1- Intro Endo/Repro & Feedback loops
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Estradiol
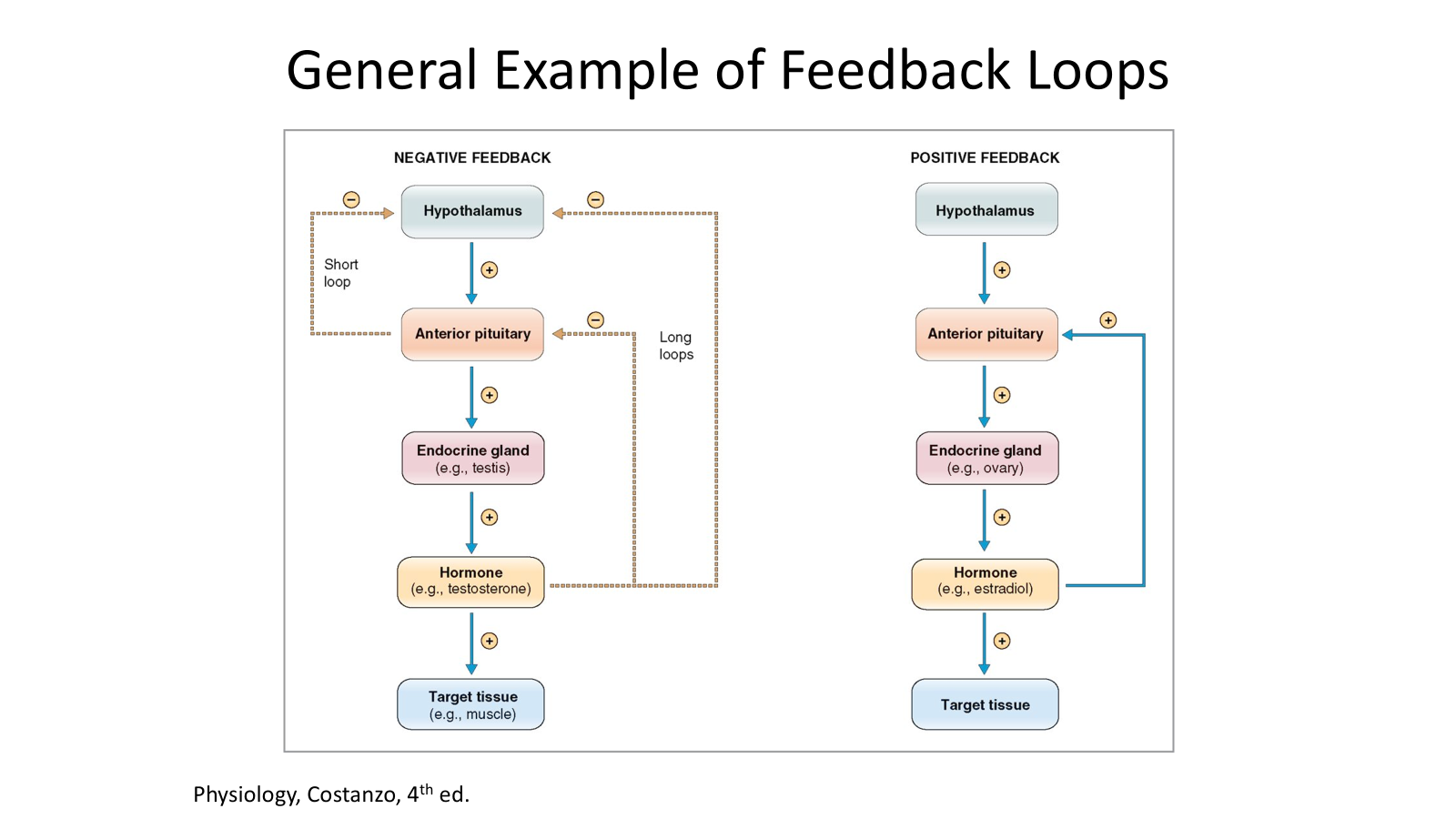
Example of positive feedback loop
Acts on anterior pituitary
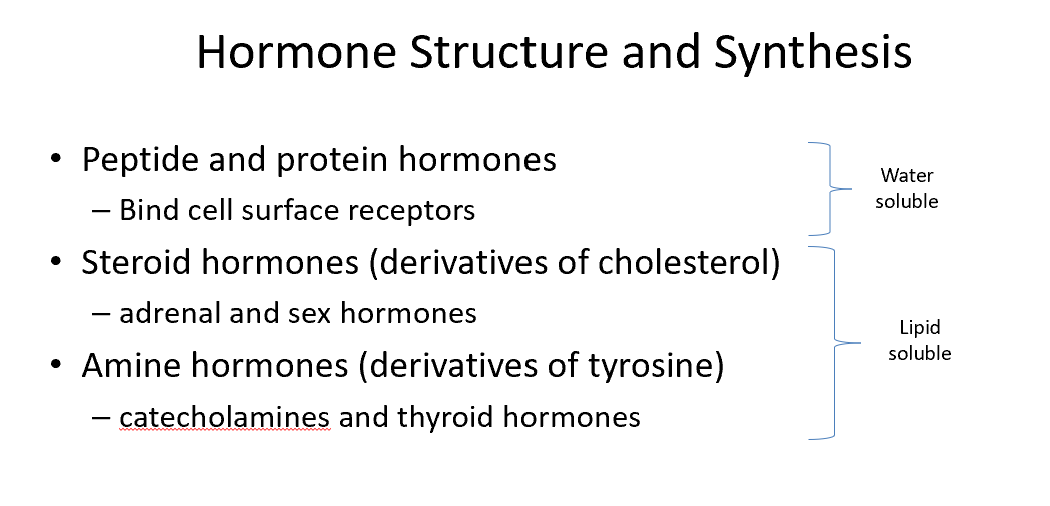
