macro exam 2 🍒
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
whats the most concentrated source of energy & how many kcals per gram
dietary fat - 9kcal/gram
role of lipids in body fat
stored energy, protects internal organs, insulates against heat loss
role of lipids as molecular components
cell membrane, steroid hormone precursor, and precursor for bile acids
whats the simplest lipid
fatty acids
how do fatty acids travel throughout the body
lipoproteins or albumin. due to their hydrophobic nature, they cannot travel in the blood.
whats the general structure of a fatty acid
straight hydrocarbon chain with a methyl end (hydrophobic) and a carboxylic end (hydrophillic)
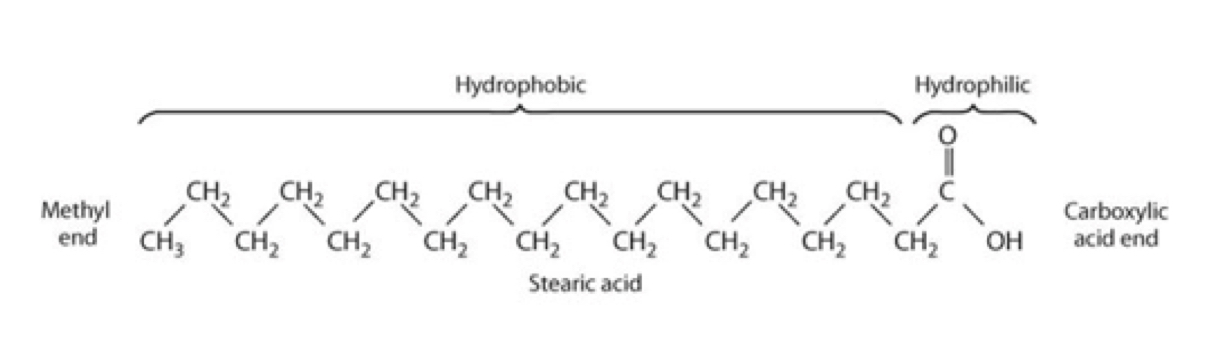
how many C does a SCFA contain
6 or less
how many C does a MCFA contain
8-14
how many C does a LCFA contain
14 or moreho
how many C does a very long chain FA contain
22 or more
how many double bonds does a SFA contain
none, its saturated with hydrogens
how many double bonds does a MUFA contain
one
how many double bonds does a PUFA cotain
more than one
how does a diet higher in SFA associate with CVD risk
increased risk
how does a diet higher in MUFA associate with CVD risk
reduced risk
how does a diet higher in PUFA associate with CVD risk
reduces risk
which two SFAs increase LDL cholesterol
myristic and palmitic
which SFA has a little affect on LDL cholesterol
stearic
what are some reasons that CVD and SFA literature is inconsistent?
they dont contrast high/low intake well
they lack multiple diet assessments
assessing diet is tricky
which fat sources are higher in SFA
tropical oils and animal fats
which fat source is uniquely high in MUFA
olive oil
which fat sources are higher in PUFA
vegetable oils
whats the number 1 source of calories
cooking oils
whats the number 1 source of SFA
red meat and dairy
whats the meaning of cis
same side
the primary configuration in naturally occurring foods
whats the meaning of trans
opposite side
the result of partial hydrogenation of veggie oils
increased shelf life
fatty acid nomenclature: delta system
starts counting carbons from the carboxyl end
includes chain length, number of bonds, and position of double bonds
fatty acid nomenclature: omega system
counts from the methyl end (CH3)
includes the number of bonds and the position of the first double bond
what are the two essential fatty acids
linoleic acid and linolenic acid
linoleic acid properties
plant & vegetable oils
omego-6-fatty acids
18:2 n-6
linolenic acid properties
flax products
omega-3-fatty acid
18:3 n-3
what is the primary storage form of fat
triglycerides
which fats are liquid at room temp
short chain or unsaturatedwhi
which fats are solid at room temperature
longer chain or saturatedh
how can TGs in the adipose be used for energy
FAs can be cleaved and oxidized via the TCA cycle
glycerol can be used in gluconeogenesis
cholestrol characteristics
important in plasma membranes
precursor for steroids (bile acid, sex hormone, cortisol, vitamin d)
found in animal products, shellfish, and shrimp
phytosterols characteristics
plant sterols, similar to cholestrol in animals
can lower cholesterol (excretion)
phospholipid characteristics
component of cell membranes
intracellular signaling
found in soy, egg yolk, fish
sphingolipids
found in the plasma membrane, abundant in the CNS
includes ceramide, sphingomyelin, cerebrosides, and gangliosides
ceramide characteristics
simplest sphingolipid
in excess and in certain tissues
role in metabolic dz
sphingomyelin
important for nervous system function (mylein sheath)
cerebrosides
formed when a sugar attatches to ceramide
facillitates nerve impulses
gangliosides
multiple sugar units attatched to a ceramide
function as receptors and important in cell communication
where does TG digestion begin
the mouth with lingual lipase yielding FAs and diglycerides
how are TGs digested in the stomach
gastric lipase digests short & medium chain FAs yielding FAs and diglycerides
TG digestion in the SI
CCK facillitates:
gallbladder releases bile to emulsify lipids
pancreas releases pancreatic lipase and bicarbonate
pancreatic lipase does most of the digestion yielding monglycerides and FAs
what enzyme facillitates the most of lipid digestion
pancreatic lipase
cholesteroll digestion in the SI
free cholesterol doesnt require action
dietary chholesterol is esterified to a FA (FA removed by cholesterol eterase)
phospholipid digestion in the SI
hydrolyzed by phospholipase A producing a lysophospholipid and a FFA
how are lipids absorbed?
