1b patterns of human rights violations are influenced by a range of factors
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
define forced labour and what does it involve
situations where people are coerced to work through the use or violence or intimidation, or by more subtle means i.e. accumulation of debt or retention of identity papers
children who are denied education to work
women and girls exploited as unpaid, abused domestic workers
global forced labour facts
21 million people are victims of forced labour - 11.4 million women and girls and 9.5 million men and boys (around 55% women)
22% are victims of forced sexual exploitation → 98% of this happens to women
2.2 million (10%) are in state-imposed forms of labour i.e. in prisons, or by the state military
migrant workers and indigenous people are particularly vulnerable to forced labour
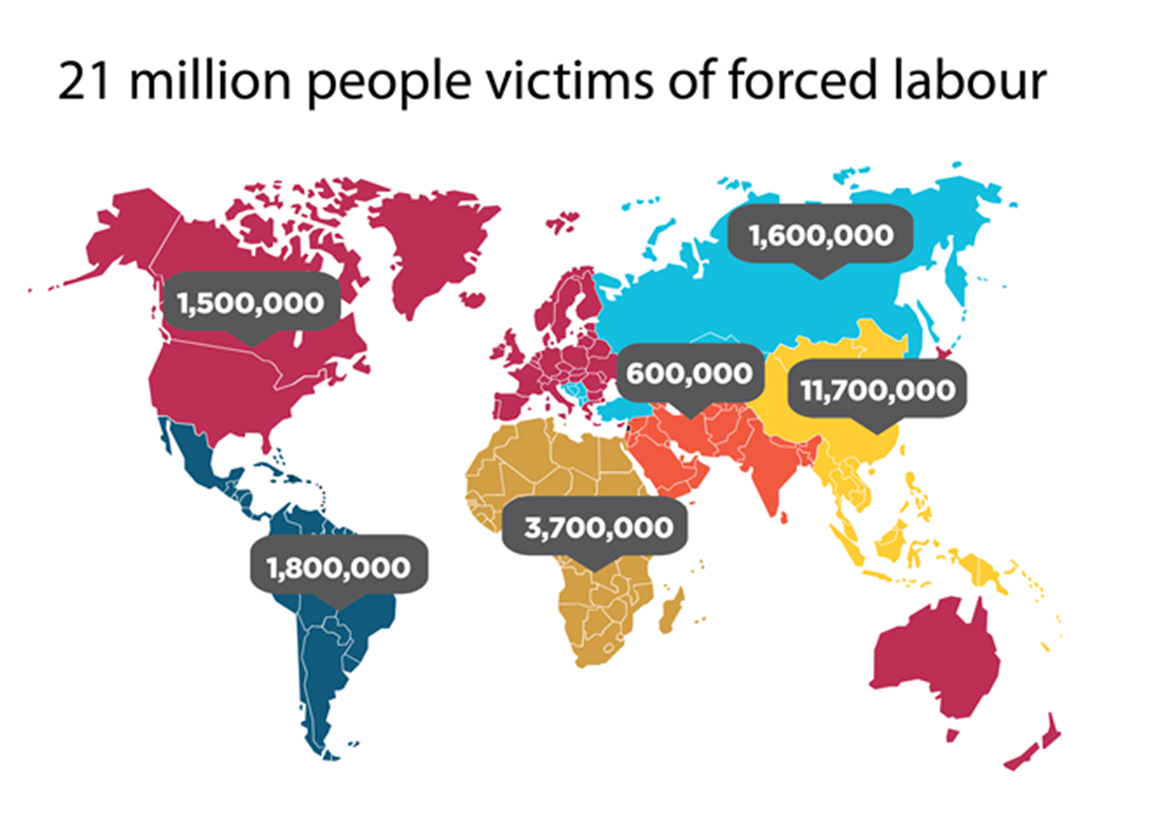
spatial distribution of forced labour
southeast Asia has the highest overall incidence but no region is unaffected
Asia-Pacific region is 56% of global forced labour
Africa accounts for 18%
Developed Economies and EU accounts for only 7%
Low rates in North America - USA and Canada only 0.04%
factors that influence global variations of forced labour with example - economic
poverty
lack of economic opportunities + unemployment
migration + seeking work
low wages
forced labour prevalent in economies that are dependent on cheap labour
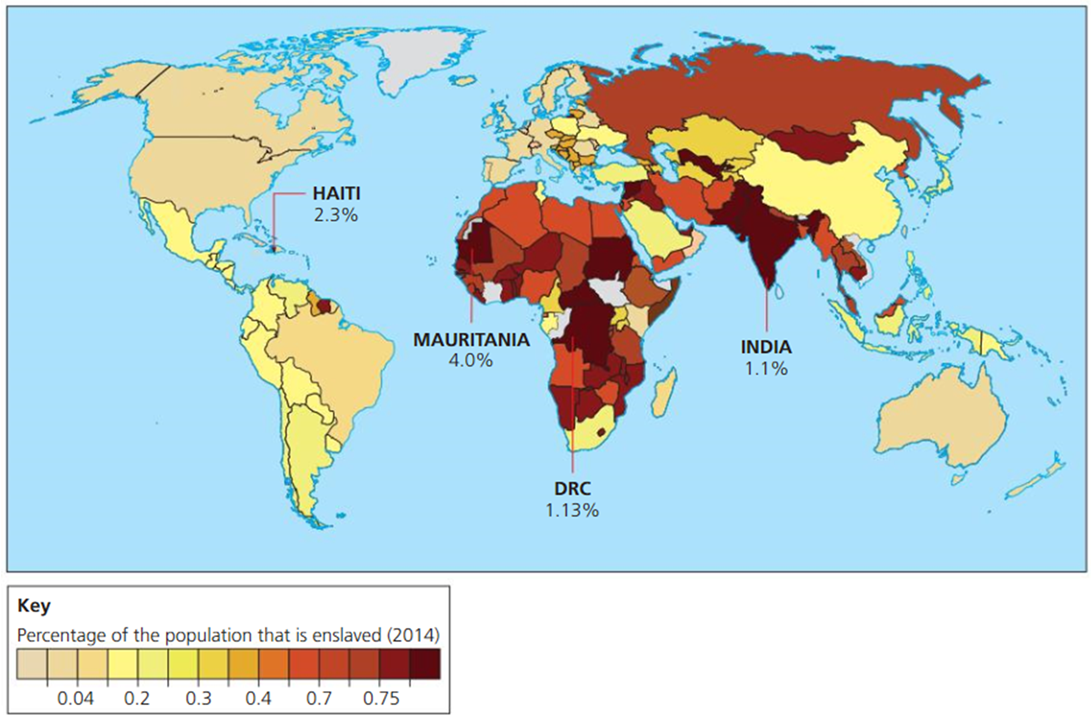
e.g. Mauritania in Africa has 33% of its population living in poverty, people have few skills and little choice over the jobs in which they do → higher risk of forced labour. 4% of its population is enslaved
migrant workers are at higher risk because they have limited rights and may be dependent on their employers
Thailand: fishing industry depends on low-skilled workers from neighbouring countries i.e. Myanmar → trafficking. Thailand on Tier 2 watchlist for human trafficking. Work up to 20 hours a day. Casual use of violence, workers tortured and murdered
factors that influence global variations of forced labour with example - social
gender inequality
age
women and children trafficking for sexual exploitation
indigenous people
descent-based slavery
e.g. descent based slavery found in Mali + Sudan → born into slavery due to ancestors
migrant workers may not speak the language + dependency on employers → higher risk
factors that influence global variations of forced labour - political
political instability + corruption
conflict
state sponsorship of modern slavery e.g. cotton harvest in Uzbekistan
e.g. in Uzbekistan, the government makes use of forced labour to produce cotton on a large scale. Workers are forced to leave their jobs with the risk of losing it if they refuse to comply. profits from the cotton only benefits the privileged elite which is evidence of political corruption within society → leads to increased inequalities between different classes → detrimental because wealthier population have higher influence in the gov → increasing forced labour