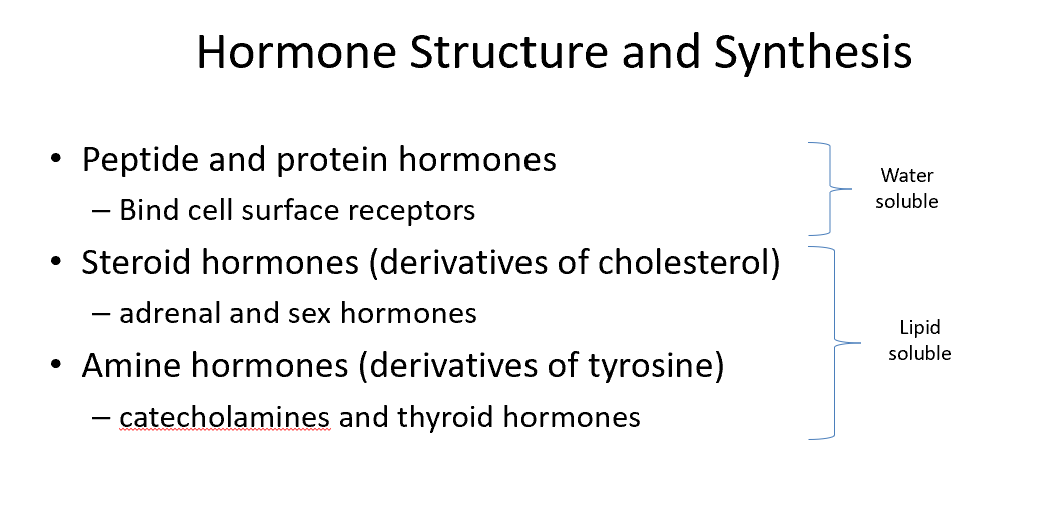
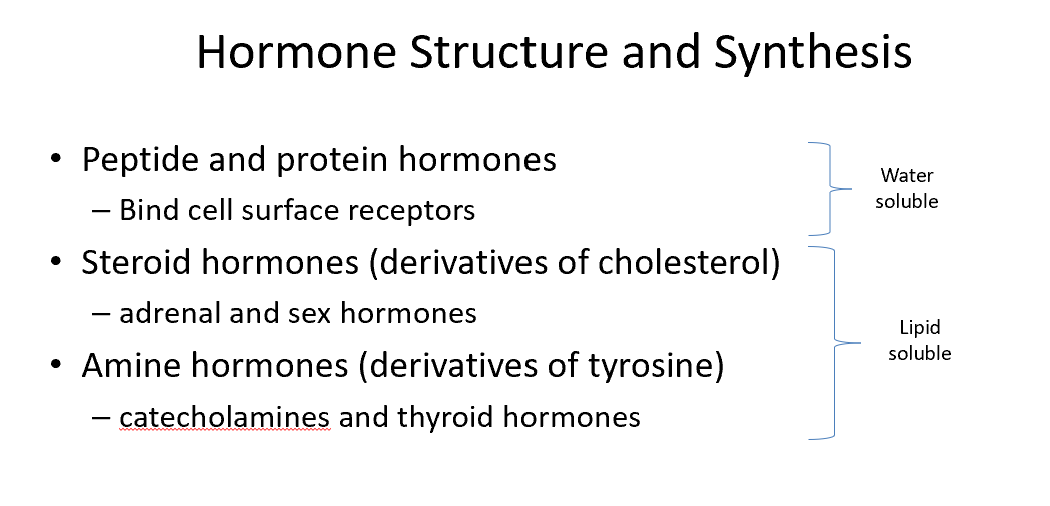
Steroid Hormones
Derivatives of cholesterol
Amine Hormones
Derivatives of tyrosine
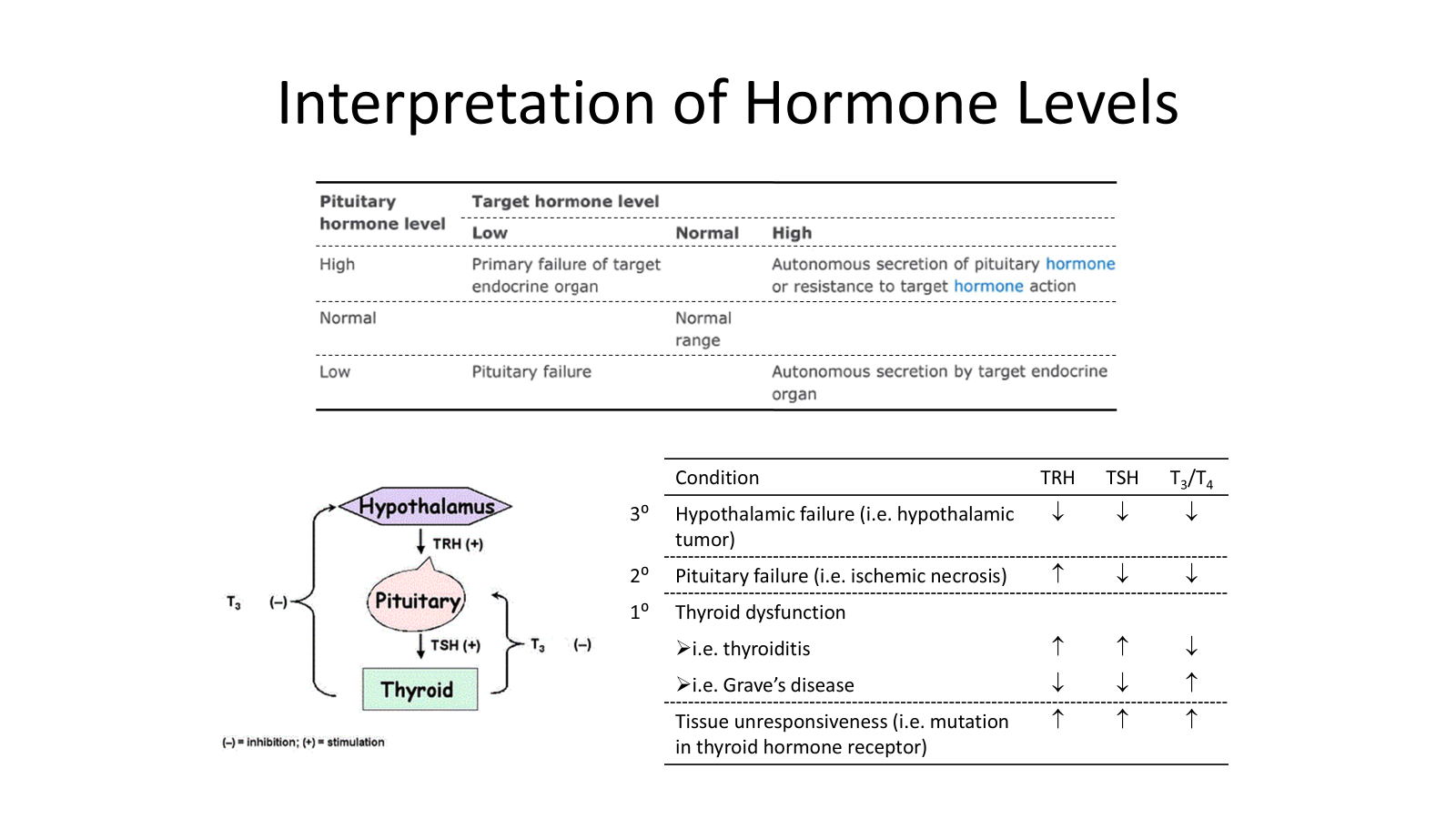
Interpreting Hormone Measurements
Hormones should be evaluated with their regulatory factor
Simultaneous elevation of a pair = hormone resistance state
Target hormone excess should be evaluated with the right tropic hormone (insulin/glucose, PTH/Ca)
Neural or Nutrient/Ion
Additional regulators of hormone release are due to THIS control.
