Clinical microbio I: Anaerobes Flashcards
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Varying degrees of oxygen intolerance
strict anaerobe
aerotolerant anaerobe
facultative anaerobes
Strict (or obligate) anaerobe
use alternate electron acceptor for respiration such as sulfate, nitrate, iron, manganese, mercury, and CO2
tolerate <0.5% O2
are killed after exposure to air for only a few minutes
Treponema denticola, Selenomonas ruminatium, Clostridium novyi type B, Peptostreptococcus spp.
Aerotolerant anaerobe
majority of anaerobic organisms
tolerate 2-8% O2
survive exposure to air for several hours on an agar plate without loss of viability
require anaerobic environment to multiply
Bacteriodes fragilis, Porphyromonas melaninogenicus and Clostridium tertium
Oxygen tolerance
correlated with concentration of super oxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, or peroxidases
gives ability to breakdown toxic O2 radicals
no enzymes = toxicity
oxidation reduction (redox) potential (Eh)
O2 tolerance also linked to redox potential
Eh +150mV = normal tissue
Eh = -420mV = lowest in nature
large bowel = -250 mV
any decrease in BF results in decrease in the Eh to that tissue
anaerobic bacteria don’t survive is Eh is above -100mV
some organisms need both low O2 & low redox potential
Growth in thioglycolate broth
thioglycolate is a reducing agent that takes away O2 from tube (more O2 on top vs less on bottom)
gradient of O2 is created
semi-solid medium

Anaerobic rod-shaped bacteria
GBP spore forming
Clostridium spp
GPB non spore forming
actinomyces
bifidobacterium
propionibacterium
anaerobe lactobacillus
GNB
bacteroides fragilis
prevotella
porphyromonas
Anaerobic cocci
GNC
Veilonella spp
GPC
Peptostreptococcus spp
Peptococcus spp
Specimen collection
use needle + syringe
tissue samples or biopsies
if swab is used, sample should be transported using special transport medium (e.g. Amies)
Specimen transport
depends on nature of specimen
large volumes of material keep viability of anaerobes for longer periods
small volumes, small biopsies require anaerobic transport device
avoid extreme heat or cold
never transport material for culture in a syringe with needle
Specimen processing
visual examination
purulent, bloody, necrotic tissue, foul odor sulfur, granules, etc.
specimen prep
vortex purulent material, grind bone or tissue, centrifuge non-purulent material and use sediment
