Benzene & Aromaticity
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
3rd type of unsaturated hydrocarbon together with alkenes and alkynes.
Do NOT undergo electrophilic addition.
Considering the structure of benzene ring, the structures has a special type of bonding depicting both localized and delocalized bonds
C6H6
Benzene
Benzene
Simplest aromatic hydrocarbon with a special type of bonding that stabilizes the structures
A general aromatic hydrocarbon substituent is called “aryl group” (Ar)
For monosubstitution
Benzene is used as parent name
methylbenzene, chlorobenzene, hydroxybenzene
For disubstitution
-ortho, -meta, and -para are terms used to refer to the position of one of the substituents in reference to the position of the other
ortho (o-)
1,2-substitution on the ring
meta (m-)
1,3-substitution on the ring
para (p-)
1,4-substitution on the ring
For trisubstitution or more
Numbers are assigned to refer to the position of the substituents in the ring.
The lowest set of numbering system is used and substituents are arranged in alphabetical order.
Aromatic compounds
Represented by benzene (simplest) are cyclic, conjugated, stable, planar and undergoes substitution reaction.
Hückel’s Rule
Aromatic compounds follow this rule
Hückel’s Rule
Predicts that a compound which is planar, cyclic, has a conjugated double bonds will have total of 4n + 2 pi-electrons.
Polar Mechanism
Aromatic compound (benzene) reaction follow this which creates an electrophile (R+).
Electrophilic substitution reaction (SE)
When the reaction follows a polar mechanism that creates an electrophile.
Reaction Catalyst
This aids in the polarization of the reagents forming an electrophile product.
Pi bond in the benzene
This is cleaved as the electrons are attracted to accommodate the incoming electrophile.
Neighboring Carbon Cleves
This happens when —— the H attached to it, takes the electrons from the bond and delocalizes it back to the carbocation — restoring the benzene double bonds.
Common electrophilic substitution reaction (SE)
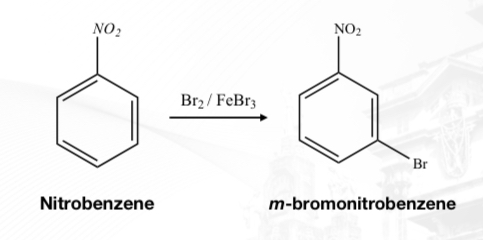
Halogenation
Nitration
Sulfonation
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation
Friedel-Crafts Acylation
Halogenation
Substitution of halogens (X2) to a benzene ring.
Electrophile (+X)
Aromatic compound can be substituted with a polarized halogen which serves as an ——-
Catalyst
Aids in creating a polarized halogen (X+). This creates the electrophile to be added to the aromatic compound.
Nitration
Substitution of a nitro group (+NO2) to a benzene ring
Presence of Acid Catalyst; H₂SO₄
Form nitro substituted ring product (ArNO₂)
Reducing Agent Fe/SnCl₂
Nitro substituted product is reduced into an arylamine (ArNH2) product
Sulfonation
Substitution of +SO3H (sulfonic acid) to a benzene ring.
Reagent & Catalyst; Mixture of SO₃ and H₂SO₄
Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) reacts with sulfur trioxide (SO₃) forming the electrophile (+SO3H, sulfonic acid).
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation
Substitution with +R (alkyl group) to a benzene ring.
Done with alkyl halides (RX) with aluminum halide (AlX3) catalyst to produce the alkyl electrophile (R+, alkyl).
Hydride shift / Alkyl shift may occur to form more stable product
Hydride/Methide shift
When a negatively-charged hydrogen (-H, hydride) or a negatively-charged alkyl, usually a methyl (-CH3, methide) is translocated to a nearby carbocation to form a more stable carbocation.
Friedel-Crafts Acylation
Substitution with +COR (acyl group) to a benzene ring
Done with acyl halides (RCOX) with aluminum halide (AlX3) catalyst to produce the alkyl electrophile (+COR, acyl)
The RCOX that are commonly used are RCO-Cl and RCO-Br with AlCl3 and AlBr3 respectively
Does NOT follow the SE mechanism.
Hydrogenation
Bromination of alkyl side chain
Oxidation of Alkyl side chains
Reduction of Aryl Alkyl ketone
Hydrogenation
Addition of hydrogen (H2) to a benzene ring to create a saturated product.
Follows the same mechanism of alkene hydrogenation.
It adds H2 atoms in the presence of Pt or Rh (Rhodium) metal catalyst under high pressure
Bromination
Addition of bromine (Br2) to an alkyl side chain of a benzene ring
Follows an SR mechanism similar to alkanes
Occurs on the benzylic position with an alkylbenzene treated with N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) and benzoyl peroxide (Ph(CO2)2) acting as radical initiator.
Oxidation reaction
Complete oxidation of alkyl side chain on a benzene ring
The alkyl side chains (benzylic position) is rapidly affected by this, and converts to -COOH, regardless of the initial alkyl group attached to the ring.
The alkyl side chain will only be oxidized if there is a benzylic hydrogen (H attached to the benzylic carbon) present in the structure
Reduction reaction
The reduction oxygen bonds in a ketone (C=O) and nitro group (-NO2).
Both aryl alkyl ketones (product of FC Acylation) and nitro substituted (product of nitration) can be reduced via a process called catalytic hydrogenation with a Pd as catalyst (H2 / Pd).
Substituents
Can affect SE reactions in 2 ways: reactivity and orientation
Reactivity
Can be affected by any substitution.
It can activate (increase reactivity) and deactivate (decrease reactivity) of the ring.
Can affect whether subsequent reactions can still take place on the ring
Orientation
Consequent substitutions attached on the ring are affected by pre-existing substituents.
Substitutions can be directed at the ortho-,meta-, and para- positions of the ring.
Ortho-/Para-directing activators
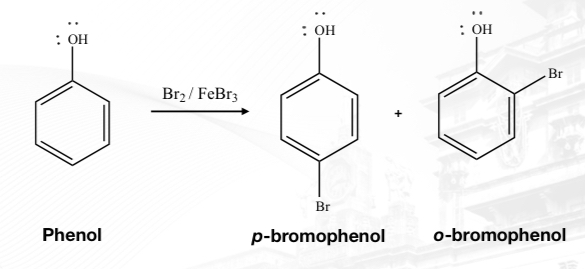
Meta-directing deactivators