Neural=ADH
Ion=Glucose

Physiologic Responses
Can provide some negative feedback on hypophysiotropic parvicellular neurons (hypothalamus)
Peripheral Hormone
Can give negative feedback to tropic hormones
Can give negative feedback to hypothalamus (hypophysiotropic parvicellular neurons)
Urine Analysis
THIS of hormones is restricted to the measurement of catecholamines and steroid hormones.
Being an integrated sample helps to counteract the variability of hormone levels
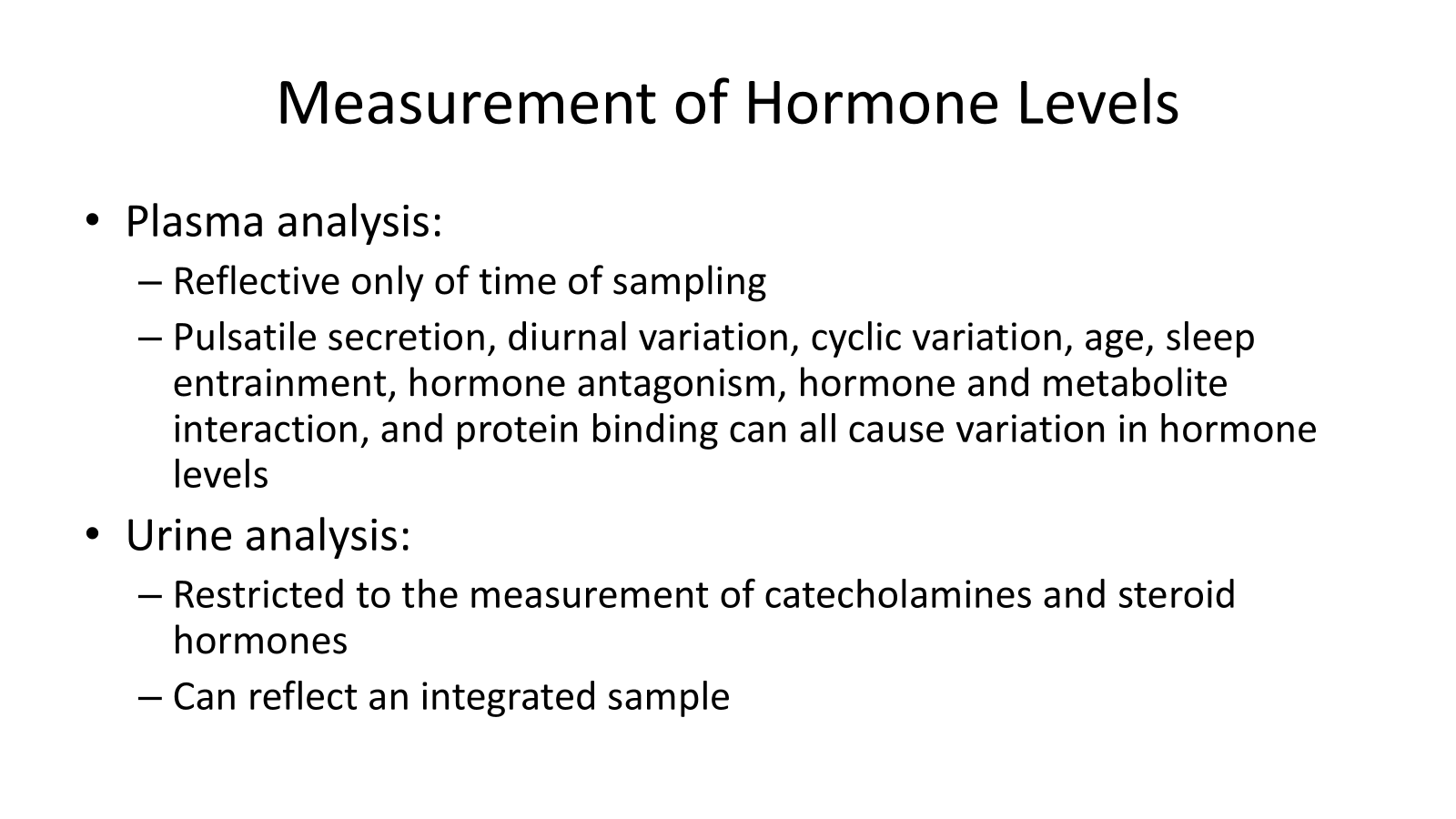