Specimen inoculation
inoculate specimen in aerobic and anaerobic media, and liquid medium
place inoculated plates immediately into an anaerobic atmosphere
incubate the rest of the plates in 5% CO2 or aerobic incubator
Media for anaerobic culture
Pre-reduced anaerobically sterilized media (PRAS)
made in anaerobic conditions
no O2 contamination
PRAS media - non-selective
Trypticase soy agar (TSA)
Brain-heart infusion (BHI)
Columbia, Brucella, or Schaedler’s
they all have 5-10% sheep RBC, a nutrient base and added enrichments
PRAS media - selective
Kanamycin and Vancomycin (KV)
inhibits GP organisms
selective for GN (like MAC)
no color differential
Phenyl ethyl alcohol agar (PEA)
aka rose agar = smells like roses
selective for GP
inhibits most GN, facultative-anaerobic bacteria and prevents swarming
Bacteroides and Prevotella (GNB) grow in PEA
Bacteroides bile esculin agar (BBE)
selective for certain Bacteroides species - bile tolerance
Differential based on esculin hydrolysis - dark brown color
Laked blood agar
lysis of sheep RBC by freeze-thaw method
produces clear red lysate
similar nutritional value to chocolate agar
everything grows
Laked blood agar with antibiotics
with kanamycin and vancomycin (CDC medium)
enriched, but also selective for GN anaerobes
however, not all GN grow on LKV
Cycloserin-cefoxitin fructose agar (CCFA)
selective for Clostridium difficile
growth in this medium is not definitive diagnosis
Glove box chamber
mixture of gases such as nitrogen or argon and H is flushed through the glove box to assure that the interior of the chamber is maintained anoxic

Anaerobic jars
tablets in pouch
citric acid with Na bicarbonate
Na borohydrate with cobalt chloride
add water
generates CO2 + H2 which combines with ambient O2 → H2O
anaerobic indicators
mechanism to detect O2 in system and media
dyes act as electron receptors or donors
colorless = reduced
color = oxidized
methylene blue
resazurin (pink if O2)
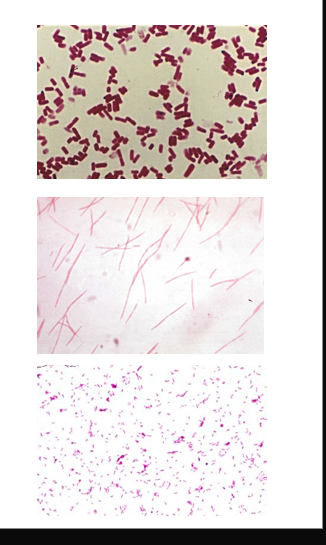
Microscopic examination
large GPB box car shape
Clostridium perfringens
Thin GNB with tapered ends
Fusobacterium nucleatum
Pleomorphic palely stained GNB
Bacteroides
Identification of anaerobe organisms
RapID ANA strips or Vitek ANI cards with a set of biochemical reactions
always correlate with:
microscopy
colonial morphology
source of specimen
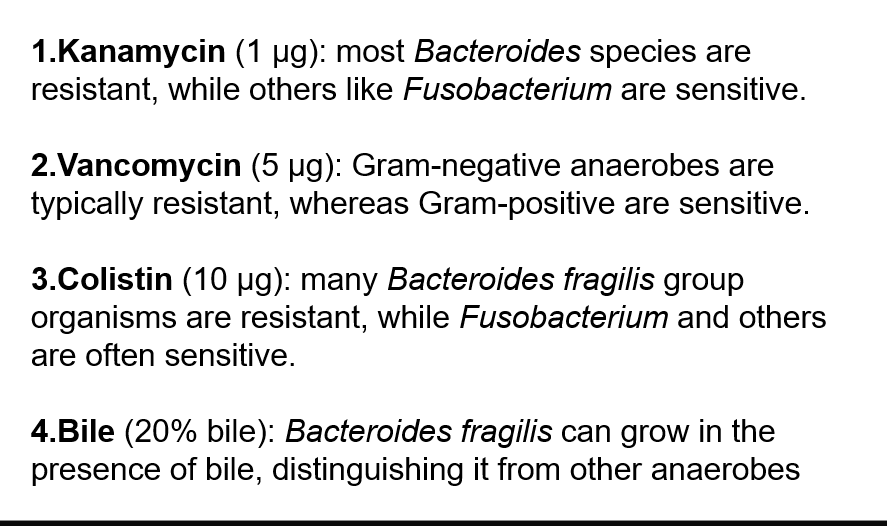