digestion products: monoglycerides, FAs, free cholesterol, and lysophospholipids
these products combine with bile and micelles (circular structures that transport lipids)
micelles allow lipids to travel
TG & cholesterol absorbtion
lipid absorbtion is mostly facillitated diffision and some passive diffusion
FATP: fatty acid transport protein and NPC1L1 transports cholesterol and phytosterol
within the enterocyte, cholesteol and longer chain FA travel to the ER for reformation
what enzyme is primarily responsible for lipid digestion?
pancreatic lipase
what are the three classes of lipoproteins
exogenous lipid transport (dietary), endogenous lipid transport (stored fat), and reverse cholesterol transport
exogenous lipid transport (dietary)
CM with apoB48
endogenous lipid transport (stored fat)
VLDL lineage with apoB100
lineage: VLDL slowly become IDL and then LDL as lipids are removed
reverse cholesterol transport
HDL with apo-A1
excess cholesterol transported back to the live for excretion
when ready to export from the gut, what happens to longer chain fatty acids
they are packaged into CM within the ER. they exit the enterocyte and enter the lymphatic system where they fuse with the membrane and are released (exocytosis) to enter the blood stream through the left subclavian vein.
where to the CM deliver the TGs
tissues for energy (heart, muscle, adipose)
what happens to adipose when FAs enter
they are converted back to TG and stored (high fat meals), ready to be used when energy demand exceeds energy intake.
what happens to muscle when FAs enter
they are used for energy (greedy)
what happens to the liver when FAs enter
glycerol will enter and go to glycolysis
T/F: if fat is stored in your adipose tissue, you will gain weight long term
false
what happens (generally) when we fast (about 3 hours)
we start mobilizing stored adipose tissue for fuel
when we fast and see a rise in glucagon and a drop in insulin, what else occurs
the hormone sensitive lipase is stimulated to yield FAs (and glycerol) which will attach to albumin and circulate in the blood. they will then go to the liver to be secreted as VLDL
where does VLDL assembly (using TG) occur
the ER of the liver
when the VLDL travels through the blood, it looses TGs. what is the progression VLDL undergoes
VLDL → IDL → LDL
what happens to leftover LDL after it circulates as VLDL in the blood
they are rich in cholesterol and they are removed by LCL receptors
what is LDL clearance
taking LDL out of the blood via LDL receptor
when fasting (high glucagon) what is increased and what is decreased?
CM
VLDL secretion
adipose lipolysis
fatty acid secretion
glycerol used in gluconeogenesis
decreased:
CM
increased:
VLDL secretion
adipose lipolysis
fatty acid secretion
glycerol used in gluconeogenesis
when postprandial (high insulin) what is increased and what is decreased?
increased:
CM
decreased:
VLDL secretion
adipose lipolysis
fatty acid secretion
what happens during prolonged fasting
we run out of stored glycogen and need to rely on our body fat. the skeletal muscle uses FAs, the liver produces ketones, and glucose is saved for the tissues that absolutely need it.
HDL cholesterol is secreted by:
the liver and some by the gut
HDL carries out
reverse cholesterol transport
cholesterol is removed
which of the following lipoproteins contains cholesterol?
HDL
IDL
VLDL
CM
LDL
which lipoprotein is the most enriched with cholesterol
LDL
whats the purpose of beta oxidation
to extract energy from fatty acids
when and where does beta oxidation occur
in the mitochondria within the muscle and liver during prolonged fasting/starvation or overnight
what two things need to happen before beta oxidation
fatty acid activation and transportation into the mitochondrial matrix
whats the process of fatty acid activation
coA is added to the FA. this requires ATP and will create a fatty acyl coA
what is the process of fatty acid transports to the mitochondrial matric
the carnatine shuttlewha
whats the process of the carnitine shuttle
CAT 1: passes the FA from coA to carnitine
CAT 2: passes the FA from carnitine back to coA
what happens in each cycle of beta oxidation
a fatty acid loses 2 carbons
acetyl coA is produced and can enter the TCA
NADH and FADH2 is produced and can enter the ETC
what is the first step in beta oxidation of saturated FAs
inserting a double bond
what happens to the first step in beta oxidation for unsaturated FAs
it is skipped
we get 1.5 fewer ATPs
what does an odd numbered carbobn chain FA produce
several acetyl coA and one propionyl Coa (which can be converted to glucose)
what is the basis of ketogenesis
ketones forming when we rely on adipose tissue for energy in long periods of fasting or dietary CHO is restricted
when does ketogenesis ramp up
when acetyl coa is abundant
TCA cannot keep running (OAA) is limiting
where does ketogenesis occur
the mitochondria of the liver
what are the three ketones
acetoacetate (most abundant)
beta hydroxybuterate
acetone
what uses ketones
heart and skeletal muscle
brain (long period)wha
what cannot use ketones
the liver (lacks an enzyme)
how are ketones used for energy
beta hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate can become acetyl coa and enert the TCA
acetone cannot be used for energy
what is ketosis
a mild increase in ketone bodies (low carb/energy diets)ket
what is ketoacidosis
a serious complication of T1 or advanced T2DM
extreme hyperglycemia, unrestrained breakdown of adipose
blood pH drops inducing low BP, dehydration, coma, and death
what happens when we fast, eat low CHO, or exersise at low intensity for long periods
insulin is low
glucagon is high
how does insulin and glucagon promote/inhibit beta oxidation and ketogenesis
glucagon promotes and insulin inhibits
what happens to excess FAs
stored in adipose
what happens to excess CHO
glycolysis and glycogen replenishment, reamining converts to FA
what happens with excess PRO
can be converted to FA
where does FAS occur
lipogenic tissues (liver, adipose)