Lecture 39: Medial patellar luxation
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
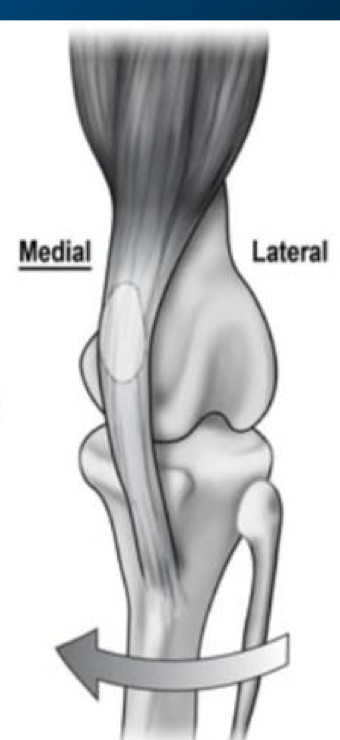
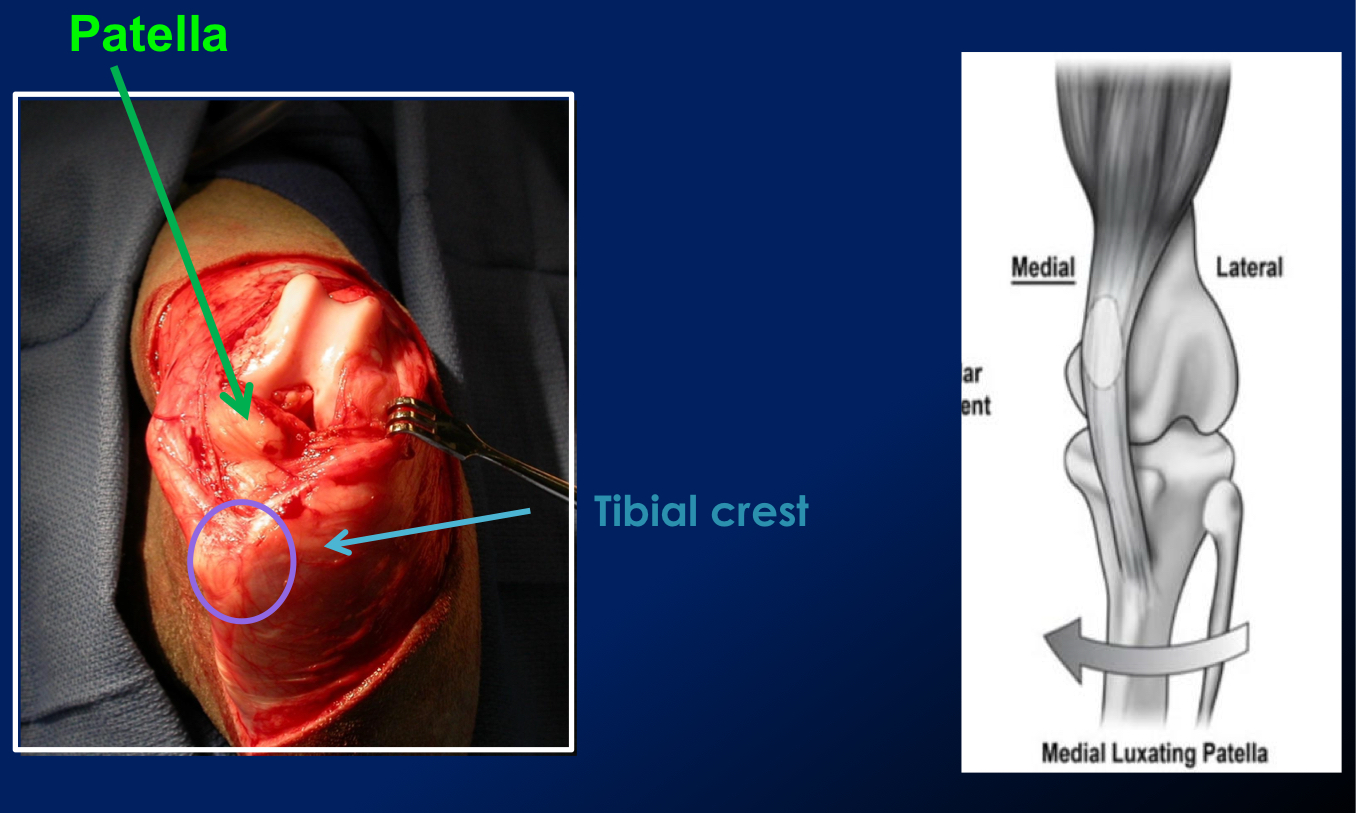
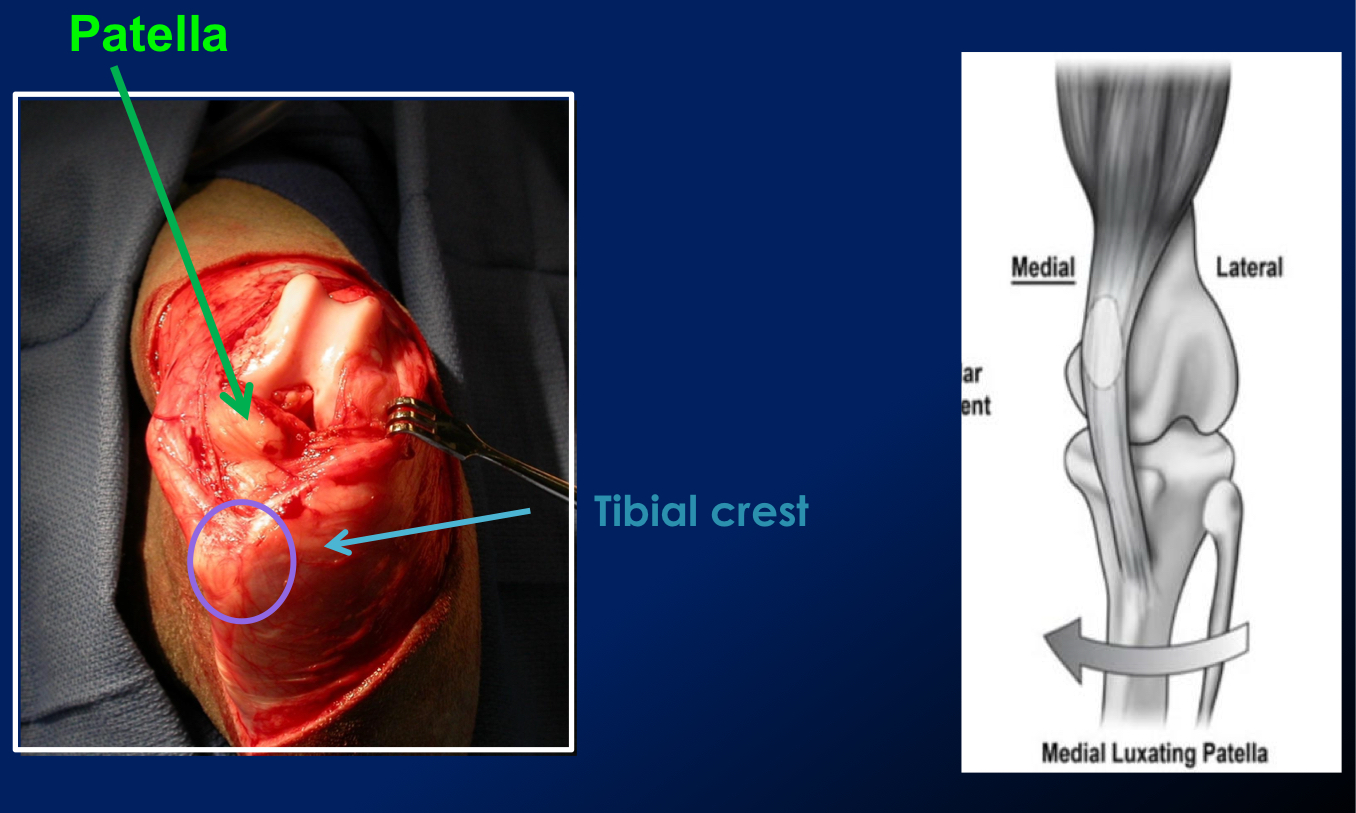
What are most patellar luxation?