Plasma analysis
Reflects only the hormone(s) levels at the time of sampling

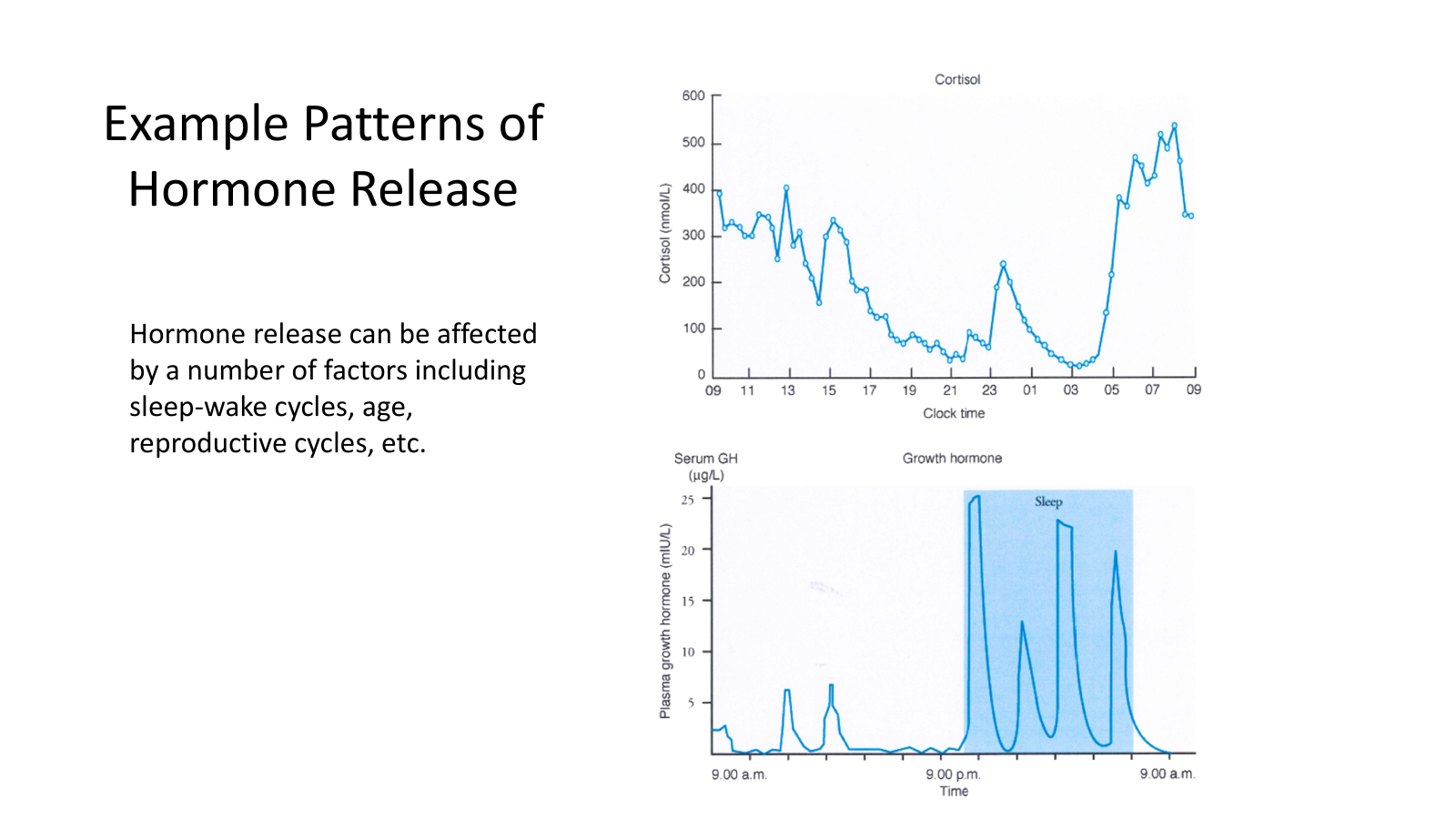
Hormone Release
Can be affected by:
Sleep/wake cycle - Cortisol
Age - GH (growth hormone)
Reproductive cycles - Estrogen/Progesterone
Protein & Peptide Hormones
Have short half lives
Are stored in vesicles, dissolve in plasma
Faster acting than the others
Produce second messengers
Exception= insulin (doesn’t use cAMP, activates tyrosine kinase)
Water soluble!
Steroid & Amine Hormones