If biochemicals give equivocal results, use antibiotic identification disks
Colistin 10ug
Vancomycin 5ug
Kanamycin 1ug
typical susceptibility pattern
Additional tests for identificaiton

Stormy clot formation
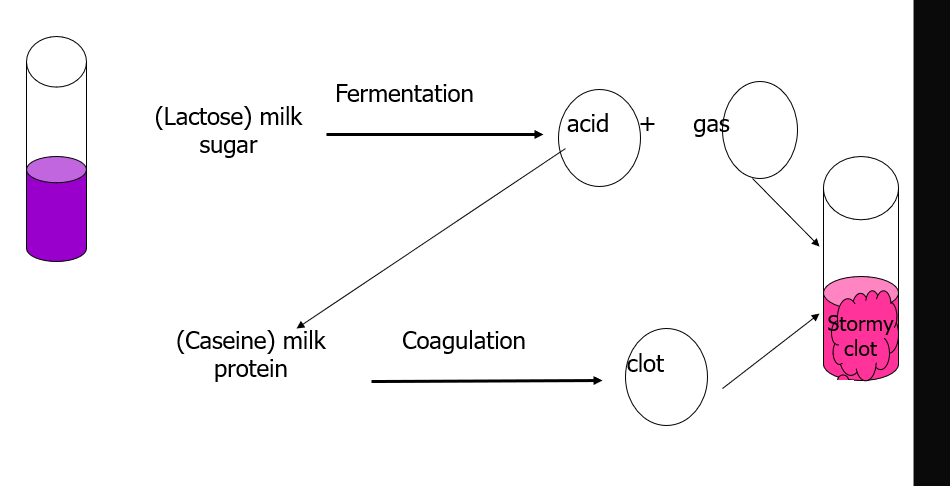
Gas liquid chromatography
heats liquids to vaporize
temp and time to vaporize is distinct for each product
detects acid or alcohol products from glucose or amino acid fermentations
patterns give primarily genus identification
Bacteroides, Prevotella, Porphyromonas
Clostridium
Fusobacterium
Polymicrobic anaerobic infection
many species in human flora
many grow simultaneously
opportunistic growth
injured tissue *limited blood/O2
No growth
healthy tissues *high O2 content
facultative anerobe
diminishes O2 supply further
aids growth of obligate anaerobes
Clostridium
C. tetani
C. botulinum
C. perfringens
C. difficile
Clostridium tetani
GPB
produces terminal spherical swollen spores (drumstick, tennis racquet, lollipop)
slow grower
swarming growth on lab media
rarely isolated
C. tetani virulence factors
produces toxin = tetanospasmin
responsible for pathological effects
heavy chain binds receptors on motor neuron
lighter chain taken up through endocytosis
tetanospasmin blocks inhibition of motor neurons, causing paralysis
muscle contraction is uncontrolled
muscles don’t relax
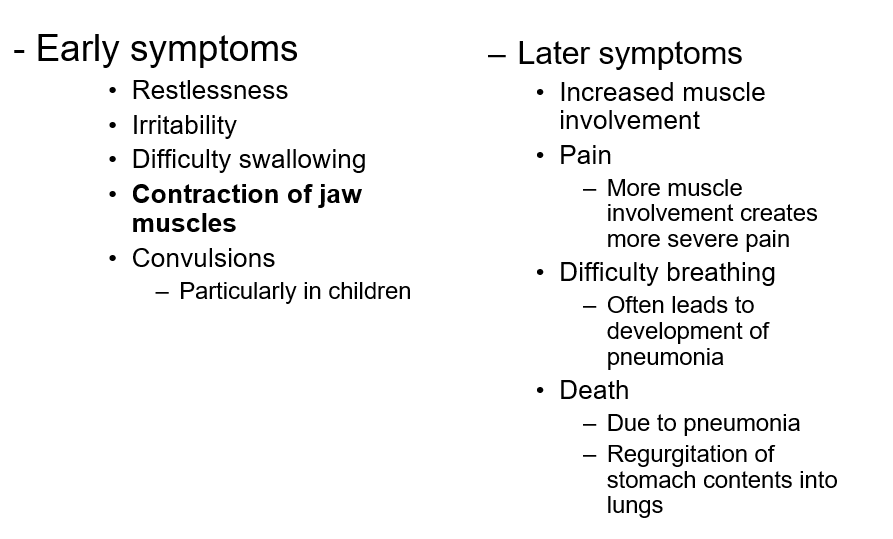
paralysis usually begins in the jaw (locked jaw)
Tetanus
spastic paralysis
aka “lockjaw”
frequently fatal
bacterial spores prevalent in dust and soil
difficult to avoid exposure
Tetanus epdemiology/treatment/prevention
found in dirt/dust and GI tract of humans and other animals
nearly half of infections result from puncture wounds including
body piercing, tattoo, animal bites, injected drug abuse
30-60 cases in US annually with 25% mortality rate
immunization has decreased incidences in economically advanced countries
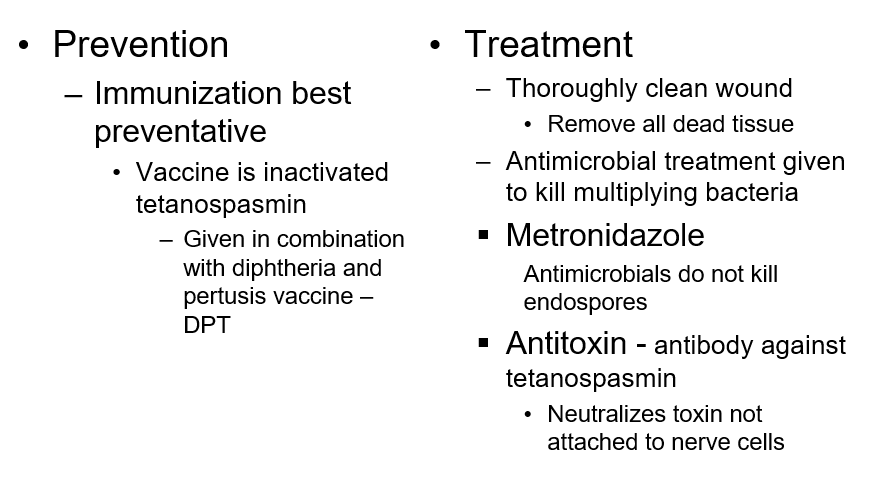
Clostridium botulinum
causes botulism, rare but serious paralytic illness caused by Botulinum neurotoxin
Foodborne botulism
Wound botulism
injected drug users are at increased risk
infant botulism
caused by consuming the spores, which then grow in the intestines and release toxin

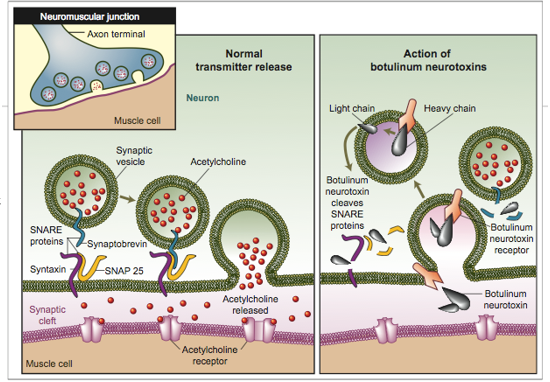
Botulinum toxin: neurotoxin
BTX is the most potent toxin known
1ug is deadly for humans