Bilateral, most commonly medial
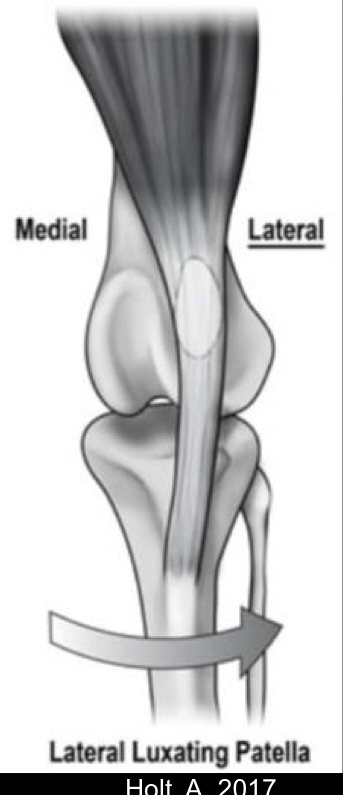
What is the most common patella luxation in small and large breed dogs?
Small breed → Medial patellar luxation
Large breed → Lateral patellar luxation
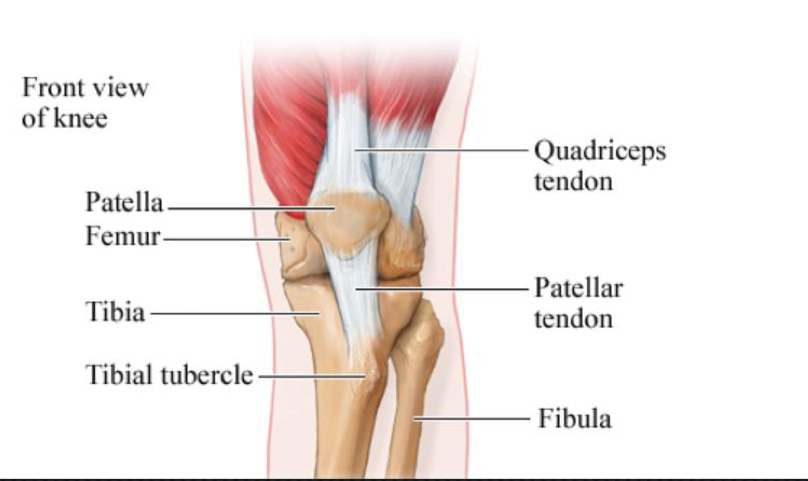
Musculature found around patellar?
Quadriceps
Rectus femoris
Vastus lateralis, intermedius, medius
Insert on patella and continue as patella ligament
Inserts on a tibial tuberosity
Bone embedded w/ a tendon
Provides smooth surface for tendon to glide over moving joint
Acts like pulley mechanism, changes the direction of the force. Magnifies the force w/ less effort
Patella/sessamoid bone
What is the normal patella mechanism?
Extensor appartus of stifle must be properly aligned for normal function
All elements must align with femoral shaft trochlear groove and tibial tuberosity for stable patella
Luxations cause malignment of quadriceps mechanism
What common femoral malformations cause medial patellar luxation?
Coxa cara
Decrease angle of anteversion
Distal external torsion
Distal varus
Hypoplasia of medial condyle
When should you decrease coxa vary?