Have long half-lives
Attach to transport carriers in the plasma
Are synthesized as needed
Stimulate synthesis of new proteins
Take longer to act than the others
Lipid soluble!
Amine Hormones
Examples are catecholamines and thyroid hormones
Derivatives of tyrosine
Steroid Hormones
Examples are adrenal and sex hormones
Derivatives of cholesterol!
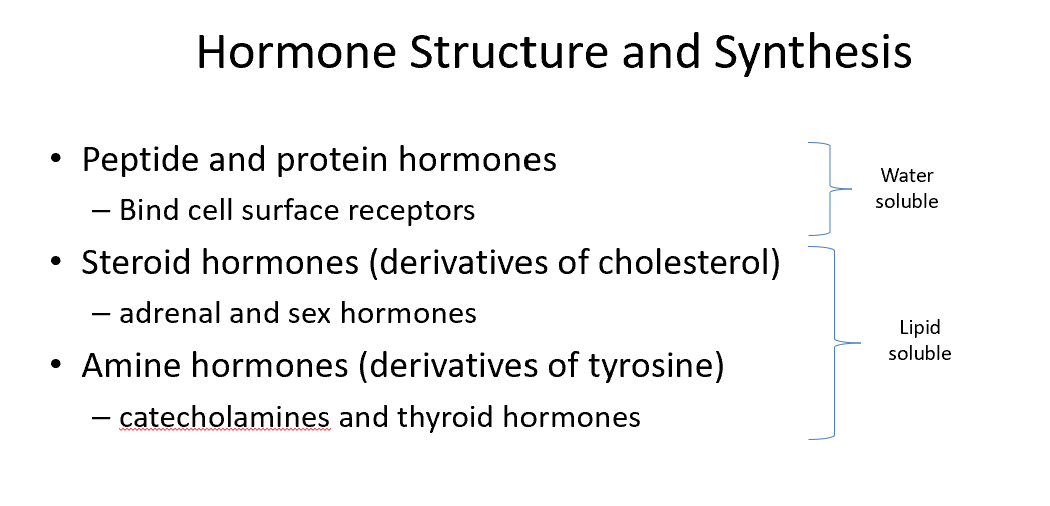
Peptide/Protein Hormones
Bind cell surface receptors
Endocrinology
Study of communication and control within a living organism by means of chemical messengers