metalloproteinase that acts as on presynaptic membranes at the neuromuscular junctions
it cleaves SNAREs, proteins involved in release of acetylcholine at the synapse
w/o release of acetylcholine, paralysis of the motor system occurs
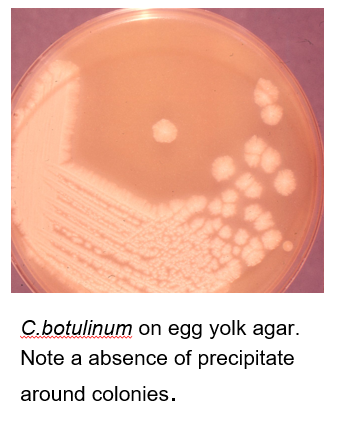
Identification of C. botulinum
the definitive diagnosis is ID of toxin in serum, stool, or gastric contents (bioassay) only done in reference labs such as CDC
identifying it alone in food is not enough
cells are gram variable bacilli that show profuse sub-terminal and free spores
Hemolysis is variable, but odor is strong and reminiscent of rotten eggs due to production of H2S
Lipase + Indole/urease -
can be isolated from clinical samples such as - feces, wounds, tissues, and pus as well as from foods
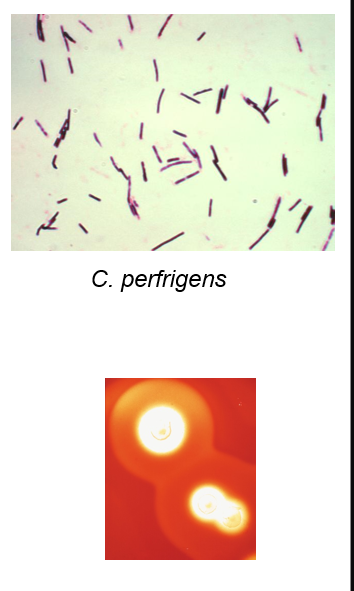
Clostridium perfringens
large rectangular GPB
subterminal spores, seldom seen
non motile
produces several toxins
alpha (lecithinase)
beta (necrotizing enteritis)
Enterotoxin
double zone of hemolysis
where is C, perfringens found
feces of humans and animals
vaginal tract
established in vaginal tract of 1-9% of healthy women
gas gangrene of uterus
fairly common after self-induced abortion
rarely seen after miscarriage and childbirth
C. perfringens diseases
bacteremia
myonecrosis
food poisoning
enteritis necrotica (pig bel)
Clostridial myonecrosis or Gas gangrene
caused by
presence of dirt and dead tissue in wound
long delays in treatment
primarily disease of wartime

Clostridial myonecrosis or Gas gangrene pathogenesis
Produces α toxin
Toxin attacks host cell membrane
diffuses and kills tissue cells
Other enzymes breakdown macromolecules of dead tissues
C. perfringens unable to grow in healthy tissue
Survives well in dead or poorly oxygenated tissue
Releases toxin in tissue
Bacteria produces gas through fermentation
Gas accumulates in tissue, contributing to spread
Clostridium difficile
large, straight, thin GPB
produces oval, subterminal spores rarely seen
motile
circular or rhizoid colonies
2-5mm
characteristic odor: manure, stable
in BAP fluoresce chartreuse under UV light
grows in cycloserine, cefoxitin-fructose agar (CCFA)
yellow colonies w ground appearance
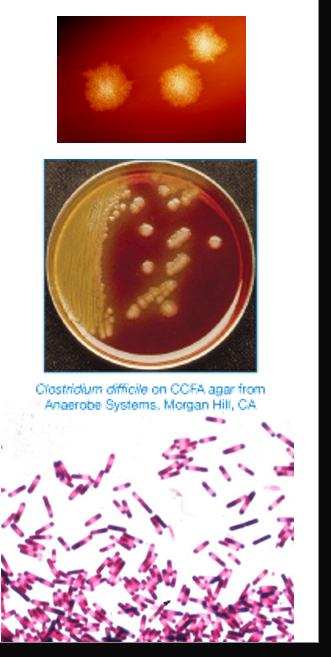
C. difficile pathogenesis
found in human GI tract in small #s
associated with antibiotic use
clindamycin, ampicillin, cephalosporins
kill NF, increase number of C. diff in GI tract