Inclination of the femoral head angle
Femoral head <120 degrees
Coxa vara
Femoral head >135 degrees
Coxa valga
Angle formed by the axis of the femoral neck and the transcondylar axis. Basically the femoral neck leans forward w/ respect to the rest of the femur causing the limb to rotate internally so the knee and foot twist toward midline
Aneteversio angle
External rotation
Internal rotation
Distal femoral torsion
Distal femoral torsion
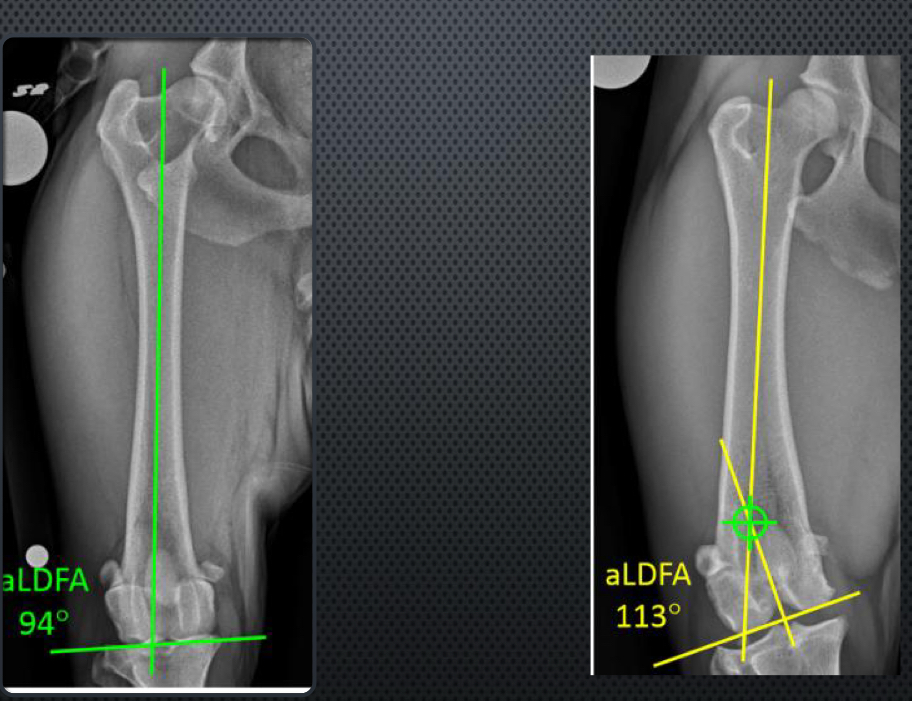
Distal femoral varus
When does hypoplasia of femoral condyles occur?
Secnodary to luxated patella during growth because there is no pressure on trochlear groove
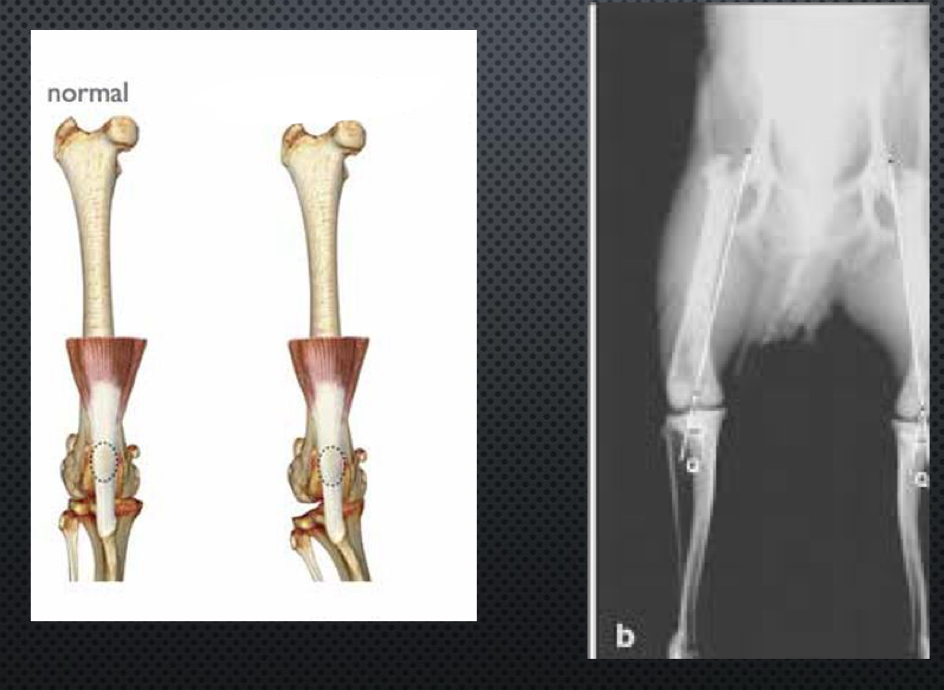
What tibial malformations can cause MPL?
