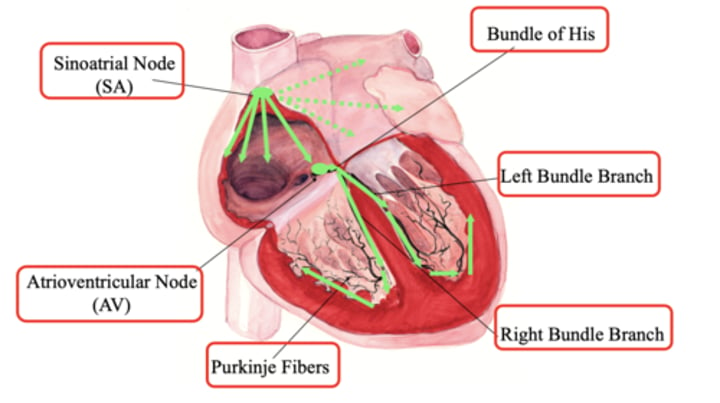
flow of electricity through the heart
SA node, AV node, bundle of his, right/left bundle branch, purkinje fibers
differences between the veins and arteries
arteries carry blood away from the heart, veins carry blood back to the heart
difference between arteries and arterioles
arteries are the blood vessels that carry blood from the heart while arterioles are smaller arteries which receive blood from the larger arteries and pass to capillaries
difference between veins and venules
the vein is a larger blood vessel that carries blood towards the heart while, the venule is a smaller minute blood vessel that drains blood from capillaries to the veins
function of capillaries
to exchange of materials such as oxygen & carbon dioxide between the blood and body cells.
difference between deoxygenated blood and oxygenated blood/where in the heart each flows
deoxygenated blood brings carbon dioxide to the lungs, oxygenated blood brings oxygen to metabolizing tissues; deoxygenated flows in the right side of the heart, oxygenated flows in the left side of the heart
difference between systolic and diastolic pressure/how to read blood pressure
the top number is the maximum pressure the heart exerts while beating (systolic pressure). the bottom number is the amount of pressure in the arteries between beats (diastolic pressure).
contributing factors of high blood pressure
kidney disease, high sodium intake, obesity, psychological stress, arteriosclerosis
contributing factors of low blood pressure
dehydration, diabetes, irregular heartbeat, pregnancy
average blood pressure/blood pressure numbers in prehypertension and hypertension
average: 120/80
prehypertension: 90/60
hypertension: 130/80
blood the heart pumps per day
7000 liters
difference between systemic and pulmonary circuit
systemic: moves blood between the heart and body
pulmonary: moves blood between the heart and lungs
function of papillary muscles
to prevent prolapse/inversion of valves.
artery that supplies blood to the heart and what happens when it's clogged
coronary artery/heart attack
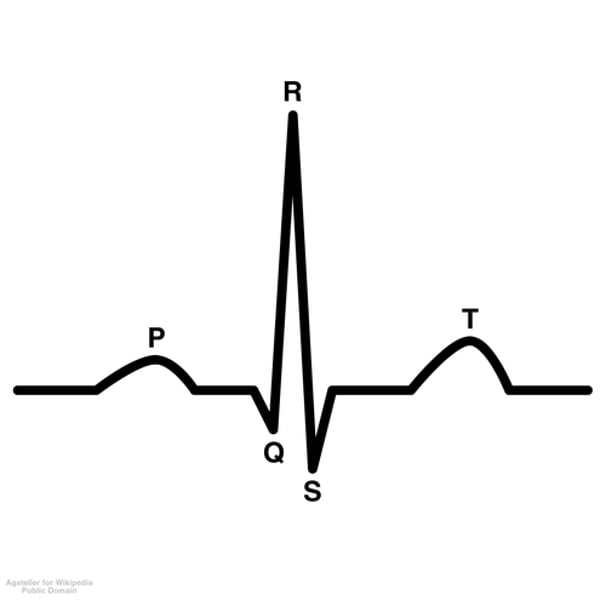
the parts of the electrocardiogram and what each part means
P wave: time right before contraction of the atria
QRS complex:
Q - time right before ventricular contraction
R - contraction of ventricles
S - after ventricles contract
T wave: repolarization of the ventricular muscles/rest
P-Q interval: time it takes for the impulse to travel from the SA node to the AV node
angina pectoris
chest pain that results when the heart does not get enough oxygen
bradycardia
abnormally slow heartbeat
congestive heart failure
heart is unable to pump its required amount of blood
arrhythmia
irregular heartbeat
myocardial infarction
heart attack
tachycardia
rapid heart rate
mitral valve prolapse
improper closure of the mitral valve
Veins
any of the tubes forming part of the blood circulation system of the body, carrying in most cases oxygen-depleted blood toward the heart
Arteries
A blood vessel that carries blood from the heart to tissues and organs in the body.
Arterioles
a very small blood vessel that branches off from your artery and carries blood away from your heart to your tissues and organs
Venules
Smallest veins and receive blood from capillaries
Deoxygenated Blood
the blood which is received to the heart and has greater concentration of carbon dioxide as compared to oxygen
Oxygenated Blood
a blood cell that has a high proportion of oxygen and a low amount of carbon dioxide
Systolic Pressure
Max blood pressure during contraction of ventricles
Diastolic Pressure
Minimum pressure recorded right b4 the next contraction
Systemic Circuit
provides the functional blood supply to all body tissue
Pulmonary Circuit
This transportation system moves oxygen-depleted blood from the heart to the lungs to pick up oxygen before sending it back into the body.