Toxin A-enterotoxin & toxin B -cytotoxin
C. difficile diagnosis
detection of toxins in stools (EIA, cell culture, NAAT)
culture of organism
Clinical - AAC (ATB associated colitis) or Pseudomembranous colitis (PMC)
treatment: omit antibiotic if possible/oral vancomycin, or fecal transplant
Actinomyces
strict anaerobic GP bacilli typically arranged in hyphae-like structures which fragment into short bacilli
NF of upper respiratory tract, GI tract, and female genital tract
low virulence
produce disease when mucosal barrier is breached (dental trauma or surgery)
establishes chronic infection that spreads through normal anatomical barriers
Actinomycosis
Chronic suppurative disease
Cervicofacial, abdominal, and thoracic
progresses slowly; painful swelling under the skin
swollen regions open and drain pus
chronic condition
openings usually heal
lesions reappear at the same or nearby region within days or weeks
most cases involve jaw or neck
recurrent lesions can develop on chest and abdominal wall or genital tract of women
scars and swelling give rise to name “lumpy jaw”
Actinomycosis diagnosis
Gram stain of ‘sulphur’ granules
culture
treatment - surgery and long term penicillin
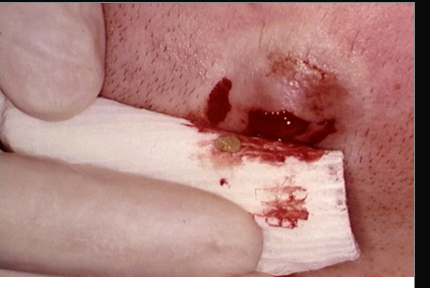
Actinomycosis pathogenesis
A. israeli cannot penetrate healthy mucosa
infection is characterized by cycles
abscess formation → scarring → formation of sinus tracts
passageways underneath the skin that can extend in any direction through soft tissue and allows for spread
disease progresses to skin and can penetrate bone or CNS
in tissue, culture grows as dense yellow colonies
nearly 50% cases originate in mouth
Actinomyces israelii
GP
filamentous
branching
anaerobic
slow growing

Cutibacterium acnes
previously known as Propionibacterium acnes
GP pleomorphic rod
inhabits human skin, sebaceous glands, nasopharynx, GI/GU tracts
most common, non-spore forming anaerobic rod found in clinical specimens
ACNE
frequent blood culture contaminant
most frequent serious infection: CNS shunt infection
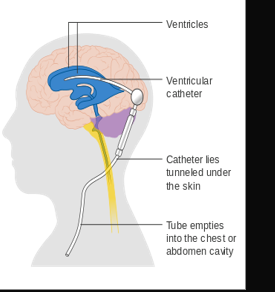
Lactobacillus
GPB
major part of the lactic acid bacteria group
convert lactose and other sugars to lactic acid
NF of vagina and GI tract
symbiotic and make up small portion of gut flora
production of lactic acid makes the vaginal environment acidic, which inhibits the growth of some harmful bacteria and yeast
Bifidobacterium