medial displacement of tibial tuberosity
Internal proximal tibial torsion
Proximal tibial valgus
Distal varus
Medial displacement of tibial tuberosity
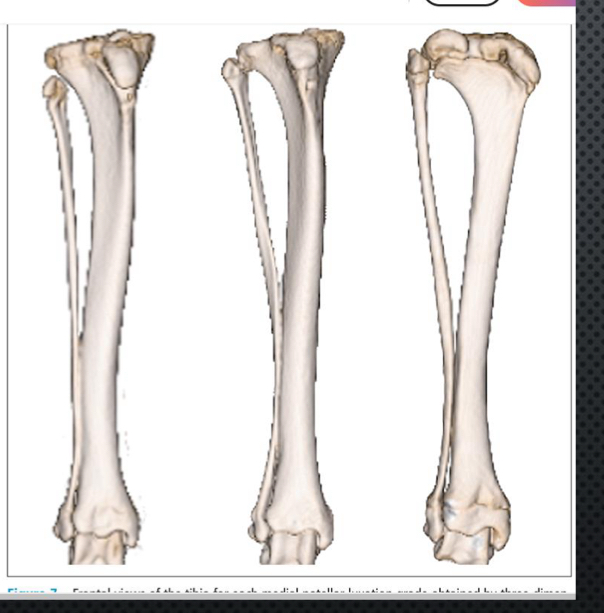
Internal proximal tibial torsion
Proximal tibial valgus
Less common causes of MPL
Luxation secondary to trauma, patellar alta, tightness or atrophy of quads muscle complex
Common signalement of MPL
Small breed dogs, usually detected in younger dogs w/out CCL tear
Middle aged to older dogs MPL/CCL
Usually no history of trauma
Owner may be “skipping” hindlimb lameness
Non-weight bearing lameness (NWB) can be indicative
Standing and walking with MPL
Decreased to normal muscle mass hind limbs
Decreased to normal weight bearing hindlimb
Unilateral or bilateral skipping gait
Lameness may come and go
Dog may limp than extend leg which eliminates the limp and keep walking
Orthopedic exam findings with MPL
Discomforta w/palpation and ROM
Medially displaced patella, may feel grinding as patella move
Stifle effusion
Crepitus w/ROM
Check for tibial thrust and or cranial drawer
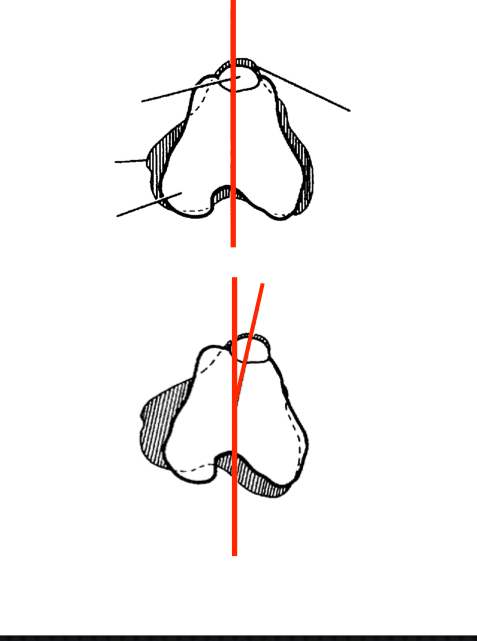
Minimal malalignment
Patella wants to ride in the grove
Can be luxated by force
Asymptomatic
Often incidental on PE
No treatment necessary
Grade I MPL
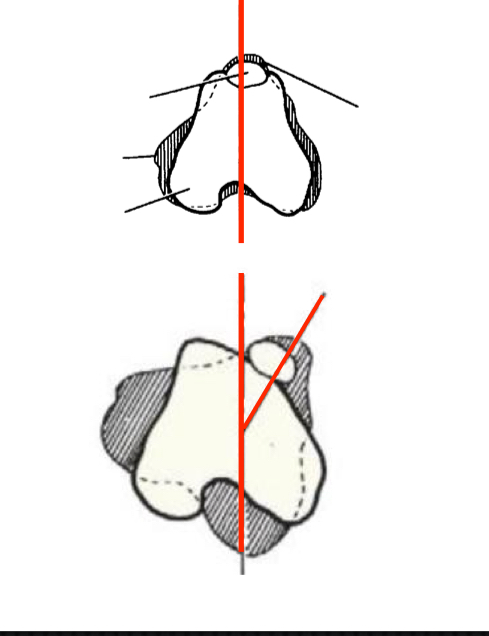
Luxation occurs intermittently
On palpation, patella luxates easily but still wants to stay in groove
In more than out
Surgery indicated if CS or are progressive
Grade II MPL
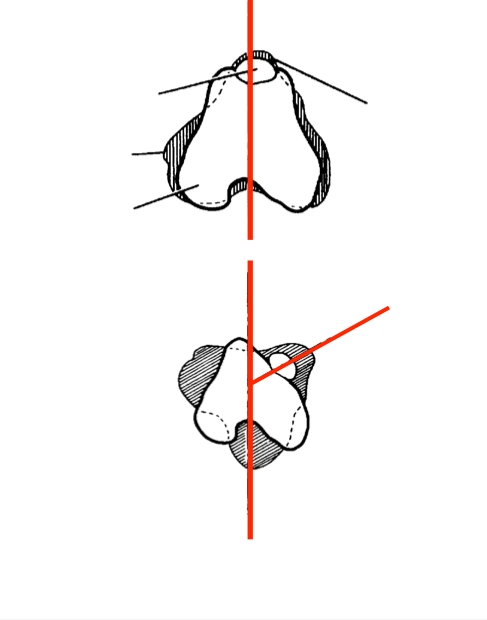
Patella permanently luxated
Can be manually reduced, automatically re-luxates when releasing
Significant lameness and gait abnormalities
Surgery is indicated
Grade III MPL
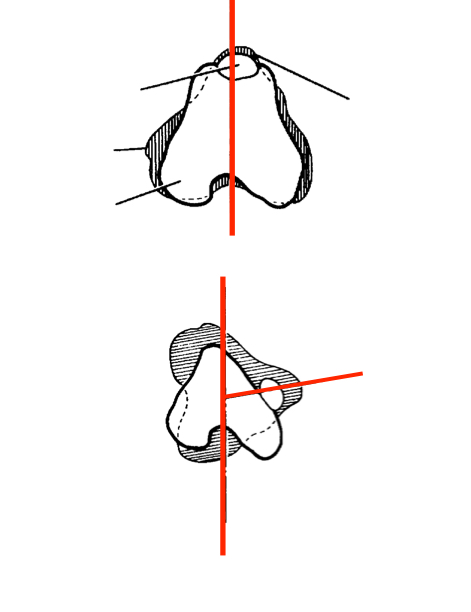
Permenant luxation
Cannot be reduced manually
Trochlear groove absent or severely eroded trochlear ridges
Severe gait abnormalities
Look for concurrent cruciate ligament tears
Surgery indicated- prognosis is more guarded
Grade IV MPL
What cases should you select for surgical MPL repair?
Minimal limb deformaiites
Hyaline cartilage preserving techiniques
Trochlear block resection