define maternal mortality
the death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, from any cause related to or aggravated by the pregnancy or its management.
MMR facts
In 2013, 289,000 women died during and following pregnancy and childbirth
Most of these deaths occurred in developing countries - 99%
young adolescents (under 15) face a higher risk of complications + death as a result of pregnancy
spatial patterns of MMR
99% of all maternal deaths occur in developing countries - over half of these in SS Africa and 1/3rd in South Asia (partially attributed to the fact that more babies are born in there regions than others)
the worst affected countries were all in sub-Saharan Africa: Sierra Leone → 1100 per 100,000 live births, Chad → 980
Lowest were in more developed countries in Europe: Belarus → 1 and Italy → 4
also low in North America
factors that affect global variations in MMR
access to treatments for pregnancy and birth complications (i.e. in rural areas)
poor accessibility in rural areas i.e. roads and transportation
quality of medical services inc. provision of skilled attendance at birth
availability of information and education
poverty
social norms i.e. where there is prevalence of child marriage, MMR would be high (gender inequality)
level of government investment
examples of factors
In 2009, 1 in 8 women died during childbirth in Sierra Leone due to inadequacy of the healthcare system
low gov investment → high rates of illegal abortion in Uganda
in 2017, the gov of India doubled maternity leave available
In Kenya pregnant women are often 100km from a health clinic
what is capital punishment
This is when the sentence given for crimes is the death penalty.
This contradicts the basic human right to life.
capital punishment facts
According to Amnesty International there were over 600 executions globally in 2014
over 1,000 people were executed in 23 countries in 2016
Iran, Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Pakistan and China are the world’s top five in carrying out capital punishment
Factors influencing global variations of capital punishment
it’s legality under national law → currently legal in 55 countries
increase in no of countries in which it is being abolished → executions reduced by 37% from 2015 to 2016
differences between countries in the range of crimes for which it is imposed → e.g. in China it is used for many serious and also arguably minor crimes such as robbery + arson. However, in other countries (Belize) there is a smaller range of crimes for which penalty is imposed
political state of country → dictatorships (North Korea) could sentence death for people who use media not approved by gov
social factors i.e. religion + culture → what is deemed appropriate in some cultures is not in others. e.g. homosexuality is punishable by death in countries such as Saudi Arabia. Apostacy is a capital crime in Afghanistan due to their strict rules on Islam