GPB non motile
NF of the vagina and GI tract
make up big portion of the gut flora in colon
aid in digestion, associated with lower incidence of allergies
used as probiotics
Mobiluncus
GPB
part of polymicrobial bacterial vaginitis
crescent-shaped or curved rods
motile with polar flagella
inconsistently GP
Peptostreptococci
GPC, non-spore forming
slow grower
NF of muco-cutaneous surfaces
mouth, intestinal tract, vagina, urethra, skin
P. magnus is the most commonly isolated anaerobic cocci
includes species within the genus formerly known as peptococcus
Anaerobic GN bacilli
Bacteroides, Prevotella, Porphyromonas and Fusobacterium
large component of NF of GI tract
>80% infections associated with B. fragilis
grow in leaked blood agar KV
stimulates pigmentation of porphyromonas
Clinical- Endogenous infections
intra-abdominal pyogenic infections
pleuro-pulmonary infections
genital infection
Bacteroides
slender rods or cocobacilli
Prevotella and Porphyromonas were previously classified as Bacteroides
infection cause by injury of the colon (peritonitis)
ID: grow in laked blood agar KV
colonial characteristic
short chain fatty acid by LGC
biochemical features
Bacteroides fragilis
rapid ID is important bc is more resistant to ATB than other anaerobes
bacteroides bile esculin agar is selective for Bacteroides (contains gentamicin and bile salts)
differential for hydrolysis of esculin
other bacteroides grow but don’t turn medium brown

Prevotella
GNB similar to Bacteroides
mostly in upper respiratory tract (mouth)
P. melaninogenica
tooth gum infection
also in female GT
P. bivia and P. disiens
brain and lung abscess
PID and tubo-ovarian abscesses
associated with other ANA
Porphyromonas
GNB
produce porphyrin pigments
dark brown/black pigments
red brick fluorescence under UV
also breast and axillaries(armpit) infections
male GT and perianal infections
found in gingival or tooth infection
P. gingivalis
Fusobacterium
GNB pleomorphic
fusiform, tapered ends
produce butyric acid and propionic acid
mix bacterial infection
also neck, breast and axillaries infections
male GT and perianal infections
F. necrophorum, F. nucleatum, F. novum
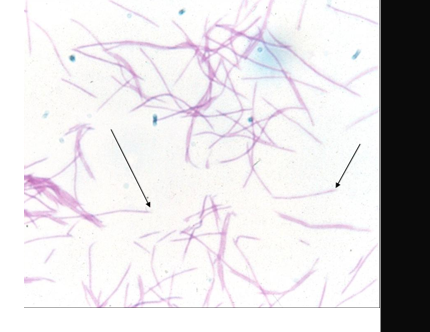
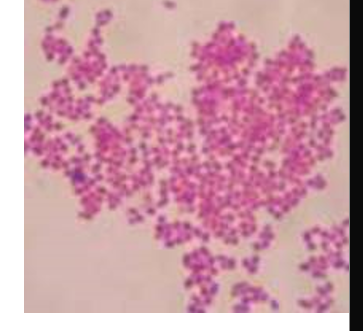
Veillonella
GN coccus
NF of the mouth and nasopharynx
implicated in cases of osteomyelitis and endocarditis
polymicrobic infection
Antibiotic disks for ID of GN anaerobes