Trochlear wedge recession
Abrasion sulcoplasty
Trohleoplasty
Deepens the trochlear groove
Preserves articular cartilage
Narrows proximally and distally
Wedge created w/ hobby saw or sagittal saw
Wedge trocheloplasty
How do you assess patellar stability?
Flex and extend the stifle, then again with both internal and external rotation of the tibia
Goal of tibial crest transposition
Realign quads, shifts insertion patellar ligament
Risk tibial crest transposition
Create LPL
Implant failure
Tibial tuberosity avulsion fracture
Techniques for addressing ST aspects of MPL
Releasing incision
Retinacular imbrication
Anti-rotational suture, concurrent CCLD
Correct retinacular laxity
Perform as final step of luxation correction
Excessive tension predisposing to luxation in opposite direction
Goal is the equal tension medial and lateral
Retinacular imbrication
Which of the following is the most common direction of patellar luxation overall? a) Lateral b) Medial c) Cranial d) Caudal
b) Medial
In which size category of dog are medial patellar luxations (MPLs) most prevalent, accounting for approximately 98% of patellar luxations in those breeds? a) Large breeds b) Medium breeds c) Toy and Miniature breeds d) Giant breeds
c) Toy and Miniature breeds
According to the sources, patellar luxation is considered a: a) Primarily traumatic injury b) Degenerative condition c) Genetic and heritable developmental disease d) Infectious disease
c) Genetic and heritable developmental disease
The patella is classified as what type of bone? a) Long bone b) Short bone c) Sesamoid bone d) Flat bone
c) Sesamoid bone
Which of the following best describes the function of the patella? a) It primarily provides structural support to the stifle joint. b) It acts like a hinge, allowing flexion and extension of the stifle. c) It provides a smooth surface for the tendon to glide over, acting like a pulley mechanism and magnifying force. d) It is the primary site of muscle attachment for the hamstring muscles.
c) It provides a smooth surface for the tendon to glide over, acting like a pulley mechanism and magnifying force.