Metabolism
Study of the biochemical control mechanisms that occur within living organisms
Hormones
Endogenous informational molecules that are involved in both intracellular and extracellular communication
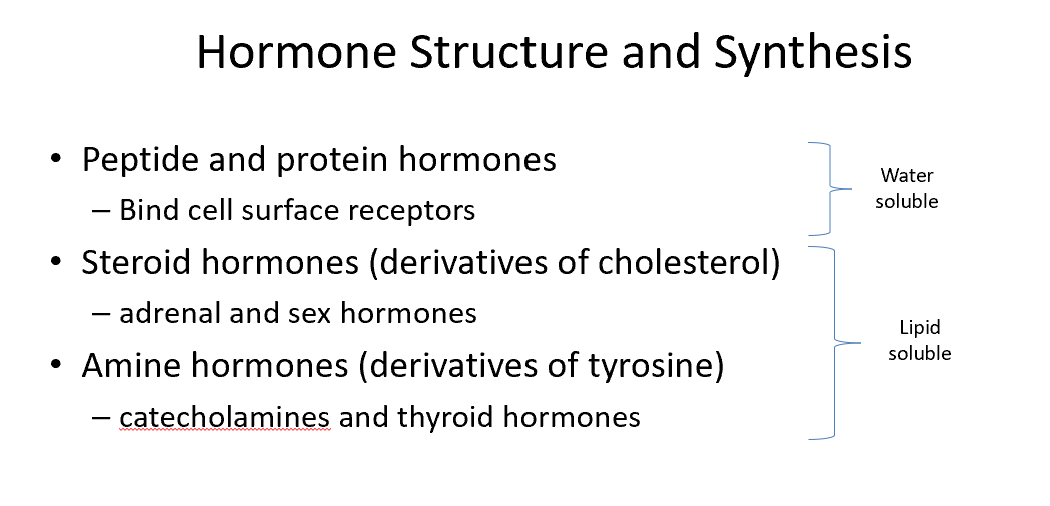
Endocrine Organs
Hypothalamus
Pituitary Gland
Thyroid Gland
Parathyroid Glands
Adrenal Glands
Pancreas
Ovaries
Testes
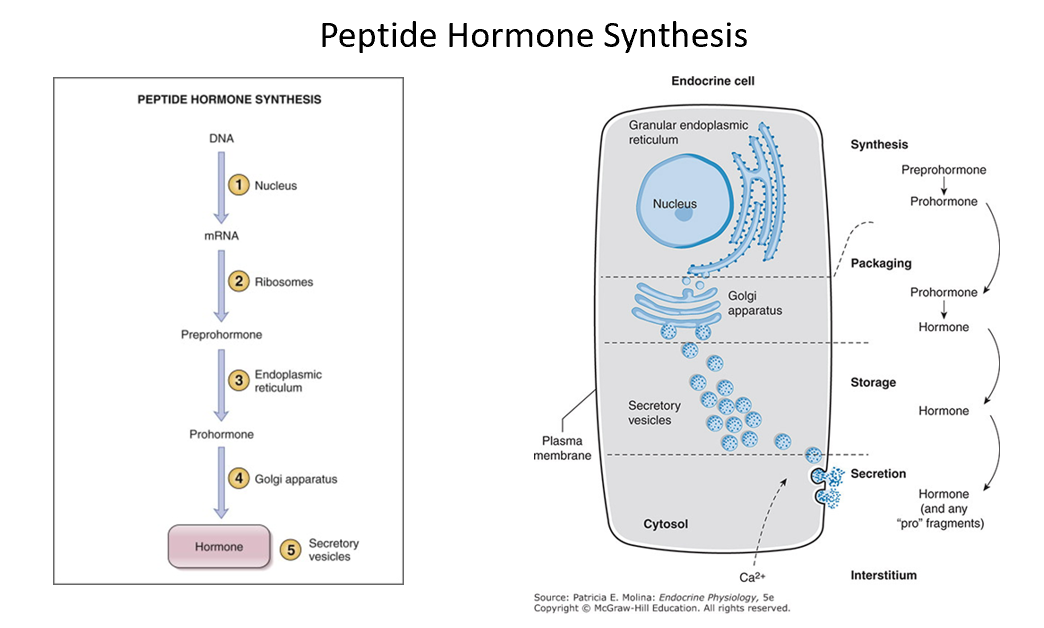
Peptide Hormone Synthesis
Preprohormone → Prohormone → Hormone