For normal patellar function, which of the following must be properly aligned? a) Femoral condyles and menisci b) Patella and cruciate ligaments c) Extensor apparatus of the stifle, femoral shaft, trochlear groove, and tibial tuberosity d) Fibula and tarsal bones
c) Extensor apparatus of the stifle, femoral shaft, trochlear groove, and tibial tuberosity
Malalignment of which mechanism is the underlying issue in patellar luxations? a) Hock joint b) Hip joint c) Quadriceps mechanism d) Elbow joint
c) Quadriceps mechanism
A veterinarian is examining a young Cavalier King Charles Spaniel presenting with intermittent hind limb lameness described by the owner as a "skipping" gait. Based on the signalment and history, which of the following is the most likely differential diagnosis? a) Cranial cruciate ligament tear b) Hip dysplasia c) Medial patellar luxation d) Elbow dysplasia
c) Medial patellar luxation
Coxa vara, a femoral malformation associated with MPL, is characterized by: a) A femoral head angle greater than 135 degrees. b) A normal femoral head angle between 120-135 degrees. c) A femoral head angle less than 120 degrees. d) An increased angle of anteversion.
c) A femoral head angle less than 120 degrees.
A decreased angle of anteversion of the femur can cause the limb to rotate: a) Externally b) Cranially c) Internally d) Caudally
c) Internally
Hypoplasia of the medial femoral condyle in MPL is often secondary to: a) Trauma to the stifle joint b) Infection within the joint c) Lack of pressure on the trochlear groove due to a luxated patella during growth d) Excessive weight bearing
c) Lack of pressure on the trochlear groove due to a luxated patella during growth
During an orthopedic exam for suspected MPL, what might a veterinarian palpate in the stifle joint? a) Increased range of motion b) A laterally displacing patella c) A medially displacing patella, possibly with a grinding sensation d) Decreased joint effusion
c) A medially displacing patella, possibly with a grinding sensation
A dog with Grade III medial patellar luxation is characterized by which of the following? a) The patella can be luxated with force but returns to the groove when released. b) The patella luxates intermittently but returns to the groove spontaneously. c) The patella is permanently luxated but can be manually reduced, although it re-luxates upon release. d) The patella is permanently luxated and cannot be manually reduced.
c) The patella is permanently luxated but can be manually reduced, although it re-luxates upon release.
A 5-year-old Pomeranian has a patella that can be easily luxated during a stifle examination but spontaneously returns to the trochlear groove when pressure is released. The dog is asymptomatic. What grade of patellar luxation is most likely? a) Grade I b) Grade II c) Grade III d) Grade IV
a) Grade I
Surgical intervention is generally recommended for which grades of MPL when clinical signs are present or progressive? a) Only Grade IV b) Grades I and II c) Grades II, III, and IV d) Only Grade III
c) Grades II, III, and IV
Which of the following surgical procedures aims to deepen the trochlear groove to provide better stability for the patella? a) Tibial tuberosity transposition b) Retinacular imbrication c) Trochleoplasty d) Capsulotomy
c) Trochleoplasty
Tibial tuberosity transposition (TTT) is a surgical technique used in MPL treatment to: a) Deepen the trochlear groove. b) Tighten the joint capsule. c) Re-align the quadriceps mechanism by shifting the insertion of the patellar ligament. d) Release tension on the lateral retinaculum.
c) Re-align the quadriceps mechanism by shifting the insertion of the patellar ligament.
During surgery for a Grade III MPL, the surgeon assesses the trochlear groove and finds it to be very shallow. Which surgical technique would be most appropriate to address this specific finding? a) Tibial tuberosity transposition b) Retinacular release c) Trochleoplasty d) Retinacular imbrication
c) Trochleoplasty
Retinacular imbrication is a soft tissue surgical technique performed on which side of the stifle joint relative to the direction of patellar luxation? a) The same side as the luxation b) The opposite side as the luxation c) Both sides of the luxation d) The cranial aspect of the stifle
b) The opposite side as the luxation
A Labrador Retriever presents with lateral patellar luxation. Based on the information in the sources, this is: a) The most common type of patellar luxation in all breeds. b) More common in small breeds. c) More common in large breeds compared to medial luxation in large breeds. d) Equally common as medial patellar luxation in large breeds.
c) More common in large breeds compared to medial luxation in large breeds.